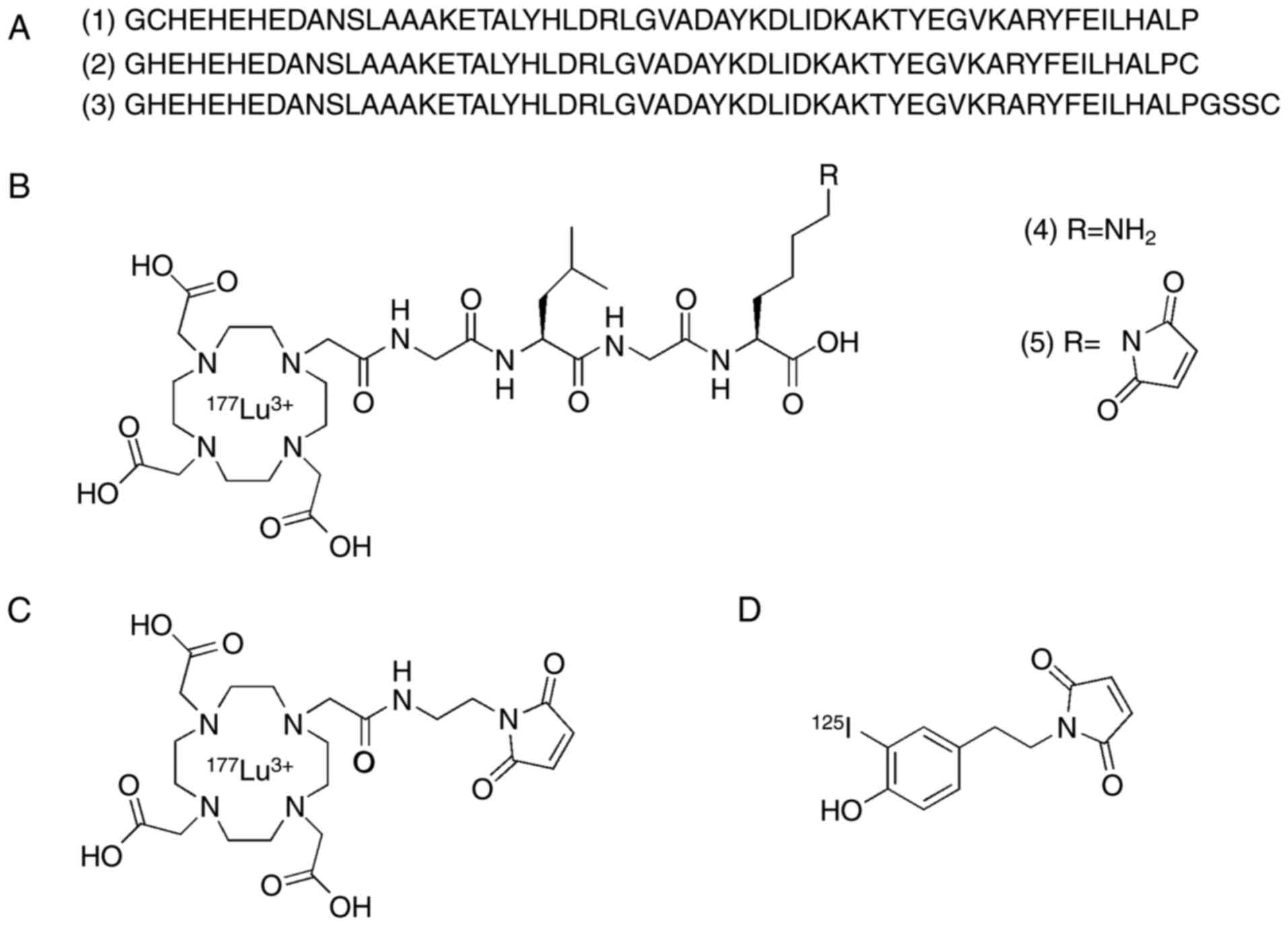
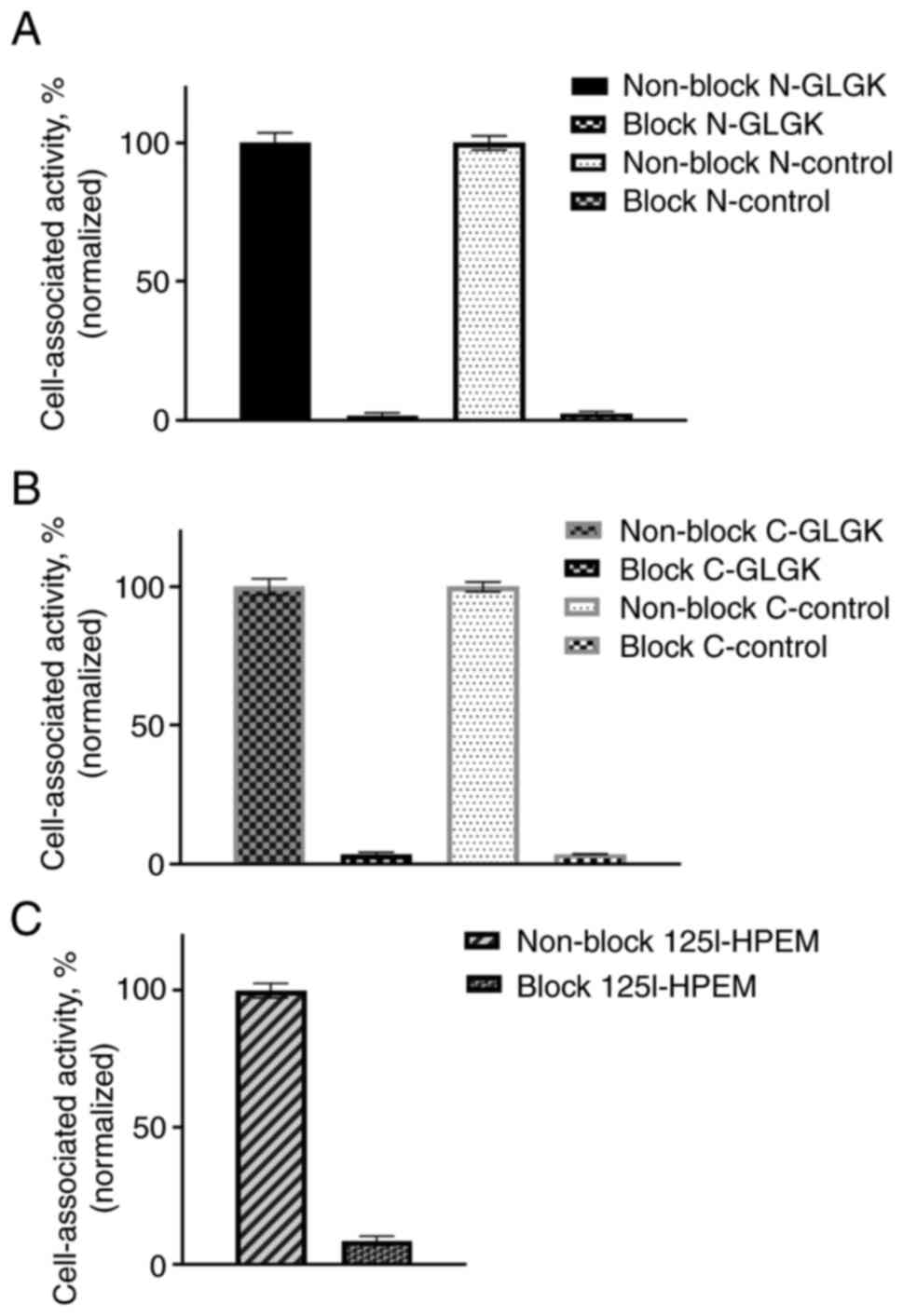
