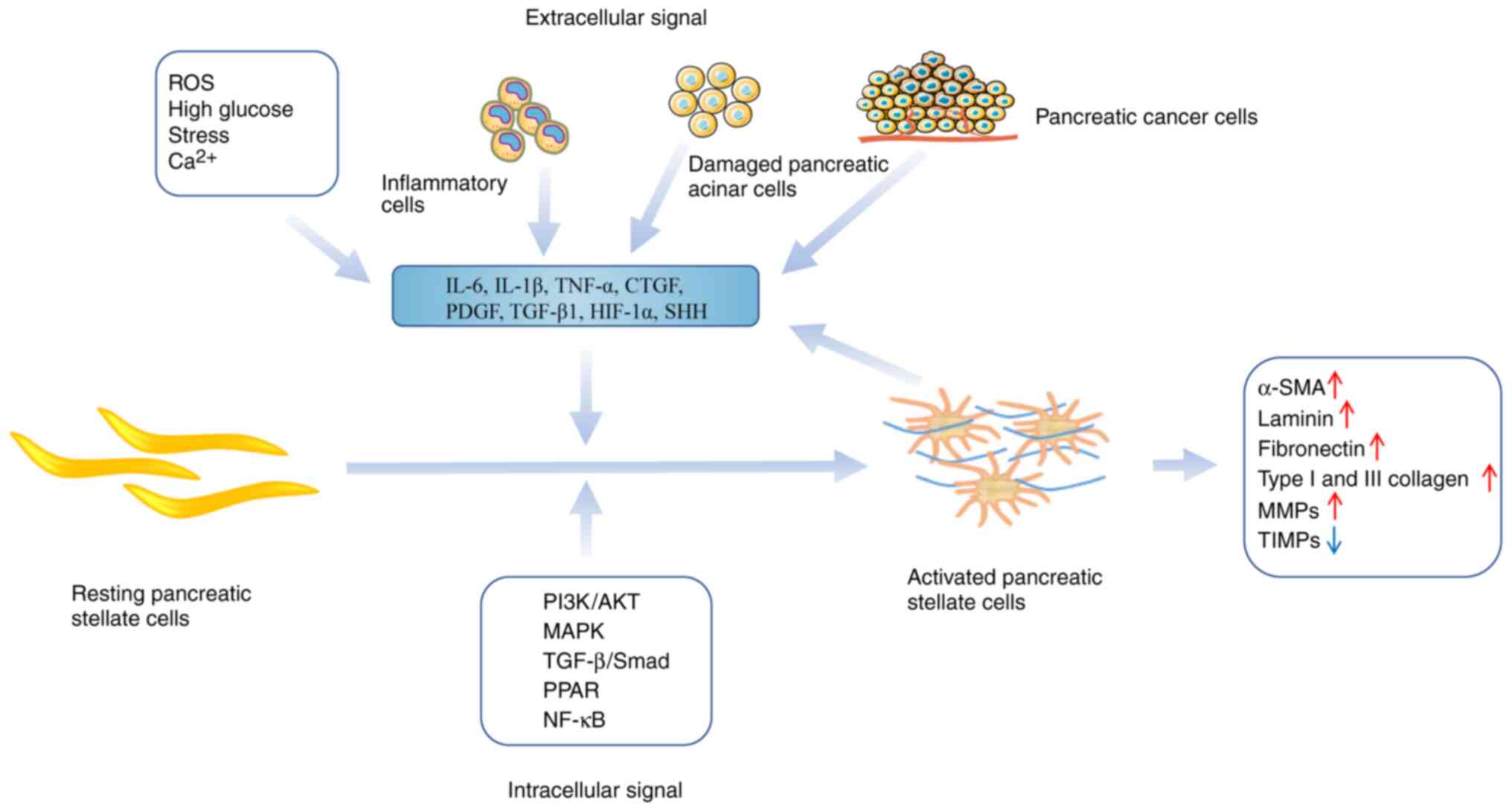
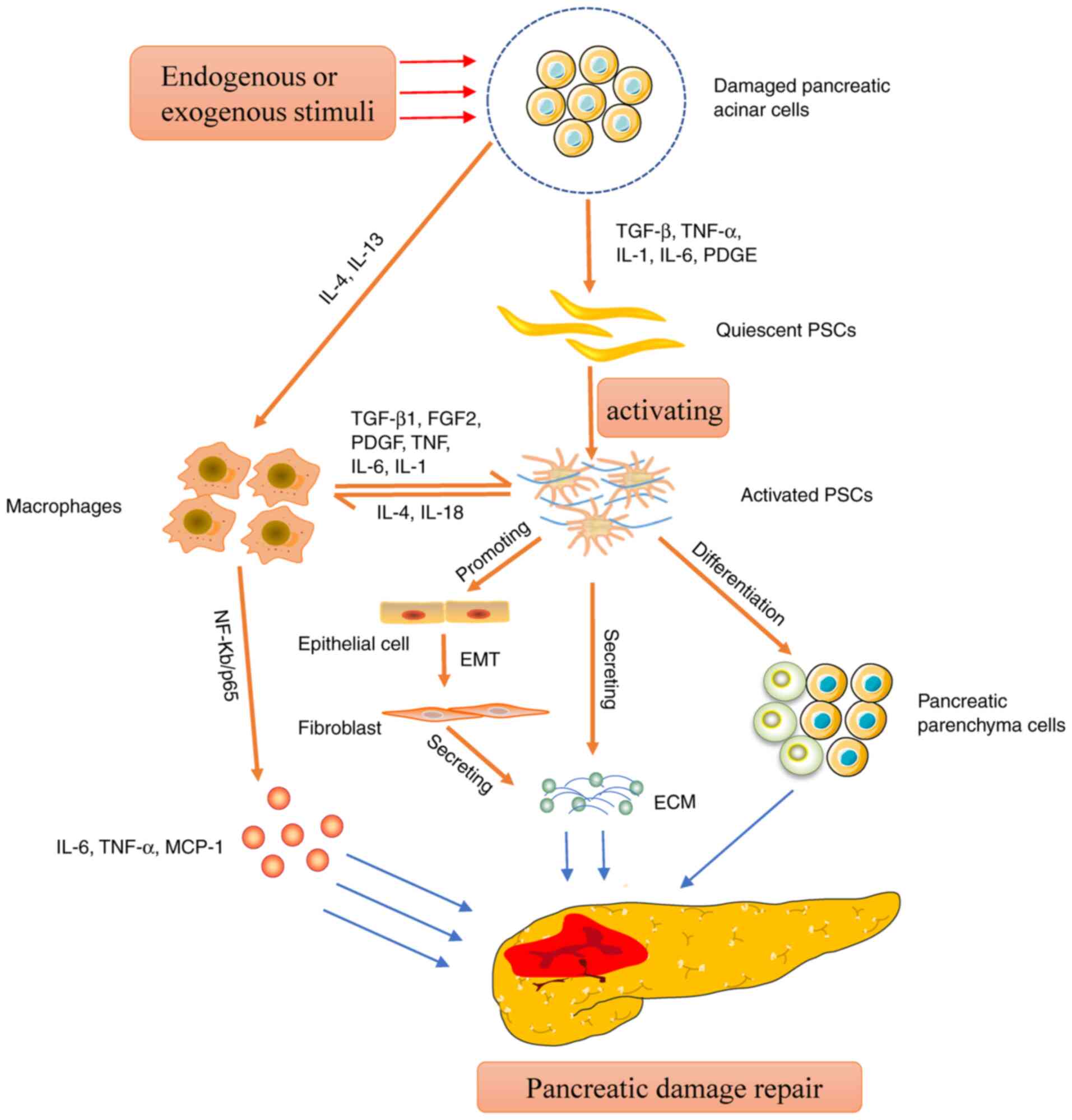
|
1
|
Wang Y, Li HT, Liu G, Jiang CS, Ni YH,
Zeng JH, Lin X, Wang QY, Li DZ, Wang W and Zeng XP: COMP promotes
pancreatic fibrosis by activating pancreatic stellate cells through
CD36-ERK/AKT signaling pathways. Cell Signal. 118:1111352024.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
Apte MV, Pirola RC and Wilson JS:
Pancreatic stellate cells: A starring role in normal and diseased
pancreas. Front Physiol. 3:3442012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
Omary MB, Lugea A, Lowe AW and Pandol SJ:
The pancreatic stellate cell: A star on the rise in pancreatic
diseases. J Clin Invest. 117:50–59. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
Apte M, Pirola R and Wilson J: The
fibrosis of chronic pancreatitis: New insights into the role of
pancreatic stellate cells. Antioxid Redox Signal. 15:2711–2722.
