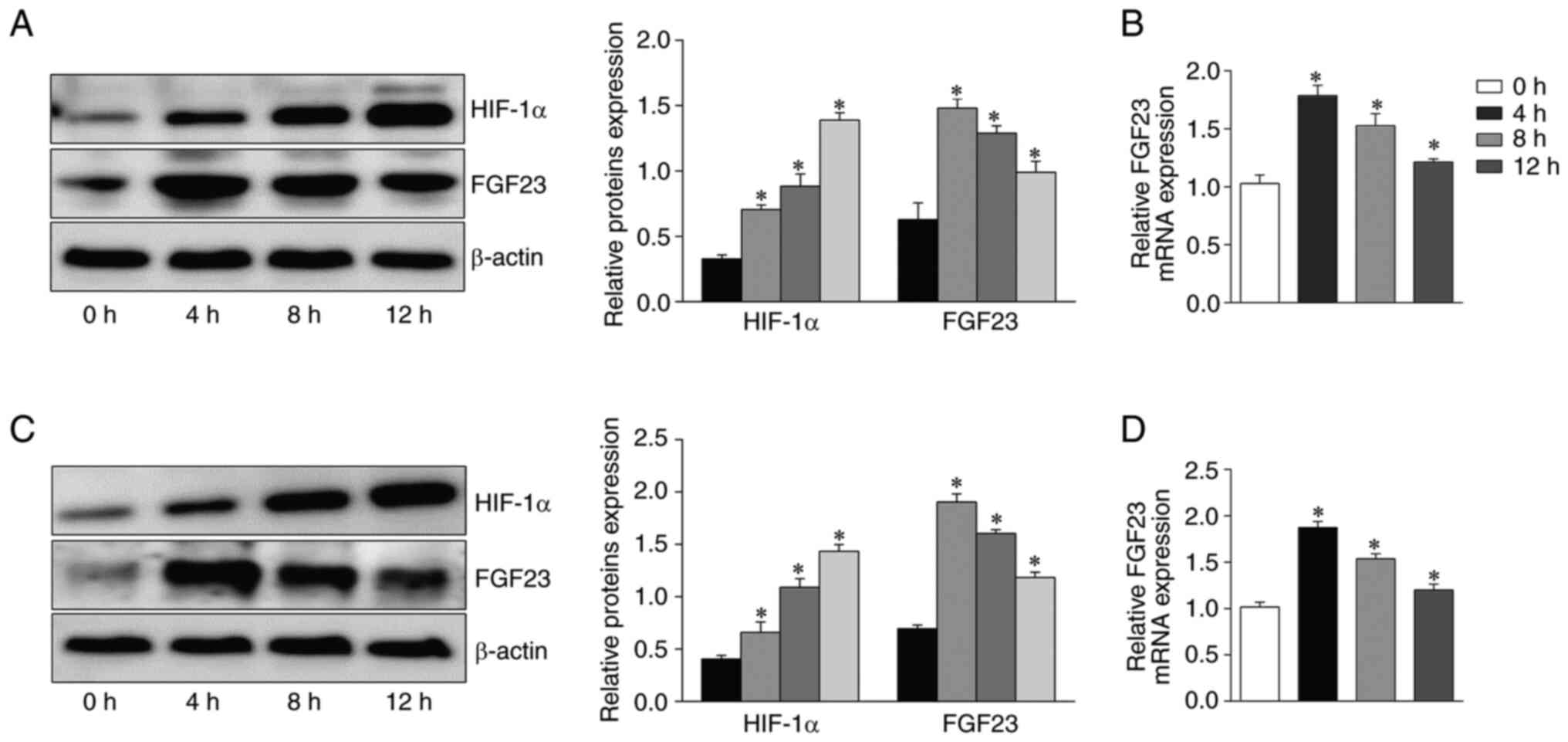
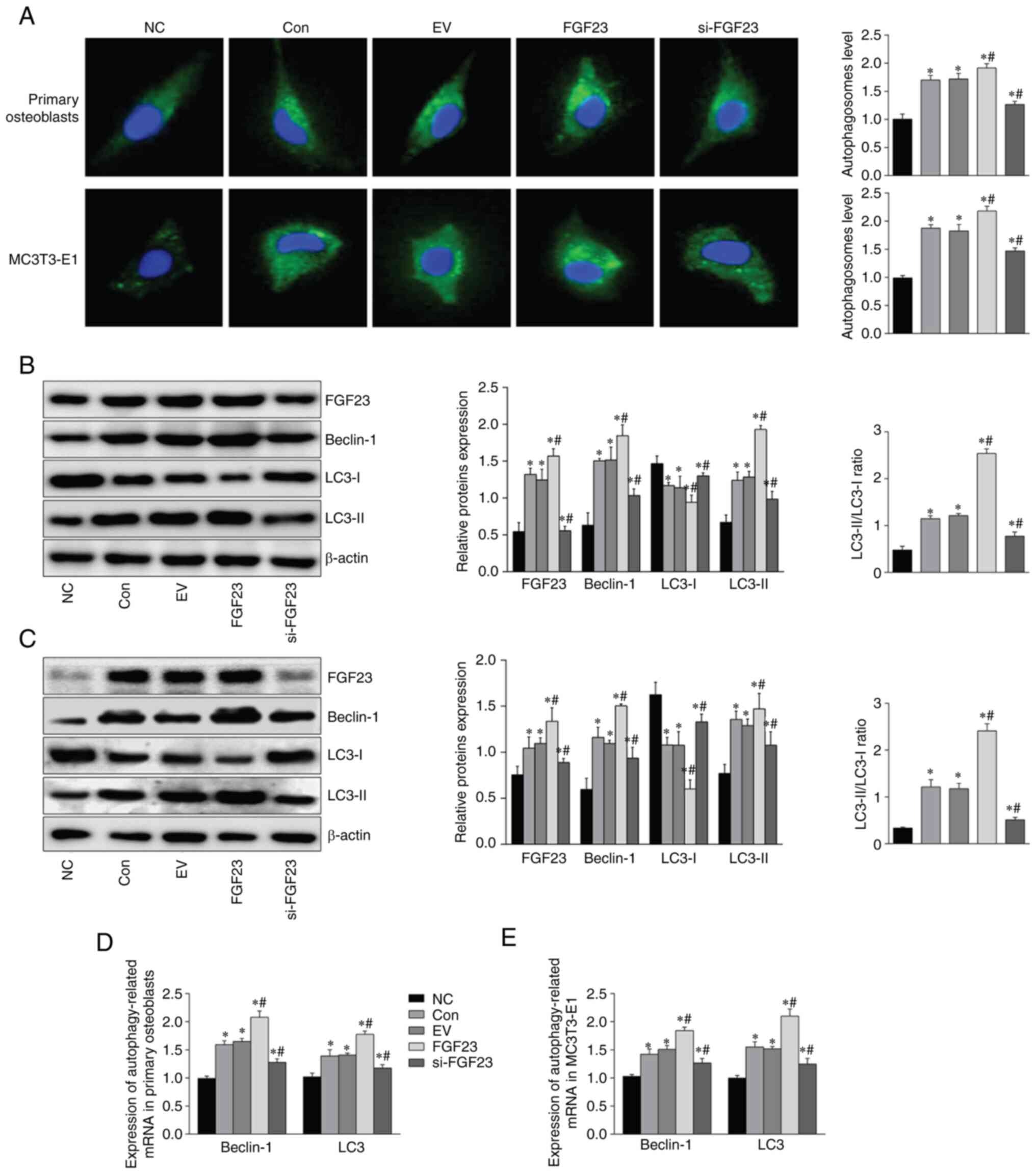
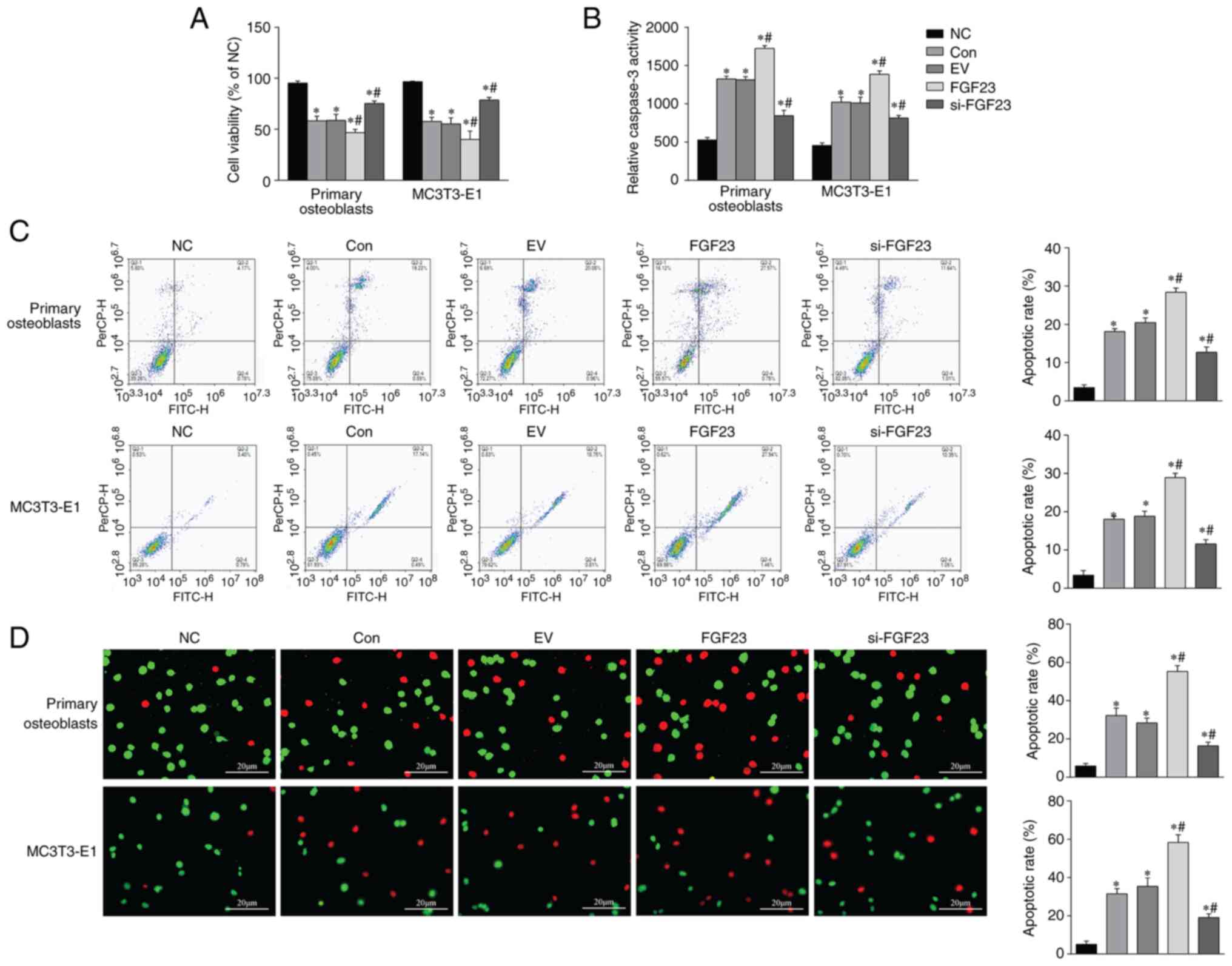
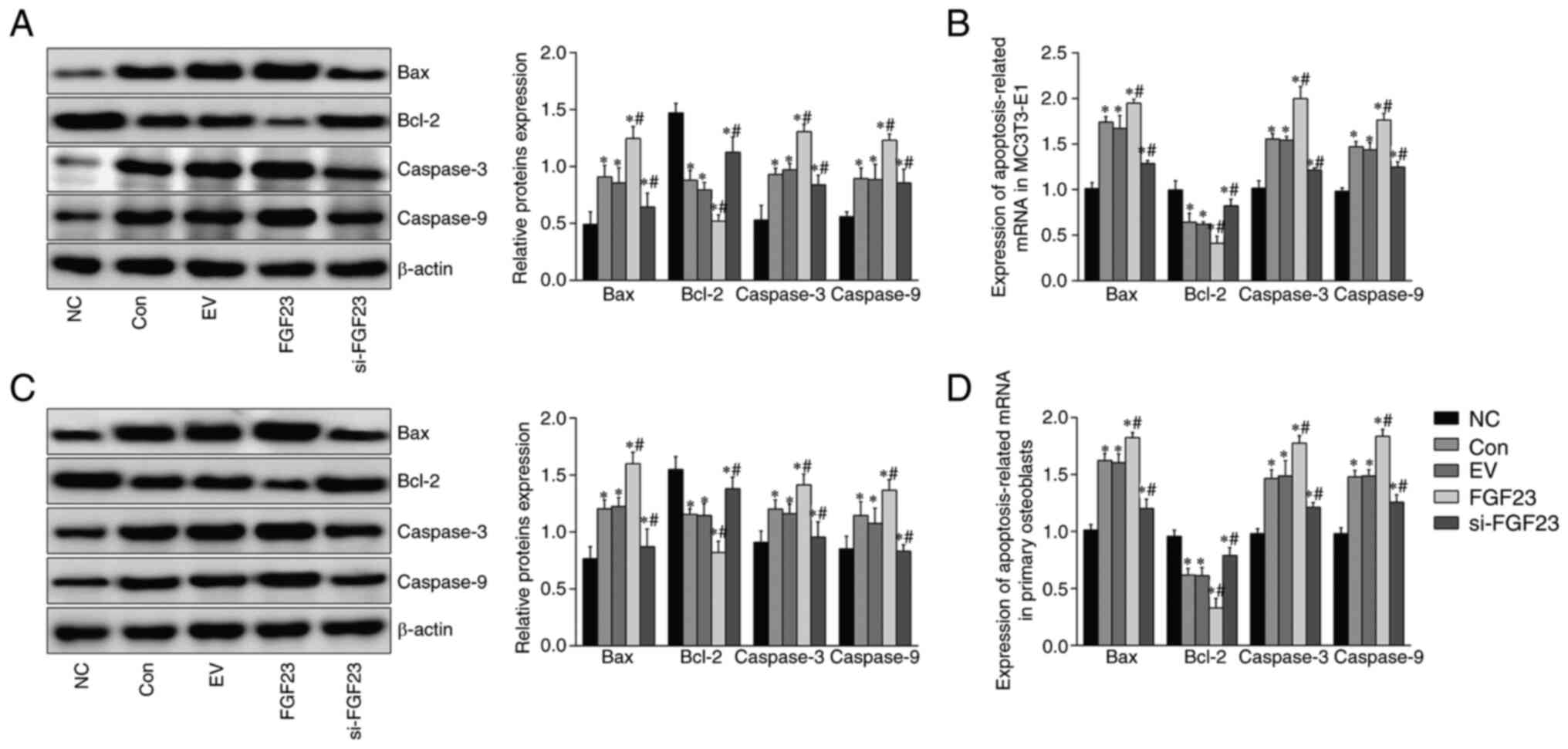
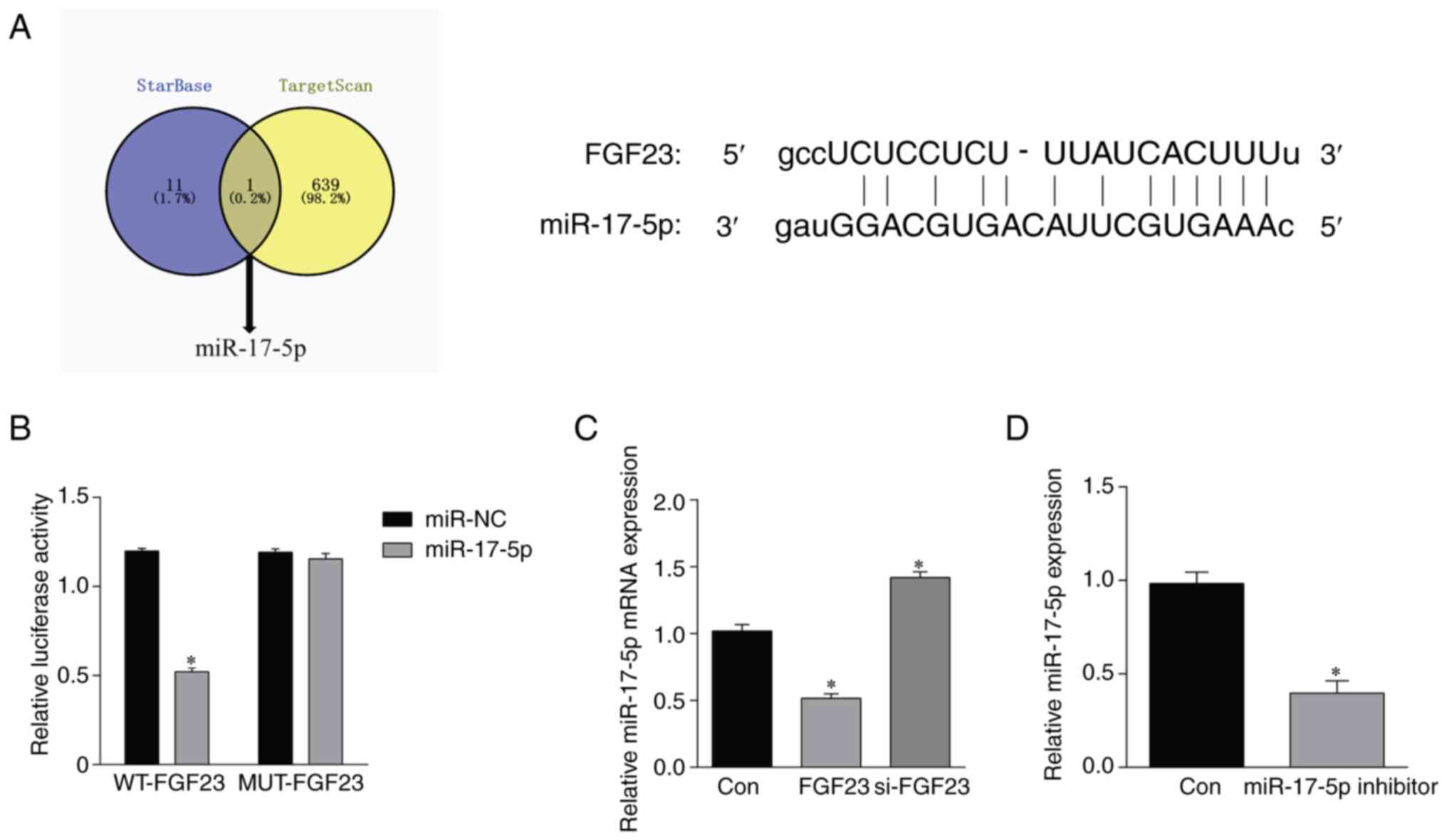
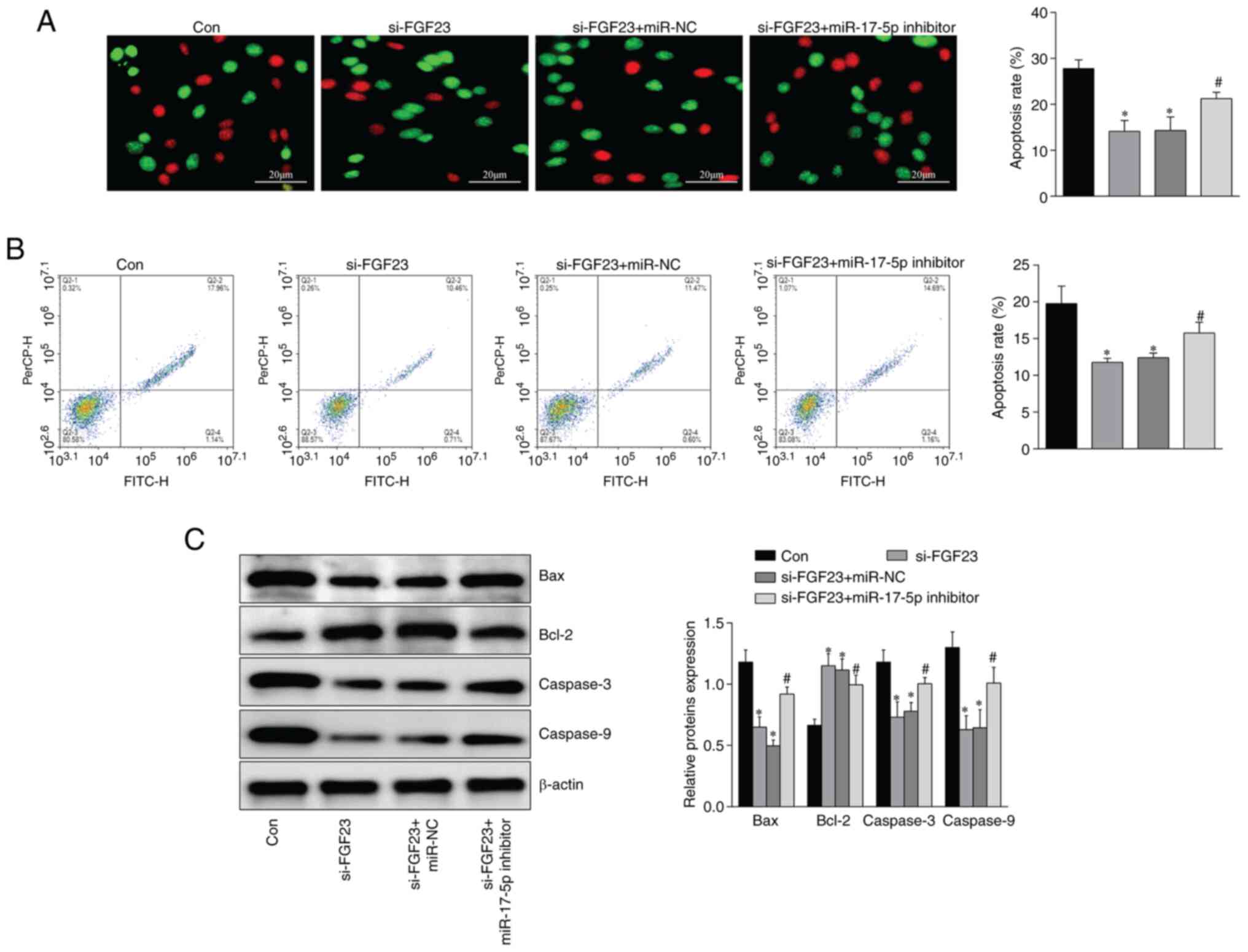
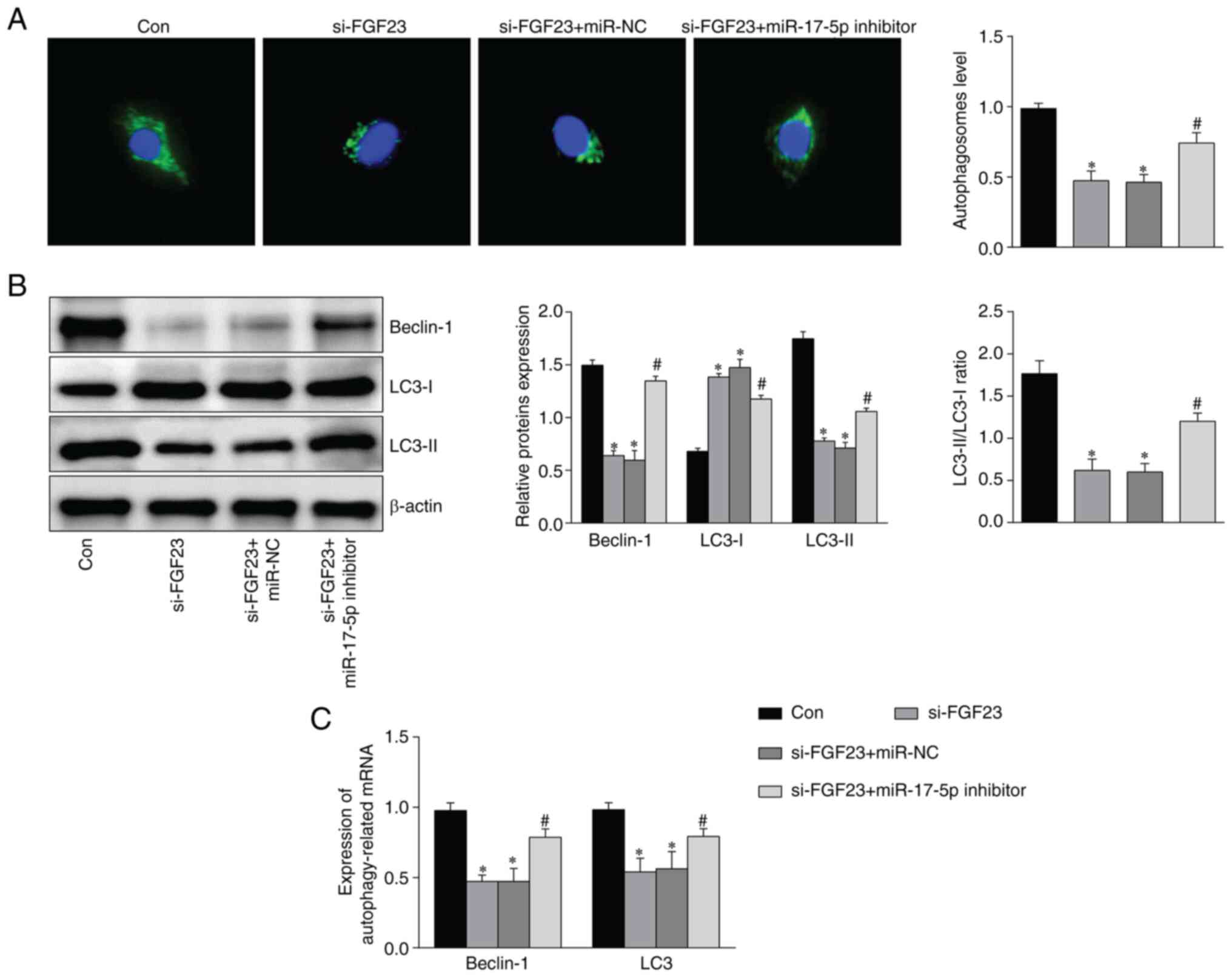
|
1
|
Cohen-Rosenblum A and Cui Q: Osteonecrosis
of the femoral head. Orthop Clin North Am. 50:139–149. 2019.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
Zhou L, Wang SI, Moon YJ, Kim KM, Lee KB,
Park BH, Jang KY and Kim JR: Overexpression of SIRT1 prevents
hypoxia-induced apoptosis in osteoblast cells. Mol Med Rep.
