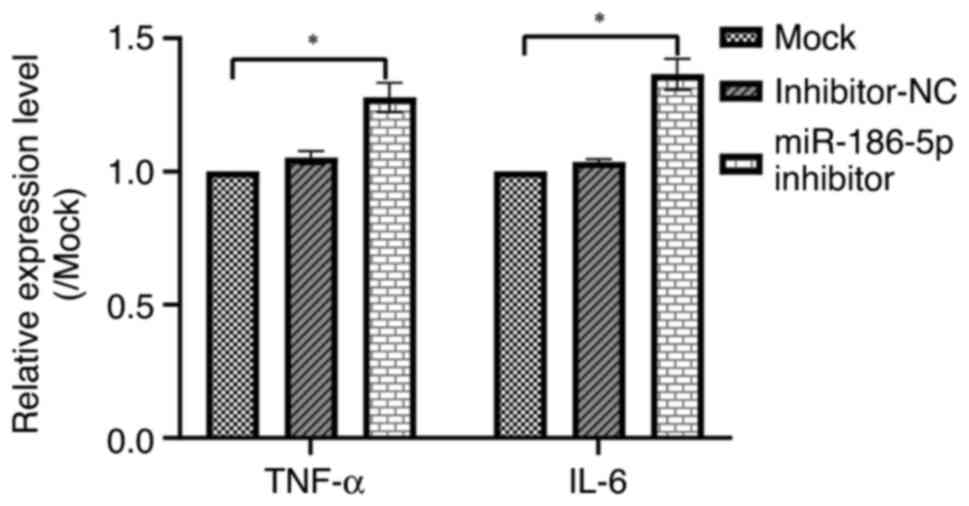
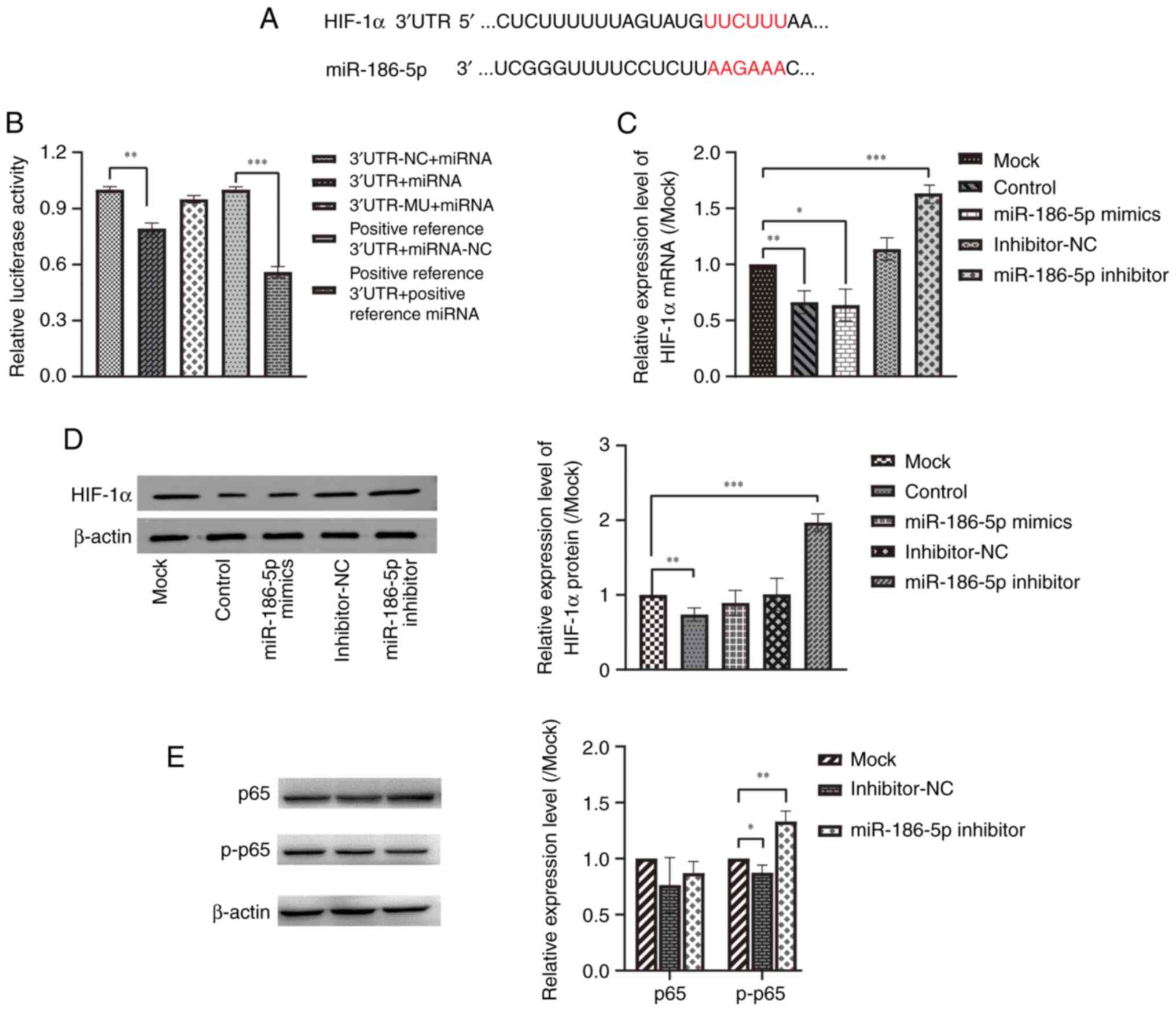
|
1
|
Christenson SA, Smith BM, Bafadhel M and
Putcha N: Chronic obstructive pulmonary disease. Lancet.
