|
1
|
Duan K, Gao X and Zhu D: The clinical
relevance and mechanism of skeletal muscle wasting. Clin Nutr.
40:27–37. 2021. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
Larsson L, Degens H, Li M, Salviati L, Lee
YI, Thompson W, Kirkland JL and Sandri M: Sarcopenia: Aging-Related
loss of muscle mass and function. Physiol Rev. 99:427–511. 2019.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
Damluji AA, Alfaraidhy M, AlHajri N,
Rohant NN, Kumar M, Al Malouf C, Bahrainy S, Ji Kwak M, Batchelor
WB, Forman DE, et al: Sarcopenia and cardiovascular diseases.
Circulation. 147:1534–1553. 2023. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
Nishio H, Niba ETE, Saito T, Okamoto K,
Takeshima Y and Awano H: Spinal muscular atrophy: The past,
present, and future of diagnosis and treatment. Int J Mol Sci.
24:119392023. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
O'Brien J, Hayder H, Zayed Y and Peng C:
Overview of MicroRNA biogenesis, mechanisms of actions, and
circulation. Front Endocrinol (Lausanne). 9:4022018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Gebert LFR and MacRae IJ: Regulation of
microRNA function in animals. Nat Rev Mol Cell Biol. 20:21–37.
2019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Brzeszczynska J, Brzeszczynski F, Hamilton
DF, McGregor R and Simpson AHRW: Role of microRNA in muscle
regeneration and diseases related to muscle dysfunction in atrophy,