16:2969–2975. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
Wang G, Wang J, Sun D, Xin J, Wang L,
Huang D, Wu W and Xian CJ: Short-term hypoxia accelerates bone loss
in ovariectomized rats by suppressing osteoblastogenesis but
enhancing osteoclastogenesis. Med Sci Monit. 22:2962–2971. 2016.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
Ma HP, Ma XN, Ge BF, Zhen P, Zhou J, Gao
YH, Xian CJ and Chen KM: Icariin attenuates hypoxia-induced
oxidative stress and apoptosis in osteoblasts and preserves their
osteogenic differentiation potential in vitro. Cell Prolif.
47:527–539. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Itoh N and Ornitz DM: Evolution of the Fgf
and Fgfr gene families. Trends Genet. 20:563–569. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Gohil A and Imel EA: FGF23 and associated
disorders of phosphate wasting. Pediatr Endocrinol Rev. 17:17–34.
2019.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Chen G, Liu Y, Goetz R, Fu L, Jayaraman S,
Hu MC, Moe OW, Liang G, Li X and Mohammadi M: α-Klotho is a
non-enzymatic molecular scaffold for FGF23 hormone signalling.
Nature. 553:461–466. 2018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Andrukhova O, Zeitz U, Goetz R, Mohammadi
M, Lanske B and Erben RG: FGF23 acts directly on renal proximal
tubules to induce phosphaturia through activation of the
ERK1/2-SGK1 signaling pathway. Bone. 51:621–628. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Prié D, Forand A, Francoz C, Elie C, Cohen
I, Courbebaisse M, Eladari D, Lebrec D, Durand F and Friedlander G:
Plasma fibroblast growth factor 23 concentration is increased and
predicts mortality in patients on the liver-transplant waiting
list. PLoS One. 8:e661822013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Fukumoto S: FGF23 and bone and mineral
