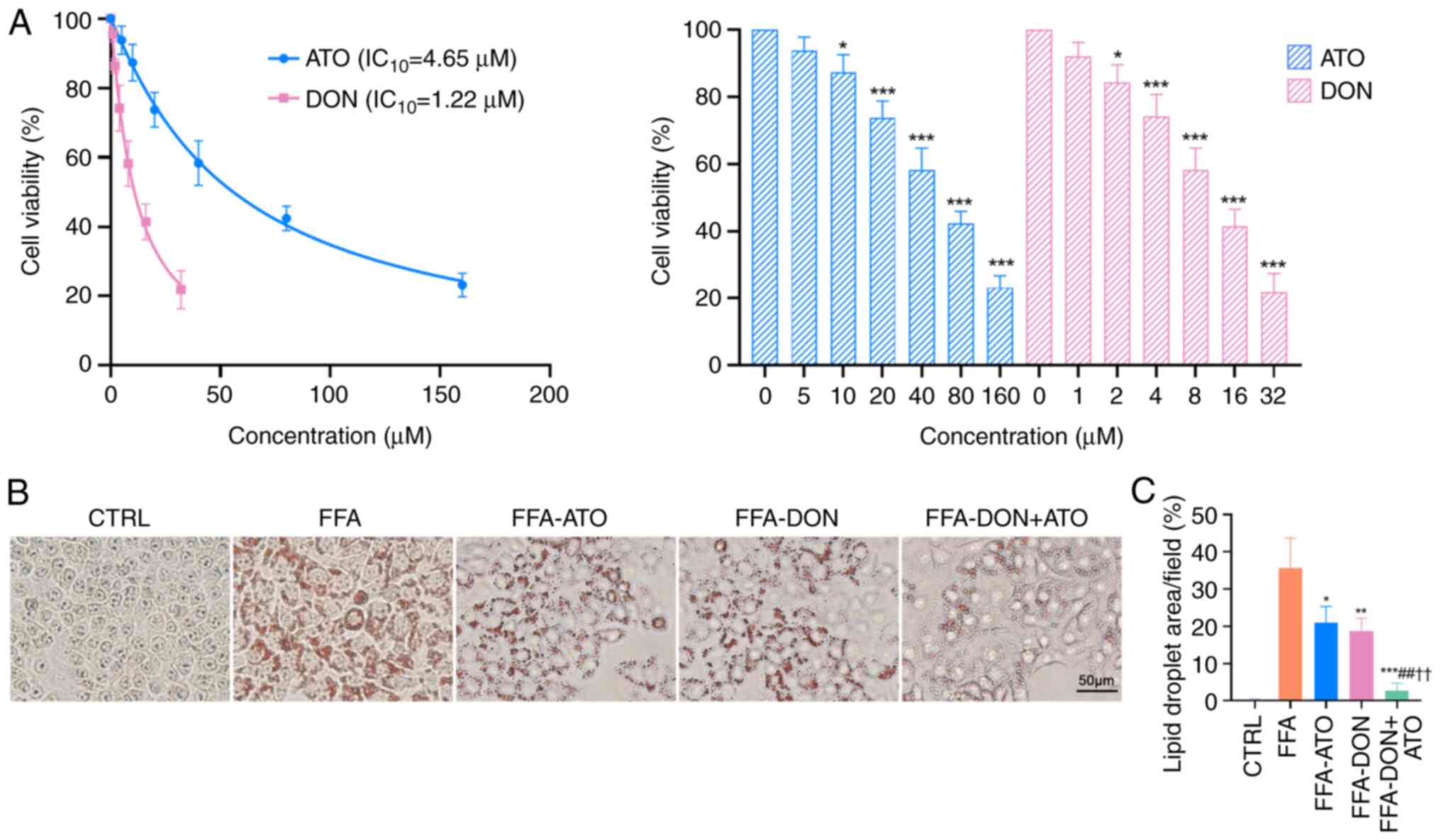
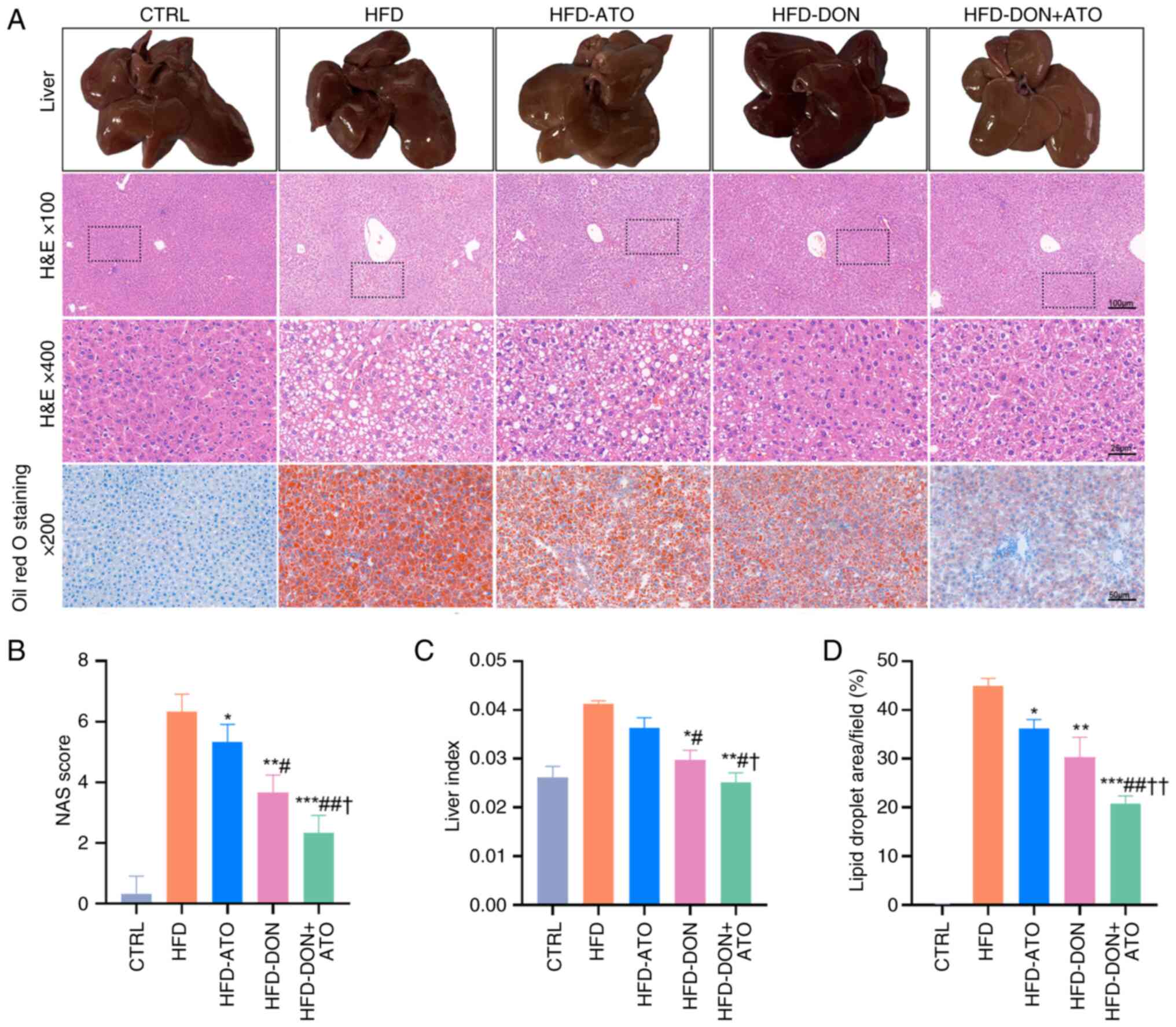
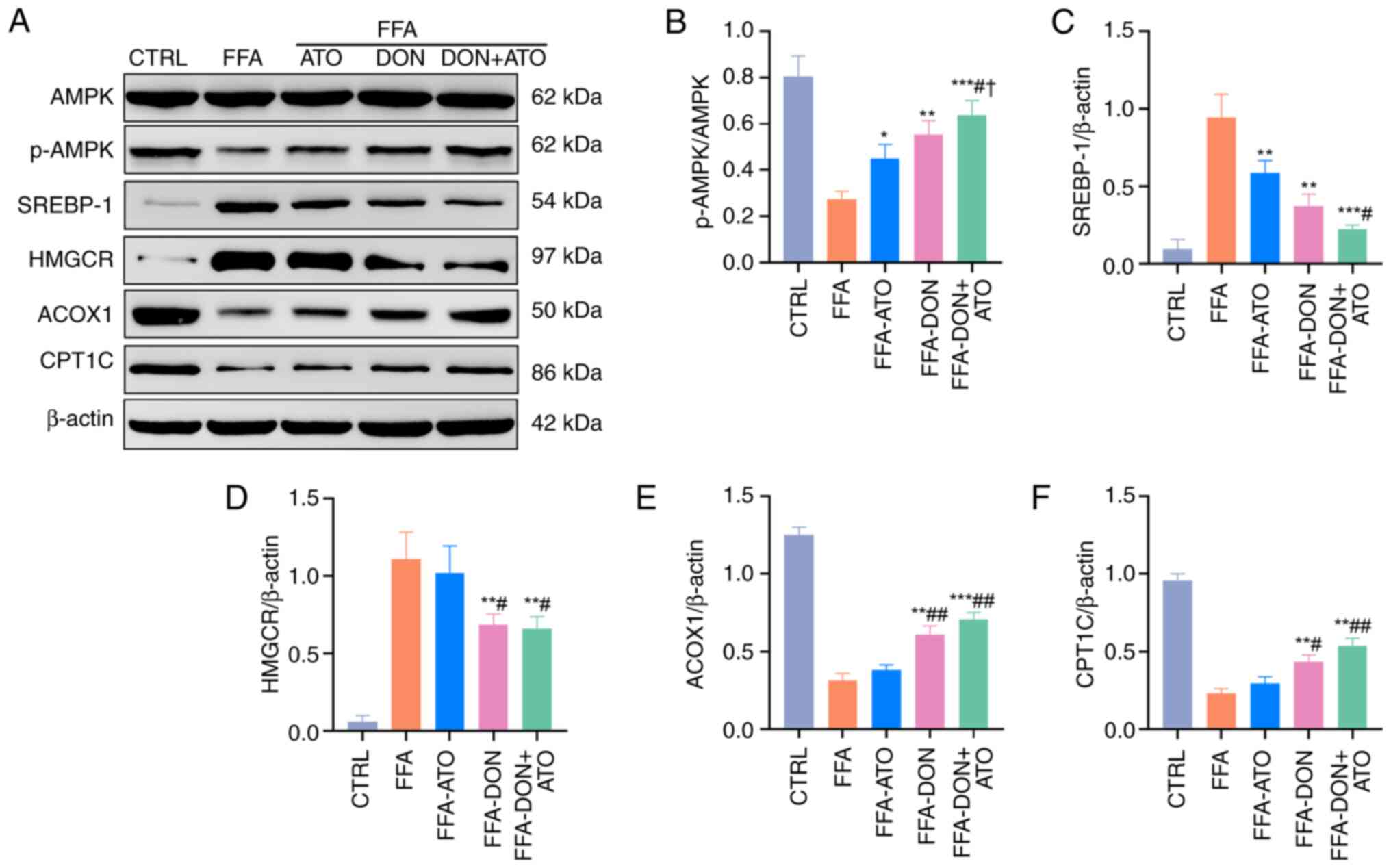
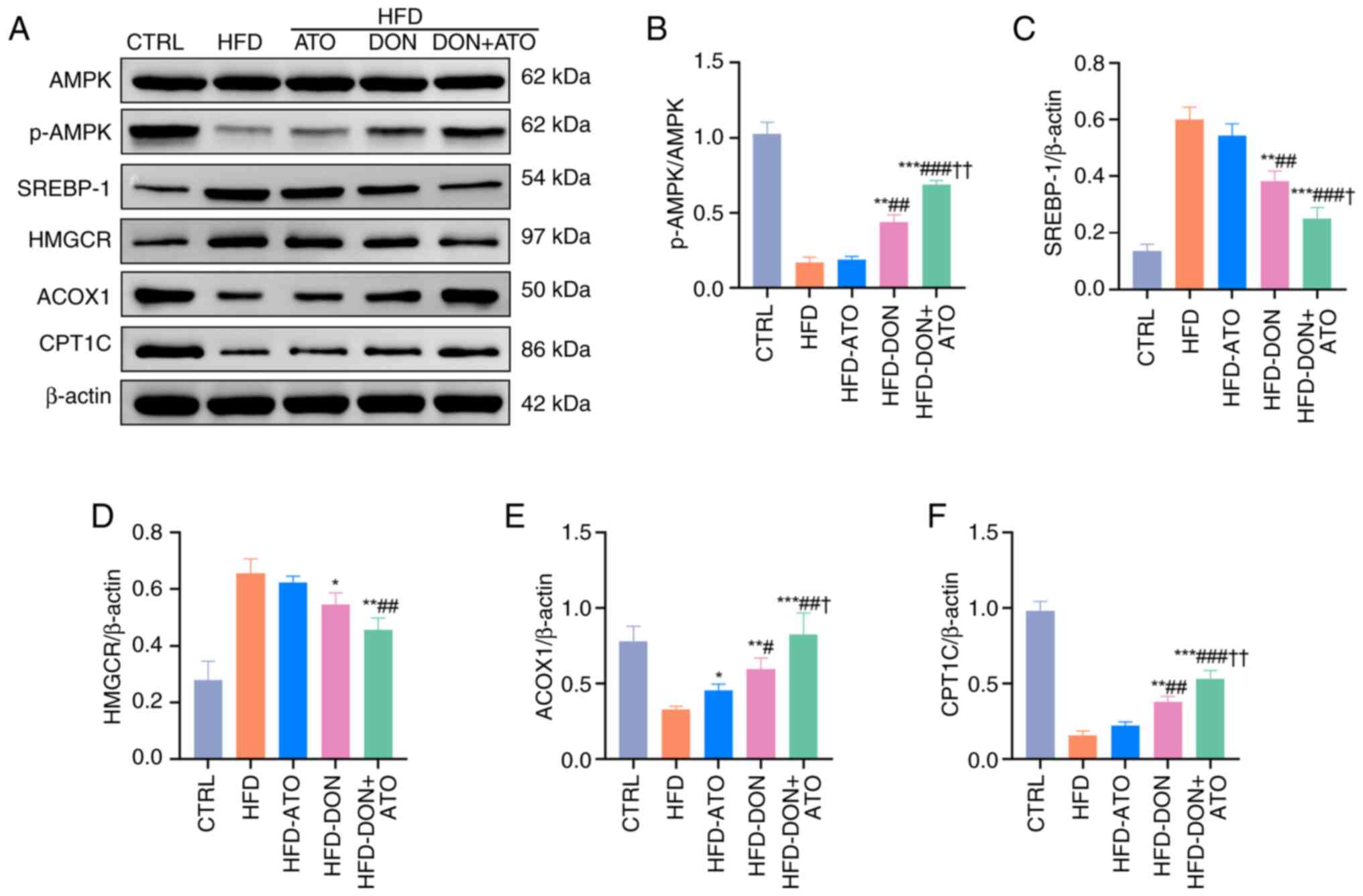
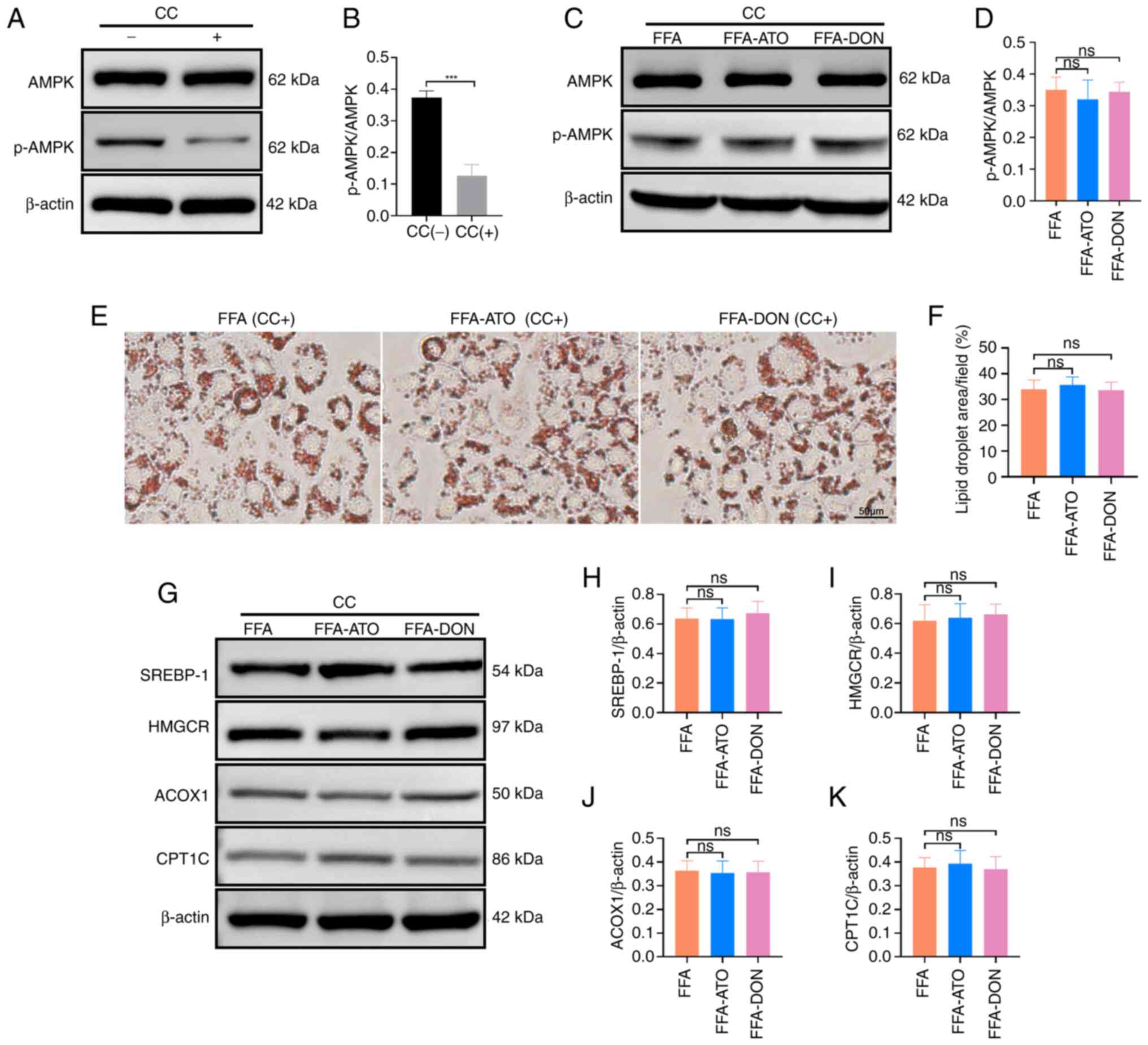
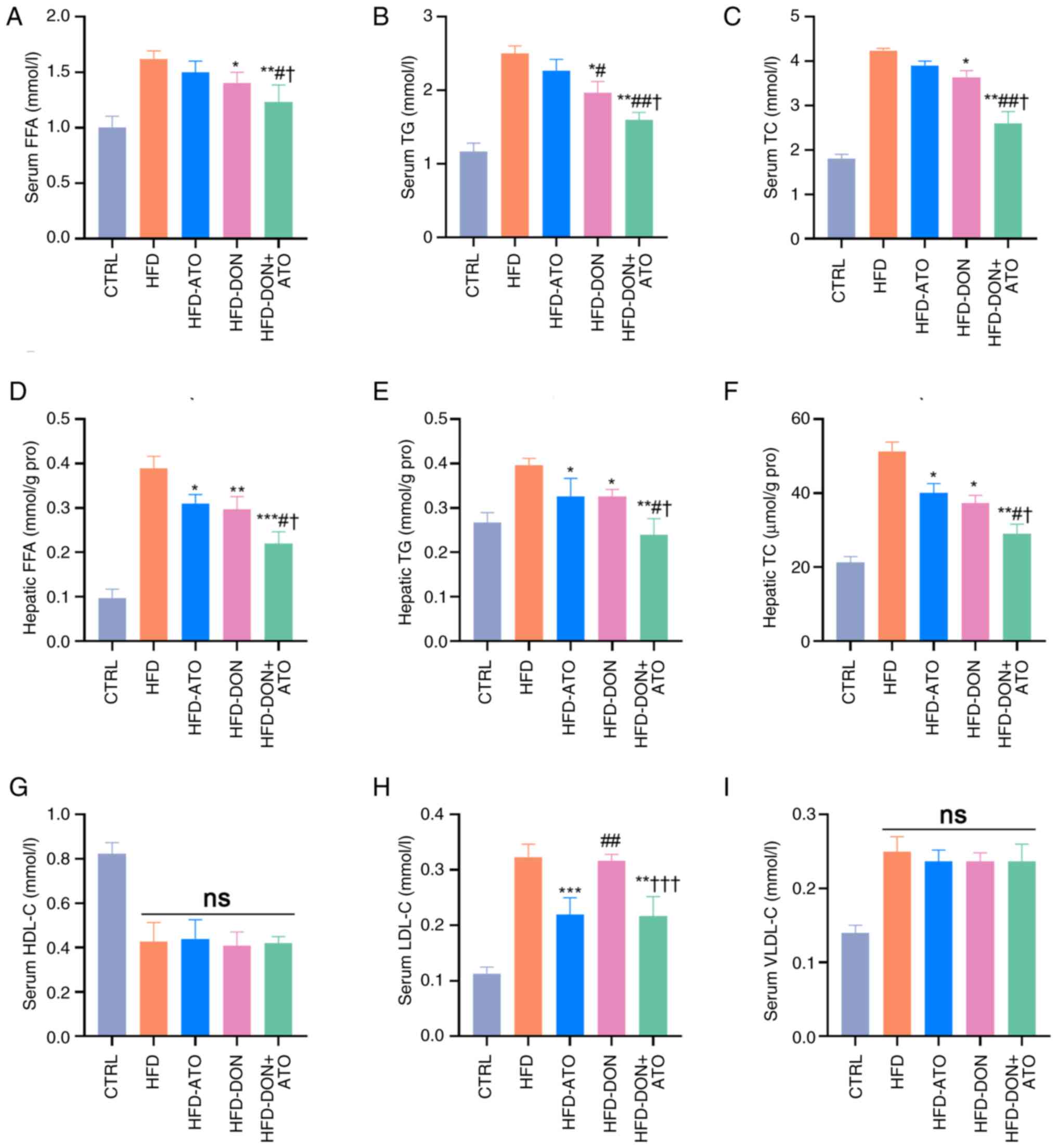
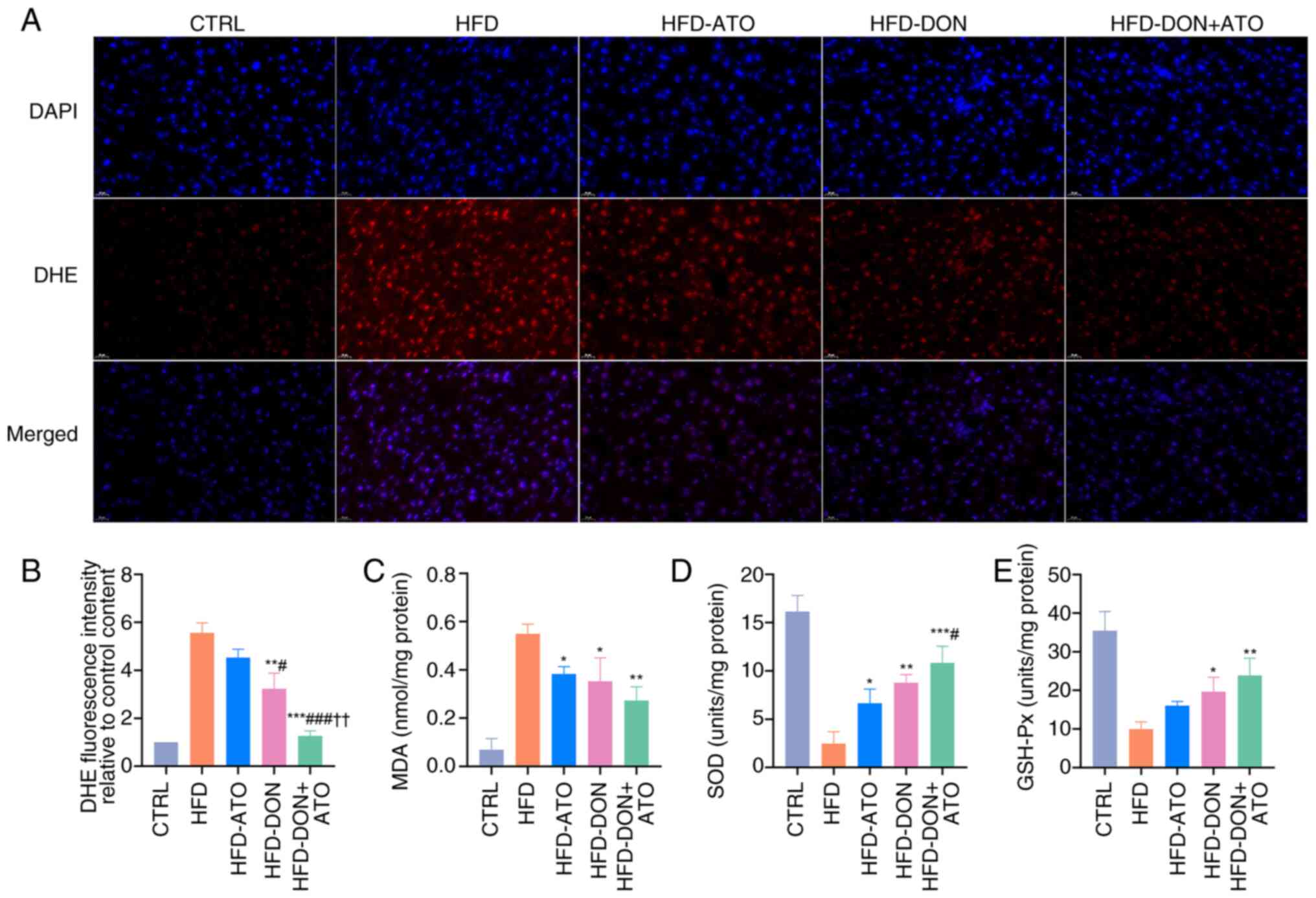
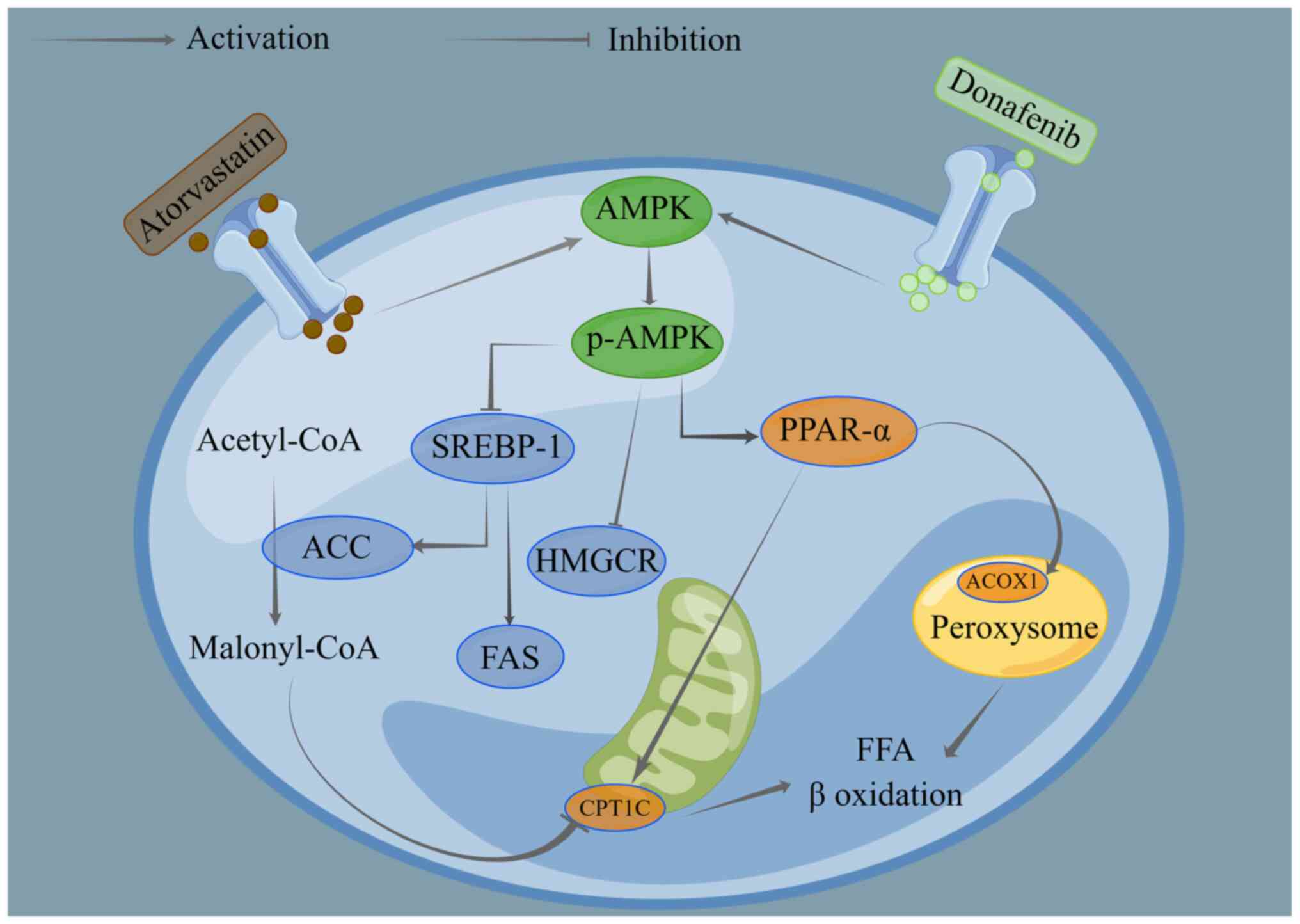
|
1
|
Younossi Z, Anstee QM, Marietti M, Hardy
T, Henry L, Eslam M, George J and Bugianesi E: Global burden of
NAFLD and NASH: Trends, predictions, risk factors and prevention.