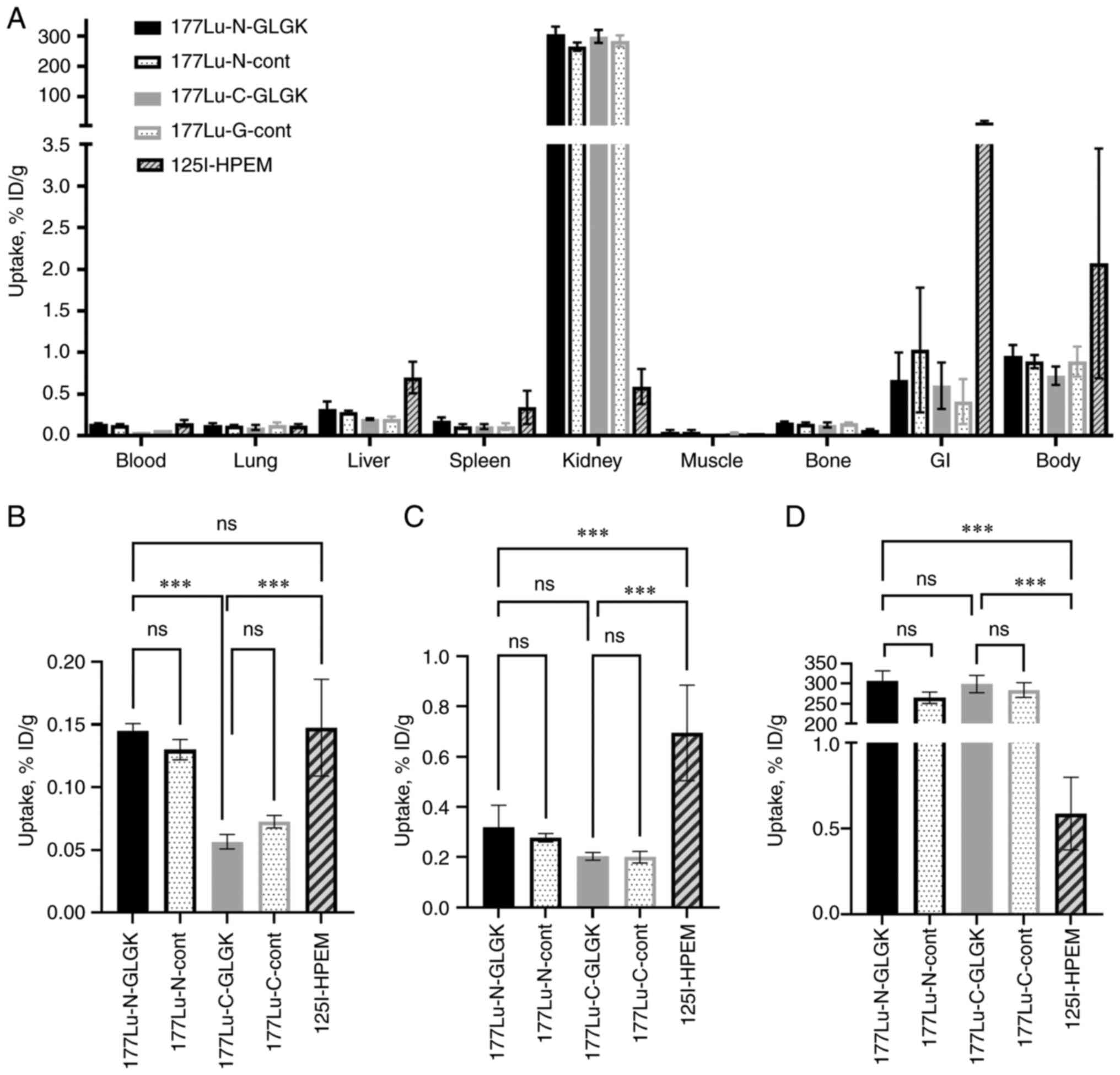
|
1
|
Tolmachev VM, Chernov VI and Deyev SM:
Targeted nuclear medicine. Seek and destroy. Russ Chem Rev.