metabolism. Handb Exp Pharmacol. 262:281–308. 2020. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Millar SA, Anderson SI and O'Sullivan SE:
Osteokines and the vasculature: A review of the in vitro effects of
osteocalcin, fibroblast growth factor-23 and lipocalin-2. PeerJ.
7:e71392019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Domazetovic V, Falsetti I, Ciuffi S,
Iantomasi T, Marcucci G, Vincenzini MT and Brandi ML: Effect of
oxidative stress-induced apoptosis on active FGF23 levels in MLO-Y4
cells: The protective role of 17-β-estradiol. Int J Mol Sci.
23:21032022. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Ramzan F, Vickers MH and Mithen RF:
Epigenetics, microRNA and metabolic syndrome: A comprehensive
review. Int J Mol Sci. 22:50472021. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Wen J, Huang Y, Li H, Zhang X, Cheng P,
Deng D, Peng Z, Luo J, Zhao W, Lai Y and Liu Z: Over-expression of
miR-196b-5p is significantly associated with the progression of
myelodysplastic syndrome. Int J Hematol. 105:777–783. 2017.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Liu GZ, Chen C, Kong N, Tian R, Li YY, Li
Z, Wang KZ and Yang P: Identification of potential miRNA biomarkers
for traumatic osteonecrosis of femoral head. J Cell Physiol.
