Introduction
Osteoarthritis (OA) is the most common joint disease
in the world, with a prevalence of ~10% of the population (1). The characteristic structural changes
include synovial inflammation, a loss of articular cartilage,
subchondral bone changes, meniscal injuries, and tendon and
ligament degeneration (2). OA is
the leading cause of joint pain, loss of function and disability in
older adults, with the knee being the most commonly affected joint
(3). The pathogenesis of OA has
not yet been clarified, but previous studies have suggested that
inflammation, pyroptosis and apoptosis serve important roles in the
progression of OA (3,4).
The NLR family pyrin domain containing 3 (NLRP3)
inflammasome has become the most widely studied inflammasome in
recent years, and it can be activated by various pathogenic events,
such as reactive oxygen species generation, mitochondrial
dysfunction and numerous types of pathogens, such as bacteria and
viruses (5). The NLRP3
inflammasome has an important role in inflammatory bowel disease,
cardiovascular disease, diabetes mellitus, autoimmune disease and
lung disease (5–7). Previous studies have shown that the
NLRP3 inflammasome is widely involved in the development of OA
(8,9). Therefore, targeting the NLRP3
inflammasome may be considered an important strategy for the
treatment of OA. For example, in chondrocytes, icariin antagonizes
NLRP3 inflammasome-mediated activation of caspase-1 signaling,
thereby attenuating inflammation during osteoporosis (10). In addition, the use of n-3
polyunsaturated fatty acid (PUFA)-enriched diets has been shown to
protect mice from obesity-associated post-traumatic OA, and an
in-depth study revealed that this phenomenon is related to the
inhibition of NLRP3/caspase-1 signaling by PUFAs (11).
Tributyltin (TBT) was once widely used as an
antifouling paint for ships; however, it was subsequently found to
cause serious harm to marine organisms, especially mollusks, and it
was thus banned globally in 2003 (12). Owing to its long-term residue, even
after a long period of time, TBT still exists in seawater and
sediments; it can therefore accumulate in marine organisms and is
still present after cooking, thus suggesting that the consumption
of seafood may be a potential TBT hazard (13,14).
TBT chloride (TBTC) is the main form of TBT present in water.
Studies have shown that TBTC is an endocrine disruptor in mammals
and can affect the reproductive function of animals (12,15).
However, the understanding of the effects of TBTC on the articular
cartilage remains limited. The present study explored the effects
and molecular mechanisms of TBTC on chondrocytes in vitro
and in vivo to reveal the potential effects of TBTC on joint
damage.
Materials and methods
Rat chondrocyte culture
Rat primary chondrocytes (cat. no. CP-R087) were
obtained from Procell Life Science & Technology Co., Ltd. The
cells were suspended in rat chondrocyte complete medium (cat. no.
CM-R087; Procell Life Science & Technology Co., Ltd.)
supplemented with 10% fetal bovine serum (Thermo Fisher Scientific,
Inc.) and 100 U/ml penicillin-100 µg/ml streptomycin
(penicillin-streptomycin liquid; Beijing Solarbio Science &
Technology Co., Ltd.), and were incubated at 37°C in 5%
CO2. The cells were divided into control,
low-concentration (25 nM) TBTC (MilliporeSigma),
medium-concentration (50 nM) TBTC and high-concentration (100 nM)
TBTC groups at 37°C for 24 h. The experiments were repeated three
times for each group.
Cell Counting Kit-8 (CCK-8) assay
The cells were resuspended and seeded in 96-well
plates at a density of 1×104 cells/well. When the cells
reached 50–60% confluence, the medium was discarded, and TBTC was
added at final concentrations of 0, 25, 50 and 100 nM for 24 h at
37°C. The cells were then incubated with CCK-8 reagent (Beijing
Solarbio Science & Technology Co., Ltd.) for 1 h at 37°C and
the absorbance values were determined at 450 nm.
