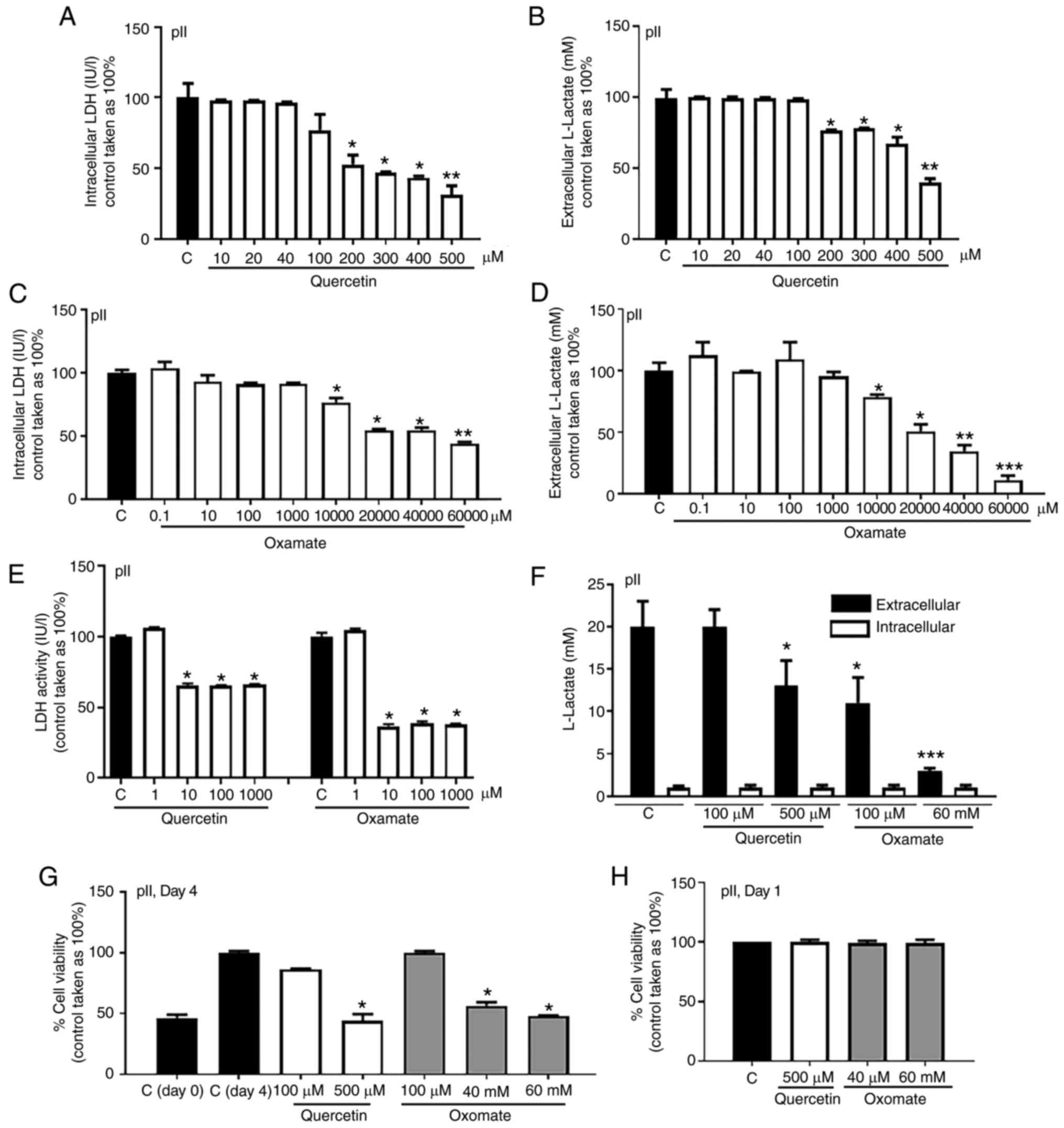
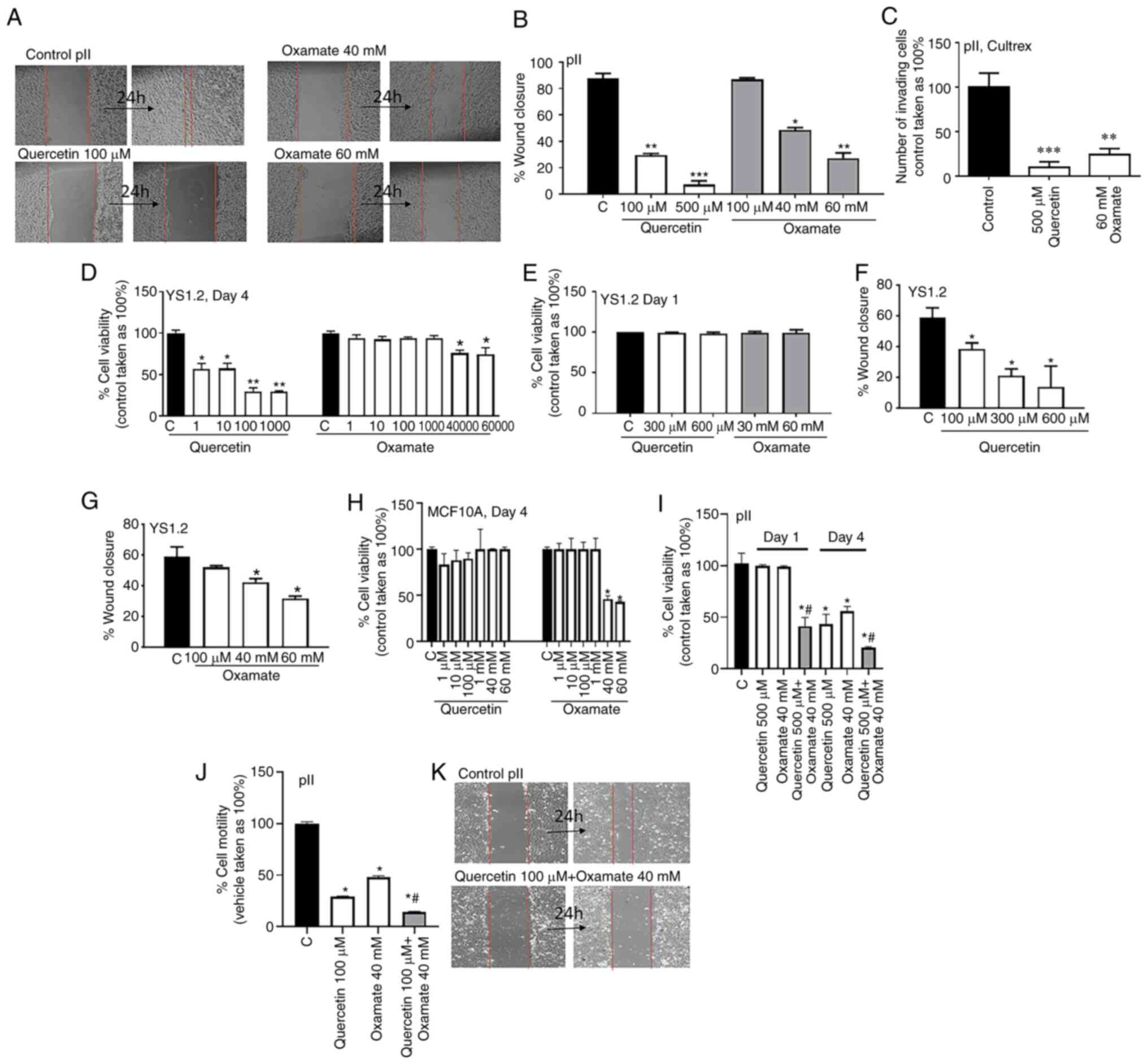
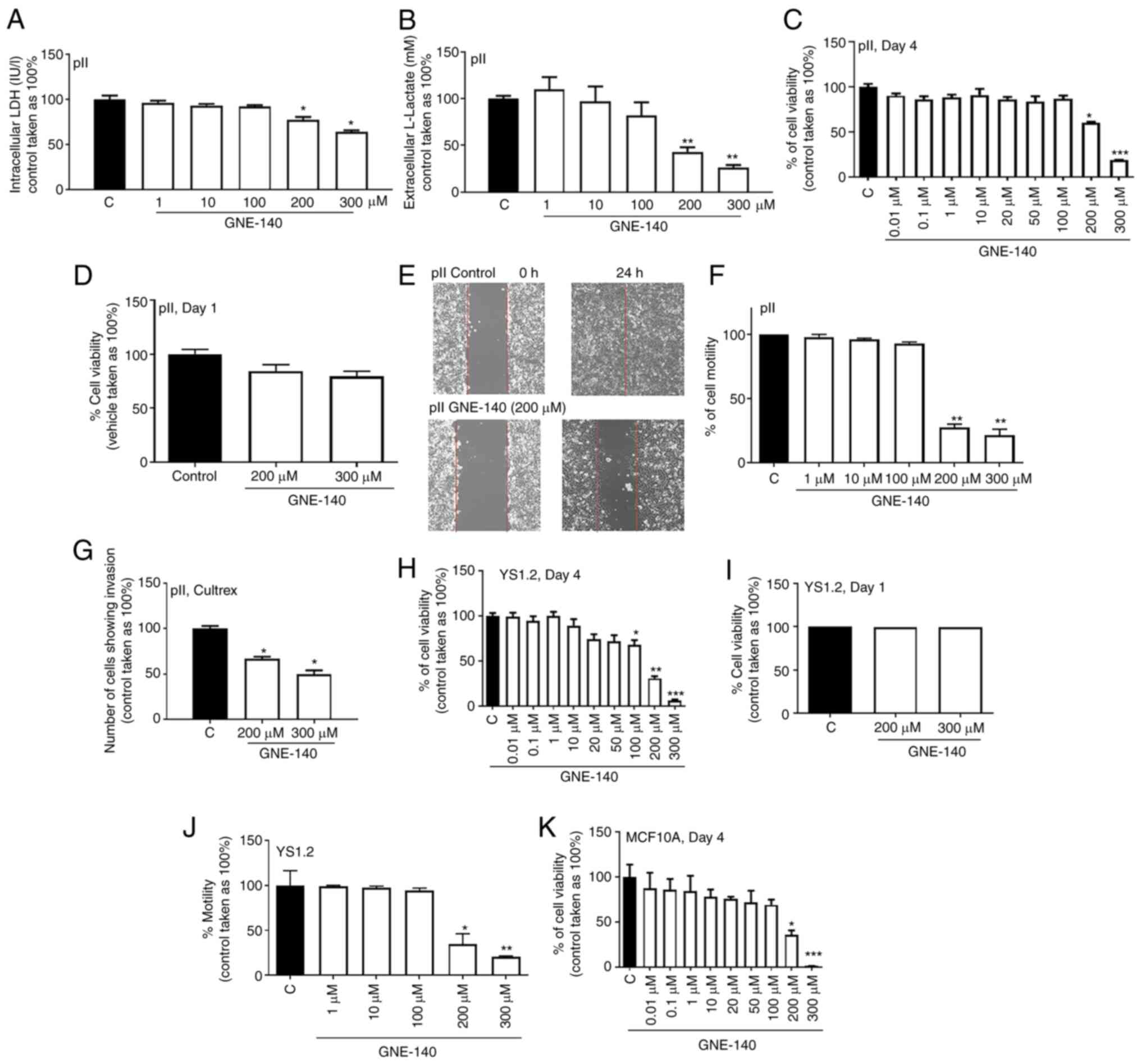
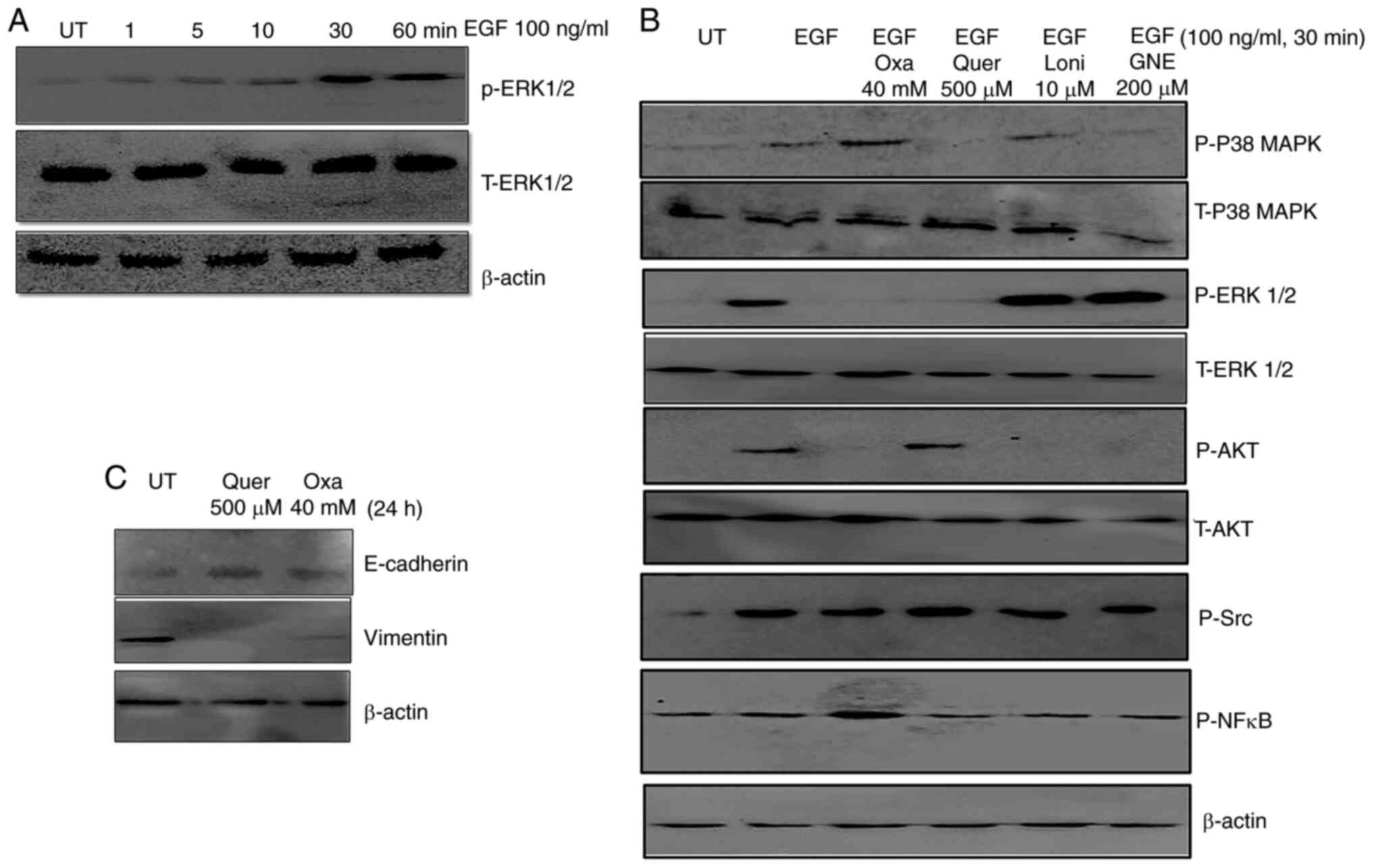
|
1
|
Schwartz MK: Enzymes as prognostic markers
and therapeutic indicators in patients with cancer. Clin Chim Acta.
206:77–82. 1992. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
Wang ZY, Loo TY, Shen JG, Wang N, Wang DM,
Yang DP, Mo SL, Guan XY and Chen JP: LDH-A silencing suppresses
breast cancer tumorigenicity through induction of oxidative stress
mediated mitochondrial pathway apoptosis. Breast Cancer Res Treat.
