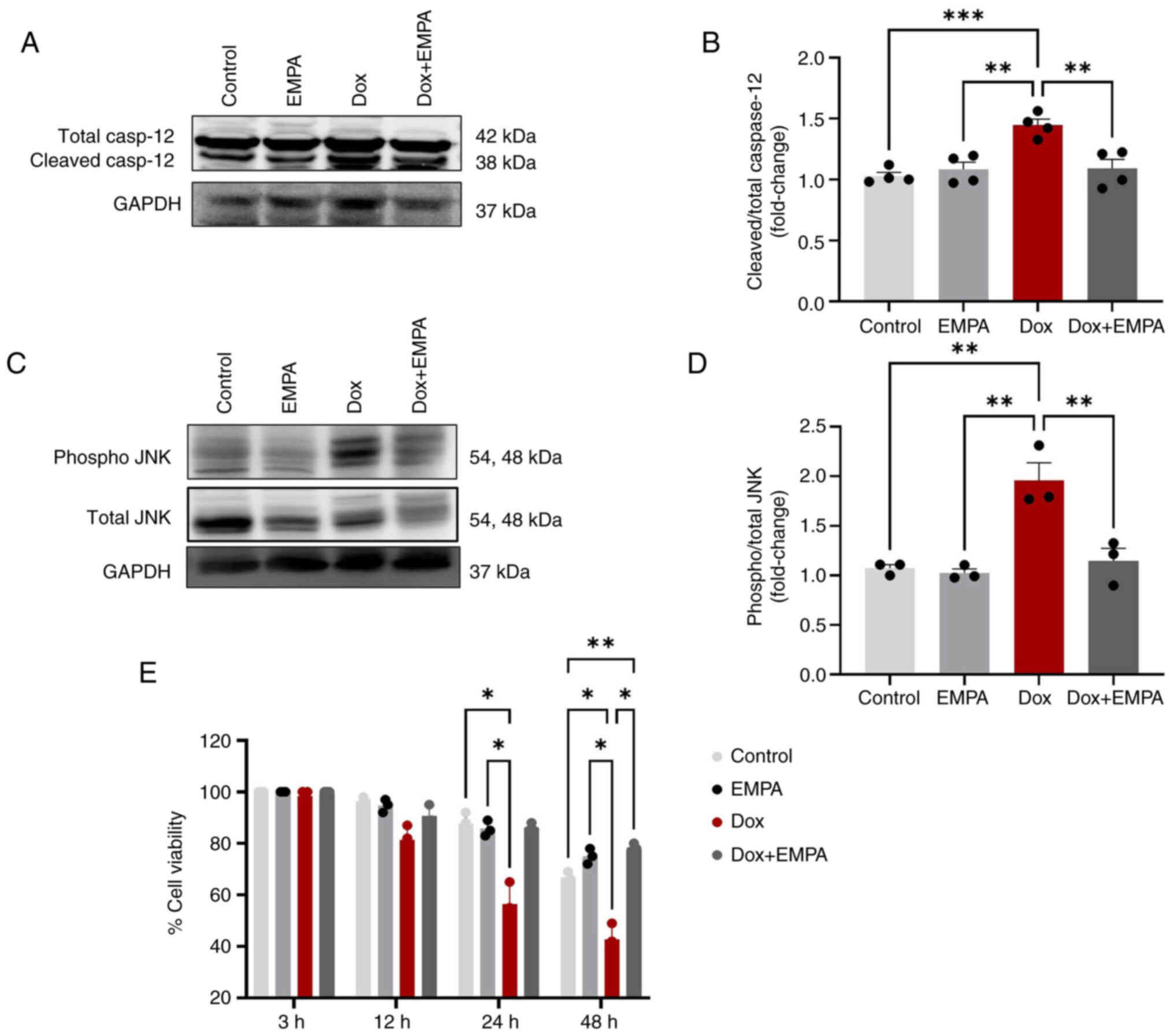
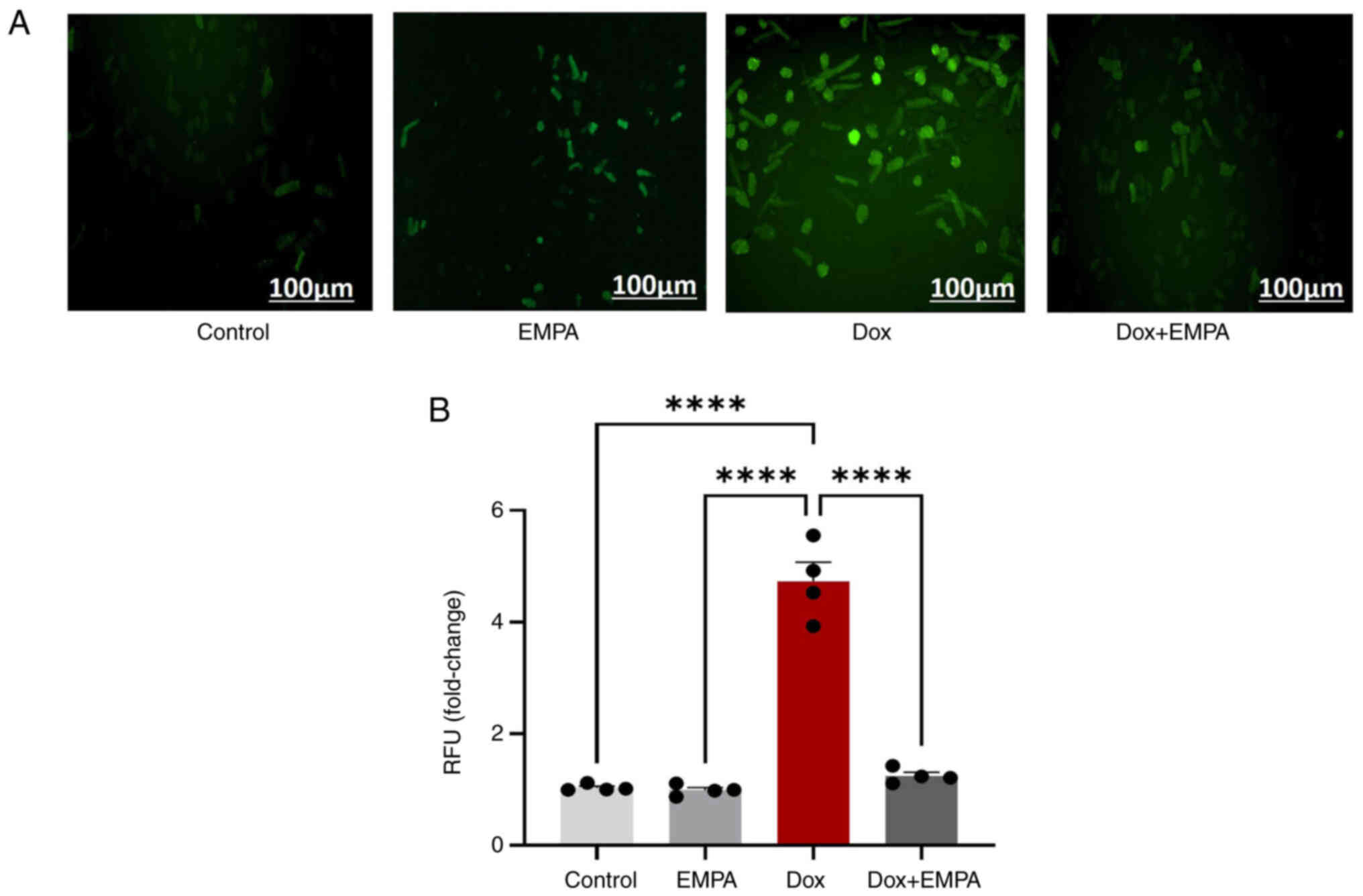
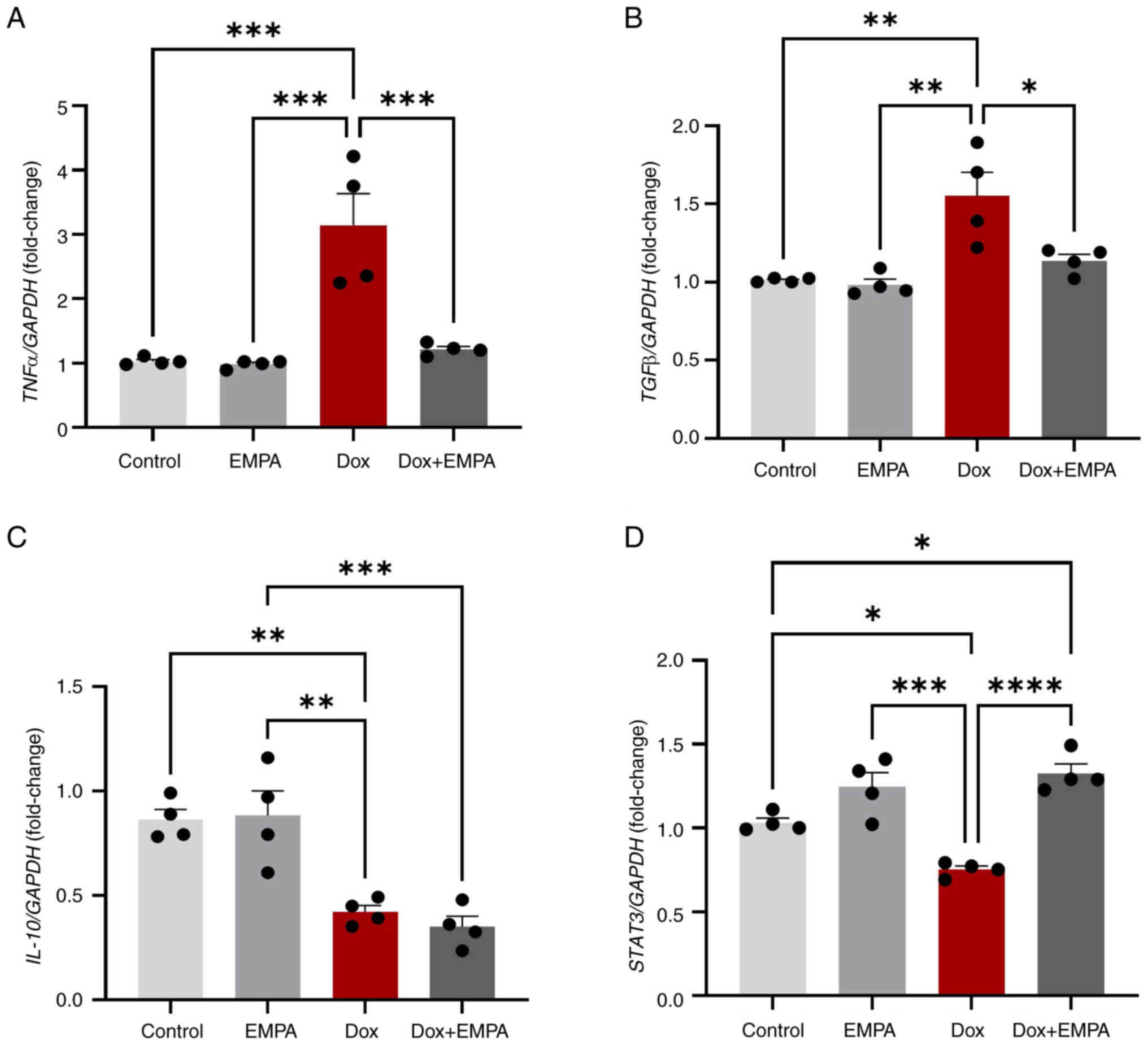
|
1
|
Lefrak EA, Pitha J, Rosenheim S and
Gottlieb JA: A clinicopathologic analysis of adriamycin
cardiotoxicity. Cancer. 32:302–314. 1973. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
Singal PK and Iliskovic N:
Doxorubicin-induced cardiomyopathy. N Engl J Med. 339:900–905.
1998. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
Ludke AR, Sharma AK, Akolkar G, Bajpai G
and Singal PK: Downregulation of vitamin C transporter SVCT-2 in
doxorubicin-induced cardiomyocyte injury. Am J Physiol Cell
Physiol. 303:C645–C653. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
Singal PK, Siveski-Iliskovic N, Hill M,
Thomas TP and Li T: Combination therapy with probucol prevents
adriamycin-induced cardiomyopathy. J Mol Cell Cardiol.
27:1055–1063. 1995. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Torti FM, Bristow MM, Lum BL, Carter SK,
Howes AE, Aston DA, Brown BW Jr, Hannigan JF Jr, Meyers FJ,
Mitchell EP, et al: Cardiotoxicity of epirubicin and doxorubicin:
Assessment by endomyocardial biopsy. Cancer Res. 46:3722–3727.
1986.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Singal PK, Deally CM and Weinberg LE:
Subcellular effects of adriamycin in the heart: A concise review. J
Mol Cell Cardiol. 19:817–828. 1987. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Krebs J, Agellon LB and Michalak M: Ca(2+)
homeostasis and endoplasmic reticulum (ER) stress: An integrated
view of calcium signaling. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 460:114–121.