2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Erkan M, Adler G, Apte MV, Bachem MG,
Buchholz M, Detlefsen S, Esposito I, Friess H, Gress TM, Habisch
HJ, et al: StellaTUM: Current consensus and discussion on
pancreatic stellate cell research. Gut. 61:172–178. 2012.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Ulmasov B, Neuschwander-Tetri BA, Lai J,
Monastyrskiy V, Bhat T, Yates MP, Oliva J, Prinsen MJ, Ruminski PG
and Griggs DW: Inhibitors of Arg-Gly-Asp-Binding integrins reduce
development of pancreatic fibrosis in mice. Cell Mol Gastroenterol
Hepatol. 2:499–518. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Masamune A and Shimosegawa T: Pancreatic
stellate cells-multi-functional cells in the pancreas.
Pancreatology. 13:102–105. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Murray ER, Menezes S, Henry JC, Williams
JL, Alba-Castellón L, Baskaran P, Quétier I, Desai A, Marshall JJT,
Rosewell I, et al: Disruption of pancreatic stellate cell
myofibroblast phenotype promotes pancreatic tumor invasion. Cell
Rep. 38:1102272022. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Yu L, Li JJ, Liang XL, Wu H and Liang Z:
PSME3 Promotes TGFB1 secretion by PC cells to induce pancreatic
stellate cell proliferation. J Cancer. 10:2128–2138. 2019.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Derynck R and Budi EH: Specificity,
versatility, and control of TGF-β family signaling. Sci Signal.
12:eaav51832019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Gough NR, Xiang X and Mishra L: TGF-β
signaling in liver, pancreas, and gastrointestinal diseases and
cancer. Gastroenterology. 161:434–452.e15. 2021. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Wu B, Zhang S, Guo Z, Bi Y, Zhou M, Li P,
Seyedsadr M, Xu X, Li JL, Markovic-Plese S and Wan YY: The TGF-β
superfamily cytokine Activin-A is induced during autoimmune
neuroinflammation and drives pathogenic Th17 cell differentiation.
Immunity. 54:308–323.e6. 2021. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Apte MV, Haber PS, Darby SJ, Rodgers SC,
McCaughan GW, Korsten MA, Pirola RC and Wilson JS: Pancreatic
stellate cells are activated by proinflammatory cytokines:
Implications for pancreatic fibrogenesis. Gut. 44:534–541. 1999.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Lee H, Lim C, Lee J, Kim N, Bang S, Lee H,
Min B, Park G, Noda M, Stetler-Stevenson WG and Oh J: TGF-beta
signaling preserves RECK expression in activated pancreatic
stellate cells. J Cell Biochem. 104:1065–1074. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Shek FW, Benyon RC, Walker FM, McCrudden
PR, Pender SL, Williams EJ, Johnson PA, Johnson CD, Bateman AC,
Fine DR and Iredale JP: Expression of transforming growth
factor-beta 1 by pancreatic stellate cells and its implications for
matrix secretion and turnover in chronic pancreatitis. Am J Pathol.
160:1787–1798. 2002. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Apte MV and Wilson JS: Dangerous liaisons:
Pancreatic stellate cells and pancreatic cancer cells. J
Gastroenterol Hepatol. 27 (Suppl 2):S69–S74. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
17
|
Sarper M, Cortes E, Lieberthal TJ and Del
Río Hernández A: ATRA modulates mechanical activation of TGF-β by
pancreatic stellate cells. Sci Rep. 6:276392016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
Zheng M, Li H, Sun L, Brigstock DR and Gao
R: Interleukin-6 participates in human pancreatic stellate cell
activation and collagen I production via TGF-β1/Smad pathway.
Cytokine. 143:1555362021. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
Shen YW, Zhou YD, Chen HZ, Luan X and
Zhang WD: Targeting CTGF in cancer: An emerging therapeutic
opportunity. Trends Cancer. 7:511–524. 2021. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
Huang G and Brigstock DR: Regulation of
hepatic stellate cells by connective tissue growth factor. Front
Biosci (Landmark Ed). 17:2495–2507. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
di Mola FF, Friess H, Riesle E, Koliopanos
A, Büchler P, Zhu Z, Brigstock DR, Korc M and Büchler MW:
Connective tissue growth factor is involved in pancreatic repair
and tissue remodeling in human and rat acute necrotizing
pancreatitis. Ann Surg. 235:60–67. 2002. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22
|
di Mola FF, Friess H, Martignoni ME, Di
Sebastiano P, Zimmermann A, Innocenti P, Graber H, Gold LI, Korc M
and Büchler MW: Connective tissue growth factor is a regulator for
fibrosis in human chronic pancreatitis. Ann Surg. 230:63–71. 1999.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23
|
Wenger C, Ellenrieder V, Alber B, Lacher
U, Menke A, Hameister H, Wilda M, Iwamura T, Beger HG, Adler G and
Gress TM: Expression and differential regulation of connective
tissue growth factor in pancreatic cancer cells. Oncogene.
18:1073–1080. 1999. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24
|
Gao R and Brigstock DR: A novel integrin
alpha5beta1 binding domain in module 4 of connective tissue growth
factor (CCN2/CTGF) promotes adhesion and migration of activated
pancreatic stellate cells. Gut. 55:856–862. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
25
|
Charrier A, Chen R, Chen L, Kemper S,
Hattori T, Takigawa M and Brigstock DR: Connective tissue growth
factor (CCN2) and microRNA-21 are components of a positive feedback
loop in pancreatic stellate cells (PSCs) during chronic
pancreatitis and are exported in PSCs-derived exosomes. J Cell
Commun Signal. 8:147–156. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
26
|
Tamura T, Kodama T, Sato K, Murai K,
Yoshioka T, Shigekawa M, Yamada R, Hikita H, Sakamori R, Akita H,
et al: Dysregulation of PI3K and Hippo signaling pathways
synergistically induces chronic pancreatitis via CTGF upregulation.