91:RCR50342022. View
Article : Google Scholar
|
|
2
|
Krasniqi A, D'Huyvetter M, Devoogdt N,
Frejd FY, Sörensen J, Orlova A, Keyaerts M and Tolmachev V:
Same-Day imaging using small proteins: Clinical experience and
translational prospects in oncology. J Nucl Med. 59:885–891. 2018.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
Bragina OD, Deyev SM, Chernov VI and
Tolmachev VM: The evolution of targeted radionuclide diagnosis of
HER2-Positive breast cancer. Acta Naturae. 14:4–15. 2022.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
Stern LA, Case BA and Hackel BJ:
Alternative Non-Antibody protein scaffolds for molecular imaging of
cancer. Curr Opin Chem Eng. 2:10.1016/j.coche.2013.08.009. 2013.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Sörensen J, Velikyan I, Sandberg D,
Wennborg A, Feldwisch J, Tolmachev V, Orlova A, Sandström M,
Lubberink M, Olofsson H, et al: Measuring HER2-Receptor expression
in metastatic breast cancer using [68Ga]ABY-025 affibody
PET/CT. Theranostics. 6:262–271. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Bragina O, von Witting E, Garousi J,
Zelchan R, Sandström M, Medvedeva A, Orlova A, Doroshenko A,
Vorobyeva A, Lindbo S, et al: Phase I Study of
99mTc-ADAPT6, a scaffold protein-based probe for
visualization of HER2 expression in breast cancer. J Nucl Med.
62:493–499. 2021. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Bragina O, Chernov V, Schulga A,
Konovalova E, Hober S, Deyev S, Sörensen J and Tolmachev V: Direct
intra-patient comparison of scaffold protein-based tracers,
[99mTc]Tc-ADAPT6 and
[99mTc]Tc-(HE)3-G3, for imaging of
HER2-Positive breast cancer. Cancers (Basel). 15:31492023.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Rothe C and Skerra A:
Anticalin® proteins as therapeutic agents in human
diseases. BioDrugs. 32:233–243. 2018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Ackerman SE, Currier NV, Bergen JM and
Cochran JR: Cystine-knot peptides: Emerging tools for cancer
imaging and therapy. Expert Rev Proteomics. 11:561–572. 2014.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Vorobyeva A, Schulga A, Konovalova E,
Güler R, Löfblom J, Sandström M, Garousi J, Chernov V, Bragina O,
Orlova A, et al: Optimal composition and position of
histidine-containing tags improves biodistribution of
99mTc-labeled DARPin G3. Sci Rep. 9:94052019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Deyev SM, Vorobyeva A, Schulga A,
Abouzayed A, Günther T, Garousi J, Konovalova E, Ding H, Gräslund
T, Orlova A, et al: Effect of a radiolabel biochemical nature on
tumor-targeting properties of EpCAM-binding engineered scaffold
protein DARPin Ec1. Int J Biol Macromolecules. 145:216–225. 2020.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Bragina O, Chernov V, Schulga A,
Konovalova E, Garbukov E, Vorobyeva A, Orlova A, Tashireva L,
Sörensen J, Zelchan R, et al: Phase I Trial of
99mTc-(HE)3-G3, a DARPin-Based probe for
imaging of HER2 Expression in Breast Cancer. J Nucl Med.
63:528–535. 2022. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Garousi J, Lindbo S, Nilvebrant J, Åstrand
M, Buijs J, Sandström M, Honarvar H, Orlova A, Tolmachev V and
Hober S: ADAPT, a novel scaffold protein-based probe for
radionuclide imaging of molecular targets that are expressed in
disseminated cancers. Cancer Res. 75:4364–4371. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Garousi J, Lindbo S, Borin J, von Witting
E, Vorobyeva A, Oroujeni M, Mitran B, Orlova A, Buijs J, Tolmachev
V, et al: Comparative evaluation of dimeric and monomeric forms of
ADAPT scaffold protein for targeting of HER2-expressing tumours.
Eur J Pharm Biopharm. 134:37–48. 2019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Garousi J, Lindbo S, Mitran B, Buijs J,
Vorobyeva A, Orlova A, Tolmachev V and Hober S: Comparative
evaluation of tumor targeting using the anti-HER2 ADAPT scaffold
protein labeled at the C-terminus with indium-111 or
technetium-99m. Sci Rep. 7:147802017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Lindbo S, Garousi J, Mitran B, Vorobyeva
A, Oroujeni M, Orlova A, Hober S and Tolmachev V: Optimized
molecular design of ADAPT-Based HER2-Imaging probes labeled with
111In and 68Ga. Mol Pharm. 15:2674–2683.