Western blotting
The cells were lysed with RIPA buffer (high; Beijing
Solarbio Science & Technology Co., Ltd.) and the lysate was
centrifuged at 11,000 × g for 15 min at 4°C, after which the
supernatant was collected. The protein concentration was quantified
using a BCA protein assay kit (Beijing Solarbio Science &
Technology Co., Ltd.), and proteins (20 µg) were separated by
SDS-PAGE on 10% gels. The proteins were then transferred to PVDF
membranes, which were incubated with 5% nonfat milk for 1 h at
37°C. Subsequently, primary antibodies against β-actin (1:1,000;
cat. no. 4970; Cell Signaling Technology, Inc.), NLRP3 (1:1,000;
cat. no. ab263899; Abcam), interleukin (IL)-1β (1:1,000; cat. no.
ab315084; Abcam), IL-18 (1:1,000; cat. no. ab223293; Abcam), matrix
metalloproteinase (MMP)-1 (1:500; cat. no. 70R-50066; AmyJet
Scientific, Inc.), MMP-13 (1:1,000; cat. no. ab219620; Abcam),
caspase-1 (1:1,000; cat. nos. ab286125 for rat or ab138483 for
mouse; Abcam), PYD and CARD domain containing (ASC; 1:1,000; cat.
no. ab307560; Abcam) and gasdermin D (GSDMD; 1:1,000; cat. no.
ab219800; Abcam) were incubated with the PVDF membranes overnight
at 4°C. The membranes were then incubated with an HRP-labeled goat
anti-rabbit IgG (H+L) secondary antibody (1:3,000; cat. no. A0208
Beyotime Institute of Biotechnology) at room temperature for 1 h.
After washing the membranes three times with TBS-Tween (0.1%), the
protein bands were detected using an ECL western blotting substrate
(Beijing Solarbio Science & Technology Co., Ltd.). The
intensities of the protein bands were analyzed using ImageJ 1.8.0
software (National Institutes of Health), and the relative protein
expression levels were calculated using β-actin as a reference.
Lactate dehydrogenase (LDH) leakage
rate assay
Rat primary chondrocytes (1×106
cells/well in a 6-well plate) were divided into control,
low-concentration (25 nM) TBTC, medium-concentration (50 nM) TBTC
and high-concentration (100 nM) TBTC groups and were treated at
37°C for 24 h. Cytotoxicity was evaluated by determining the LDH
leakage rate in cell supernatants using a cytotoxicity LDH assay
kit (MedChemExpress) according to the manufacturer's
instructions.
Immunofluorescence (IF)
Rat primary chondrocytes (1×106
cells/well in a 6-well plate) were divided into control,
low-concentration (25 nM) TBTC, medium-concentration (50 nM) TBTC
and high-concentration (100 nM) TBTC groups and were treated at
37°C for 24 h. The chondrocytes were fixed with 4% paraformaldehyde
(Beijing Solarbio Science & Technology Co., Ltd.) at room
temperature for 20 min and then blocked with 5% donkey serum at
room temperature for 2 h (Beijing Solarbio Science & Technology
Co., Ltd.). Subsequently, the cells were incubated with a primary
antibody against NLRP3 (1:50; cat. no. ab263899; Abcam) or GSDMD
(1:50; cat. no. ab219800; Abcam) at 4°C overnight. After being
washed three times with PBS, the slides were incubated with Alexa
Fluor 350-labeled goat anti-rabbit IgG (H+L) (1:200; cat. no.
A0408; Beyotime Institute of Biotechnology) at room temperature for
1 h, followed by incubation with antifade mounting medium
containing DAPI (Beyotime Institute of Biotechnology). Images were
observed under a fluorescence microscope (magnification, ×20;
Olympus Corporation).
Cell cycle assay
Rat primary chondrocytes (1×106
cells/well in a 6-well plate) were divided into control,
low-concentration (25 nM) TBTC, medium-concentration (50 nM) TBTC
and high-concentration (100 nM) TBTC groups and were treated at
37°C for 24 h. The cell cycle assay was performed using the DNA
Content Quantitation Assay (Cell Cycle) (cat. no. CA1510; Beijing
Solarbio Science & Technology Co., Ltd.). Briefly, cells were
collected and fixed with 70% precooled ethanol (500 µl) at 4°C
overnight. The cells were then centrifuged at 800 × g at 4°C for 15
min, 100 µl RNase A solution was added to the cell precipitate and
the resuspended cells were incubated in a water bath at 37°C for 30
min. Subsequently, 400 µl PI staining solution was added to the
cell suspension, which was incubated at 4°C for 30 min in the dark.
Finally, the cells were analyzed using a BD FACSCanto II flow
cytometer (BD Biosciences) and data analysis was performed using
FlowJo 10 software (FlowJo, LLC).