235:8129–8140. 2020. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Li Y, Yuan F, Song Y and Guan X: miR-17-5p
and miR-19b-3p prevent osteoarthritis progression by targeting
EZH2. Exp Ther Med. 20:1653–1663. 2020. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Su Y, Meng X, Wang W, Gu G and Chen Y:
LncRNA HOTAIR regulates fracture healing in osteoporotic rats
through inhibition on MiR-17-5p. Minerva Med. 112:525–527. 2021.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
Jia J, Feng X, Xu W, Yang S, Zhang Q, Liu
X, Feng Y and Dai Z: MiR-17-5p modulates osteoblastic
differentiation and cell proliferation by targeting SMAD7 in
non-traumatic osteonecrosis. Exp Mol Med. 46:e1072014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
Hou W, Song L, Zhao Y, Liu Q and Zhang S:
Inhibition of beclin-1-mediated autophagy by MicroRNA-17-5p
enhanced the radiosensitivity of glioma cells. Oncol Res. 25:43–53.
2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
Chen B, Yang Y, Wu J, Song J and Lu J:
microRNA-17-5p downregulation inhibits autophagy and myocardial
remodelling after myocardial infarction by targeting STAT3.
Autoimmunity. 55:43–51. 2022. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
Fang T, Wu Q, Zhou L, Mu S and Fu Q:
miR-106b-5p and miR-17-5p suppress osteogenic differentiation by
targeting Smad5 and inhibit bone formation. Exp Cell Res.
347:74–82. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22
|
Hou Z, Wang Z, Tao Y, Bai J, Yu B, Shen J,
Sun H, Xiao L, Xu Y, Zhou J, et al: KLF2 regulates osteoblast
differentiation by targeting of Runx2. Lab Invest. 99:271–280.
2019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23
|
Huang X, Chen C, Chen Y, Xu J and Liu L:
Omentin-1 alleviate interleukin-1β(IL-1β)-induced nucleus pulposus
cells senescence. Bioengineered. 13:13849–13859. 2022. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24
|
Liu X, Bian H, Dou QL, Huang XW, Tao WY,
Liu WH, Li N and Zhang WW: Ginkgetin alleviates inflammation,
oxidative stress, and apoptosis induced by hypoxia/reoxygenation in
h9c2 cells via caspase-3 dependent pathway. Biomed Res Int.
2020:19284102020. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
25
|
Wang W, Zhu M, Xu Z, Li W, Dong X, Chen Y,
Lin B and Li M: Ropivacaine promotes apoptosis of hepatocellular
carcinoma cells through damaging mitochondria and activating
caspase-3 activity. Biol Res. 52:362019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
26
|
Xiong H, Li Y and Liu M: DEPDC1B is
involved in the proliferation, metastasis, cell cycle arrest and
apoptosis of colon cancer cells by regulating NUP37. Mol Med Rep.
27:1262023. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
27
|
Qi J, Cao F, Han Y, Xie D, Song H, Chen B
and Zhou L: Reliability of cartilage digestion and FDA-EB
fluorescence staining for the detection of chondrocyte viability in
osteochondral grafts. Cell Tissue Bank. 19:399–404. 2018.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
28
|
Livak KJ and Schmittgen TD: Analysis of
relative gene expres- sion data using real-time quantitative PCR
and the 2(−Delta Delta C(T)) method. Methods. 25:402–408. 2001.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
29
|
Yi WR, Tu MJ, Yu AX, Lin J and Yu AM:
Bioengineered miR-34a modulates mitochondrial inner membrane
protein 17 like 2 (MPV17L2) expression toward the control of cancer
cell mitochondrial functions. Bioengineered. 13:12489–12503. 2022.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
30
|
Pang X, Wang SS, Zhang M, Jiang J, Fan HY,
Wu JS, Wang HF, Liang XH and Tang YL: OSCC cell-secreted exosomal
CMTM6 induced M2-like macrophages polarization via ERK1/2 signaling
pathway. Cancer Immunol Immunother. 70:1015–1029. 2021. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
31
|
Song J, Liu Y, Wang T, Li B and Zhang S:
MiR-17-5p promotes cellular proliferation and invasiveness by
targeting RUNX3 in gastric cancer. Biomed Pharmacother.
128:1102462020. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
32
|
Lu P, Shen YM, Hua T, Pan T, Chen G, Dai T
and Shi KQ: Overexpression of FGF2 delays the progression of
osteonecrosis of the femoral head activating the PI3K/Akt signaling
pathway. J Orthop Surg Res. 16:6132021. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
33
|
Bai Y, Liu Y, Jin S, Su K, Zhang H and Ma
S: Expression of microRNA-27a in a rat model of osteonecrosis of
the femoral head and its association with TGF-β/Smad7 signalling in
osteoblasts. Int J Mol Med. 43:850–860. 2019.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
34
|
Savchenko E, Teku GN, Boza-Serrano A, Russ
K, Berns M, Deierborg T, Lamas NJ, Wichterle H, Rothstein J,
Henderson CE, et al: FGF family members differentially regulate
maturation and proliferation of stem cell-derived astrocytes. Sci
Rep. 9:96102019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
35
|
Mancias JD and Kimmelman AC: Mechanisms of
selective autophagy in normal physiology and cancer. J Mol Biol.
