|
1
|
Ollivere B, Wimhurst JA, Clark IM and
Donell ST: Current concepts in osteolysis. J Bone Joint Surg Br.
94:10–15. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
Hodges NA, Sussman EM and Stegemann JP:
Aseptic and septic prosthetic joint loosening: Impact of
biomaterial wear on immune cell function, inflammation, and
infection. Biomaterials. 278:1211272021. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
Tay ML, Matthews BG, Monk AP and Young SW:
Disease progression, aseptic loosening and bearing dislocations are
the main revision indications after lateral unicompartmental knee
arthroplasty: A systematic review. J ISAKOS. 7:132–141. 2022.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
Eger M, Sterer N, Liron T, Kohavi D and
Gabet Y: Scaling of titanium implants entrains inflammation-induced
osteolysis. Sci Rep. 7:396122017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
McArthur BA, Scully R, Patrick Ross F,
Bostrom MPG and Falghren A: Mechanically induced periprosthetic
osteolysis: A systematic review. HSS J. 15:286–296. 2019.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Eliaz N: Corrosion of metallic
biomaterials: A review. Materials (Basel). 12:4072019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
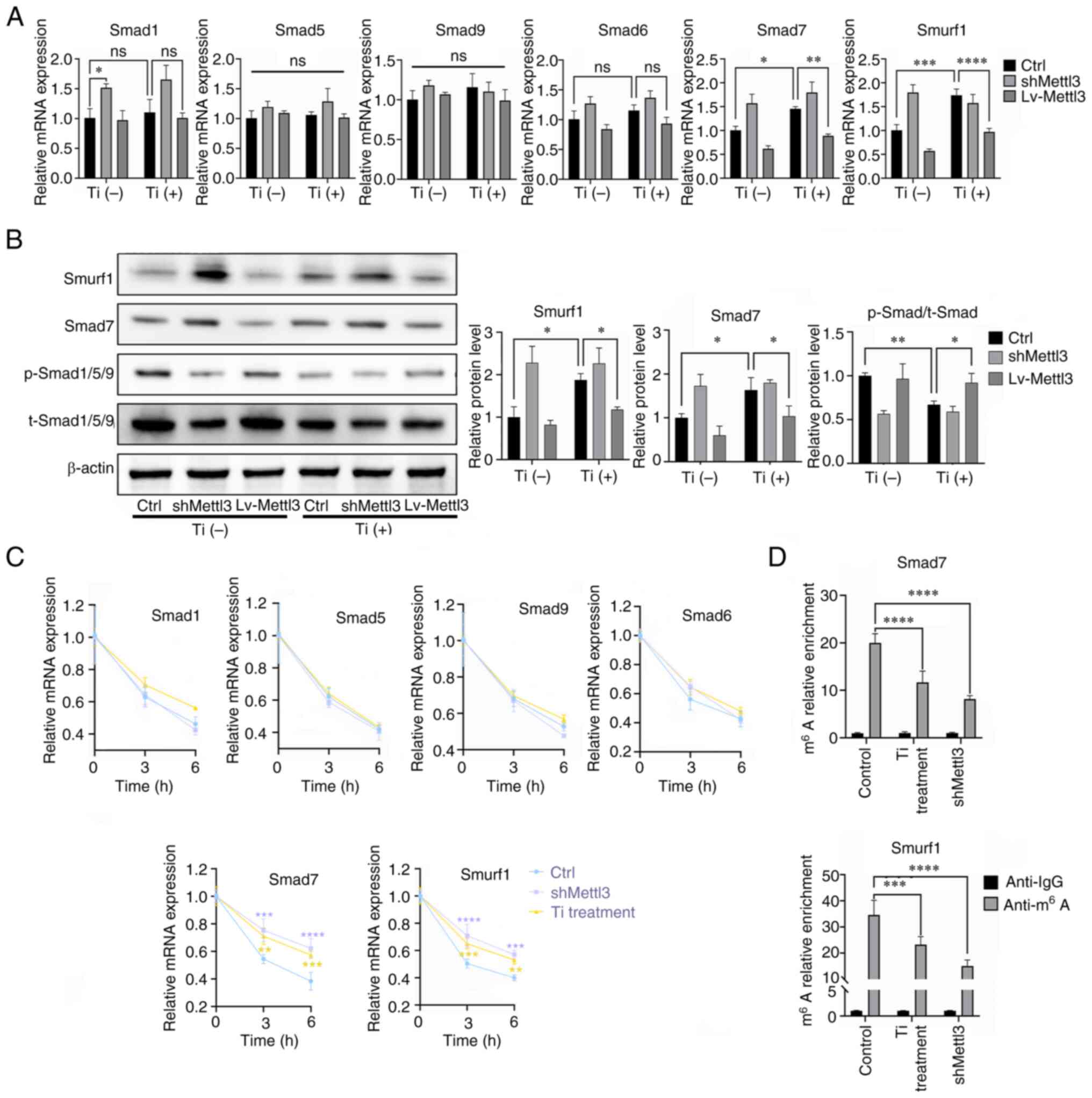
7
|
Prestat M and Thierry D: Corrosion of
titanium under simulated inflammation conditions: Clinical context
and in vitro investigations. Acta Biomater. 136:72–87. 2021.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Delanois RE, Mistry JB, Gwam CU, Mohamed
NS, Choksi US and Mont MA: Current epidemiology of revision total
knee arthroplasty in the United States. J Arthroplasty.