Nat Rev Gastroenterol Hepatol. 15:11–20. 2018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
Greenhill C: Phase IIa results for
potential NAFLD therapy. Nat Rev Endocrinol. 18:22022. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
3
|
Rinella ME, Lazarus JV, Ratziu V, Francque
SM, Sanyal AJ, Kanwal F, Romero D, Abdelmalek MF, Anstee QM, Arab
JP, et al: A multi-society Delphi consensus statement on new fatty
liver disease nomenclature. Hepatology. 78:1966–1986. 2023.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
Song SJ, Lai JCT, Wong GLH, Wong GLH, Wong
VWS and Yip TCF: Can we use old NAFLD data under the new MASLD
definition? J Hepatol. 2:S0168–S8278. 2023.
|
|
5
|
De A, Bhagat N, Mehta M, Taneja S and
Duseja A: Metabolic dysfunction-associated steatotic liver disease
(MASLD) definition is better than MAFLD criteria for lean patients
with non-alcoholic fatty liver disease (NAFLD). J Hepatol.
7:S0168–S0827. 2023.
|
|
6
|
Friedman SL, Neuschwander-Tetri BA,
Rinella M and Sanyal AJ: Mechanisms of NAFLD development and
therapeutic strategies. Nat Med. 24:908–922. 2018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Estes C, Anstee QM, Arias-Loste MT, Bantel
H, Bellentani S, Caballeria J, Colombo M, Craxi A, Crespo J, Day
CP, et al: Modeling NAFLD disease burden in China, France, Germany,
Italy, Japan, Spain, United Kingdom, and United States for the
period 2016–2030. J Hepatol. 69:896–904. 2018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Régnier M, Carbinatti T, Parlati L,
Benhamed F and Postic C: The role of ChREBP in carbohydrate sensing
and NAFLD development. Nat Rev Endocrinol. 19:336–349. 2023.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Loneker AE, Alisafaei F, Kant A, Li D,
Janmey PA, Shenoy VB and Wells RG: Lipid droplets are intracellular
mechanical stressors that impair hepatocyte function. Proc Natl
Acad Sci USA. 120:e22168111202023. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Mazilescu LI, Selzner M and Selzner N:
Defatting strategies in the current era of liver steatosis. JHEP
Rep. 3:1002652021. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Parlati L, Régnier M, Guillou H and Postic
C: New targets for NAFLD. JHEP Rep. 3:1003462021. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Inci MK, Park SH, Helsley RN, Attia SL and
Softic S: Fructose impairs fat oxidation: Implications for the
mechanism of western diet-induced NAFLD. J Nutr Biochem.