cachexia, osteoporosis, and osteoarthritis. Bone Joint Res.
9:798–807. 2020. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
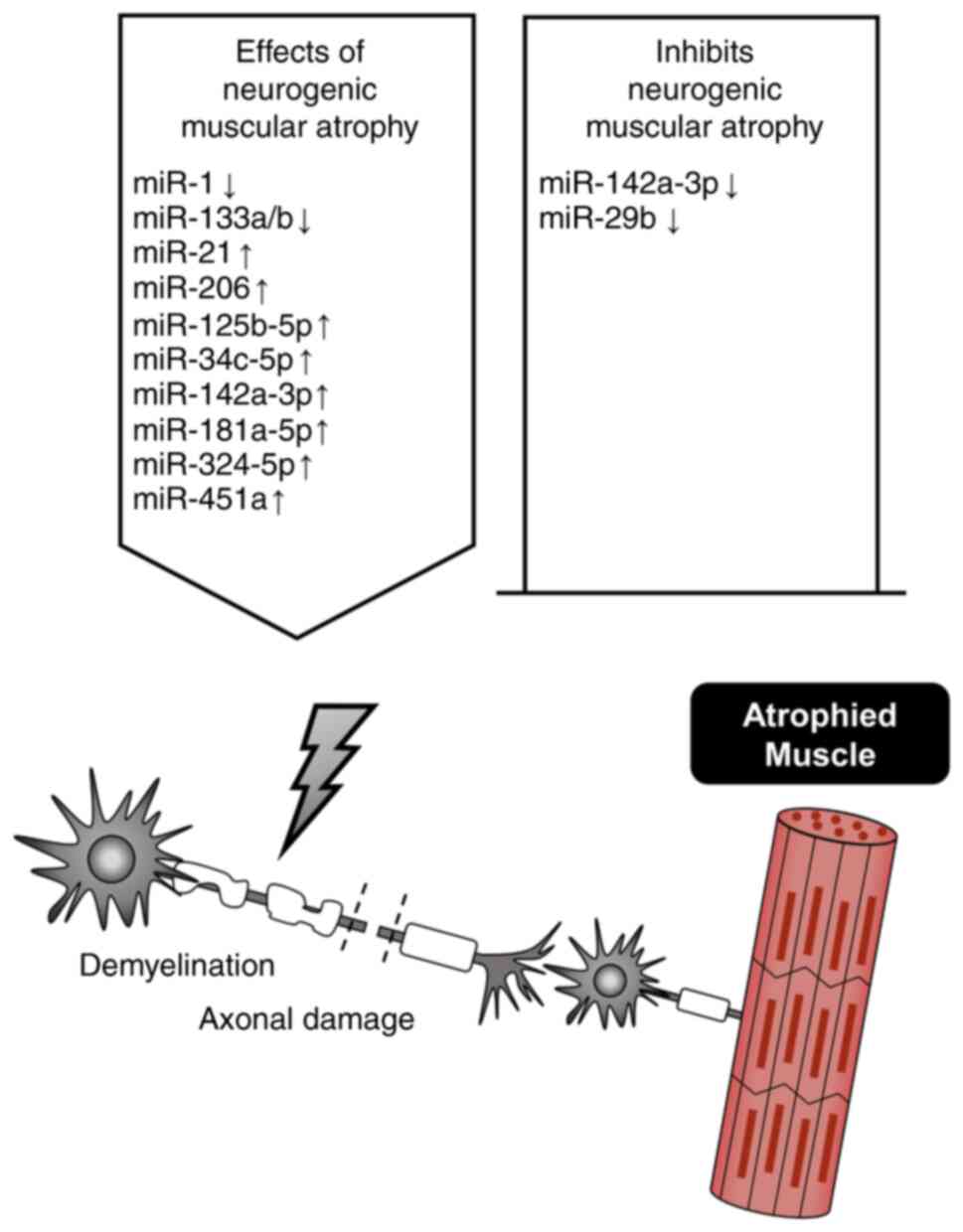
|
|
8
|
De Paepe B: Progressive skeletal muscle
atrophy in muscular dystrophies: A role for toll-like
receptor-signaling in disease pathogenesis. Int J Mol Sci.
21:44402020. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
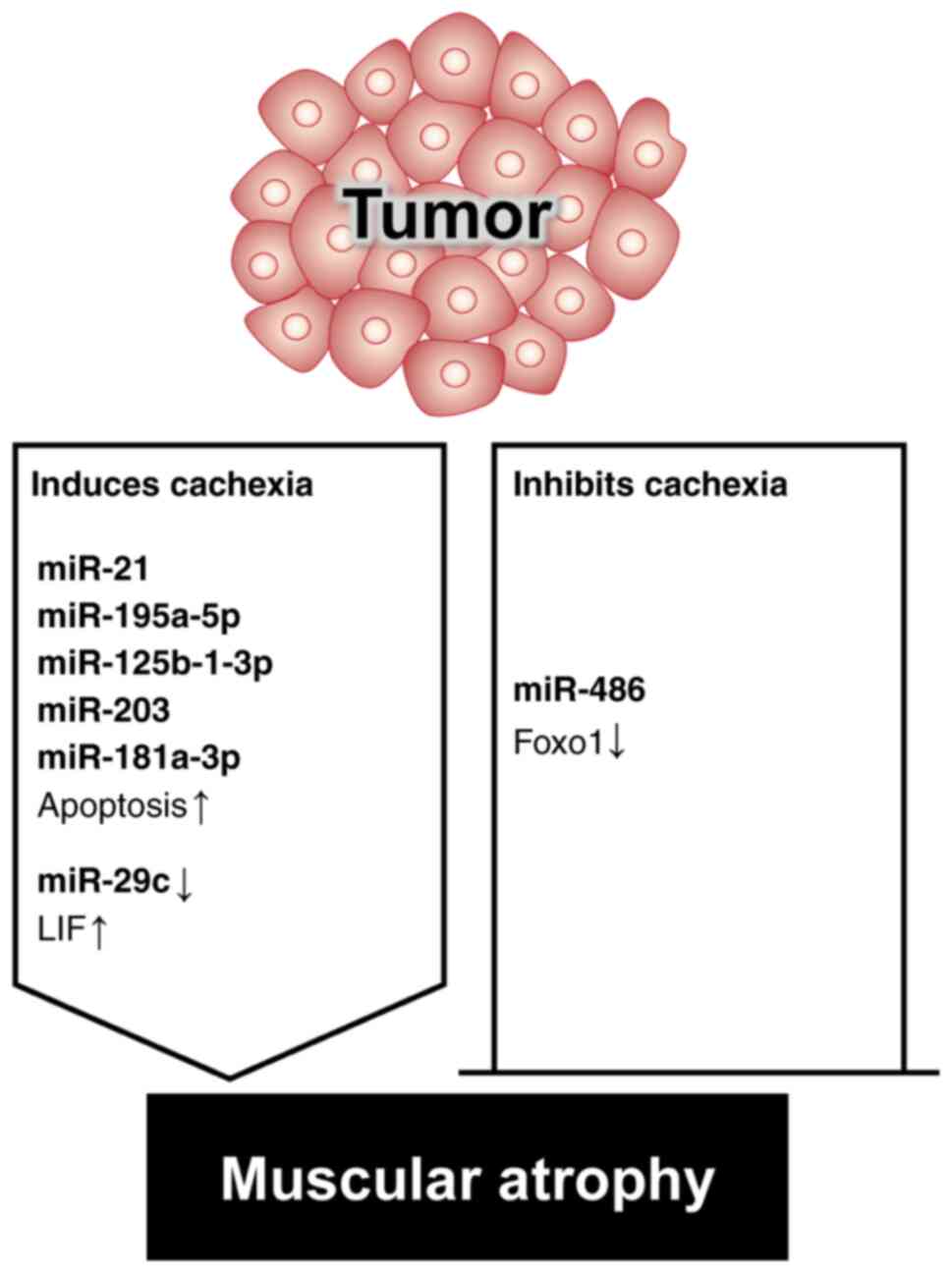
9
|
Vo TT, Kong G, Kim C, Juang U, Gwon S,
Jung W, Nguyen H, Kim SH and Park J: Exploring scavenger receptor
class F member 2 and the importance of scavenger receptor family in
prediagnostic diseases. Toxicol Res. 39:341–353. 2023. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Jun L, Robinson M, Geetha T, Broderick TL
and Babu JR: Prevalence and mechanisms of skeletal muscle atrophy
in metabolic conditions. Int J Mol Sci. 24:29732023. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Cruz-Jentoft AJ, Baeyens JP, Bauer JM,
Boirie Y, Cederholm T, Landi F, Martin FC, Michel JP, Rolland Y,
Schneider SM, et al: Sarcopenia: European consensus on definition
and diagnosis: Report of the European working group on sarcopenia
in older people. Age Ageing. 39:412–423. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Cho MR, Lee S and Song SK: A review of
sarcopenia pathophysiology, diagnosis, treatment and future