131:791–800. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
Bonuccelli G, Whitaker-Menezes D,
Castello-Cros R, Pavlides S, Pestell RG, Fatatis A, Witkiewicz AK,
Vander Heiden MG, Migneco G, Chiavarina B, et al: The reverse
warburg effect: Glycolysis inhibitors prevent the tumor promoting
effects of caveolin-1 deficient cancer associated fibroblasts. Cell
cycle. 9:1960–1971. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
Khajah MA, Khushaish S and Luqmani YA:
Lactate dehydrogenase A or B knockdown reduces lactate production
and inhibits breast cancer cell motility in vitro. Front Pharmacol.
12:7470012021. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Rizwan A, Serganova I, Khanin R, Karabeber
H, Ni X, Thakur S, Zakian KL, Blasberg R and Koutcher JA:
Relationships between LDH-A, lactate, and metastases in 4T1 breast
tumors. Clin Cancer Res. 19:5158–5169. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Zha X, Wang F, Wang Y, He S, Jing Y, Wu X
and Zhang H: Lactate dehydrogenase B is critical for hyperactive
mTOR-mediated tumorigenesis. Cancer Res. 71:13–18. 2011.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Huang WC, Swietach P, Vaughan-Jones RD,
Ansorge O and Glitsch MD: Extracellular acidification elicits
spatially and temporally distinct Ca2+ signals. Curr Biol.
18:781–785. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Fukumura D, Xu L, Chen Y, Gohongi T, Seed
B and Jain RK: Hypoxia and acidosis independently up-regulate
vascular endothelial growth factor transcription in brain tumors in
vivo. Cancer Res. 61:6020–6024. 2001.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Shi Q, Le X, Wang B, Abbruzzese JL, Xiong
Q, He Y and Xie K: Regulation of vascular endothelial growth factor
expression by acidosis in human cancer cells. Oncogene.
20:3751–3756. 2001. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Xu L, Fukumura D and Jain RK: Acidic
extracellular pH induces vascular endothelial growth factor (VEGF)
in human glioblastoma cells via ERK1/2 MAPK signaling pathway:
Mechanism of low pH-induced VEGF. J Biol Chemistry.
277:11368–11374. 2002. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Graham RM, Frazier DP, Thompson JW, Haliko
S, Li H, Wasserlauf BJ, Spiga MG, Bishopric NH and Webster KA: A
unique pathway of cardiac myocyte death caused by hypoxia-acidosis.
J Exp Biol. 207:3189–3200. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Fischer K, Hoffmann P, Voelkl S,
Meidenbauer N, Ammer J, Edinger M, Gottfried E, Schwarz S, Rothe G,
Hoves S, et al: Inhibitory effect of tumor cell-derived lactic acid
on human T cells. Blood. 109:3812–3819. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Zhai X, Yang Y, Wan J, Zhu R and Wu Y:
Inhibition of LDH-A by oxamate induces G2/M arrest, apoptosis and
increases radiosensitivity in nasopharyngeal carcinoma cells. Oncol
Rep. 30:2983–2991. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Ye W, Zheng Y, Zhang S, Yan L, Cheng H and
Wu M: Oxamate improves glycemic control and insulin sensitivity via
inhibition of tissue lactate production in db/db mice. PLoS One.
11:e01503032016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Liu H, Zeng L, Yang Y, Huang Z, Guo C,
Huang L, Niu X, Zhang C and Wang H: Bcl-3 regulates the function of
Th17 cells through raptor mediated glycolysis metabolism. Front
Immunol. 13:9297852022. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Mazzio E, Mack N, Badisa RB and Soliman
KFA: Triple isozyme lactic acid dehydrogenase inhibition in fully
viable MDA-MB-231 cells induces cytostatic effects that are not
reversed by exogenous lactic acid. Biomolecules. 11:17512021.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Zhai M, Cui S, Li L, Cheng C, Zhang Z, Liu
J and Wei F: Mechanical force modulates alveolar bone marrow
mesenchymal cells characteristics for bone remodeling during
orthodontic tooth movement through lactate production. Cells.