J Clin Invest. 131:e1434142021. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
27
|
Chen X, Zhang Y, Qian W, Han L, Li W, Duan
W, Wu Z, Wang Z and Ma Q: Arl4c promotes the growth and drug
resistance of pancreatic cancer by regulating tumor-stromal
interactions. iScience. 24:1034002021. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
28
|
Qi X and Li X: Mechanistic insights into
the generation and transduction of hedgehog signaling. Trends
Biochem Sci. 45:397–410. 2020. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
29
|
Bausch D, Fritz S, Bolm L, Wellner UF,
Fernandez-Del-Castillo C, Warshaw AL, Thayer SP and Liss AS:
Hedgehog signaling promotes angiogenesis directly and indirectly in
pancreatic cancer. Angiogenesis. 23:479–492. 2020. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
30
|
Tang D, Wang D, Yuan Z, Xue X, Zhang Y, An
Y, Chen J, Tu M, Lu Z, Wei J, et al: Persistent activation of
pancreatic stellate cells creates a microenvironment favorable for
the malignant behavior of pancreatic ductal adenocarcinoma. Int J
Cancer. 132:993–1003. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
31
|
Olive KP, Jacobetz MA, Davidson CJ,
Gopinathan A, McIntyre D, Honess D, Madhu B, Goldgraben MA,
Caldwell ME, Allard D, et al: Inhibition of Hedgehog signaling
enhances delivery of chemotherapy in a mouse model of pancreatic
cancer. Science. 324:1457–1461. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
32
|
Li X, Wang Z, Ma Q, Xu Q, Liu H, Duan W,
Lei J, Ma J, Wang X, Lv S, et al: Sonic hedgehog paracrine
signaling activates stromal cells to promote perineural invasion in
pancreatic cancer. Clin Cancer Res. 20:4326–4338. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
33
|
Yu Y, Cheng L, Yan B, Zhou C, Qian W, Xiao
Y, Qin T, Cao J, Han L, Ma Q and Ma J: Overexpression of Gremlin 1
by sonic hedgehog signaling promotes pancreatic cancer progression.
Int J Oncol. 53:2445–2457. 2018.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
34
|
Hwang RF, Moore TT, Hattersley MM,
Scarpitti M, Yang B, Devereaux E, Ramachandran V, Arumugam T, Ji B,
Logsdon CD, et al: Inhibition of the hedgehog pathway targets the
tumor-associated stroma in pancreatic cancer. Mol Cancer Res.
10:1147–1157. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
35
|
Riera-Domingo C, Audigé A, Granja S, Cheng
WC, Ho PC, Baltazar F, Stockmann C and Mazzone M: Immunity,
Hypoxia, and Metabolism-the Ménage à trois of cancer: Implications
for immunotherapy. Physiol Rev. 100:1–102. 2020. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
36
|
Liu M, Zhong J, Zeng Z, Huang K, Ye Z,
Deng S, Chen H, Xu F, Li Q and Zhao G: Hypoxia-induced feedback of
HIF-1α and lncRNA-CF129 contributes to pancreatic cancer
progression through stabilization of p53 protein. Theranostics.
9:4795–4810. 2019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
37
|
Shi X, Wang M, Zhang Y, Guo X, Liu M, Zhou
Z, Zhao Y, He R, Gao Y, Liu Y, et al: Hypoxia activated HGF
expression in pancreatic stellate cells confers resistance of
pancreatic cancer cells to EGFR inhibition. EBioMedicine.
86:1043522022. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
38
|
Estaras M, Gonzalez-Portillo MR, Martinez
R, Garcia A, Estevez M, Fernandez-Bermejo M, Mateos JM, Vara D,
Blanco-Fernández G, Lopez-Guerra D, et al: Melatonin modulates the
antioxidant defenses and the expression of proinflammatory
mediators in pancreatic stellate cells subjected to hypoxia.
Antioxidants (Basel). 10:5772021. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
39
|
Masamune A, Kikuta K, Watanabe T, Satoh K,
Hirota M and Shimosegawa T: Hypoxia stimulates pancreatic stellate
cells to induce fibrosis and angiogenesis in pancreatic cancer. Am
J Physiol Gastrointest Liver Physiol. 295:G709–G717. 2008.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
40
|
Xiao Y, Qin T, Sun L, Qian W, Li J, Duan
W, Lei J, Wang Z, Ma J, Li X, et al: Resveratrol ameliorates the
malignant progression of pancreatic cancer by inhibiting
Hypoxia-induced pancreatic stellate cell activation. Cell
Transplant. 29:9636897209299872020. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
41
|
Zou X, Tang XY, Qu ZY, Sun ZW, Ji CF, Li
YJ and Guo SD: Targeting the PDGF/PDGFR signaling pathway for
cancer therapy: A review. Int J Biol Macromol. 202:539–557. 2022.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
42
|
Hu R, Wang YL, Edderkaoui M, Lugea A, Apte
MV and Pandol SJ: Ethanol augments PDGF-induced NADPH oxidase
activity and proliferation in rat pancreatic stellate cells.
Pancreatology. 7:332–340. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
43
|
Masamune A, Suzuki N, Kikuta K, Satoh M,
Satoh K and Shimosegawa T: Curcumin blocks activation of pancreatic
stellate cells. J Cell Biochem. 97:1080–1093. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
44
|
Zhao T, Xiao D, Jin F, Sun X, Yu J, Wang
H, Liu J, Cai W, Huang C, Wang X, et al: ESE3-positive PSCs drive
pancreatic cancer fibrosis, chemoresistance and poor prognosis via
tumour-stromal IL-1β/NF-κB/ESE3 signalling axis. Br J Cancer.
127:1461–1472. 2022. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
45
|
Guo HL, Liang XS, Zeng XP, Liu Y, Li ZS,
Wang LJ and Hu LH: Pirfenidone alleviates chronic pancreatitis via
suppressing the activation of pancreatic stellate cells and the M1
polarization of macrophages. Int Immunopharmacol. 130:1116912024.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
46
|
Masamune A, Kikuta K, Satoh M, Suzuki N
and Shimosegawa T: Green tea polyphenol epigallocatechin-3-gallate
blocks PDGF-induced proliferation and migration of rat pancreatic
stellate cells. World J Gastroenterol. 11:3368–3374. 2005.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
47
|
Ouyang W and O'Garra A: IL-10 family
cytokines IL-10 and IL-22: From basic science to clinical
translation. Immunity. 50:871–891. 2019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
48
|
Zhang LJ, Zheng WD, Shi MN and Wang XZ:
Effects of interleukin-10 on activation and apoptosis of hepatic
stellate cells in fibrotic rat liver. World J Gastroenterol.
12:1918–1923. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
49
|
Shi MN, Huang YH, Zheng WD, Zhang LJ, Chen
ZX and Wang XZ: Relationship between transforming growth factor
beta1 and anti-fibrotic effect of interleukin-10. World J
Gastroenterol. 12:2357–2362. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
50
|
Demols A, Van Laethem JL, Quertinmont E,
Degraef C, Delhaye M, Geerts A and Deviere J: Endogenous
interleukin-10 modulates fibrosis and regeneration in experimental
chronic pancreatitis. Am J Physiol Gastrointest Liver Physiol.
282:G1105–G1112. 2002. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
51
|
Mews P, Phillips P, Fahmy R, Korsten M,
Pirola R, Wilson J and Apte M: Pancreatic stellate cells respond to
inflammatory cytokines: Potential role in chronic pancreatitis.