direction. J Korean Med Sci. 37:e1462022. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Jang JY, Kim D and Kim ND: Pathogenesis,
intervention, and current status of drug development for
sarcopenia: A review. Biomedicines. 11:16352023. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Cruz-Jentoft AJ, Bahat G, Bauer J, Boirie
Y, Bruyere O, Cederholm T, Cooper C, Landi F, Rolland Y, Sayer AA,
et al: Sarcopenia: Revised European consensus on definition and
diagnosis. Age Ageing. 48:16–31. 2019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Guttikonda D and Smith AL: Sarcopenia
assessment techniques. Clin Liver Dis (Hoboken). 18:189–192. 2021.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Koo BK: Assessment of muscle quantity,
quality and function. J Obes Metab Syndr. 31:9–16. 2022. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Cheng KY, Chow SK, Hung VW, Wong CH, Wong
RM, Tsang CS, Kwok T and Cheung WH: Diagnosis of sarcopenia by
evaluating skeletal muscle mass by adjusted bioimpedance analysis
validated with dual-energy X-ray absorptiometry. J Cachexia
Sarcopenia Muscle. 12:2163–2173. 2021. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
Faron A, Sprinkart AM, Kuetting DLR,
Feisst A, Isaak A, Endler C, Chang J, Nowak S, Block W, Thomas D,
et al: Body composition analysis using CT and MRI: intra-individual
intermodal comparison of muscle mass and myosteatosis. Sci Rep.