11:37242022. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
Zhao P, Wang S, Jiang J, Gao Y, Wang Y,
Zhao Y, Zhang J, Zhang M and Huang Y: Targeting lactate metabolism
and immune interaction in breast tumor via protease-triggered
delivery. J Control Release. 358:706–717. 2023. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
Lacerda Q, Rochani A, Oeffinger B, Liu JB,
Wessner CE, Tahmasebi A, Falatah H, Lee P, Leeper DB, Forsberg F,
et al: Tumoral oxygenation and biodistribution of Lonidamine oxygen
microbubbles following localized ultrasound-triggered delivery. Int
J Pharm. 625:1220722022. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
Tian LR, Lin MZ, Zhong HH, Cai YJ, Li B,
Xiao ZC and Shuai XT: Nanodrug regulates lactic acid metabolism to
reprogram the immunosuppressive tumor microenvironment for enhanced
cancer immunotherapy. Biomater Sci. 10:3892–3900. 2022. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
Zhang R, Li R, Zhang L, Chen G, Mo L,
Jiang R, Xu X, Wang X, Zhao Y, Zhang L, et al: A dual-mechanism
based nutrient partitioning nanoregulator for enhanced
immunotherapy against anti-PD-1 resistant tumors. ACS Nano.
17:13461–13473. 2023. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22
|
Mathupala SP, Parajuli P and Sloan AE:
Silencing of monocarboxylate transporters via small interfering
ribonucleic acid inhibits glycolysis and induces cell death in
malignant glioma: An in vitro study. Neurosurgery. 55:1410–1419;
discussion 1419. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23
|
Fang J, Quinones QJ, Holman TL, Morowitz
MJ, Wang Q, Zhao H, Sivo F, Maris JM and Wahl ML: The H+-linked
monocarboxylate transporter (MCT1/SLC16A1): A potential therapeutic
target for high-risk neuroblastoma. Mol Pharmacol. 70:2108–2115.
2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24
|
Sonveaux P, Végran F, Schroeder T, Wergin
MC, Verrax J, Rabbani ZN, De Saedeleer CJ, Kennedy KM, Diepart C,
Jordan BF, et al: Targeting lactate-fueled respiration selectively
kills hypoxic tumor cells in mice. J Clin Invest. 118:3930–3942.
2008.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
25
|
Colen CB, Shen Y, Ghoddoussi F, Yu P,
Francis TB, Koch BJ, Monterey MD, Galloway MP, Sloan AE and
Mathupala SP: Metabolic targeting of lactate efflux by malignant
glioma inhibits invasiveness and induces necrosis: An in vivo
study. Neoplasia. 13:620–632. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
26
|
Belt JA, Thomas JA, Buchsbaum RN and
Racker E: Inhibition of lactate transport and glycolysis in Ehrlich
ascites tumor cells by bioflavonoids. Biochemistry. 18:3506–3511.
1979. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
27
|
Deuticke B: Monocarboxylate transport in
erythrocytes. J Membr Biol. 70:89–103. 1982. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
28
|
Wang Q and Morris ME: Flavonoids modulate
monocarboxylate transporter-1-mediated transport of
gamma-hydroxybutyrate in vitro and in vivo. Drug Metab Dispos.
35:201–208. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
29
|
Morais-Santos F, Miranda-Gonçalves V,
Pinheiro S, Vieira AF, Paredes J, Schmitt FC, Baltazar F and
Pinheiro C: Differential sensitivities to lactate transport
inhibitors of breast cancer cell lines. Endocr Relat Cancer.
21:27–38. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
30
|
Thornburg JM, Nelson KK, Clem BF, Lane AN,
Arumugam S, Simmons A, Eaton JW, Telang S and Chesney J: Targeting
aspartate aminotransferase in breast cancer. Breast Cancer Res.
10:R842008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
31
|
Eyassu F and Angione C: Modelling pyruvate
dehydrogenase under hypoxia and its role in cancer metabolism. R
Soc Open Sci. 4:1703602017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
32
|
Kong L, Du W, Cui Z, Wang L, Yang Z, Zhang
H and Lin D: Expression of lactate dehydrogenase C in MDA-MB-231
cells and its role in tumor invasion and migration. Mol Med Rep.