32:2663–2668. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Goodman SB: Wear particles, periprosthetic
osteolysis and the immune system. Biomaterials. 28:5044–5048. 2007.
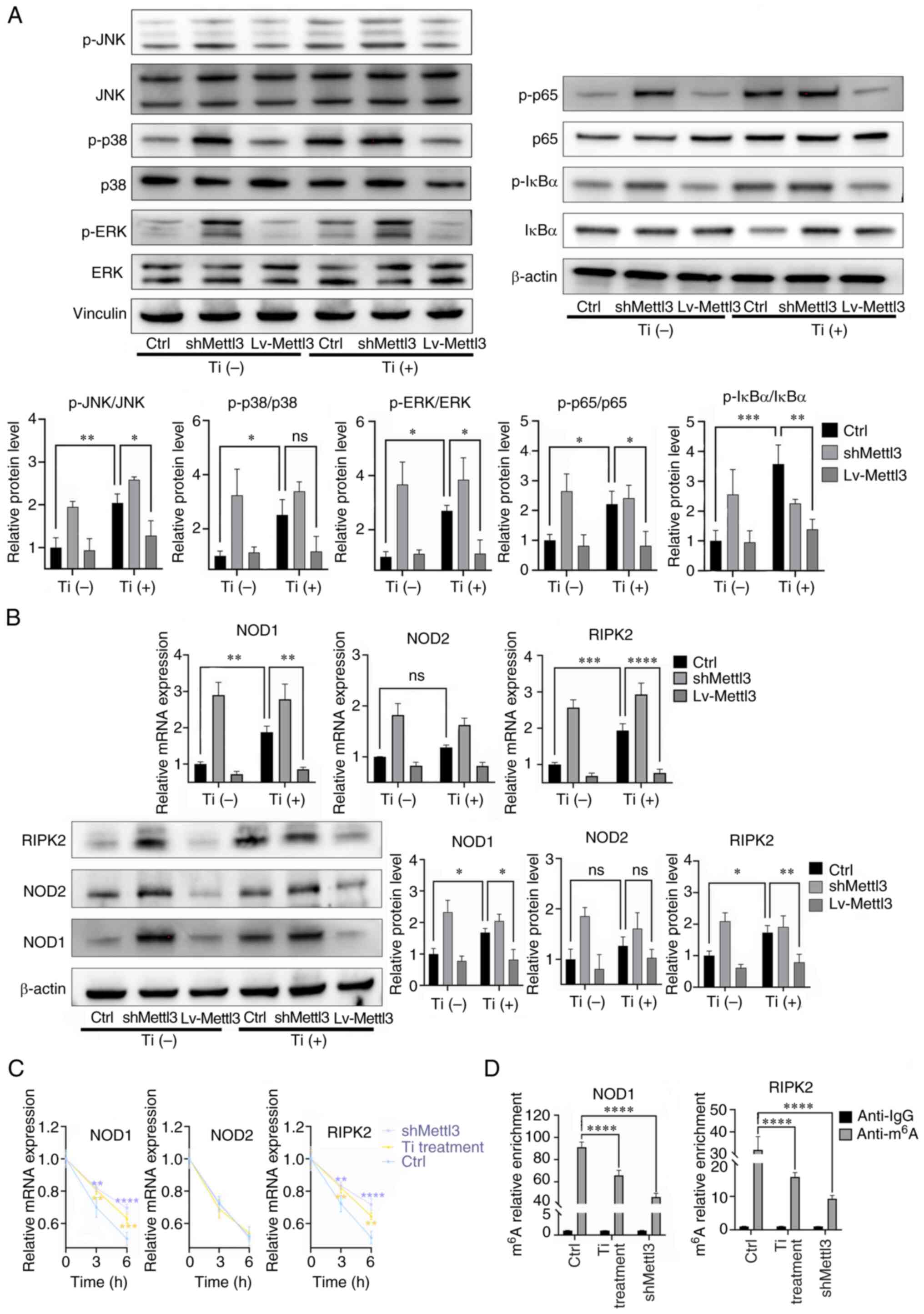
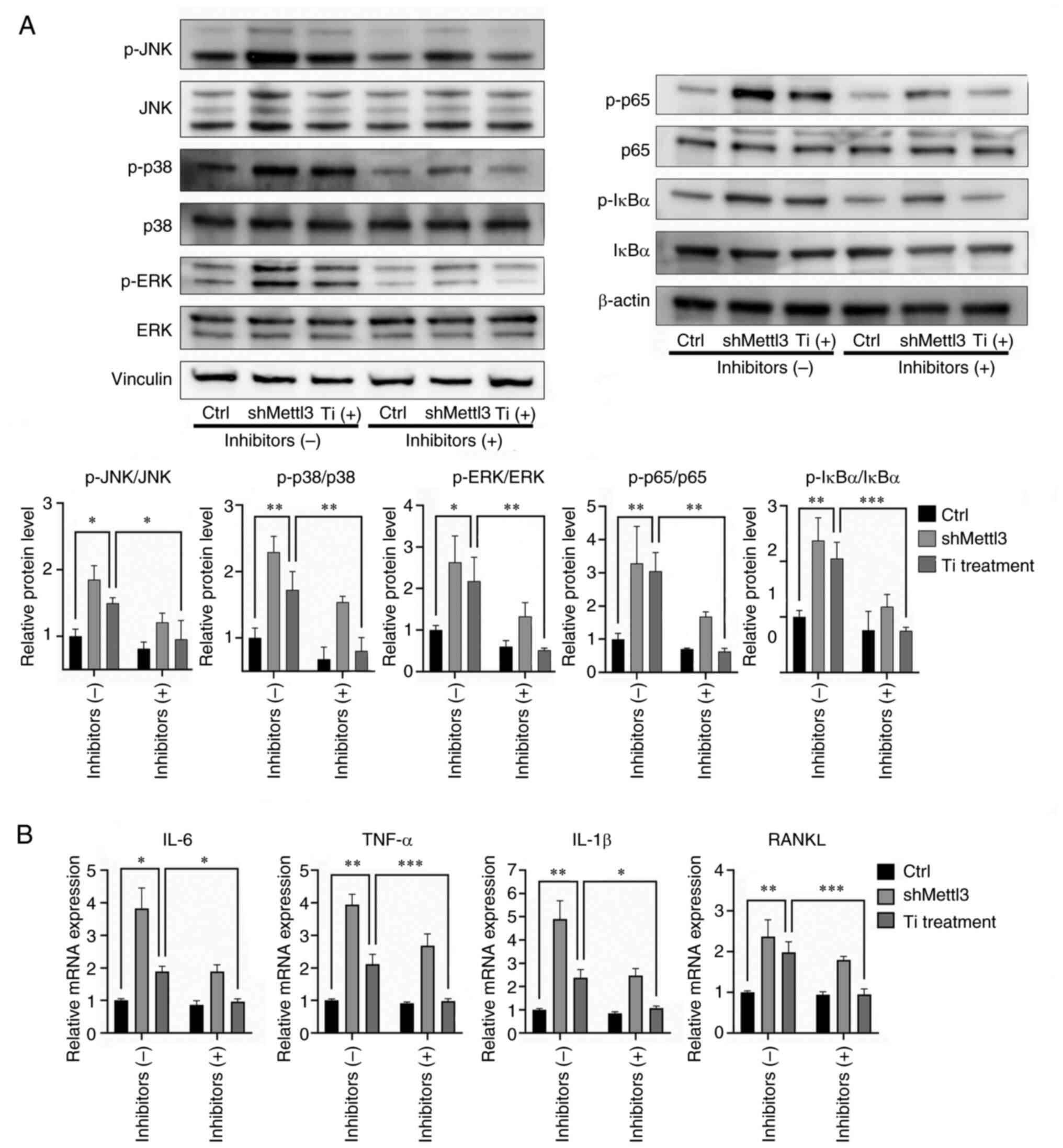
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Zheng K, Bai J, Li N, Li M, Sun H, Zhang
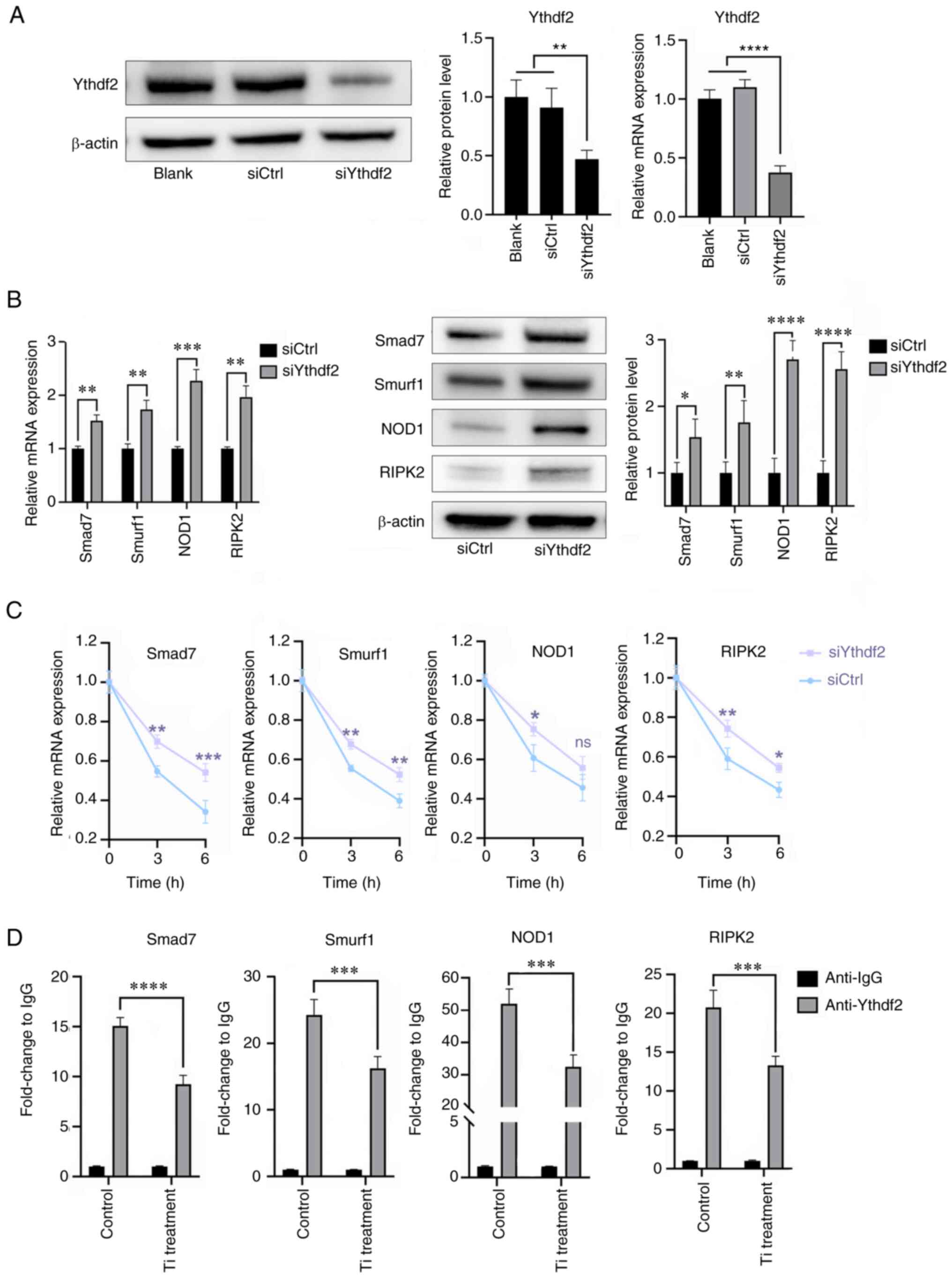
W, Ge G, Liang X, Tao H, Xue Y, et al: Protective effects of
sirtuin 3 on titanium particle-induced osteogenic inhibition by
regulating the NLRP3 inflammasome via the GSK-3β/β-catenin
signalling pathway. Bioact Mater. 6:3343–3357. 2021.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Agarwal S: Osteolysis-basic science,
incidence and diagnosis. Curr Orthop. 18:220–231. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
12
|
Dattani R: Femoral osteolysis following
total hip replacement. Postgrad Med J. 83:312–316. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Mouhyi J, Dohan Ehrenfest DM and
Albrektsson T: The peri-implantitis: Implant surfaces,
microstructure, and physicochemical aspects. Clin Implant Dent
Relat Res. 14:170–183. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Derks J and Tomasi C: Peri-implant health
and disease. A systematic review of current epidemiology. J Clin
Periodontol. 42 (Suppl 16):S158–S171. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Bauer TW: Particles and periimplant bone
resorption. Clin Orthop Relat Res. 138–143. 2002. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Voggenreiter G, Leiting S, Brauer H,
Leiting P, Majetschak M, Bardenheuer M and Obertacke U:
Immuno-inflammatory tissue reaction to stainless-steel and titanium
plates used for internal fixation of long bones. Biomaterials.