10:117652020. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
Dufour AB, Hannan MT, Murabito JM, Kiel DP
and McLean RR: Sarcopenia definitions considering body size and fat
mass are associated with mobility limitations: The Framingham
Study. J Gerontol A Biol Sci Med Sci. 68:168–174. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
Singh H, Kim D, Kim E, Bemben MG, Anderson
M, Seo DI and Bemben DA: Jump test performance and sarcopenia
status in men and women, 55 to 75 years of age. J Geriatr Phys
Ther. 37:76–82. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
Lee J, Hong YP, Shin HJ and Lee W:
Associations of sarcopenia and sarcopenic obesity with metabolic
syndrome considering both muscle mass and muscle strength. J Prev
Med Public Health. 49:35–44. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22
|
Hunter GR, McCarthy JP and Bamman MM:
Effects of resistance training on older adults. Sports Med.
34:329–348. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23
|
Hepple RT: Sarcopenia-a critical
perspective. Sci Aging Knowledge Environ. 2003:pe312003. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24
|
Hunter GR, Singh H, Carter SJ, Bryan DR
and Fisher G: Sarcopenia and its implications for metabolic health.
J Obes. 2019:80317052019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
25
|
Zhang A, Li M, Wang B, Klein JD, Price SR
and Wang XH: miRNA-23a/27a attenuates muscle atrophy and renal
fibrosis through muscle-kidney crosstalk. J Cachexia Sarcopenia
Muscle. 9:755–770. 2018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
26
|
Xu R, Cui S, Chen L, Chen XC, Ma LL, Yang
HN and Wen FM: Circulating miRNA-1-3p as biomarker of accelerated
sarcopenia in patients diagnosed with chronic heart failure. Rev
Invest Clin. 74:276–268. 2022.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
27
|
Yang X, Xue P, Chen H, Yuan M, Kang Y,
Duscher D, Machens HG and Chen Z: Denervation drives skeletal
muscle atrophy and induces mitochondrial dysfunction, mitophagy and
apoptosis via miR-142a-5p/MFN1 axis. Theranostics. 10:1415–1432.
2020. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
28
|
Wang B, Zhang A, Wang H, Klein JD, Tan L,
Wang ZM, Du J, Naqvi N, Liu BC and Wang XH: miR-26a limits muscle
wasting and cardiac fibrosis through exosome-mediated microRNA
transfer in chronic kidney disease. Theranostics. 9:1864–1877.
2019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
29
|
Oikawa S, Yuan S, Kato Y and Akimoto T:
Skeletal muscle-enriched miRNAs are highly unstable in vivo and may
be regulated in a Dicer-independent manner. FEBS J. 290:5692–5703.
2023. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
30
|
Meng Q, Zhang J, Zhong J, Zeng D and Lan
D: Novel miRNA biomarkers for patients with duchenne muscular
dystrophy. Front Neurol. 13:9217852022. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
31
|
Saad NY, Al-Kharsan M, Garwick-Coppens SE,
Chermahini GA, Harper MA, Palo A, Boudreau RL and Harper SQ: Human
miRNA miR-675 inhibits DUX4 expression and may be exploited as a
potential treatment for Facioscapulohumeral muscular dystrophy. Nat
Commun. 12:71282021. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
32
|
De Felice B, Annunziata A, Fiorentino G,
Borra M, Biffali E, Coppola C, Cotrufo R, Brettschneider J,
Giordana ML, Dalmay T, et al: miR-338-3p is over-expressed in
blood, CFS, serum and spinal cord from sporadic amyotrophic lateral
sclerosis patients. Neurogenetics. 15:243–253. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
33
|
Dumont NA, Wang YX and Rudnicki MA:
Intrinsic and extrinsic mechanisms regulating satellite cell
function. Development. 142:1572–1581. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
34
|
Feige P, Brun CE, Ritso M and Rudnicki MA:
Orienting muscle stem cells for regeneration in homeostasis, aging,
and disease. Cell Stem Cell. 23:653–664. 2018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
35
|
Yafe A, Shklover J, Weisman-Shomer P,
Bengal E and Fry M: Differential binding of quadruplex structures
of muscle-specific genes regulatory sequences by MyoD, MRF4 and
myogenin. Nucleic Acids Res. 36:3916–3925. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
36
|
Gunther S, Kim J, Kostin S, Lepper C, Fan
CM and Braun T: Myf5-positive satellite cells contribute to
Pax7-dependent long-term maintenance of adult muscle stem cells.