2018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Lindbo S, Garousi J, Mitran B, Altai M,
Buijs J, Orlova A, Hober S and Tolmachev V: Radionuclide tumor
targeting using ADAPT scaffold proteins: Aspects of label
positioning and residualizing properties of the label. J Nucl Med.
59:93–99. 2018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
von Witting E, Garousi J, Lindbo S,
Vorobyeva A, Altai M, Oroujeni M, Mitran B, Orlova A, Hober S and
Tolmachev V: Selection of the optimal macrocyclic chelators for
labeling with 111In and 68Ga improves
contrast of HER2 imaging using engineered scaffold protein ADAPT6.
Eur J Pharm Biopharm. 140:109–120. 2019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
Lindbo S, Garousi J, Åstrand M, Honarvar
H, Orlova A, Hober S and Tolmachev V: Influence of
Histidine-Containing tags on the biodistribution of ADAPT scaffold
proteins. Bioconjug Chem. 27:716–726. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
Garousi J, von Witting E, Borin J,
Vorobyeva A, Altai M, Vorontsova O, Konijnenberg MW, Oroujeni M,
Orlova A, Tolmachev V, et al: Radionuclide therapy using ABD-fused
ADAPT scaffold protein: Proof of Principle. Biomaterials.
266:1203812021. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
Tolmachev V, Orlova A, Pehrson R, Galli J,
Baastrup B, Andersson K, Sandström M, Rosik D, Carlsson J,
Lundqvist H, et al: Radionuclide therapy of HER2-positive
microxenografts Using a 177Lu-Labeled HER2-Specific
affibody molecule. Cancer Res. 67:2773–2782. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22
|
Goldenberg DM, Chatal JF, Barbet J,
Boerman O and Sharkey RM: Cancer imaging and therapy with
bispecific antibody pretargeting. Update Cancer Ther. 2:19–31.
2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23
|
Honarvar H, Westerlund K, Altai M,
Sandström M, Orlova A, Tolmachev V and Karlström AE: Feasibility of
affibody Molecule-Based PNA-Mediated radionuclide pretargeting of
malignant tumors. Theranostics. 6:93–103. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24
|
Westerlund K, Altai M, Mitran B,
Konijnenberg M, Oroujeni M, Atterby C, de Jong M, Orlova A,
Mattsson J, Micke P, et al: Radionuclide therapy of HER2-Expressing
human xenografts using Affibody-Based Peptide nucleic acid-mediated
pretargeting: In Vivo proof of principle. J Nucl Med. 59:1092–1098.
2018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
25
|
Vegt E, de Jong M, Wetzels JFM, Masereeuw
R, Melis M, Oyen WJG, Gotthardt M and Boerman OC: Renal toxicity of
radiolabeled peptides and antibody fragments: Mechanisms, impact on
radionuclide therapy, and strategies for prevention. J Nucl Med.
51:1049–1058. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
26
|
Altai M, Garousi J, Rinne SS, Schulga A,
Deyev S and Vorobyeva A: On the prevention of kidney uptake of
radiolabeled DARPins. EJNMMI Res. 10:72020. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
27
|
Garousi J, Vorobyeva A and Altai M:
Influence of several compounds and drugs on the renal uptake of
radiolabeled affibody molecules. Molecules. 25:26732020. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
28
|
Vorobyeva A, Oroujeni M, Lindbo S, Hober
S, Xu T, Liu Y, Rinne SS and Garousi J: Investigation of a
pharmacological approach for reduction of renal uptake of
radiolabeled ADAPT scaffold protein. Molecules. 25:44482020.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
29
|
Arano Y: Strategies to reduce renal
radioactivity levels of antibody fragments. Q J Nucl Med.