Gut. 50:535–541. 2002. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
52
|
Talukdar R and Tandon RK: Pancreatic
stellate cells: New target in the treatment of chronic
pancreatitis. J Gastroenterol Hepatol. 23:34–41. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
53
|
Marzoq AJ, Mustafa SA, Heidrich L,
Hoheisel JD and Alhamdani MSS: Impact of the secretome of activated
pancreatic stellate cells on growth and differentiation of
pancreatic tumour cells. Sci Rep. 9:53032019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
54
|
Kandikattu HK, Venkateshaiah SU and Mishra
A: Chronic pancreatitis and the development of pancreatic cancer.
Endocr Metab Immune Disord Drug Targets. 20:1182–1210. 2020.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
55
|
Lugea A and Waldron RT: Exosome-mediated
intercellular communication between stellate cells and cancer cells
in pancreatic ductal adenocarcinoma. Pancreas. 46:1–4. 2017.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
56
|
Hu F, Lou N, Jiao J, Guo F, Xiang H and
Shang D: Macrophages in pancreatitis: Mechanisms and therapeutic
potential. Biomed Pharmacother. 131:1106932020. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
57
|
Ng B, Viswanathan S, Widjaja AA, Lim WW,
Shekeran SG, Goh JWT, Tan J, Kuthubudeen F, Lim SY, Xie C, et al:
IL11 Activates pancreatic stellate cells and causes pancreatic
inflammation, fibrosis and atrophy in a mouse model of
pancreatitis. Int J Mol Sci. 23:35492022. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
58
|
Filomeni G, De Zio D and Cecconi F:
Oxidative stress and autophagy: The clash between damage and
metabolic needs. Cell Death Differ. 22:377–388. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
59
|
Ryu GR, Lee E, Chun HJ, Yoon KH, Ko SH,
Ahn YB and Song KH: Oxidative stress plays a role in high
glucose-induced activation of pancreatic stellate cells. Biochem
Biophys Res Commun. 439:258–263. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
60
|
Zhang J, Bai J, Zhou Q, Hu Y, Wang Q, Yang
L, Chen H, An H, Zhou C, Wang Y, et al: Glutathione prevents high
glucose-induced pancreatic fibrosis by suppressing pancreatic
stellate cell activation via the ROS/TGFβ/SMAD pathway. Cell Death
Dis. 13:4402022. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
61
|
An W, Zhu JW, Jiang F, Jiang H, Zhao JL,
Liu MY, Li GX, Shi XG, Sun C and Li ZS: Fibromodulin is upregulated
by oxidative stress through the MAPK/AP-1 pathway to promote
pancreatic stellate cell activation. Pancreatology. 20:278–287.
2020. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
62
|
Xia B, Gao J, Li S, Huang L, Zhu L, Ma T,
Zhao L, Yang Y, Luo K, Shi X, et al: Mechanical stimulation of
Schwann cells promote peripheral nerve regeneration via
extracellular vesicle-mediated transfer of microRNA 23b-3p.
Theranostics. 10:8974–8995. 2020. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
63
|
Asaumi H, Watanabe S, Taguchi M, Tashiro M
and Otsuki M: Externally applied pressure activates pancreatic
stellate cells through the generation of intracellular reactive
oxygen species. Am J Physiol Gastrointest Liver Physiol.
293:G972–G978. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
64
|
Radoslavova S, Fels B, Pethö Z, Gruner M,
Ruck T, Meuth SG, Folcher A, Prevarskaya N, Schwab A and
Ouadid-Ahidouch H: TRPC1 channels regulate the activation of
pancreatic stellate cells through ERK1/2 and SMAD2 pathways and
perpetuate their pressure-mediated activation. Cell Calcium.
106:1026212022. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
65
|
Kalli M, Papageorgis P, Gkretsi V and
Stylianopoulos T: Solid stress facilitates fibroblasts activation
to promote pancreatic cancer cell migration. Ann Biomed Eng.
46:657–669. 2018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
66
|
Pethő Z, Najder K, Bulk E and Schwab A:
Mechanosensitive ion channels push cancer progression. Cell
Calcium. 80:79–90. 2019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
67
|
Martinac B: Mechanosensitive ion channels:
Molecules of mechanotransduction. J Cell Sci. 117:2449–2460. 2004.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
68
|
Nielsen N, Kondratska K, Ruck T, Hild B,
Kovalenko I, Schimmelpfennig S, Welzig J, Sargin S, Lindemann O,
Christian S, et al: TRPC6 channels modulate the response of
pancreatic stellate cells to hypoxia. Pflugers Arch. 469:1567–1577.
2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
69
|
Jakubowska MA, Ferdek PE, Gerasimenko OV,
Gerasimenko JV and Petersen OH: Nitric oxide signals are
interlinked with calcium signals in normal pancreatic stellate
cells upon oxidative stress and inflammation. Open Biol.
6:1601492016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
70
|
Hennigs JK, Seiz O, Spiro J, Berna MJ,
Baumann HJ, Klose H and Pace A: Molecular basis of
P2-receptor-mediated calcium signaling in activated pancreatic
stellate cells. Pancreas. 40:740–746. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
71
|
Jiang T, Wang H, Liu L, Song H, Zhang Y,
Wang J, Liu L, Xu T, Fan R, Xu Y, et al: CircIL4R activates the
PI3K/AKT signaling pathway via the miR-761/TRIM29/PHLPP1 axis and
promotes proliferation and metastasis in colorectal cancer. Mol
Cancer. 20:1672021. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
72
|
Liu B, Deng X, Jiang Q, Li G, Zhang J,
Zhang N, Xin S and Xu K: Scoparone improves hepatic inflammation
and autophagy in mice with nonalcoholic steatohepatitis by
regulating the ROS/P38/Nrf2 axis and PI3K/AKT/mTOR pathway in
macrophages. Biomed Pharmacother. 125:1098952020. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
73
|
Xue R, Wang J, Yang L, Liu X, Gao Y, Pang
Y, Wang Y and Hao J: Coenzyme Q10 ameliorates pancreatic fibrosis
via the ROS-Triggered mTOR signaling pathway. Oxid Med Cell Longev.
2019:80396942019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
74
|
Cui LH, Li CX, Zhuo YZ, Yang L, Cui NQ and
Zhang SK: Saikosaponin d ameliorates pancreatic fibrosis by
inhibiting autophagy of pancreatic stellate cells via PI3K/Akt/mTOR
pathway. Chem Biol Interact. 300:18–26. 2019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
75
|
Schwer CI, Stoll P, Rospert S, Fitzke E,
Schallner N, Bürkle H, Schmidt R and Humar M: Carbon monoxide
releasing molecule-2 CORM-2 represses global protein synthesis by
inhibition of eukaryotic elongation factor eEF2. Int J Biochem Cell
Biol. 45:201–212. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
76
|
Zhang P, Guan H, Yuan S, Cheng H, Zheng J,
Zhang Z, Liu Y, Yu Y, Meng Z, Zheng X and Zhao L: Targeting myeloid
derived suppressor cells reverts immune suppression and sensitizes
BRAF-mutant papillary thyroid cancer to MAPK inhibitors. Nat
Commun. 13:15882022. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
77
|
Zou ZL, Sun MH, Yin WF, Yang L and Kong
LY: Avicularin suppresses cartilage extracellular matrix
degradation and inflammation via TRAF6/MAPK activation.