EdU staining
Rat primary chondrocytes (1×106
cells/well in a 6-well plate) were divided into control,
low-concentration (25 nM) TBTC, medium-concentration (50 nM) TBTC
and high-concentration (100 nM) TBTC groups and were treated at
37°C for 24 h. EdU staining was performed using an EdU cell
proliferation assay kit (Shanghai Recordbio Biological Technology).
Rat primary chondrocytes (1×106 cells/well in a 6-well
plate) were incubated with 50 µM EdU (20 µl total volume) for 2 h
at 37°C. After three washes with PBS, the cells were incubated with
4% paraformaldehyde for 15 min at room temperature and then with
0.5% Triton X-100 for 15 min at room temperature. Subsequently, the
samples were blocked with antifade mounting medium containing DAPI
(Beyotime Institute of Biotechnology) and were observed under a
fluorescence microscope (Olympus Corporation). Cell proliferation
rate was calculated as follows: Cell proliferation rate
(%)=EdU-positive cells/DAPI-positive cells ×100.
Animal grouping and an OA mouse
model
The present study used rat primary chondrocytes
in vitro and a mouse model in vivo. The present study
aimed to verify that TBTC damaged articular chondrocytes in
different species and, compared with rat models, mouse models are
easier to generate and are less costly. C57BL/6J male mice [n=20;
Shulaibao (Wuhan) Biotechnology Co., Ltd.] were acclimated for 1
week at 22–24°C and 45% humidity. All mice were given free access
to food and water under a 12-h light/dark cycle. All mice were
randomly divided into the following four groups: Control, OA, TBTC
and TBTC + OA groups (n=5 mice/group). The mouse OA model was
induced by injection of monosodium iodoacetate (MIA; cat. no.
I2512; MilliporeSigma) as previously described (16). Specifically, MIA was dissolved in a
0.9% NaCl solution to a final concentration of 60 mg/ml, and 50 µl
MIA solution was injected into the right knee joint cavity of the
mice in the OA groups. The control mice were injected with 50 µl
0.9% NaCl solution. After 2 weeks of modeling, the OA model mice
were further divided into two groups: In the TBTC group, the mice
were injected with 50 µl 0.9% NaCl solution and were also
administered TBTC daily at a dose of 10 µg/kg for 2 weeks, and in
the other groups, the mice were administered an equal volume of
saline for a total of 2 weeks. All of the mice were euthanized at
the termination of the experiment, ensuring minimal suffering. No
mice died naturally during the study. All mice were monitored twice
daily for signs of discomfort, illness or distress by trained
personnel. To minimize suffering and distress, isoflurane was
utilized at an induction concentration of 5% and a maintenance
concentration of 2% prior to cervical dislocation. Humane endpoints
were established based on the guidelines from the Institutional
Animal Care and Use Committee of Yangzhou University, and included
>20% weight loss or gain, inability to eat or drink, persistent
lack of mobility, signs of severe and chronic pain, and any
conditions notably interfering with daily activities. When the mice
were fully unresponsive to nociceptive stimuli indicating that they
were fully anesthetized, cervical dislocation was used for
euthanasia. Death was verified by the absence of respiration,
heartbeat and reflexes. The knee joint tissues were subsequently
collected.
Safranin O-Fast Green staining
Cartilage sections (1.0×1.0×0.5 cm) were cut from
the mouse subchondral bone and fixed in 4% formaldehyde (Beijing
Solarbio Science & Technology Co., Ltd.) for 3 days at 4°C.
Subsequently, the sections were decalcified in a 30% formic acid
solution for 14 days at room temperature, dehydrated in an
increasing ethanol gradient, embedded in paraffin and cut into 5-µm
sections. The sections were stained using the modified Safranin-O
and Fast Green stain kit (for bone) (Beijing Solarbio Science &
Technology Co., Ltd.) according to the manufacturer's instructions.
Finally, the sections were blocked with neutral gum (Beijing
Solarbio Science & Technology Co., Ltd.). Normal cartilage was
red in color, and the background was green, and staining was
observed under a light microscope (Olympus Corporation).
Hematoxylin and eosin (H&E)
staining
Cartilage samples were cut into 5-µm sections as
aforementioned and were incubated using a H&E stain kit
(Beijing Solarbio Science & Technology Co., Ltd.) according to
the manufacturer's instructions. Briefly, the sections were
incubated with hematoxylin at room temperature for 10 min, rinsed
in tap water, and then stained with eosin at room temperature for
30 sec. After rinsing in tap water, and following dehydration,
clearing and sealing, the sections were observed under a light
microscope (Olympus Corporation).