Cell Stem Cell. 13:590–601. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
37
|
Chen JF, Mandel EM, Thomson JM, Wu Q,
Callis TE, Hammond SM, Conlon FL and Wang DZ: The role of
microRNA-1 and microRNA-133 in skeletal muscle proliferation and
differentiation. Nat Genet. 38:228–233. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
38
|
Lee SW, Yang J, Kim SY, Jeong HK, Lee J,
Kim WJ, Lee EJ and Kim HS: MicroRNA-26a induced by hypoxia targets
HDAC6 in myogenic differentiation of embryonic stem cells. Nucleic
Acids Res. 43:2057–2073. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
39
|
Wu R, Li H, Zhai L, Zou X, Meng J, Zhong
R, Li C, Wang H, Zhang Y and Zhu D: MicroRNA-431 accelerates muscle
regeneration and ameliorates muscular dystrophy by targeting Pax7
in mice. Nat Commun. 6:77132015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
40
|
Ma G, Wang Y, Li Y, Cui L, Zhao Y, Zhao B
and Li K: MiR-206, a key modulator of skeletal muscle development
and disease. Int J Biol Sci. 11:345–352. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
41
|
Dey P, Soyer MA and Dey BK: MicroRNA-24-3p
promotes skeletal muscle differentiation and regeneration by
regulating HMGA1. Cell Mol Life Sci. 79:1702022. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
42
|
Lee B, Shin YJ, Lee SM, Son YH, Yang YR
and Lee KP: miR-3074-3p promotes myoblast differentiation by
targeting Cav1. BMB Rep. 53:278–283. 2020. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
43
|
Zhang Y, Yao Y, Wang Z, Lu D, Zhang Y,
Adetula AA, Liu S, Zhu M, Yang Y, Fan X, et al: MiR-743a-5p
regulates differentiation of myoblast by targeting Mob1b in
skeletal muscle development and regeneration. Genes Dis.
9:1038–1048. 2022. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
44
|
Holstein I, Singh AK, Pohl F, Misiak D,
Braun J, Leitner L, Huttelmaier S and Posern G:
Post-transcriptional regulation of MRTF-A by miRNAs during myogenic
differentiation of myoblasts. Nucleic Acids Res. 48:8927–8942.
2020. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
45
|
Zhao X, Gu H, Wang L, Zhang P, Du J, Shen
L, Jiang D, Wang J, Li X, Zhang S, et al: MicroRNA-23a-5p mediates
the proliferation and differentiation of C2C12 myoblasts. Mol Med
Rep. 22:3705–3714. 2020.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
46
|
Crist CG, Montarras D, Pallafacchina G,
Rocancourt D, Cumano A, Conway SJ and Buckingham M: Muscle stem
cell behavior is modified by microRNA-27 regulation of Pax3
expression. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA. 106:13383–13387. 2009.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
47
|
Kong D, He M, Yang L, Zhou R, Yan YQ,
Liang Y and Teng CB: MiR-17 and miR-19 cooperatively promote
skeletal muscle cell differentiation. Cell Mol Life Sci.
76:5041–5054. 2019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
48
|
Attaix D, Combaret L, Bechet D and
Taillandier D: Role of the ubiquitin-proteasome pathway in muscle
atrophy in cachexia. Curr Opin Support Palliat Care. 2:262–266.
2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
49
|
Hartmann-Petersen R and Gordon C: Proteins
interacting with the 26S proteasome. Cell Mol Life Sci.