114:1092242023. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Yau T, Park JW, Finn RS, Cheng AL,
Mathurin P, Edeline J, Kudo M, Harding JJ, Merle P, Rosmorduc O, et
al: Nivolumab versus sorafenib in advanced hepatocellular carcinoma
(CheckMate 459): A randomised, multicentre, open-label, phase 3
trial. Lancet Oncol. 23:77–90. 2022. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Jian C, Fu J, Cheng X, Shen LJ, Ji YX,
Wang X, Pan S, Tian H, Tian S, Liao R, et al: Low-Dose Sorafenib
acts as a mitochondrial uncoupler and Ameliorates Nonalcoholic
Steatohepatitis. Cell Metab. 31:12062020. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Qin S, Bi F, Gu S, Bai Y, Chen Z, Wang Z,
Ying J, Lu Y, Meng Z, Pan H, et al: Donafenib Versus Sorafenib in
first-line treatment of unresectable or metastatic hepatocellular
carcinoma: A randomized, open-label, parallel-controlled phase
II–III trial. J Clin Oncol. 39:3002–3011. 2021. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Dongiovanni P, Petta S, Mannisto V,
Mancina RM, Pipitone R, Karja V, Maggioni M, Kakela P, Wiklund O,
Mozzi E, et al: Statin use and non-alcoholic steatohepatitis in at
risk individuals. J Hepatol. 63:705–712. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Dehnavi S, Kiani A, Sadeghi M, Biregani
AF, Banach M, Atkin SL, Jamialahmadi T and Sahebkar A: Targeting
AMPK by Statins: A potential therapeutic approach. Drugs.
81:923–933. 2021. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
Tanaka S, Hikita H, Tatsumi T, Sakamori R,
Nozaki Y, Sakane S, Shiode Y, Nakabori T, Saito Y, Hiramatsu N, et
al: Rubicon inhibits autophagy and accelerates hepatocyte apoptosis
and lipid accumulation in nonalcoholic fatty liver disease in mice.
Hepatology. 64:1994–2014. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
Zhang P, Ge Z, Wang H, Feng W, Sun X, Chu
X, Jiang C, Wang Y, Zhu D and Bi Y: Prolactin improves hepatic
steatosis via CD36 pathway. J Hepatol. 68:1247–1255. 2018.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
Jiang JJ, Zhang GF, Zheng JY, Sun JH and
Ding SB: Targeting mitochondrial ROS-mediated ferroptosis by
quercetin alleviates high-fat diet-induced hepatic lipotoxicity.
Front Pharmacol. 13:8765502022. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
Vucicevic L, Misirkic M, Janjetovic K,
Vilimanovich U, Sudar E, Isenovic E, Prica M, Harhaji-Trajkovic L,
Kravic-Stevovic T, Bumbasirevic V and Trajkovic V: Compound C
induces protective autophagy in cancer cells through AMPK
inhibition-independent blockade of Akt/mTOR pathway. Autophagy.
7:40–50. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22
|
Wu Y, Yan B, Xu W, Guo L, Wang Z, Li G,
Hou N, Zhang J and Ling R: Compound C enhances the anticancer
effect of aspirin in HER-2-positive breast cancer by regulating
lipid metabolism in an AMPK-independent pathway. Int J Biol Sci.
16:583–597. 2020. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23
|
Liu B, Xu J, Lu L, Gao L, Zhu S, Sui Y,
Cao T and Yang T: Metformin induces pyroptosis in leptin
receptor-defective hepatocytes via overactivation of the AMPK axis.
Cell Death Dis. 14:822023. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24
|
Bravo M, Raurell I, Barberá A, Hide D, Gil
M, Estrella F, Salcedo MT, Augustin S, Genescà J and Martell M:
Synergic effect of atorvastatin and ambrisentan on sinusoidal and
hemodynamic alterations in a rat model of NASH. Dis Model Mech.
14:dmm0488842021. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
25
|
Matafome P, Louro T, Rodrigues L,
Crisóstomo J, Nunes E, Amaral C, Monteiro P, Cipriano A and Seiça
R: Metformin and atorvastatin combination further protect the liver
in type 2 diabetes with hyperlipidaemia. Diabetes Metab Res Rev.
27:54–62. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
26
|
Li HY, Huang SY, Zhou DD, Xiong RG, Luo M,
Saimaiti A, Han MK, Gan RY, Zhu HL and Li HB: Theabrownin inhibits
obesity and non-alcoholic fatty liver disease in mice via
serotonin-related signaling pathways and gut-liver axis. J Adv Res.
52:59–72. 2023. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
27
|
Kebbel A and Röcken C: Immunohistochemical
classification of amyloid in surgical pathology revisited. Am J
Surg Pathol. 30:673–683. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
28
|
Devarbhavi H, Asrani SK, Arab JP, Nartey
YA, Pose E and Kamath PS: Global burden of liver disease: 2023
Update. J Hepatol. 79:516–537. 2023. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
29
|
Amorim R, Simões ICM, Veloso C, Carvalho
A, Simões RF, Pereira FB, Thiel T, Normann A, Morais C, Jurado AS,
et al: Exploratory data analysis of cell and mitochondrial
high-fat, high-sugar toxicity on human HepG2 cells. Nutrients.