Toluidine blue staining
Cartilage samples were cut into 5-µm sections as
aforementioned and were deparaffinized and stained with a 1%
toluidine blue O solution (Beijing Solarbio Science &
Technology Co., Ltd.) for 20 min at 55°C, according to the
manufacturer's instructions. After being rinsed with distilled
water, the sections were dehydrated with 95% ethanol, cleared with
xylene and blocked with resin. Subsequently, the tissues were
observed under a light microscope (Olympus Corporation).
Reverse transcription-quantitative PCR
(RT-qPCR)
Rat primary chondrocytes (1×106
cells/well in a 6-well plate) were divided into control,
low-concentration (25 nM) TBTC, medium-concentration (50 nM) TBTC
and high-concentration (100 nM) TBTC groups and were treated at
37°C for 24 h. Total RNA was extracted from chondrocytes using
TRIzol® reagent (Invitrogen; Thermo Fisher Scientific,
Inc.) and was reverse transcribed into cDNA using
PrimeScript™ RT master mix (cat. no. RR036A; Takara Bio,
Inc.) according to the manufacturer's protocol. qPCR was performed
on an ABI StepOnePlus real-time fluorescence qPCR instrument
(Thermo Fisher Scientific, Inc.) using the SYBR® Select
master mix (Beijing Think-Far Technology Co., Ltd.). The
thermocycling conditions were as follows: Denaturation at 95°C for
30 sec, followed by 35 cycles of annealing at 60°C for 1 min and
extension at 95°C for 5 sec. The sequences of the primers used were
as follows: NLRP3, forward 5′-ATAGCGTCATACGGGGGAAG-3′, reverse
5′-CACCCACGGGCAAGATGAAA-3′; GAPDH, forward
5′-TGAGGAGTCCCCATCCCAAC-3′ and reverse
5′-ATGGTATTCGAGAGAAGGGAGG-3′. Relative gene expression was
calculated using the 2−∆∆Cq method (17) with GAPDH as an internal
control.
Small interfering RNA (siRNA)
transfection
The siRNA targeting NLRP3 (sense
5′-AAUUUAAAUACAUUUCACCCA-3′; antisense 5′-TGGGTGAAATGTATTTAAATT-3′)
and the negative control (NC) siRNA (sense
5′-UUCUCCGAACGUGUCACGUUU-3′; antisense 5′-AAACGUGACACGUUCGGAGAA-3′)
were purchased from Shanghai GenePharma Co., Ltd. Briefly, primary
rat chondrocytes (1×106 cells/well in a 6-well plate)
were transfected with si-NLRP3 or NC at a final concentration of 20
nM using Lipofectamine® 3000 (Invitrogen; Thermo Fisher
Scientific, Inc.) at 37°C for 24 h, according to the manufacturer's
instructions before TBTC treatment. Subsequently, the cells were
collected immediately for subsequent experiments.
Statistical analysis
SPSS 18.0 statistical software (SPSS, Inc.) was used
for data analysis and all experiments were repeated at least three
times. The data are presented as the mean ± standard deviation.
Differences among more than two groups were examined by one-way
ANOVA, followed by Tukey's post hoc test. P<0.05 was considered
to indicate a statistically significant difference.