61:1589–1595. 2004.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
50
|
Bodine SC, Latres E, Baumhueter S, Lai VK,
Nunez L, Clarke BA, Poueymirou WT, Panaro FJ, Na E, Dharmarajan K,
et al: Identification of ubiquitin ligases required for skeletal
muscle atrophy. Science. 294:1704–1708. 2001. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
51
|
Eddins MJ, Marblestone JG, Suresh Kumar
KG, Leach CA, Sterner DE, Mattern MR and Nicholson B: Targeting the
ubiquitin E3 ligase MuRF1 to inhibit muscle atrophy. Cell Biochem
Biophys. 60:113–118. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
52
|
Clavel S, Coldefy AS, Kurkdjian E, Salles
J, Margaritis I and Derijard B: Atrophy-related ubiquitin ligases,
atrogin-1 and MuRF1 are up-regulated in aged rat Tibialis Anterior
muscle. Mech Ageing Dev. 127:794–801. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
53
|
Gu X, Wang S, Li D, Jin B, Qi Z, Deng J,
Huang C and Yin X: MicroRNA-142a-3p regulates neurogenic skeletal
muscle atrophy by targeting Mef2a. Mol Ther Nucleic Acids.
33:191–204. 2023. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
54
|
Xhuti D, Nilsson MI, Manta K, Tarnopolsky
MA and Nederveen JP: Circulating exosome-like vesicle and skeletal
muscle microRNAs are altered with age and resistance training. J
Physiol. 601:5051–5073. 2023. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
55
|
Ahmad N, Kushwaha P, Karvande A, Tripathi
AK, Kothari P, Adhikary S, Khedgikar V, Mishra VK and Trivedi R:
MicroRNA-672-5p identified during weaning reverses osteopenia and
sarcopenia in ovariectomized mice. Mol Ther Nucleic Acids.
14:536–549. 2019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
56
|
Webster JM, Kempen LJAP, Hardy RS and
Langen RCJ: Inflammation and skeletal muscle wasting during
cachexia. Front Physiol. 11:5976752020. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
57
|
Emery PW, Edwards RH, Rennie MJ, Souhami
RL and Halliday D: Protein synthesis in muscle measured in vivo in
cachectic patients with cancer. Br Med J (Clin Res Ed).
289:584–586. 1984. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
58
|
Warnold I, Lundholm K and Schersten T:
Energy balance and body composition in cancer patients. Cancer Res.
38:1801–1807. 1978.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
59
|
Chang VT, Xia Q and Kasimis B: The
functional assessment of anorexia/cachexia therapy (FAACT) Appetite
Scale in veteran cancer patients. J Support Oncol. 3:377–382.
2005.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
60
|
Martin L, Birdsell L, Macdonald N, Reiman
T, Clandinin MT, McCargar LJ, Murphy R, Ghosh S, Sawyer MB and
Baracos VE: Cancer cachexia in the age of obesity: Skeletal muscle
depletion is a powerful prognostic factor, independent of body mass
index. J Clin Oncol. 31:1539–1547. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
61
|
Yang W, Huang J, Wu H, Wang Y, Du Z, Ling
Y, Wang W, Wu Q and Gao W: Molecular mechanisms of cancer
cachexia-induced muscle atrophy (Review). Mol Med Rep.
22:4967–4980. 2020. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
62
|
Bilodeau PA, Coyne ES and Wing SS: The
ubiquitin proteasome system in atrophying skeletal muscle: Roles
and regulation. Am J Physiol Cell Physiol. 311:C392–C403. 2016.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
63
|
Reed SA, Sandesara PB, Senf SM and Judge
AR: Inhibition of FoxO transcriptional activity prevents muscle
fiber atrophy during cachexia and induces hypertrophy. FASEB J.
26:987–1000. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
64
|
Xu J, Li R, Workeneh B, Dong Y, Wang X and
Hu Z: Transcription factor FoxO1, the dominant mediator of muscle
wasting in chronic kidney disease, is inhibited by microRNA-486.