2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Hetz C and Papa FR: The unfolded protein
response and cell fate control. Mol Cell. 69:169–181. 2018.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Harding HP, Zhang Y, Bertolotti A, Zeng H
and Ron D: Perk is essential for translational regulation and cell
survival during the unfolded protein response. Mol Cell. 5:897–904.
2000. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Glembotski CC: Roles for ATF6 and the
sarco/endoplasmic reticulum protein quality control system in the
heart. J Mol Cell Cardiol. 71:11–15. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Yoshida H, Matsui T, Yamamoto A, Okada T
and Mori K: XBP1 mRNA is induced by ATF6 and spliced by IRE1 in
response to ER stress to produce a highly active transcription
factor. Cell. 107:881–891. 2001. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Bertolotti A, Zhang Y, Hendershot LM,
Harding HP and Ron D: Dynamic interaction of BiP and ER stress
transducers in the unfolded-protein response. Nat Cell Biol.
2:326–332. 2000. View
Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Bagchi AK, Malik A, Akolkar G, Zimmer A,
Belló-Klein A, De Angelis K, Jassal DS, Fini MA, Stenmark KR and
Singal PK: Study of ER stress and apoptotic proteins in the heart
and tumor exposed to doxorubicin. Biochim Biophys Acta Mol Cell
Res. 1868:1190392021. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Hitomi J, Katayama T, Taniguchi M, Honda
A, Imaizumi K and Tohyama M: Apoptosis induced by endoplasmic
reticulum stress depends on activation of caspase-3 via caspase-12.
Neurosci Lett. 357:127–130. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Hsia DS, Grove O and Cefalu WT: An update
on sodium-glucose co-transporter-2 inhibitors for the treatment of
diabetes mellitus. Curr Opin Endocrinol Diabetes Obes. 24:73–79.
2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Zinman B, Wanner C and Lachin JM; EMPA-REG
OUTCOME Investigators, : Empagliflozin, cardiovascular outcomes,
and mortality in type 2 diabetes. N Engl J Med. 373:2117–2128.
2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Butler J, Anker SD, Filippatos G, Khan MS,
Ferreira JP, Pocock SJ, Giannetti N, Januzzi JL, Piña IL, Lam CSP,
et al: Empagliflozin and health-related quality of life outcomes in
patients with heart failure with reduced ejection fraction: The
EMPEROR-reduced trial. Eur Heart J. 42:1203–1212. 2021. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
Packer M, Anker SD, Butler J, Filippatos
G, Pocock SJ, Carson P, Januzzi J, Verma S, Tsutsui H, Brueckmann
M, et al: Cardiovascular and Renal outcomes with empagliflozin in
heart failure. N Engl J Med. 383:1413–1424. 2020. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
Anker SD, Butler J, Filippatos G, Ferreira
JP, Bocchi E, Böhm M, Brunner-La Rocca HP, Choi DJ, Chopra V,
Chuquiure-Valenzuela E, et al: Empagliflozin in heart failure with
a preserved ejection fraction. N Engl J Med. 385:1451–1461. 2021.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
McDonald M, Virani S, Chan M, Ducharme A,
Ezekowitz JA, Giannetti N, Heckman GA, Howlett JG, Koshman SL,
Lepage S, et al: CCS/CHFS heart failure guidelines update: Defining
a new pharmacologic standard of care for heart failure with reduced
ejection fraction. Can J Cardiol. 37:531–546. 2021. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
Sabatino J, De Rosa S, Tammè L, Iaconetti
C, Sorrentino S, Polimeni A, Mignogna C, Amorosi A, Spaccarotella
C, Yasuda M and Indolfi C: Empagliflozin prevents
doxorubicin-induced myocardial dysfunction. Cardiovasc Diabetol.
19:662020. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22
|
Chang WT, Lin YW, Ho CH, Chen ZC, Liu PY
and Shih JY: Dapagliflozin suppresses ER stress and protects
doxorubicin-induced cardiotoxicity in breast cancer patients. Arch
Toxicol. 95:659–671. 2021. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23
|
Bagchi AK, Malik A, Akolkar G, Jassal DS
and Singal PK: Endoplasmic reticulum stress promotes iNOS/NO and
influences inflammation in the development of doxorubicin-induced
cardiomyopathy. Antioxidants (Basel). 10:18972021. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24
|
Malik A, Bagchi AK, Jassal DS and Singal
PK: Interleukin-10 mitigates doxorubicin-induced endoplasmic
reticulum stress as well as cardiomyopathy. Biomedicines.