42:262–270. 1998.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
30
|
Arano Y, Fujioka Y, Akizawa H, Ono M,
Uehara T, Wakisaka K, Nakayama M, Sakahara H, Konishi J and Saji H:
Chemical design of radiolabeled antibody fragments for low renal
radioactivity levels. Cancer Res. 59:128–134. 1999.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
31
|
Fujioka Y, Arano Y, Ono M, Uehara T, Ogawa
K, Namba S, Saga T, Nakamoto Y, Mukai T, Konishi J, et al: Renal
metabolism of 3′-iodohippuryl N(epsilon)-maleoyl-L-lysine
(HML)-conjugated Fab fragments. Bioconjug Chem. 12:178–185. 2001.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
32
|
Uehara T, Koike M, Nakata H, Hanaoka H,
Iida Y, Hashimoto K, Akizawa H, Endo K and Arano Y: Design,
synthesis, and evaluation of [188Re]organorhenium-labeled antibody
fragments with renal enzyme-cleavable linkage for low renal
radioactivity levels. Bioconjug Chem. 18:190–198. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
33
|
Uehara T, Yokoyama M, Suzuki H, Hanaoka H
and Arano Y: A Gallium-67/68-Labeled antibody fragment for
Immuno-SPECT/PET shows low renal radioactivity without loss of
tumor uptake. Clin Cancer Res. 24:3309–3316. 2018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
34
|
Bendre S, Zhang Z, Kuo HT, Rousseau J,
Zhang C, Merkens H, Roxin Á, Bénard F and Lin KS: Evaluation of
Met-Val-Lys as a renal brush border Enzyme-Cleavable linker to
reduce kidney uptake of 68Ga-Labeled DOTA-Conjugated peptides and
peptidomimetics. Molecules. 25:38542020. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
35
|
Altai M, Westerlund K, Velletta J, Mitran
B, Honarvar H and Karlström AE: Evaluation of affibody
molecule-based PNA-mediated radionuclide pretargeting: Development
of an optimized conjugation protocol and 177Lu labeling.
Nucl Med Biol. 54:1–9. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
36
|
Tolmachev V, Mume E, Sjöberg S, Frejd FY
and Orlova A: Influence of valency and labelling chemistry on in
vivo targeting using radioiodinated HER2-binding Affibody
molecules. Eur J Nucl Med Mol Imaging. 36:692–701. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
37
|
Wållberg H and Orlova A: Slow
internalization of anti-HER2 synthetic affibody monomer
111In-DOTA-ZHER2:342-pep2: Implications for development of labeled
tracers. Cancer Biother Radiopharm. 23:435–442. 2008.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
38
|
Yeong CH, Cheng M and Ng KH: Therapeutic
radionuclides in nuclear medicine: current and future prospects. J
Zhejiang Univ Sci B. 15:845–863. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
39
|
Li L, Olafsen T, Anderson AL, Wu A,
Raubitschek AA and Shively JE: Reduction of kidney uptake in
radiometal labeled peptide linkers conjugated to recombinant
antibody fragments. Site-specific conjugation of DOTA-peptides to a
Cys-diabody. Bioconjug Chem. 13:985–995. 2002. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
40
|
Arano Y: Renal brush border strategy: A
developing procedure to reduce renal radioactivity levels of
radiolabeled polypeptides. Nucl Med Biol. 92:149–155. 2021.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
41
|
Biber J, Stieger B, Stange G and Murer H:
Isolation of renal proximal tubular brush-border membranes. Nat
Protoc. 2:1356–1359. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
42
|
Hosseinimehr SJ, Tolmachev V and Orlova A:
Liver uptake of radiolabeled targeting proteins and peptides:
Considerations for targeting peptide conjugate design. Drug Discov
Today. 17:1224–1232. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
43
|
Hofstrom C, Orlova A, Altai M, Wangsell F,
Graslund T and Tolmachev V: Use of a HEHEHE purification tag
instead of a hexahistidine tag improves biodistribution of affibody
molecules site-specifically labeled with (99m)Tc, (111)In, and
(125)I. J Med Chem. 54:3817–3826. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
44
|
Vorobyeva A, Sсhulga A, Konovalova E,
Güler R, Mitran B, Garousi J, Rinne S, Löfblom J, Orlova A, Deyev S
and Tolmachev V: Comparison of tumor-targeting properties of
directly and indirectly radioiodinated designed ankyrin repeat
protein (DARPin) G3 variants for molecular imaging of HER2. Int J
Oncol. 54:1209–1220. 2019.PubMed/NCBI
|