Phytomedicine. 91:1536572021. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
78
|
Zhang Y, Ware MB, Zaidi MY, Ruggieri AN,
Olson BM, Komar H, Farren MR, Nagaraju GP, Zhang C, Chen Z, et al:
Heat shock Protein-90 inhibition alters activation of pancreatic
stellate cells and enhances the efficacy of PD-1 blockade in
pancreatic cancer. Mol Cancer Ther. 20:150–160. 2021. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
79
|
McCarroll JA, Phillips PA, Santucci N,
Pirola RC, Wilson JS and Apte MV: Vitamin A inhibits pancreatic
stellate cell activation: Implications for treatment of pancreatic
fibrosis. Gut. 55:79–89. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
80
|
Roach KM and Bradding P: Ca2+ signalling
in fibroblasts and the therapeutic potential of KCa3.1 channel
blockers in fibrotic diseases. Br J Pharmacol. 177:1003–1024. 2020.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
81
|
Murphy-Ullrich JE and Suto MJ:
Thrombospondin-1 regulation of latent TGF-β activation: A
therapeutic target for fibrotic disease. Matrix Biol. 68–69. 28–43.
2018.
|
|
82
|
Itatani Y, Kawada K and Sakai Y:
Transforming Growth Factor-β signaling pathway in colorectal cancer
and its tumor microenvironment. Int J Mol Sci. 20:58222019.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
83
|
Kanda T, Jiang X and Yokosuka O: Androgen
receptor signaling in hepatocellular carcinoma and pancreatic
cancers. World J Gastroenterol. 20:9229–9236. 2014.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
84
|
Zhang X, Yun JS, Han D, Yook JI, Kim HS
and Cho ES: TGF-β pathway in salivary gland fibrosis. Int J Mol
Sci. 21:91382020. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
85
|
Ren Y, Zhang J, Wang M, Bi J, Wang T, Qiu
M, Lv Y, Wu Z and Wu R: Identification of irisin as a therapeutic
agent that inhibits oxidative stress and fibrosis in a murine model
of chronic pancreatitis. Biomed Pharmacother. 126:1101012020.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
86
|
Colaianni G, Cinti S, Colucci S and Grano
M: Irisin and musculoskeletal health. Ann N Y Acad Sci. 1402:5–9.
2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
87
|
Petta S, Valenti L, Svegliati-Baroni G,
Ruscica M, Pipitone RM, Dongiovanni P, Rychlicki C, Ferri N, Cammà
C, Fracanzani AL, et al: Fibronectin Type III Domain-containing
protein 5 rs3480 A>G polymorphism, irisin, and liver fibrosis in
patients with nonalcoholic fatty liver disease. J Clin Endocrinol
Metab. 102:2660–2669. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
88
|
Peng H, Wang Q, Lou T, Qin J, Jung S,
Shetty V, Li F, Wang Y, Feng XH, Mitch WE, et al: Myokine mediated
muscle-kidney crosstalk suppresses metabolic reprogramming and
fibrosis in damaged kidneys. Nat Commun. 8:14932017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
89
|
Chen RR, Fan XH, Chen G, Zeng GW, Xue YG,
Liu XT and Wang CY: Irisin attenuates angiotensin II-induced
cardiac fibrosis via Nrf2 mediated inhibition of ROS/TGFβ1/Smad2/3
signaling axis. Chem Biol Interact. 302:11–21. 2019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
90
|
Ren Y, Zhang J, Wang M, Bi J, Wang T, Qiu
M, Lv Y, Wu Z and Wu R: Identification of irisin as a therapeutic
agent that inhibits oxidative stress and fibrosis in a murine model
of chronic pancreatitis. Biomed Pharmacother. 126:1101012020.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
91
|
Bansod S, Doijad N and Godugu C: Berberine
attenuates severity of chronic pancreatitis and fibrosis via
AMPK-mediated inhibition of TGF-β1/Smad signaling and M2
polarization. Toxicol Appl Pharmacol. 403:1151622020. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
92
|
Choi JW, Lee SK, Kim MJ, Kim DG, Shin JY,
Zhou Z, Jo IJ, Song HJ, Bae GS and Park SJ: Piperine ameliorates
the severity of fibrosis via inhibition of TGF-β/SMAD signaling in
a mouse model of chronic pancreatitis. Mol Med Rep. 20:3709–3718.
2019.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
93
|
Mirza AZ, Althagafi II and Shamshad H:
Role of PPAR receptor in different diseases and their ligands:
Physiological importance and clinical implications. Eur J Med Chem.
166:502–513. 2019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
94
|
Christofides A, Konstantinidou E, Jani C
and Boussiotis VA: The role of peroxisome proliferator-activated
receptors (PPAR) in immune responses. Metabolism. 114:1543382021.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
95
|
Wang Q, Wang H, Jing Q, Yang Y, Xue D, Hao
C and Zhang W: Regulation of pancreatic fibrosis by acinar
cell-Derived exosomal miR-130a-3p via targeting of stellate cell
PPAR-γ. J Inflamm Res. 14:461–477. 2021. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
96
|
Kim N, Choi S, Lim C, Lee H and Oh J:
Albumin mediates PPAR-gamma or C/EBP-alpha-induced phenotypic
changes in pancreatic stellate cells. Biochem Biophys Res Commun.
391:640–644. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
97
|
Che M, Kweon SM, Teo JL, Yuan YC, Melstrom
LG, Waldron RT, Lugea A, Urrutia RA, Pandol SJ and Lai KKY:
Targeting the CBP/β-Catenin interaction to suppress activation of
Cancer-Promoting pancreatic stellate cells. Cancers (Basel).
12:14762020. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
98
|
Yu H, Lin L, Zhang Z, Zhang H and Hu H:
Targeting NF-κB pathway for the therapy of diseases: Mechanism and
clinical study. Signal Transduct Target Ther. 5:2092020. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
99
|
Treiber M, Neuhöfer P, Anetsberger E,
Einwächter H, Lesina M, Rickmann M, Liang S, Kehl T, Nakhai H,
Schmid RM and Algül H: Myeloid, but not pancreatic, RelA/p65 is
required for fibrosis in a mouse model of chronic pancreatitis.
Gastroenterology. 141:1473–1485.e14857. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
100
|
Wu N, Xu XF, Xin JQ, Fan JW, Wei YY, Peng
QX, Duan LF, Wang W and Zhang H: The effects of nuclear
factor-kappa B in pancreatic stellate cells on inflammation and
fibrosis of chronic pancreatitis. J Cell Mol Med. 25:2213–2227.
2021. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
101
|
Chen H, Tan P, Qian B, Du Y, Wang A, Shi
H, Huang Z, Huang S, Liang T and Fu W: Hic-5 deficiency protects
cerulein-induced chronic pancreatitis via down-regulation of the
NF-κB (p65)/IL-6 signalling pathway. J Cell Mol Med. 24:1488–1503.
2020. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
102
|
Carrière C, Gore AJ, Norris AM, Gunn JR,
Young AL, Longnecker DS and Korc M: Deletion of Rb accelerates
pancreatic carcinogenesis by oncogenic Kras and impairs senescence
in premalignant lesions. Gastroenterology. 141:1091–1101. 2011.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
103
|
Sun HZ, Gong XY, Wu L, Wang XX, Nie YN,
Shang R, Wang H, Li YC, Sun QF, Gao PF and Bi JX: Hydrogen sulfide
modulates gastric acid secretion in rats via involvement of
substance P and nuclear factor-κB signaling. J Physiol Pharmacol.