399:2227–2242. 2022. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
Celli B, Fabbri L, Criner G, Martinez FJ,
Mannino D, Vogelmeier C, Montes de Oca M, Papi A, Sin DD, Han MK
and Agusti A: Definition and nomenclature of chronic obstructive
pulmonary disease: Time for its revision. Am J Respir Crit Care
Med. 206:1317–1325. 2022. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
Safiri S, Carson-Chahhoud K, Noori M,
Nejadghaderi SA, Sullman MJM, Ahmadian Heris J, Ansarin K,
Mansournia MA, Collins GS, Kolahi AA and Kaufman JS: Burden of
chronic obstructive pulmonary disease and its attributable risk
factors in 204 countries and territories, 1990–2019: results from
the Global Burden of Disease Study 2019. BMJ. 378:e0696792022.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
Silverman EK: Genetics of COPD. Annu Rev
Physiol. 82:413–431. 2020. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Zhang PD, Zhang XR, Zhang A, Li ZH, Liu D,
Zhang YJ and Mao C: Associations of genetic risk and smoking with
incident COPD. Eur Respir J. 59:21013202022. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Adeloye D, Song P, Zhu Y, Campbell H,
Sheikh A and Rudan I: Global, regional, and national prevalence of,
and risk factors for, chronic obstructive pulmonary disease (COPD)
in 2019: A systematic review and modelling analysis. Lancet Respir
Med. 10:447–458. 2022. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Yin P, Wu J, Wang L, Luo C, Ouyang L, Tang
X, Liu J, Liu Y, Qi J, Zhou M and Lai T: The Burden of COPD in
China and Its Provinces: Findings From the Global Burden of Disease
Study 2019. Front Public Health. 10:8594992022. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Barnes PJ: Inflammatory mechanisms in
patients with chronic obstructive pulmonary disease. J Allergy Clin
Immunol. 138:16–27. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Ghanbarian H, Yıldız MT and Tutar Y:
MicroRNA Targeting. Methods Mol Biol. 2257:105–130. 2022.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Vishnoi A and Rani S: miRNA Biogenesis and
Regulation of Diseases: An Updated Overview. Methods Mol Biol.
2595:1–12. 2023. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Specjalski K and Jassem E: MicroRNAs:
Potential Biomarkers and Targets of Therapy in Allergic Diseases?
Arch Immunol Ther Exp (Warsz). 67:213–223. 2019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Liang Q, He J, Yang Q, Zhang Q and Xu Y:
MicroRNA-335-5p alleviates inflammatory response, airway fibrosis,
and autophagy in childhood asthma through targeted regulation of
autophagy related 5. Bioengineered. 13:1791–1801. 2022. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Li X, Gong Y, Lin X, Lin Q, Luo J, Yu T,
Xu J, Chen L, Xu L and Hu Y: Down-regulation of microRNA-155
suppressed Candida albicans induced acute lung injury by activating
SOCS1 and inhibiting inflammation response. J Microbiol.
60:402–410. 2022. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Huang X, Zhu Z, Guo X and Kong X: The
roles of microRNAs in the pathogenesis of chronic obstructive
pulmonary disease. Int Immunopharmacol. 67:335–347. 2019.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Roffel MP, Bracke KR, Heijink IH and Maes
T: miR-223: A key regulator in the innate immune response in asthma
and COPD. Front Med (Lausanne). 7:1962020. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Zhang J, Xu Z, Kong L, Gao H, Zhang Y,
Zheng Y and Wan Y: miRNA-486-5p promotes COPD progression by
targeting HAT1 to regulate the TLR4-Triggered inflammatory response
of alveolar macrophages. Int J Chron Obstruct Pulmon Dis.
15:2991–3001. 2020. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Kim RY, Sunkara KP, Bracke KR, Jarnicki
AG, Donovan C, Hsu AC, Ieni A, Beckett EL, Galvão I, Wijnant S, et
al: A microRNA-21-mediated SATB1/S100A9/NF-κB axis promotes chronic
obstructive pulmonary disease pathogenesis. Sci Transl Med.