13:17232021. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
30
|
Green CJ, Johnson D, Amin HD, Sivathondan
P, Silva MA, Wang LM, Stevanato L, McNeil CA, Miljan EA, Sinden JD,
et al: Characterization of lipid metabolism in a novel immortalized
human hepatocyte cell line. Am J Physiol Endocrinol Metab.
309:E511–E522. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
31
|
Besse-Patin A, Léveillé M, Oropeza D,
Nguyen BN, Prat A and Estall JL: Estrogen signals through
peroxisome proliferator-activated receptor-γ coactivator 1α to
reduce oxidative damage associated with diet-induced fatty liver
disease. Gastroenterology. 152:243–256. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
32
|
Dongiovanni P, Crudele A, Panera N, Romito
I, Meroni M, De Stefanis C, Palma A, Comparcola D, Fracanzani AL,
Miele L, et al: β-Klotho gene variation is associated with liver
damage in children with NAFLD. J Hepatol. 72:411–419. 2020.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
33
|
Iturrospe E, Robeyns R, da Silva KM, van
de Lavoi M, Boeckmans J, Vanhaeck T, van Nuij ALN and Covaci A:
Metabolic signature of HepaRG cells exposed to ethanol and tumor
necrosis factor alpha to study alcoholic steatohepatitis by
LC-MS-based untargeted metabolomics. Arch Toxicol. 97:1335–1353.
2023. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
34
|
Kakimoto PA and Kowaltowski AJ: Effects of
high fat diets on rodent liver bioenergetics and oxidative
imbalance. Redox Biol. 8:216–225. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
35
|
Chen H, Tan H, Wan J, Zeng Y, Wang J, Wang
H and Lu X: PPAR-γ signaling in nonalcoholic fatty liver disease:
Pathogenesis and therapeutic targets. Pharmacol Ther.
245:1083912023. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
36
|
Fang C, Pan J, Qu N, Lei Y, Han J, Zhang J
and Han D: The AMPK pathway in fatty liver disease. Front Physiol.
13:9702922022. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
37
|
Day EA, Ford RJ and Steinberg GR: AMPK as
a therapeutic target for treating metabolic diseases. Trends
Endocrinol Metab. 28:545–560. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
38
|
Wakil SJ and Abu-Elheiga LA: Fatty acid
metabolism: Target for metabolic syndrome. J Lipid Res. 50
(Suppl):S138–S143. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
39
|
Kelly B and O'Neill LAJ: Metabolic
reprogramming in macrophages and dendritic cells in innate
immunity. Cell Res. 25:771–784. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
40
|
Zhao P and Saltiel AR: From overnutrition
to liver injury: AMP-activated protein kinase in nonalcoholic fatty
liver diseases. J Biol Chem. 295:12279–12289. 2020. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
41
|
Tziomalos K, Athyros VG, Paschos P and
Karagiannis A: Nonalcoholic fatty liver disease and statins.
Metabolism. 64:1215–1223. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
42
|
Huang TS, Wu T, Wu YD, Li XH, Tan J, Shen
CH, Xiong SJ, Feng ZQ, Gao SF, Li H and Cai WB: Long-term statins
administration exacerbates diabetic nephropathy via ectopic fat
deposition in diabetic mice. Nat Commun. 14:3902023. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
43
|
Lally JSV, Ghoshal S, DePeralta DK, Moaven
O, Wei L, Masia R, Erstad DJ, Fujiwara N, Leong V, Houde VP, et al:
Inhibition of Acetyl-CoA carboxylase by phosphorylation or the
inhibitor ND-654 suppresses lipogenesis and hepatocellular
carcinoma. Cell Metab. 29:174–182. 2019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
44
|
Lee SM, Koh DH, Jun DW, Roh YJ, Kang HT,
Oh JH and Kim HS: Auranofin attenuates hepatic steatosis and
fibrosis in nonalcoholic fatty liver disease via NRF2 and NF-κB
signaling pathways. Clin Mol Hepatol. 28:827–840. 2022. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
45
|
Yu H, Yan S, Jin M, Wei Y, Zhao L, Cheng
J, Ding L and Feng H: Aescin can alleviate NAFLD through Keap1-Nrf2
by activating antioxidant and autophagy. Phytomedicine.
113:1547462023. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
46
|
Chen X, Xue H, Fang W, Chen K, Chen S,
Yang W, Shen T, Chen X, Zhang P and Ling W: Adropin protects
against liver injury in nonalcoholic steatohepatitis via the Nrf2
mediated antioxidant capacity. Redox Biol. 21:1010682019.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
47
|
Chalasani N, Younossi Z, Lavine JE,
Charlton M, Cusi K, Rinella M, Harrison SA, Brunt EM and Sanyal AJ:
The diagnosis and management of nonalcoholic fatty liver disease:
Practice guidance from the american association for the study of
liver diseases. Hepatology. 67:328–357. 2018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
48
|
Reagan-Shaw S, Nihal M and Ahmad N: Dose
translation from animal to human studies revisited. FASEB J.
22:659–661. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
49
|
Davidson MH and Robinson JG: Safety of
aggressive lipid management. J Am Coll Cardiol. 49:1753–1762. 2007.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
50
|
Stone NJ, Robinson JG, Lichtenstein AH,
Merz CN, Blum CB, Eckel RH, Goldberg AC, Gordon D, Levy D,
Lloyd-Jones DM, et al: 2013 ACC/AHA guideline on the treatment of
blood cholesterol to reduce atherosclerotic cardiovascular risk in
adults: A report of the American college of Cardiology/American
heart association task force on practice guidelines. Circulation.
129:S1–45. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|