24:247–254. 2003. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Kotsakis GA and Olmedo DG:
Peri-implantitis is not periodontitis: Scientific discoveries shed
light on microbiome-biomaterial interactions that may determine
disease phenotype. Periodontol. 2000.86:231–240. 2021. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
Magone K, Luckenbill D and Goswami T:
Metal ions as inflammatory initiators of osteolysis. Arch Orthop
Trauma Surg. 135:683–695. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
Man K, Jiang LH, Foster R and Yang XB:
Immunological responses to total hip arthroplasty. J Funct
Biomater. 8:332017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
Guglielmotti MB, Olmedo DG and Cabrini RL:
Research on implants and osseointegration. Periodontol.
2000.79:178–189. 2019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
Mombelli A, Hashim D and Cionca N: What is
the impact of titanium particles and biocorrosion on implant
survival and complications? A critical review. Clin Oral Implants
Res. 29 (Suppl 18):S37–S53. 2018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22
|
Xiong L, Liu Y, Zhu F, Lin J, Wen D, Wang
Z, Bai J, Ge G, Xu C, Gu Y, et al: Acetyl-11-keto-β-boswellic acid
attenuates titanium particle-induced osteogenic inhibition via
activation of the GSK-3β/β-catenin signaling pathway. Theranostics.
9:7140–7155. 2019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23
|
Shah R, Penmetsa DSL, Thomas R and Mehta
DS: Titanium corrosion: Implications for dental implants. Eur J
Prosthodont Restor Dent. 24:171–180. 2016.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24
|
Urban RM, Jacobs JJ, Tomlinson MJ,
Gavrilovic J, Black J and Peoc'h M: Dissemination of wear particles
to the liver, spleen, and abdominal lymph nodes of patients with
hip or knee replacement. J Bone Joint Surg Am. 82:457–476. 2000.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
25
|
Choi MG, Koh HS, Kluess D, O'Connor D,
Mathur A, Truskey GA, Rubin J, Zhou DX and Sung KL: Effects of
titanium particle size on osteoblast functions in vitro and in
vivo. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA. 102:4578–4583. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
26
|
Fritz EA, Jacobs JJ, Glant TT and Roebuck
KA: Chemokine IL-8 induction by particulate wear debris in
osteoblasts is mediated by NF-kappaB. J Orthop Res. 23:1249–1257.
2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
27
|
Chen D, Li Y, Guo F, Lu Z, Hei C, Li P and
Jin Q: Protective effect of p38 MAPK inhibitor on wear
debris-induced inflammatory osteolysis through downregulating
RANK/RANKL in a mouse model. Genet Mol Res. 14:40–52. 2015.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
28
|
Geng D, Wu J, Shao H, Zhu S, Wang Y, Zhang
W, Ping Z, Hu X, Zhu X, Xu Y and Yang H: Pharmaceutical inhibition
of glycogen synthetase kinase 3 beta suppresses wear debris-induced
osteolysis. Biomaterials. 69:12–21. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
29
|
Gu Y, Wang Z, Shi J, Wang L, Hou Z, Guo X,
Tao Y, Wu X, Zhou W, Liu Y, et al: Titanium particle-induced
osteogenic inhibition and bone destruction are mediated by the
GSK-3β/β-catenin signal pathway. Cell Death Dis. 8:e28782017.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
30
|
Wang L, Bai J, Wang Q, Ge G, Lin J, Xu N,
Xu C, Xu Y, Wang Y and Geng D: Inhibition of protein phosphatase 2A
attenuates titanium-particle induced suppression of bone formation.
Int J Biol Macromol. 142:142–151. 2020. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
31
|
Zhu Z, Xie Q, Huang Y, Zhang S and Chen Y:
Aucubin suppresses titanium particles-mediated apoptosis of
MC3T3-E1 cells and facilitates osteogenesis by affecting the
BMP2/Smads/RunX2 signaling pathway. Mol Med Rep. 18:2561–2570.
2018.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
32
|
Wang J, Tao Y, Ping Z, Zhang W, Hu X, Wang
Y, Wang L, Shi J, Wu X, Yang H, et al: Icariin attenuates
titanium-particle inhibition of bone formation by activating the
Wnt/β-catenin signaling pathway in vivo and in vitro. Sci Rep.