13:eaav72232021. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
Ding Y, Tian Z, Yang H, Yao H, He P,
Ouyang Y, Yao J, Li M and Jin T: MicroRNA expression profiles of
whole blood in chronic obstructive pulmonary disease. Int J Clin
Experiment Pathol. 10:4860–4865. 2017.
|
|
19
|
Cai SC, Li XP, Li X, Tang GY, Yi LM and Hu
XS: Oleanolic Acid Inhibits Neuronal Pyroptosis in Ischaemic Stroke
by Inhibiting miR-186-5p Expression. Exp Neurobiol. 30:401–414.
2021. View
Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
Yang P, Liang K, Wang W, Zhou D, Chen Y,
Jiang X, Fu R, Zhu B and Lin X: LncRNA SOX2-OTinhibitionprotects
against myocardialischemia/reperfusion-inducedinjury via
themicroRNA-186-5p (miR-186-5p)/Yin Yang 1 (YY1) pathway.
Bioengineered. 13:280–290. 2022. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
Nie Y and Wang F: Inhibiting miR-186-5p
relieves traumatic brain injury by regulating insulin-like growth
factor-I-NLRP3/ASC/caspase-1 signaling pathway. Neuroreport.
34:156–164. 2023. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22
|
Li R, Xu F, Wu X, Ji S and Xia R:
CUL1-Mediated organelle fission pathway inhibits the development of
chronic obstructive pulmonary disease. Comput Math Methods Med.
2020:53901072020. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23
|
Rong B, Liu Y, Li M, Fu T, Gao W and Liu
H: Correlation of serum levels of HIF-1α and IL-19 with the disease
progression of COPD: A retrospective study. Int J Chron Obstruct
Pulmon Dis. 13:3791–3803. 2018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24
|
Fu X and Zhang F: Role of the HIF-1
signaling pathway in chronic obstructive pulmonary disease. Exp
Ther Med. 16:4553–4561. 2018.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
25
|
Alharbi KS, Fuloria NK, Fuloria S, Rahman
SB, Al-Malki WH, Javed Shaikh MA, Thangavelu L, Singh SK, Rama Raju
Allam VS, Jha NK, et al: Nuclear factor-kappa B and its role in
inflammatory lung disease. Chem Biol Interact. 345:1095682021.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
26
|
Tan H and Zhao L: lncRNA nuclear-enriched
abundant transcript 1 promotes cell proliferation and invasion by
targeting miR-186-5p/HIF-1α in osteosarcoma. J Cell Biochem.
120:6502–6514. 2019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
27
|
Livak KJ and Schmittgen TD: Analysis of
relative gene expression data using real-time quantitative PCR and
the 2(−Delta Delta C(T)) method. Methods. 25:402–408. 2001.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
28
|
Wang Z, Sha HH and Li HJ: Functions and
mechanisms of miR-186 in human cancer. Biomed Pharmacother.
119:1094282019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
29
|
Becker V, Yuan X, Boewe AS, Ampofo E,
Ebert E, Hohneck J, Bohle RM, Meese E, Zhao Y, Menger MD, et al:
Hypoxia-induced downregulation of microRNA-186-5p in endothelial
cells promotes non-small cell lung cancer angiogenesis by
upregulating protein kinase C alpha. Molecular therapy. Mol Ther
Nucleic Acids. 31:421–436. 2023. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
30
|
Lin L, Sun J, Wu D, Lin D, Sun D, Li Q,
Chen J, Niu H, He P and Ding Y: MicroRNA-186 is associated with
hypoxia-inducible factor-1α expression in chronic obstructive
pulmonary disease. Mol Genet Genomic Med. 7:e5312019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
31
|
De la Garza MM, Cumpian AM, Daliri S,
Castro-Pando S, Umer M, Gong L, Khosravi N, Caetano MS,
Ramos-Castañeda M, Flores AG, et al: COPD-Type lung inflammation
promotes K-ras mutant lung cancer through epithelial HIF-1α
mediated tumor angiogenesis and proliferation. Oncotarget.
9:32972–32983. 2018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
32
|
Zhang HX, Yang JJ, Zhang SA, Zhang SM,
Wang JX, Xu ZY and Lin RY: HIF-1α promotes inflammatory response of
chronic obstructive pulmonary disease by activating EGFR/PI3K/AKT
pathway. Eur Rev Med Pharmacol Sci. 22:6077–6084. 2018.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
33
|
Xu YR, Wang AL and Li YQ:
Hypoxia-inducible factor 1-alpha is a driving mechanism linking
chronic obstructive pulmonary disease to lung cancer. Front Oncol.
12:9845252022. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
34
|
Jiang H, Zhu Y, Xu H, Sun Y and Li Q:
Activation of hypoxia-inducible factor-1α via nuclear factor-κB in
rats with chronic obstructive pulmonary disease. Acta Biochim
Biophys Sin (Shanghai). 42:483–488. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
35
|
Schuliga M: NF-kappaB signaling in chronic
inflammatory airway disease. Biomolecules. 5:1266–1283. 2015.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|