Kidney Int. 82:401–411. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
65
|
He WA, Calore F, Londhe P, Canella A,
Guttridge DC and Croce CM: Microvesicles containing miRNAs promote
muscle cell death in cancer cachexia via TLR7. Proc Natl Acad Sci
USA. 111:4525–4529. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
66
|
Xie K, Xiong H, Xiao W, Xiong Z, Hu W, Ye
J, Xu N, Shi J, Yuan C, Chen Z, et al: Downregulation of miR-29c
promotes muscle wasting by modulating the activity of leukemia
inhibitory factor in lung cancer cachexia. Cancer Cell Int.
21:6272021. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
67
|
Miao C, Zhang W, Feng F, Gu X, Shen Q, Lu
S, Fan M, Li Y, Guo X, Ma Y, et al: Cancer-derived exosome miRNAs
induce skeletal muscle wasting by Bcl-2-mediated apoptosis in colon
cancer cachexia. Mol Ther Nucleic Acids. 24:923–938. 2021.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
68
|
Okugawa Y, Toiyama Y, Hur K, Yamamoto A,
Yin C, Ide S, Kitajima T, Fujikawa H, Yasuda H, Koike Y, et al:
Circulating miR-203 derived from metastatic tissues promotes
myopenia in colorectal cancer patients. J Cachexia Sarcopenia
Muscle. 10:536–548. 2019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
69
|
Qiu L, Chen W, Wu C, Yuan Y and Li Y:
Exosomes of oral squamous cell carcinoma cells containing
miR-181a-3p induce muscle cell atrophy and apoptosis by
transmissible endoplasmic reticulum stress signaling. Biochem
Biophys Res Commun. 533:831–837. 2020. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
70
|
Su SF, Chang YW, Andreu-Vieyra C, Fang JY,
Yang Y, Han B, Lee AS and Liang G: miR-30d, miR-181a and
miR-199a-5p cooperatively suppress the endoplasmic reticulum
chaperone and signaling regulator GRP78 in cancer. Oncogene.
32:4694–4701. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
71
|
Liu J, Huang Y, Cai F, Dang Y, Liu C and
Wang J: MicroRNA-181a regulates endoplasmic reticulum stress in
offspring of mice following prenatal microcystin-LR exposure.
Chemosphere. 240:1249052020. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
72
|
Wei Y, Tao X, Xu H, Chen Y, Zhu L, Tang G,
Li M, Jiang A, Shuai S, Ma J, et al: Role of miR-181a-5p and
endoplasmic reticulum stress in the regulation of myogenic
differentiation. Gene. 592:60–70. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
73
|
Zhang M, Zhang Q, Hu Y, Xu L, Jiang Y,
Zhang C, Ding L, Jiang R, Sun J, Sun H and Yan G: miR-181a
increases FoxO1 acetylation and promotes granulosa cell apoptosis
via SIRT1 downregulation. Cell Death Dis. 8:e30882017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
74
|
Cisterna BA, Vargas AA, Puebla C,
Fernandez P, Escamilla R, Lagos CF, Matus MF, Vilos C, Cea LA,
Barnafi E, et al: Active acetylcholine receptors prevent the
atrophy of skeletal muscles and favor reinnervation. Nat Commun.
11:10732020. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
75
|
Burke RE: Sir Charles Sherrington's the
integrative action of the nervous system: A centenary appreciation.
Brain. 130:887–894. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
76
|
Dulhunty AF: Excitation-contraction
coupling from the 1950s into the new millennium. Clin Exp Pharmacol
Physiol. 33:763–772. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
77
|
Canfora I, Tarantino N and Pierno S:
Metabolic pathways and ion channels involved in skeletal muscle
atrophy: A starting point for potential therapeutic strategies.