13:3533–3538. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
33
|
Al Saleh S, Al Mulla F and Luqmani YA:
Estrogen receptor silencing induces epithelial to mesenchymal
transition in human breast cancer cells. PLoS One. 6:e206102011.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
34
|
Luqmani YA, Al Azmi A, Al Bader M, Abraham
G and El Zawahri M: Modification of gene expression induced by
siRNA targeting of estrogen receptor alpha in MCF7 human breast
cancer cells. Int J Oncol. 34:231–242. 2009.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
35
|
Khajah MA, Al Saleh S, Mathew PM and
Luqmani YA: Differential effect of growth factors on invasion and
proliferation of endocrine resistant breast cancer cells. PLoS One.
7:e418472012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
36
|
Luqmani YA and Alam-Eldin N: Overcoming
resistance to endocrine therapy in breast cancer: New approaches to
a nagging problem. Med Princ Pract. 25 (Suppl 2):28–40. 2016.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
37
|
Al Saleh S, Sharaf LH and Luqmani YA:
Signalling pathways involved in endocrine resistance in breast
cancer and associations with epithelial to mesenchymal transition
(review). Int J Oncol. 38:1197–1217. 2011.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
38
|
Zhao Z, Han F, Yang S, Wu J and Zhan W:
Oxamate-mediated inhibition of lactate dehydrogenase induces
protective autophagy in gastric cancer cells: Involvement of the
Akt-mTOR signaling pathway. Cancer Lett. 358:17–26. 2015.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
39
|
Valvona CJ and Fillmore HL: Oxamate, but
not selective targeting of LDH-A, inhibits medulloblastoma cell
glycolysis, growth and motility. Brain Sci. 8:562018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
40
|
Boudreau A, Purkey HE, Hitz A, Robarge K,
Peterson D, Labadie S, Kwong M, Hong R, Gao M, Del Nagro C, et al:
Metabolic plasticity underpins innate and acquired resistance to
LDHA inhibition. Nat Chem Biol. 12:779–786. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
41
|
Ždralević M, Brand A, Di Ianni L, Dettmer
K, Reinders J, Singer K, Peter K, Schnell A, Bruss C, Decking SM,
et al: Double genetic disruption of lactate dehydrogenases A and B
is required to ablate the ‘Warburg effect’ restricting tumor growth
to oxidative metabolism. J Biol Chem. 293:15947–15961. 2018.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
42
|
De Lena M, Lorusso V, Latorre A, Fanizza
G, Gargano G, Caporusso L, Guida M, Catino A, Crucitta E, Sambiasi
D and Mazzei A: Paclitaxel, cisplatin and lonidamine in advanced
ovarian cancer. A phase II study. Eur J Cancer. 37:364–368. 2001.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
43
|
Portalone L, Lombardi A, Antilli A,
Cruciani AR, Magliacani V, Mugnaini L, Nunziati F, Perrone N,
Signora M and Salvati F: Treatment of inoperable non-small cell
lung carcinoma stage IIIb and IV with cisplatin, epidoxorubicin,
vindesine and lonidamine: A phase II study. Tumori. 85:239–242.