692018.doi: 10.26402/jpp.2018.3.08.
|
|
104
|
Sundar V and Tamizhselvi R: Inhibition of
Rb phosphorylation leads to H2S-mediated inhibition of NF-kB in
acute pancreatitis and associated lung injury in mice.
Pancreatology. 20:647–658. 2020. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
105
|
Nulali J, Zhan M, Zhang K, Tu P, Liu Y and
Song H: Osteoglycin: An ECM factor regulating fibrosis and
tumorigenesis. Biomolecules. 12:16742022. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
106
|
Guan P, Liu C, Xie D, Mao S, Ji Y, Lin Y,
Chen Z, Wang Q, Fan L and Sun Y: Exosome-loaded extracellular
matrix-mimic hydrogel with anti-inflammatory property
Facilitates/promotes growth plate injury repair. Bioact Mater.
10:145–158. 2021.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
107
|
Pietilä EA, Gonzalez-Molina J,
Moyano-Galceran L, Jamalzadeh S, Zhang K, Lehtinen L, Turunen SP,
Martins TA, Gultekin O, Lamminen T, et al: Co-evolution of
matrisome and adaptive adhesion dynamics drives ovarian cancer
chemoresistance. Nat Commun. 12:39042021. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
108
|
Mosquera MJ, Kim S, Bareja R, Fang Z, Cai
S, Pan H, Asad M, Martin ML, Sigouros M, Rowdo FM, et al:
Extracellular matrix in synthetic Hydrogel-based prostate cancer
organoids regulate therapeutic response to EZH2 and DRD2
inhibitors. Adv Mater. 34:e21000962022. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
109
|
Hwang HJ, Oh MS, Lee DW and Kuh HJ:
Multiplex quantitative analysis of stroma-mediated cancer cell
invasion, matrix remodeling, and drug response in a 3D co-culture
model of pancreatic tumor spheroids and stellate cells. J Exp Clin
Cancer Res. 38:2582019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
110
|
Sun L, Qu L, Brigstock DR, Li H, Li Y and
Gao R: Biological and proteomic characteristics of an immortalized
human pancreatic stellate cell line. Int J Med Sci. 17:137–144.
2020. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
111
|
Tanaka S, Hosokawa M, Yonezawa T, Hayashi
W, Ueda K and Iwakawa S: Induction of epithelial-mesenchymal
transition and down-regulation of miR-200c and miR-141 in
oxaliplatin-resistant colorectal cancer cells. Biol Pharm Bull.
38:435–440. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
112
|
Xu W, Liu H, Liu ZG, Wang HS, Zhang F,
Wang H, Zhang J, Chen JJ, Huang HJ, Tan Y, et al: Histone
deacetylase inhibitors upregulate Snail via Smad2/3 phosphorylation
and stabilization of Snail to promote metastasis of hepatoma cells.
Cancer Lett. 420:1–13. 2018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
113
|
Zou XZ, Liu T, Gong ZC, Hu CP and Zhang Z:
MicroRNAs-mediated epithelial-mesenchymal transition in fibrotic
diseases. Eur J Pharmacol. 796:190–206. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
114
|
Tian L, Lu ZP, Cai BB, Zhao LT, Qian D, Xu
QC, Wu PF, Zhu Y, Zhang JJ, Du Q, et al: Activation of pancreatic
stellate cells involves an EMT-like process. Int J Oncol.
48:783–792. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
115
|
Ling J, Kang Y, Zhao R, Xia Q, Lee DF,
Chang Z, Li J, Peng B, Fleming JB, Wang H, et al: KrasG12D-induced
IKK2/β/NF-κB activation by IL-1α and p62 feedforward loops is
required for development of pancreatic ductal adenocarcinoma.
Cancer Cell. 21:105–120. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
116
|
Masamune A, Yoshida N, Hamada S, Takikawa
T, Nabeshima T and Shimosegawa T: Exosomes derived from pancreatic
cancer cells induce activation and profibrogenic activities in
pancreatic stellate cells. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 495:71–77.
2018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
117
|
Zhang YF, Zhou YZ, Zhang B, Huang SF, Li
PP, He XM, Cao GD, Kang MX, Dong X and Wu YL: Pancreatic
cancer-derived exosomes promoted pancreatic stellate cells
recruitment by pancreatic cancer. J Cancer. 10:4397–4407. 2019.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
118
|
Xu M, Wang G, Zhou H, Cai J, Li P, Zhou M,
Lu Y, Jiang X, Huang H, Zhang Y and Gong A: TGF-β1-miR-200a-PTEN
induces epithelial-mesenchymal transition and fibrosis of
pancreatic stellate cells. Mol Cell Biochem. 431:161–168. 2017.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
119
|
Xue J, Sharma V, Hsieh MH, Chawla A,
Murali R, Pandol SJ and Habtezion A: Alternatively activated
macrophages promote pancreatic fibrosis in chronic pancreatitis.
Nat Commun. 6:71582015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
120
|
Charrier A, Chen R, Kemper S and Brigstock
DR: Regulation of pancreatic inflammation by connective tissue
growth factor (CTGF/CCN2). Immunology. 141:564–576. 2014.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
121
|
Neuzillet C, Tijeras-Raballand A, Ragulan
C, Cros J, Patil Y, Martinet M, Erkan M, Kleeff J, Wilson J, Apte
M, et al: Inter- and intra-tumoural heterogeneity in
cancer-associated fibroblasts of human pancreatic ductal
adenocarcinoma. J Pathol. 248:51–65. 2019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
122
|
Orecchioni M, Ghosheh Y, Pramod AB and Ley
K: Macrophage polarization: Different gene signatures in M1(LPS+)
vs. Classically and M2(LPS-) vs. Alternatively activated
macrophages. Front Immunol. 10:10842019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
123
|
Dey S, Udari LM, RiveraHernandez P, Kwon
JJ, Willis B, Easler JJ, Fogel EL, Pandol S and Kota J: Loss of
miR-29a/b1 promotes inflammation and fibrosis in acute
pancreatitis. JCI Insight. 6:e1495392021. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
124
|
Michalski CW, Gorbachevski A, Erkan M,
Reiser C, Deucker S, Bergmann F, Giese T, Weigand M, Giese NA,
Friess H and Kleeff J: Mononuclear cells modulate the activity of
pancreatic stellate cells which in turn promote fibrosis and
inflammation in chronic pancreatitis. J Transl Med. 5:632007.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
125
|
Schmid-Kotsas A, Gross HJ, Menke A,
Weidenbach H, Adler G, Siech M, Beger H, Grünert AC and Bachem MG:
Lipopolysaccharide-activated macrophages stimulate the synthesis of
collagen type I and C-fibronectin in cultured pancreatic stellate
cells. Am J Pathol. 155:1749–1758. 1999. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
126
|
Li N, Li Y, Li Z, Huang C, Yang Y, Lang M,
Cao J, Jiang W, Xu Y, Dong J and Ren H: Hypoxia inducible factor 1
(HIF-1) recruits macrophage to activate pancreatic stellate cells
in pancreatic ductal adenocarcinoma. Int J Mol Sci. 17:7992016.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
127
|
Gerasimenko JV, Petersen OH and
Gerasimenko OV: SARS-CoV-2 S protein subunit 1 elicits Ca2+
Influx-Dependent Ca2+ signals in pancreatic stellate cells and
macrophages in situ. Function (Oxf). 3:zqac0022022. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
128
|
Eberhardt M, Salmon P, von Mach MA,
Hengstler JG, Brulport M, Linscheid P, Seboek D, Oberholzer J,
Barbero A, Martin I, et al: Multipotential nestin and Isl-1
positive mesenchymal stem cells isolated from human pancreatic
islets. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 345:1167–1176. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
129
|
Ku HT, Zhang N, Kubo A, O'Connor R, Mao M,
Keller G and Bromberg JS: Committing embryonic stem cells to early
endocrine pancreas in vitro. Stem Cells. 22:1205–1217. 2004.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
130
|
Bai C, Gao Y, Zhang X, Yang W and Guan W:
Melatonin promotes self-renewal of nestin-positive pancreatic stem
cells through activation of the MT2/ERK/SMAD/nestin axis. Artif
Cells Nanomed Biotechnol. 46:62–74. 2018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
131
|
Augstein P, Loudovaris T, Bandala-Sanchez
E, Heinke P, Naselli G, Lee L, Hawthorne WJ, Góñez LJ, Neale AM,
Vaillant F, et al: Characterization of the human pancreas side
population as a potential reservoir of adult stem cells. Pancreas.