Cells. 11:25662022. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
78
|
Bruusgaard JC and Gundersen K: In vivo
time-lapse microscopy reveals no loss of murine myonuclei during
weeks of muscle atrophy. J Clin Invest. 118:1450–1457. 2008.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
79
|
De Gasperi R, Hamidi S, Harlow LM,
Ksiezak-Reding H, Bauman WA and Cardozo CP: Denervation-related
alterations and biological activity of miRNAs contained in exosomes
released by skeletal muscle fibers. Sci Rep. 7:128882017.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
80
|
Magnusson C, Svensson A, Christerson U and
Tagerud S: Denervation-induced alterations in gene expression in
mouse skeletal muscle. Eur J Neurosci. 21:577–580. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
81
|
Ehmsen JT and Hoke A: Cellular and
molecular features of neurogenic skeletal muscle atrophy. Exp
Neurol. 331:1133792020. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
82
|
Daeschler SC, Feinberg K, Harhaus L,
Kneser U, Gordon T and Borschel GH: Advancing nerve regeneration:
Translational perspectives of tacrolimus (FK506). Int J Mol Sci.
24:127712023. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
83
|
Zheng H, Liu X, Katsurada K and Patel KP:
Renal denervation improves sodium excretion in rats with chronic
heart failure: Effects on expression of renal ENaC and AQP2. Am J
Physiol Heart Circ Physiol. 317:H958–H968. 2019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
84
|
Tokinoya K, Shirai T, Ota Y, Takemasa T
and Takekoshi K: Denervation-induced muscle atrophy suppression in
renalase-deficient mice via increased protein synthesis. Physiol
Rep. 8:e144752020. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
85
|
Sandri M: Protein breakdown in muscle
wasting: Role of autophagy-lysosome and ubiquitin-proteasome. Int J
Biochem Cell Biol. 45:2121–2129. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
86
|
Bongers KS, Fox DK, Ebert SM, Kunkel SD,
Dyle MC, Bullard SA, Dierdorff JM and Adams CM: Skeletal muscle
denervation causes skeletal muscle atrophy through a pathway that
involves both Gadd45a and HDAC4. Am J Physiol Endocrinol Metab.
305:E907–E915. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
87
|
Weng J, Zhang P, Yin X and Jiang B: The
whole transcriptome involved in denervated muscle atrophy following
peripheral nerve injury. Front Mol Neurosci. 11:692018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
88
|
Nimmo R, Ciau-Uitz A, Ruiz-Herguido C,
Soneji S, Bigas A, Patient R and Enver T: MiR-142-3p controls the
specification of definitive hemangioblasts during ontogeny. Dev
Cell. 26:237–249. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
89
|
Huang QK, Qiao HY, Fu MH, Li G, Li WB,
Chen Z, Wei J and Liang BS: MiR-206 Attenuates Denervation-Induced
Skeletal Muscle Atrophy in Rats Through Regulation of Satellite
Cell Differentiation via TGF-beta1, Smad3, and HDAC4 Signaling. Med
Sci Monit. 22:1161–1170. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
90
|
Li J, Wang L, Hua X, Tang H, Chen R, Yang
T, Das S and Xiao J: CRISPR/Cas9-Mediated miR-29b editing as a
treatment of different types of muscle atrophy in mice. Mol Ther.
28:1359–1372. 2020. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
91
|
Srivastava S, Rathor R, Singh SN and
Suryakumar G: Emerging role of MyomiRs as biomarkers and
therapeutic targets in skeletal muscle diseases. Am J Physiol Cell
Physiol. 321:C859–C875. 2021. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
92
|
Gu XY, Jin B, Qi ZD and Yin XF: MicroRNA
is a potential target for therapies to improve the physiological
function of skeletal muscle after trauma. Neural Regen Res.
17:1617–1622. 2022. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
93
|
Abiusi E, Infante P, Cagnoli C, Lospinoso
Severini L, Pane M, Coratti G, Pera MC, D'Amico A, Diano F, Novelli
A, et al: SMA-miRs (miR-181a-5p, −324-5p, and −451a) are
overexpressed in spinal muscular atrophy skeletal muscle and serum
samples. Elife. 10:e680542021. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|