10:8902022. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
25
|
Zhao L and Zhang B: Doxorubicin induces
cardiotoxicity through upregulation of death receptors mediated
apoptosis in cardiomyocytes. Sci Rep. 7:447352017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
26
|
Yarmohammadi F, Rezaee R, Haye AW and
Karimi G: Endoplasmic reticulum stress in doxorubicin-induced
cardiotoxicity may be therapeutically targeted by natural and
chemical compounds: A review. Pharmacol Res. 164:1053832021.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
27
|
Livak KJ and Schmittgen TD: Analysis of
relative gene expression data using real-time quantitative PCR and
the 2(−Delta Delta C(T)) Method. Methods. 25:402–408. 2001.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
28
|
Heidenreich PA, Bozkurt B, Aguilar D,
Allen LA, Byun JJ, Colvin MM, Deswal A, Drazner MH, Dunlay SM,
Evers LR, et al: 2022 AHA/ACC/HFSA Guideline for the Management of
Heart Failure: A Report of the American College of
Cardiology/American Heart Association Joint Committee on Clinical
Practice Guidelines. Circulation. 145:e89–e1032. 2022. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
29
|
Di Franco A, Cantini G, Tani A, Coppini R,
Zecchi-Orlandini S, Raimondi L, Luconi M and Mannucci E:
Sodium-dependent glucose transporters (SGLT) in human ischemic
heart: A new potential pharmacological target. Int J Cardiol.
243:86–90. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
30
|
Chen J, Williams S, Ho S, Loraine H, Hagan
D, Whaley JM and Feder JN: Quantitative PCR tissue expression
profiling of the human SGLT2 gene and related family members.
Diabetes Ther. 1:57–92. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
31
|
Zhou L, Cryan EV, D'Andrea MR, Belkowski
S, Conway BR and Demarest KT: Human cardiomyocytes express high
level of Na+/glucose cotransporter 1 (SGLT1). J Cell Biochem.
90:339–346. 2003. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
32
|
Kashiwagi Y, Nagoshi T, Yoshino T, Tanaka
TD, Ito K, Harada T, Takahashi H, Ikegami M, Anzawa R and Yoshimura
M: Expression of SGLT1 in human hearts and impairment of cardiac
glucose uptake by phlorizin during ischemia-reperfusion injury in
mice. PLoS One. 10:e01306052015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
33
|
Quagliariello V, De Laurentiis M, Rea D,
Barbieri A, Monti MG, Carbone A, Paccone A, Altucci L, Conte M,
Canale ML, et al: The SGLT-2 inhibitor empagliflozin improves
myocardial strain, reduces cardiac fibrosis and pro-inflammatory
cytokines in non-diabetic mice treated with doxorubicin. Cardiovasc
Diabetol. 20:1502021. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
34
|
Nakano D, Akiba J, Tsutsumi T, Kawaguchi
M, Yoshida T, Koga H and Kawaguchi T: Hepatic expression of
sodium-glucose cotransporter 2 (SGLT2) in patients with chronic
liver disease. Med Mol Morphol. 55:304–315. 2022. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
35
|
Bertero E and Maack C: Metabolic
remodelling in heart failure. Nat Rev Cardiol. 15:457–470. 2018.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
36
|
Asnani A, Shi X, Farrell L, Lall R, Sebag
IA, Plana JC, Gerszten RE and Scherrer-Crosbie M: Changes in citric
acid cycle and nucleoside metabolism are associated with
anthracycline cardiotoxicity in patients with breast cancer. J
Cardiovasc Transl Res. 13:349–356. 2020. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
37
|
Fu HY, Sanada S, Matsuzaki T, Liao Y,
Okuda K, Yamato M, Tsuchida S, Araki R, Asano Y, Asanuma H, et al:
Chemical endoplasmic reticulum chaperone alleviates
doxorubicin-induced cardiac dysfunction. Circ Res. 118:798–809.
2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
38
|
Wang CC, Li Y, Qian XQ, Zhao H, Wang D,
Zuo GX and Wang K: Empagliflozin alleviates myocardial I/R injury
and cardiomyocyte apoptosis via inhibiting ER stress-induced
autophagy and the PERK/ATF4/Beclin1 pathway. J Drug Target.
30:858–872. 2022. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
39
|
Hetz C: The unfolded protein response:
Controlling cell fate decisions under ER stress and beyond. Nat Rev
Mol Cell Biol. 13:89–102. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
40
|
Lee AH, Iwakoshi NN and Glimcher LH: XBP-1
regulates a subset of endoplasmic reticulum resident chaperone
genes in the unfolded protein response. Mol Cell Biol.