47:25–34. 2018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
132
|
Zhou Y, Sun B, Li W, Zhou J, Gao F, Wang
X, Cai M and Sun Z: Pancreatic stellate cells: A rising
translational physiology star as a potential stem cell type for
beta cell neogenesis. Front Physiol. 10:2182019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
133
|
Kordes C, Sawitza I, Götze S and
Häussinger D: Stellate cells from rat pancreas are stem cells and
can contribute to liver regeneration. PLoS One. 7:e518782012.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
134
|
Karanu FN, Yuefei L, Gallacher L, Sakano S
and Bhatia M: Differential response of primitive human CD34- and
CD34+ hematopoietic cells to the Notch ligand Jagged-1. Leukemia.
17:1366–1374. 2003. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
135
|
Izquierdo AG and Crujeiras AB: Role of
epigenomic mechanisms in the onset and management of insulin
resistance. Rev Endocr Metab Disord. 20:89–102. 2019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
136
|
Yoon KH, Ko SH, Cho JH, Lee JM, Ahn YB,
Song KH, Yoo SJ, Kang MI, Cha BY, Lee KW, et al: Selective
beta-cell loss and alpha-cell expansion in patients with type 2
diabetes mellitus in Korea. J Clin Endocrinol Metab. 88:2300–2308.
2003. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
137
|
Ogihara T and Mirmira RG: An islet in
distress: β cell failure in type 2 diabetes. J Diabetes Investig.
1:123–133. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
138
|
Kim JW, Ko SH, Cho JH, Sun C, Hong OK, Lee
SH, Kim JH, Lee KW, Kwon HS, Lee JM, et al: Loss of beta-cells with
fibrotic islet destruction in type 2 diabetes mellitus. Front
Biosci. 13:6022–6033. 2008. View
Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
139
|
Yang Y, Kim JW, Park HS, Lee EY and Yoon
KH: Pancreatic stellate cells in the islets as a novel target to
preserve the pancreatic β-cell mass and function. J Diabetes
Investig. 11:268–280. 2020. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
140
|
Yoshikawa H, Kihara Y, Taguchi M,
Yamaguchi T, Nakamura H and Otsuki M: Role of TGF-beta1 in the
development of pancreatic fibrosis in Otsuka Long-Evans Tokushima
Fatty rats. Am J Physiol Gastrointest Liver Physiol. 282:G549–G558.
2002. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
141
|
Saito R, Yamada S, Yamamoto Y, Kodera T,
Hara A, Tanaka Y, Kimura F, Takei I, Umezawa K and Kojima I:
Conophylline suppresses pancreatic stellate cells and improves
islet fibrosis in Goto-Kakizaki rats. Endocrinology. 153:621–630.
2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
142
|
Zhou W, Dong S, Chen Z, Li X and Jiang W:
New challenges for microRNAs in acute pancreatitis: Progress and
treatment. J Transl Med. 20:1922022. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
143
|
Won JH, Zhang Y, Ji B, Logsdon CD and Yule
DI: Phenotypic changes in mouse pancreatic stellate cell Ca2+
signaling events following activation in culture and in a disease
model of pancreatitis. Mol Biol Cell. 22:421–436. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
144
|
Gryshchenko O, Gerasimenko JV, Gerasimenko
OV and Petersen OH: Ca(2+) signals mediated by bradykinin type 2
receptors in normal pancreatic stellate cells can be inhibited by
specific Ca(2+) channel blockade. J Physiol. 594:281–293. 2016.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
145
|
Gryshchenko O, Gerasimenko JV, Peng S,
Gerasimenko OV and Petersen OH: Calcium signalling in the acinar
environment of the exocrine pancreas: Physiology and
pathophysiology. J Physiol. 596:2663–2678. 2018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
146
|
Ferdek PE, Jakubowska MA, Gerasimenko JV,
Gerasimenko OV and Petersen OH: Bile acids induce necrosis in
pancreatic stellate cells dependent on calcium entry and
sodium-driven bile uptake. J Physiol. 594:6147–6164. 2016.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
147
|
Dixit A, Cheema H, George J, Iyer S,
Dudeja V, Dawra R and Saluja AK: Extracellular release of ATP
promotes systemic inflammation during acute pancreatitis. Am J
Physiol Gastrointest Liver Physiol. 317:G463–G475. 2019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
148
|
Hart PA and Conwell DL: Chronic
pancreatitis: Managing a difficult disease. Am J Gastroenterol.
115:49–55. 2020. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
149
|
Yao S, Tu Z, Yang X, Zhang L, Zhong Y,
Zheng L, Wang H, Yi Z, An J, Jin H, et al: Physiological and
pathological roles of Hic-5 in several organs (Review). Int J Mol
Med. 50:1382022. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
150
|
Gao L, Lei XF, Miyauchi A, Noguchi M,
Omoto T, Haraguchi S, Miyazaki T, Miyazaki A and Kim-Kaneyama JR:
Hic-5 is required for activation of pancreatic stellate cells and
development of pancreatic fibrosis in chronic pancreatitis. Sci
Rep. 10:191052020. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
151
|
Qiang L, Yang S, Cui YH and He YY:
Keratinocyte autophagy enables the activation of keratinocytes and
fibroblastsand facilitates wound healing. Autophagy. 17:2128–2143.
2021. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
152
|
Zhang T, Zhang G, Yang W, Chen H, Hu J,
Zhao Z, Cheng C, Li G, Xie Y, Li Y, et al: Lnc-PFAR facilitates
autophagy and exacerbates pancreatic fibrosis by reducing
pre-miR-141 maturation in chronic pancreatitis. Cell Death Dis.