6:238272016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
33
|
Geng T, Sun S, Chen X, Wang B, Guo H,
Zhang S and Jin Q: Strontium ranelate reduces the progression of
titanium particle-induced osteolysis by increasing the ratio of
osteoprotegerin to receptor activator of nuclear factor-κB ligand
in vivo. Mol Med Rep. 17:3829–3836. 2018.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
34
|
Batista PJ: The RNA modification
N6-methyladenosine and its implications in human
disease. Genomics Proteomics Bioinformatics. 15:154–163. 2017.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
35
|
Wang X, Zhao BS, Roundtree IA, Lu Z, Han
D, Ma H, Weng X, Chen K, Shi H and He C: N(6)-methyladenosine
modulates messenger RNA translation efficiency. Cell.
161:1388–1399. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
36
|
Wang X, Lu Z, Gomez A, Hon GC, Yue Y, Han
D, Fu Y, Parisien M, Dai Q, Jia G, et al:
N6-methyladenosine-dependent regulation of messenger RNA stability.
Nature. 505:117–120. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
37
|
Schwartz S, Mumbach MR, Jovanovic M, Wang
T, Maciag K, Bushkin GG, Mertins P, Ter-Ovanesyan D, Habib N,
Cacchiarelli D, et al: Perturbation of m6A writers reveals two
distinct classes of mRNA methylation at internal and 5′ sites. Cell
Rep. 8:284–296. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
38
|
Wang P, Doxtader KA and Nam Y: Structural
basis for cooperative function of Mettl3 and Mettl14
methyltransferases. Mol Cell. 63:306–317. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
39
|
Jia G, Fu Y, Zhao X, Dai Q, Zheng G, Yang
Y, Yi C, Lindahl T, Pan T, Yang YG and He C: N6-methyladenosine in
nuclear RNA is a major substrate of the obesity-associated FTO. Nat
Chem Biol. 7:885–887. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
40
|
Zheng G, Dahl JA, Niu Y, Fedorcsak P,
Huang CM, Li CJ, Vågbø CB, Shi Y, Wang WL, Song SH, et al: ALKBH5
is a mammalian RNA demethylase that impacts RNA metabolism and
mouse fertility. Mol Cell. 49:18–29. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
41
|
Shi H, Wei J and He C: Where, when, and
how: Context-dependent functions of RNA methylation writers,
readers, and erasers. Mol Cell. 74:640–650. 2019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
42
|
Xu K, Yang Y, Feng GH, Sun BF, Chen JQ, Li
YF, Chen YS, Zhang XX, Wang CX, Jiang LY, et al: Mettl3-mediated
m6A regulates spermatogonial differentiation and meiosis
initiation. Cell Res. 27:1100–1114. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
43
|
Lin Z, Hsu PJ, Xing X, Fang J, Lu Z, Zou
Q, Zhang KJ, Zhang X, Zhou Y, Zhang T, et al:
Mettl3-/Mettl14-mediated mRNA N6-methyladenosine
modulates murine spermatogenesis. Cell Res. 27:1216–1230. 2017.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
44
|
Wu Y, Xie L, Wang M, Xiong Q, Guo Y, Liang
Y, Li J, Sheng R, Deng P, Wang Y, et al: Mettl3-mediated
m6A RNA methylation regulates the fate of bone marrow
mesenchymal stem cells and osteoporosis. Nat Commun. 9:47722018.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
45
|
Tian C, Huang Y, Li Q, Feng Z and Xu Q:
Mettl3 regulates osteogenic differentiation and alternative
splicing of vegfa in bone marrow mesenchymal stem cells. Int J Mol
Sci. 20:5512019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
46
|
Zhang Y, Gu X, Li D, Cai L and Xu Q:
METTL3 regulates osteoblast differentiation and inflammatory
response via smad signaling and MAPK signaling. Int J Mol Sci.
21:1992019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
47
|
Song H, Song J, Cheng M, Zheng M, Wang T,
Tian S, Flavell RA, Zhu S, Li HB, Ding C, et al: METTL3-mediated
m6A RNA methylation promotes the anti-tumour immunity of
natural killer cells. Nat Commun. 12:55222021. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
48
|
Huang M, Xu S, Liu L, Zhang M, Guo J, Yuan
Y, Xu J, Chen X and Zou J: m6A methylation regulates osteoblastic
differentiation and bone remodeling. Front Cell Dev Biol.