23:7448–7459. 2003. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
41
|
Yoshida H, Oku M, Suzuki M and Mori K:
pXBP1(U) encoded in XBP1 pre-mRNA negatively regulates unfolded
protein response activator pXBP1(S) in mammalian ER stress
response. J Cell Biol. 172:565–575. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
42
|
Kato H, Nakajima S, Saito Y, Takahashi S,
Katoh R and Kitamura M: mTORC1 serves ER stress-triggered apoptosis
via selective activation of the IRE1-JNK pathway. Cell Death
Differ. 19:310–320. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
43
|
Ala M, Khoshdel MRF and Dehpour AR:
Empagliflozin enhances autophagy, mitochondrial biogenesis, and
antioxidant defense and ameliorates renal ischemia/reperfusion in
nondiabetic rats. Oxid Med Cell Longev. 2022:11970612022.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
44
|
Haberzettl P and Hill BG: Oxidized lipids
activate autophagy in a JNK-dependent manner by stimulating the
endoplasmic reticulum stress response. Redox Biol. 1:56–64. 2013.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
45
|
Pirklbauer M, Sallaberger S, Staudinger P,
Corazza U, Leierer J, Mayer G and Schramek H: Empagliflozin
inhibits IL-1beta-mediated inflammatory response in human proximal
tubular cells. Int J Mol Sci. 22:50892021. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
46
|
Gohari S, Reshadmanesh T, Khodabandehloo
H, Karbalaee-Hasani A, Ahangar H, Arsang-Jang S, Ismail-Beigi F,
Dadashi M, Ghanbari S, Taheri H, et al: The effect of EMPAgliflozin
on markers of inflammation in patients with concomitant type 2
diabetes mellitus and coronary ARtery disease: The EMPA-CARD
randomized controlled trial. Diabetol Metab Syndr. 14:1702022.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
47
|
Bagchi AK, Surendran A, Malik A, Jassal
DS, Ravandi A and Singal PK: IL-10 attenuates OxPCs-mediated lipid
metabolic responses in ischemia reperfusion injury. Sci Rep.
10:121202020. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
48
|
Dhingra S, Sharma AK, Arora RC, Slezak J
and Singal PK: IL-10 attenuates TNF-alpha-induced NF kappaB pathway
activation and cardiomyocyte apoptosis. Cardiovasc Res. 82:59–66.
2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
49
|
Sun Z, Schriewer J, Tang M, Marlin J,
Taylor F, Shohet RV and Konorev EA: The TGF-β pathway mediates
doxorubicin effects on cardiac endothelial cells. J Mol Cell
Cardiol. 90:129–138. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
50
|
Li J, Deane JA, Campanale NV, Bertram JF
and Ricardo SD: Blockade of p38 mitogen-activated protein kinase
and TGF-beta1/Smad signaling pathways rescues bone marrow-derived
peritubular capillary endothelial cells in adriamycin-induced
nephrosis. J Am Soc Nephrol. 17:2799–2811. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
51
|
Li G, Zhao C and Fang S: SGLT2 promotes
cardiac fibrosis following myocardial infarction and is regulated
by miR-141. Exp Ther Med. 22:7152021. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
52
|
Lim CP and Fu XY: Multiple roles of STAT3
in cardiovascular inflammatory responses. Progress in Molecular
Biology and Translational Science. Vol 106. Shenolikar S: Academic
Press; pp. 63–73. 2012, View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
53
|
de Oliveira Santos TC, Pereira G, Coutinho
AGG, Dos Santos Silva HP, Lima MMS, Dias FAL, de Almeida DC,
Resende E, Silva DT, Perez RF and Pereira RL: STAT-3 signaling role
in an experimental model of nephropathy induced by doxorubicin. Mol
Cell Biochem. 478:981–989. 2023. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
54
|
Chang WT, Shih JY, Lin YW, Chen ZC, Kan
WC, Lin TH and Hong CS: Dapagliflozin protects against
doxorubicin-induced cardiotoxicity by restoring STAT3. Arch
Toxicol. 96:2021–2032. 2022. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
55
|
Dufey E, Sepúlveda D, Rojas-Rivera D and
Hetz C: Cellular mechanisms of endoplasmic reticulum stress
signaling in health and disease. 1. An overview. Am J Physiol Cell
Physiol. 307:C582–C594. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
56
|
Gaut JR and Hendershot LM: The
modification and assembly of proteins in the endoplasmic reticulum.
Curr Opin Cell Biol. 5:589–595. 1993. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|