12:9962021. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
153
|
Yang X, Chen J, Wang J, Ma S, Feng W, Wu
Z, Guo Y, Zhou H, Mi W, Chen W, et al: Very-low-density lipoprotein
receptor-enhanced lipid metabolism in pancreatic stellate cells
promotes pancreatic fibrosis. Immunity. 55:1185–1199.e8. 2022.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
154
|
Siegel RL, Miller KD, Fuchs HE and Jemal
A: Cancer statistics, 2021. CA Cancer J Clin. 71:7–33. 2021.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
155
|
Sun W, Ren Y, Lu Z and Zhao X: The
potential roles of exosomes in pancreatic cancer initiation and
metastasis. Mol Cancer. 19:1352020. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
156
|
Pothula SP, Pirola RC, Wilson JS and Apte
MV: Pancreatic stellate cells: Aiding and abetting pancreatic
cancer progression. Pancreatology. 20:409–418. 2020. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
157
|
Li M, Guo H, Wang Q, Chen K, Marko K, Tian
X and Yang Y: Pancreatic stellate cells derived exosomal miR-5703
promotes pancreatic cancer by downregulating CMTM4 and activating
PI3K/Akt pathway. Cancer Lett. 490:20–30. 2020. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
158
|
Jiang J, Bai J, Qin T, Wang Z and Han L:
NGF from pancreatic stellate cells induces pancreatic cancer
proliferation and invasion by PI3K/AKT/GSK signal pathway. J Cell
Mol Med. 24:5901–5910. 2020. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
159
|
Geleta B, Tout FS, Lim SC, Sahni S,
Jansson PJ, Apte MV, Richardson DR and Kovačević Ž: Targeting
Wnt/tenascin C-mediated cross talk between pancreatic cancer cells
and stellate cells via activation of the metastasis suppressor
NDRG1. J Biol Chem. 298:1016082022. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
160
|
Kikuta K, Masamune A, Watanabe T, Ariga H,
Itoh H, Hamada S, Satoh K, Egawa S, Unno M and Shimosegawa T:
Pancreatic stellate cells promote epithelial-mesenchymal transition
in pancreatic cancer cells. Biochem Biophys Res Commun.
403:380–384. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
161
|
Hamada S, Masamune A, Takikawa T, Suzuki
N, Kikuta K, Hirota M, Hamada H, Kobune M, Satoh K and Shimosegawa
T: Pancreatic stellate cells enhance stem cell-like phenotypes in
pancreatic cancer cells. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 421:349–354.
2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
162
|
Chen S, Chen JZ, Zhang JQ, Chen HX, Yan
ML, Huang L, Tian YF, Chen YL and Wang YD: Hypoxia induces
TWIST-activated epithelial-mesenchymal transition and proliferation
of pancreatic cancer cells in vitro and in nude mice. Cancer Lett.
383:73–84. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
163
|
Bennewith KL, Huang X, Ham CM, Graves EE,
Erler JT, Kambham N, Feazell J, Yang GP, Koong A and Giaccia AJ:
The role of tumor cell-derived connective tissue growth factor
(CTGF/CCN2) in pancreatic tumor growth. Cancer Res. 69:775–784.
2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
164
|
Maity G, Ghosh A, Gupta V, Haque I, Sarkar
S, Das A, Dhar K, Bhavanasi S, Gunewardena SS, Von Hoff DD, et al:
CYR61/CCN1 Regulates dCK and CTGF and Causes Gemcitabine-resistant
phenotype in pancreatic ductal adenocarcinoma. Mol Cancer Ther.
18:788–800. 2019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
165
|
Cao W, Zeng Z, He Z and Lei S: Hypoxic
pancreatic stellate cell-derived exosomal mirnas promote
proliferation and invasion of pancreatic cancer through the
PTEN/AKT pathway. Aging (Albany NY). 13:7120–7132. 2021. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
166
|
Yamamoto M, Kensler TW and Motohashi H:
The KEAP1-NRF2 System: A Thiol-based Sensor-effector apparatus for
maintaining redox homeostasis. Physiol Rev. 98:1169–1203. 2018.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
167
|
Ju HQ, Gocho T, Aguilar M, Wu M, Zhuang
ZN, Fu J, Yanaga K, Huang P and Chiao PJ: Mechanisms of overcoming
intrinsic resistance to gemcitabine in pancreatic ductal
adenocarcinoma through the redox modulation. Mol Cancer Ther.
14:788–798. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
168
|
Arfmann-Knübel S, Struck B, Genrich G,
Helm O, Sipos B, Sebens S and Schäfer H: The Crosstalk between Nrf2
and TGF-β1 in the Epithelial-mesenchymal transition of pancreatic
duct epithelial cells. PLoS One. 10:e01329782015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
169
|
Wu YS, Looi CY, Subramaniam KS, Masamune A
and Chung I: Soluble factors from stellate cells induce pancreatic
cancer cell proliferation via Nrf2-activated metabolic
reprogramming and ROS detoxification. Oncotarget. 7:36719–36732.
2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
170
|
Hamada S, Taguchi K, Masamune A, Yamamoto
M and Shimosegawa T: Nrf2 promotes mutant K-ras/p53-driven
pancreatic carcinogenesis. Carcinogenesis. 38:661–670. 2017.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
171
|
Dai B, Augustine JJ, Kang Y, Roife D, Li
X, Deng J, Tan L, Rusling LA, Weinstein JN, Lorenzi PL, et al:
Compound NSC84167 selectively targets NRF2-activated pancreatic
cancer by inhibiting asparagine synthesis pathway. Cell Death Dis.
12:6932021. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
172
|
Husain A, Khan SA, Iram F, Iqbal MA and
Asif M: Insights into the chemistry and therapeutic potential of
furanones: A versatile pharmacophore. Eur J Med Chem. 171:66–92.
2019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
173
|
Sousa CM, Biancur DE, Wang X, Halbrook CJ,
Sherman MH, Zhang L, Kremer D, Hwang RF, Witkiewicz AK, Ying H, et
al: Pancreatic stellate cells support tumour metabolism through
autophagic alanine secretion. Nature. 536:479–483. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
174
|
Rauf A, Imran M, Butt MS, Nadeem M, Peters
DG and Mubarak MS: Resveratrol as an anti-cancer agent: A review.
Crit Rev Food Sci Nutr. 58:1428–1447. 2018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
175
|
Lin Z, Zheng LC, Zhang HJ, Tsang SW and
Bian ZX: Anti-fibrotic effects of phenolic compounds on pancreatic
stellate cells. BMC Complement Altern Med. 15:2592015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
176
|
Mohapatra D, Das B, Suresh V, Parida D,
Minz AP, Nayak U, Mohapatra AP, Swain RK and Senapati S:
Fluvastatin sensitizes pancreatic cancer cells toward radiation
therapy and suppresses radiation- and/or TGF-β-induced
tumor-associated fibrosis. Lab Invest. 102:298–311. 2022.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
177
|
Estaras M, Ortiz-Placin C, Castillejo-Rufo
A, Fernandez-Bermejo M, Blanco G, Mateos JM, Vara D,
Gonzalez-Cordero PL, Chamizo S, Lopez D, et al: Melatonin controls
cell proliferation and modulates mitochondrial physiology in
pancreatic stellate cells. J Physiol Biochem. 79:235–249. 2022.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
178
|
Sada M, Ohuchida K, Horioka K, Okumura T,
Moriyama T, Miyasaka Y, Ohtsuka T, Mizumoto K, Oda Y and Nakamura
M: Hypoxic stellate cells of pancreatic cancer stroma regulate
extracellular matrix fiber organization and cancer cell motility.
Cancer Lett. 372:210–218. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
179
|
Amrutkar M, Aasrum M, Verbeke CS and
Gladhaug IP: Secretion of fibronectin by human pancreatic stellate
cells promotes chemoresistance to gemcitabine in pancreatic cancer
cells. BMC Cancer. 19:5962019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
180
|
Kim SW, Oh KT, Youn YS and Lee ES:
Hyaluronated nanoparticles with pH- and enzyme-responsive drug
release properties. Colloids Surf B Biointerfaces. 116:359–364.
2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|