1999. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
44
|
Papaldo P, Lopez M, Cortesi E, Cammilluzzi
E, Antimi M, Terzoli E, Lepidini G, Vici P, Barone C, Ferretti G,
et al: Addition of either lonidamine or granulocyte
colony-stimulating factor does not improve survival in early breast
cancer patients treated with high-dose epirubicin and
cyclophosphamide. J Clin Oncol. 21:3462–3468. 2003. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
45
|
Berruti A, Bitossi R, Gorzegno G, Bottini
A, Alquati P, De Matteis A, Nuzzo F, Giardina G, Danese S, De Lena
M, et al: Time to progression in metastatic breast cancer patients
treated with epirubicin is not improved by the addition of either
cisplatin or lonidamine: Final results of a phase III study with a
factorial design. J Clin Oncol. 20:4150–4159. 2002. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
46
|
Pacini P, Rinaldini M, Algeri R, Guarneri
A, Tucci E, Barsanti G, Neri B, Bastiani P, Marzano S and Fallai C:
FEC (5-fluorouracil, epidoxorubicin and cyclophosphamide) versus EM
(epidoxorubicin and mitomycin-C) with or without lonidamine as
first-line treatment for advanced breast cancer. A multicentric
randomised study. Final results. Eur J Cancer. 36:966–975. 2000.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
47
|
Vaez S, Parivr K, Amidi F, Rudbari NH,
Moini A and Amini N: Quercetin and polycystic ovary syndrome;
inflammation, hormonal parameters and pregnancy outcome: A
randomized clinical trial. Am J Reprod Immunol. 89:e136442023.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
48
|
Shohan M, Nashibi R, Mahmoudian-Sani MR,
Abolnezhadian F, Ghafourian M, Alavi SM, Sharhani A and Khodadadi
A: The therapeutic efficacy of quercetin in combination with
antiviral drugs in hospitalized COVID-19 patients: A randomized
controlled trial. Eur J Pharmacol. 914:1746152022. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
49
|
Henning SM, Wang P, Lee RP, Trang A,
Husari G, Yang J, Grojean EM, Ly A, Hsu M, Heber D, et al:
Prospective randomized trial evaluating blood and prostate tissue
concentrations of green tea polyphenols and quercetin in men with
prostate cancer. Food Funct. 11:4114–4122. 2020. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
50
|
Peng M, Yin N, Chhangawala S, Xu K, Leslie
CS and Li MO: Aerobic glycolysis promotes T helper 1 cell
differentiation through an epigenetic mechanism. Science.
354:481–484. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
51
|
Pucino V, Bombardieri M, Pitzalis C and
Mauro C: Lactate at the crossroads of metabolism, inflammation, and
autoimmunity. Eur J Immunol. 47:14–21. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
52
|
Constant JS, Feng JJ, Zabel DD, Yuan H,
Suh DY, Scheuenstuhl H, Hunt TK and Hussain MZ: Lactate elicits
vascular endothelial growth factor from macrophages: A possible
alternative to hypoxia. Wound Repair Regen. 8:353–360. 2000.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
53
|
Végran F, Boidot R, Michiels C, Sonveaux P
and Feron O: Lactate influx through the endothelial cell
monocarboxylate transporter MCT1 supports an NF-κB/IL-8 pathway
that drives tumor angiogenesis. Cancer Res. 71:2550–2560. 2011.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
54
|
Apicella M, Giannoni E, Fiore S, Ferrari
KJ, Fernández-Pérez D, Isella C, Granchi C, Minutolo F, Sottile A,
Comoglio PM, et al: Increased lactate secretion by cancer cells
sustains non-cell-autonomous adaptive resistance to MET and EGFR
targeted therapies. Cell Metab. 28:848–865.e6. 2018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
55
|
Liu C, Wu J, Zhu J, Kuei C, Yu J, Shelton
J, Sutton SW, Li X, Yun SJ, Mirzadegan T, et al: Lactate inhibits
lipolysis in fat cells through activation of an orphan
G-protein-coupled receptor, GPR81. J Biol Chem. 284:2811–2822.
2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
56
|
Roland CL, Arumugam T, Deng D, Liu SH,
Philip B, Gomez S, Burns WR, Ramachandran V, Wang H,
Cruz-Monserrate Z and Logsdon CD: Cell surface lactate receptor
GPR81 is crucial for cancer cell survival. Cancer Res.
74:5301–5310. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
57
|
Khajah MA, Almohri I, Mathew PM and
Luqmani YA: Extracellular alkaline pH leads to increased metastatic
potential of estrogen receptor silenced endocrine resistant breast
cancer cells. PLoS One. 8:e763272013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
58
|
Khajah MA and Luqmani YA: Involvement of
membrane blebbing in immunological disorders and cancer. Med Princ
Pract. 25 Suppl 2 (Suppl 2):S18–S27. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
59
|
Khajah MA, Mathew PM, Alam-Eldin NS and
Luqmani YA: Bleb formation is induced by alkaline but not acidic pH
in estrogen receptor silenced breast cancer cells. Int J Oncol.
46:1685–1698. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|