428:1659–1680. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
36
|
Musumeci G, Castrogiovanni P, Trovato FM,
Weinberg AM, Al-Wasiyah MK, Alqahtani MH and Mobasheri A:
Biomarkers of chondrocyte apoptosis and autophagy in
osteoarthritis. Int J Mol Sci. 16:20560–20575. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
37
|
Zheng L, Wang W, Ni J, Mao X, Song D, Liu
T, Wei J and Zhou H: Role of autophagy in tumor necrosis
factor-α-induced apoptosis of osteoblast cells. J Investig Med.
65:1014–1020. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
38
|
Zheng LW, Wang WC, Mao XZ, Luo YH, Tong ZY
and Li D: TNF-α regulates the early development of avascular
necrosis of the femoral head by mediating osteoblast autophagy and
apoptosis via the p38 MAPK/NF-κB signaling pathway. Cell Biol Int.
44:1881–1889. 2020. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
39
|
Zheng J, Zhu X, He Y, Hou S, Liu T, Zhi K,
Hou T and Gao L: CircCDK8 regulates osteogenic differentiation and
apoptosis of PDLSCs by inducing ER stress/autophagy during hypoxia.
Ann N Y Acad Sci. 1485:56–70. 2021. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
40
|
Zhang T, Li Y, Park KA, Byun HS, Won M,
Jeon J, Lee Y, Seok JH, Choi SW, Lee SH, et al: Cucurbitacin
induces autophagy through mitochondrial ROS production which
counteracts to limit caspase-dependent apoptosis. Autophagy.
8:559–576. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
41
|
Ho TT, Warr MR, Adelman ER, Lansinger OM,
Flach J, Verovskaya EV, Figueroa ME and Passegué E: Autophagy
maintains the metabolism and function of young and old stem cells.
Nature. 543:205–210. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
42
|
Manai F, Azzalin A, Gabriele F, Martinelli
C, Morandi M, Biggiogera M, Bozzola M and Comincini S: The in vitro
effects of enzymatic digested gliadin on the functionality of the
autophagy process. Int J Mol Sci. 19:6352018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
43
|
Wang Z, Xie Q, Zhou H, Zhang M, Shen J and
Ju D: Amino acid degrading enzymes and autophagy in cancer therapy.
Front Pharmacol. 11:5825872021. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
44
|
Shi Y: Apoptosome: The cellular engine for
the activation of caspase-9. Structure. 10:285–288. 2002.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
45
|
Fan TJ, Han LH, Cong RS and Liang J:
Caspase family proteases and apoptosis. Acta Biochim Biophys Sin
(Shanghai). 37:719–727. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
46
|
Araya LE, Soni IV, Hardy JA and Julien O:
Deorphanizing caspase-3 and caspase-9 substrates in and out of
apoptosis with deep substrate profiling. ACS Chem Biol.
16:2280–2296. 2021. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
47
|
Perini GF, Ribeiro GN, Pinto Neto JV,
Campos LT and Hamerschlak N: BCL-2 as therapeutic target for
hematological malignancies. J Hematol Oncol. 11:652018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
48
|
Ly JD, Grubb DR and Lawen A: The
mitochondrial membrane potential (deltapsi(m)) in apoptosis; an
update. Apoptosis. 8:115–128. 2003. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
49
|
Shu Y, Yang Y, Zhao Y, Ma L, Fu P, Wei T
and Zhang L: Melittin inducing the apoptosis of renal tubule
epithelial cells through upregulation of Bax/Bcl-2 expression and
activation of TNF-α signaling pathway. Biomed Res Int.
2019:94503682019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
50
|
Orfanidou T, Malizos KN, Varitimidis S and
Tsezou A: 1,25-Dihydroxyvitamin D(3) and extracellular inorganic
phosphate activate mitogen-activated protein kinase pathway through
fibroblast growth factor 23 contributing to hypertrophy and
mineralization in osteoarthritic chondrocytes. Exp Biol Med
(Maywood). 237:241–253. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
51
|
Shi YP, Liu GL, Li S and Liu XL: miR-17-5p
knockdown inhibits proliferation, autophagy and promotes apoptosis
in thyroid cancer via targeting PTEN. Neoplasma. 67:249–258. 2020.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
52
|
Li H, Li T, Wang S, Wei J, Fan J, Li J,
Han Q, Liao L, Shao C and Zhao RC: miR-17-5p and miR-106a are
involved in the balance between osteogenic and adipogenic
differentiation of adipose-derived mesenchymal stem cells. Stem
Cell Res. 10:313–324. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
53
|
Hao MX, Wang X and Jiao KL: MicroRNA-17-5p
mediates hypoxia-induced autophagy and inhibits apoptosis by
targeting signal transducer and activator of transcription 3 in
vascular smooth muscle cells. Exp Ther Med. 13:935–941. 2017.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
54
|
Yuan Y, Li X and Li M: Overexpression of
miR-17-5p protects against high glucose-induced endothelial cell
injury by targeting E2F1-mediated suppression of autophagy and
promotion of apoptosis. Int J Mol Med. 42:1559–1568.
2018.PubMed/NCBI
|