9:7833222021. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
49
|
Nachbur U, Stafford CA, Bankovacki A, Zhan
Y, Lindqvist LM, Fiil BK, Khakham Y, Ko HJ, Sandow JJ, Falk H, et
al: A RIPK2 inhibitor delays NOD signalling events yet prevents
inflammatory cytokine production. Nat Commun. 6:64422015.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
50
|
Tan X, Wei LJ, Fan GJ, Jiang YN and Yu XP:
Effector responses of bovine blood neutrophils against Escherichia
coli: Role of NOD1/NF-κB signalling pathway. Vet Immunol
Immunopathol. 168:68–76. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
51
|
Livak KJ and Schmittgen TD: Analysis of
relative gene expression data using real-time quantitative PCR and
the 2(−Delta Delta C(T)) method. Methods. 25:402–408. 2001.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
52
|
Nguyen TTT, Shang E, Shu C, Kim S, Mela A,
Humala N, Mahajan A, Yang HW, Akman HO, Quinzii CM, et al: Aurora
kinase A inhibition reverses the Warburg effect and elicits unique
metabolic vulnerabilities in glioblastoma. Nat Commun. 12:52032021.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
53
|
Li D, Yang J, Malik V, Huang Y, Huang X,
Zhou H and Wang J: An RNAi screen of RNA helicases identifies
eIF4A3 as a regulator of embryonic stem cell identity. Nucleic
Acids Res. 50:12462–12479. 2022. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
54
|
Ratnadiwakara M and Änkö ML: mRNA
Stability assay using transcription inhibition by actinomycin D in
mouse pluripotent stem cells. Bio Protoc. 8:e30722018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
55
|
Zhou Z, Cao Y, Yang Y, Wang S and Chen F:
METTL3-mediated m6A modification of lnc KCNQ1OT1
promotes doxorubicin resistance in breast cancer by regulating
miR-103a-3p/MDR1 axis. Epigenetics. 18:22170332023. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
56
|
Luo S, Liao C, Zhang L, Ling C, Zhang X,
Xie P, Su G, Chen Z, Zhang L, Lai T and Tang J: METTL3-mediated m6A
mRNA methylation regulates neutrophil activation through targeting
TLR4 signaling. Cell Rep. 42:1122592023. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
57
|
Kim JM, Lin C, Stavre Z, Greenblatt MB and
Shim JH: Osteoblast-osteoclast communication and bone homeostasis.
Cells. 9:20732020. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
58
|
Redlich K and Smolen JS: Inflammatory bone
loss: Pathogenesis and therapeutic intervention. Nat Rev Drug
Discov. 11:234–250. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
59
|
Li Y, Ling J and Jiang Q: Inflammasomes in
alveolar bone loss. Front Immunol. 12:6910132021. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
60
|
Jiang Y, Jia T, Gong W, Wooley PH and Yang
SY: Titanium particle-challenged osteoblasts promote
osteoclastogenesis and osteolysis in a murine model of
periprosthestic osteolysis. Acta Biomater. 9:7564–7572. 2013.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
61
|
Luo J, Xu T and Sun K: N6-methyladenosine
RNA modification in inflammation: Roles, mechanisms, and
applications. Front Cell Dev Biol. 9:6707112021. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
62
|
Wu M, Chen G and Li YP: TGF-β and BMP
signaling in osteoblast, skeletal development, and bone formation,
homeostasis and disease. Bone Res. 4:160092016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
63
|
Afzal F, Pratap J, Ito K, Ito Y, Stein JL,
van Wijnen AJ, Stein GS, Lian JB and Javed A: Smad function and
intranuclear targeting share a Runx2 motif required for osteogenic
lineage induction and BMP2 responsive transcription. J Cell
Physiol. 204:63–72. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
64
|
Yan X, Liu Z and Chen Y: Regulation of
TGF-beta signaling by Smad7. Acta Biochim Biophys Sin (Shanghai).
41:263–272. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
65
|
Deng Z, Zhang R, Li M, Wang S, Fu G, Jin
J, Wang Z, Ma Y and Zheng Q: STAT3/IL-6 dependent induction of
inflammatory response in osteoblast and osteoclast formation in
nanoscale wear particle-induced aseptic prosthesis loosening.
Biomater Sci. 9:1291–1300. 2021. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
66
|
Cai Y, Yu R, Kong Y, Feng Z and Xu Q:
METTL3 regulates LPS-induced inflammatory response via the NOD1
signaling pathway. Cell Signal. 93:1102832022. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
67
|
Caruso R, Warner N, Inohara N and Núñez G:
NOD1 and NOD2: Signaling, host defense, and inflammatory disease.
Immunity. 41:898–908. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
68
|
Pei G and Dorhoi A: NOD-like receptors:
Guards of cellular homeostasis perturbation during infection. Int J
Mol Sci. 22:67142021. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
69
|
Kersse K, Bertrand MJ, Lamkanfi M and
Vandenabeele P: NOD-like receptors and the innate immune system:
Coping with danger, damage and death. Cytokine Growth Factor Rev.
22:257–276. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
70
|
Yang Y, Hsu PJ, Chen YS and Yang YG:
Dynamic transcriptomic m6A decoration: Writers, erasers,
readers and functions in RNA metabolism. Cell Res. 28:616–624.
2018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
71
|
Jiang X, Liu B, Nie Z, Duan L, Xiong Q,
Jin Z, Yang C and Chen Y: The role of m6A modification in the
biological functions and diseases. Signal Transduct Target Ther.
6:742021. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
72
|
Du H, Zhao Y, He J, Zhang Y, Xi H, Liu M,
Ma J and Wu L: YTHDF2 destabilizes m(6)A-containing RNA through
direct recruitment of the CCR4-NOT deadenylase complex. Nat Commun.
7:126262016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
73
|
Zhou J, Wan J, Gao X, Zhang X, Jaffrey SR
and Qian SB: Dynamic m(6)A mRNA methylation directs translational
control of heat shock response. Nature. 526:591–594. 2015.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
74
|
Winkler R, Gillis E, Lasman L, Safra M,
Geula S, Soyris C, Nachshon A, Tai-Schmiedel J, Friedman N,
Le-Trilling VTK, et al: m6A modification controls the
innate immune response to infection by targeting type I
interferons. Nat Immunol. 20:173–182. 2019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
75
|
Mapperley C, van de Lagemaat LN, Lawson H,
Tavosanis A, Paris J, Campos J, Wotherspoon D, Durko J, Sarapuu A,
Choe J, et al: The mRNA m6A reader YTHDF2 suppresses
proinflammatory pathways and sustains hematopoietic stem cell
function. J Exp Med. 218:e202008292021. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
76
|
Fang C, He M, Li D and Xu Q: YTHDF2
mediates LPS-induced osteoclastogenesis and inflammatory response
via the NF-κB and MAPK signaling pathways. Cell Signal.
85:1100602021. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
77
|
Tsuchiya K, Yoshimura K, Inoue Y, Iwashita
Y, Yamada H, Kawase A, Watanabe T, Tanahashi M, Ogawa H, Funai K,
et al: YTHDF1 and YTHDF2 are associated with better patient
survival and an inflamed tumor-immune microenvironment in
non-small-cell lung cancer. Oncoimmunology. 10:19626562021.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
78
|
Wu R, Liu Y, Zhao Y, Bi Z, Yao Y, Liu Q,
Wang F, Wang Y and Wang X: m6A methylation controls
pluripotency of porcine induced pluripotent stem cells by targeting
SOCS3/JAK2/STAT3 pathway in a YTHDF1/YTHDF2-orchestrated manner.
Cell Death Dis. 10:1712019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
79
|
Hsu PJ, Zhu Y, Ma H, Guo Y, Shi X, Liu Y,
Qi M, Lu Z, Shi H, Wang J, et al: Ythdc2 is an
N6-methyladenosine binding protein that regulates
mammalian spermatogenesis. Cell Res. 27:1115–1127. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
80
|
Keegan GM, Learmonth ID and Case CP:
Orthopaedic metals and their potential toxicity in the arthroplasty
patient: A review of current knowledge and future strategies. J
Bone Joint Surg Br. 89:567–573. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
81
|
Gornet MF, Singh V, Schranck FW, Skipor AK
and Jacobs JJ: Serum metal concentrations in patients with titanium
ceramic composite cervical disc replacements. Spine (Phila Pa
1976). 42:366–371. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
82
|
Day JS, Baxter RM, Ramsey ML, Morrey BF,
Connor PM, Kurtz SM and Steinbeck MJ: Characterization of wear
debris in total elbow arthroplasty. J Shoulder Elbow Surg.
22:924–931. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
83
|
Chassot E, Irigaray JL, Terver S and
Vanneuville G: Contamination by metallic elements released from
joint prostheses. Med Eng Phys. 26:193–199. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
84
|
Lukina E, Laka A, Kollerov M, Sampiev M,
Mason P, Wagstaff P, Noordeen H, Yoon WW and Blunn G: Metal
concentrations in the blood and tissues after implantation of
titanium growth guidance sliding instrumentation. Spine J.
16:380–388. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
85
|
Safioti LM, Kotsakis GA, Pozhitkov AE,
Chung WO and Daubert DM: Increased levels of dissolved titanium are
associated with peri-implantitis-a cross-sectional study. J
Periodontol. 88:436–442. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
86
|
Zeng C, Huang W, Li Y and Weng H: Roles of
METTL3 in cancer: Mechanisms and therapeutic targeting. J Hematol
Oncol. 13:1172020. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|