Results
TBTC inhibits rat chondrocyte
proliferation
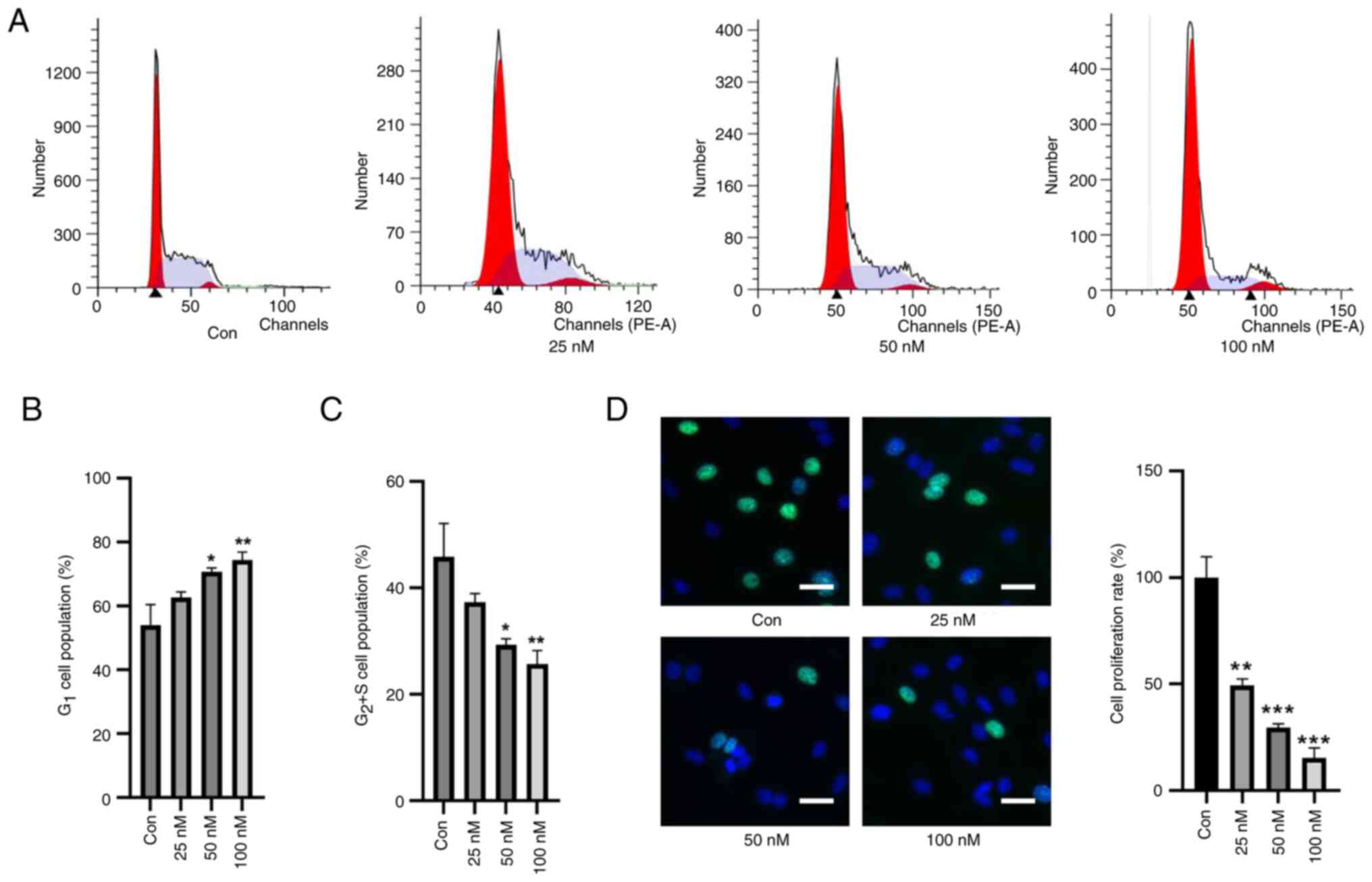
First, the effects of TBTC on the cell cycle of rat
chondrocytes were explored. Compared with in the control group,
TBTC increased the number of cells in G1 phase in a
concentration-dependent manner and decreased the number of cells in
the G2 and S phases (Fig.
1A-C). EdU staining also showed that the proliferation of rat
chondrocytes was significantly inhibited in response to an
increasing concentration of TBTC (Fig.
1D). These results preliminarily suggested that TBTC was
detrimental to the proliferation of rat chondrocytes.
TBTC induces rat chondrocyte
injury
The CCK-8 assay results showed that TBTC reduced rat
chondrocyte viability in a concentration-dependent manner (Fig. 2A). LDH leakage is the main
indicator of pyroptosis, and LDH leakage was significantly greater
in the TBTC groups than that in the control group (Fig. 2B). Furthermore, the mRNA expression
levels of NLRP3 in rat chondrocytes in the TBTC group were
significantly greater than those in the control group (Fig. 2C). After incubation with TBTC, the
protein expression levels of NRLP3, IL-1β, IL-18, MMP-1 and MMP-13
in rat chondrocytes were significantly greater than those in the
control group (Fig. 2D). These
results suggested that TBTC serves a critical role in the
destruction of chondrocytes by activating the NLRP3
inflammasome.
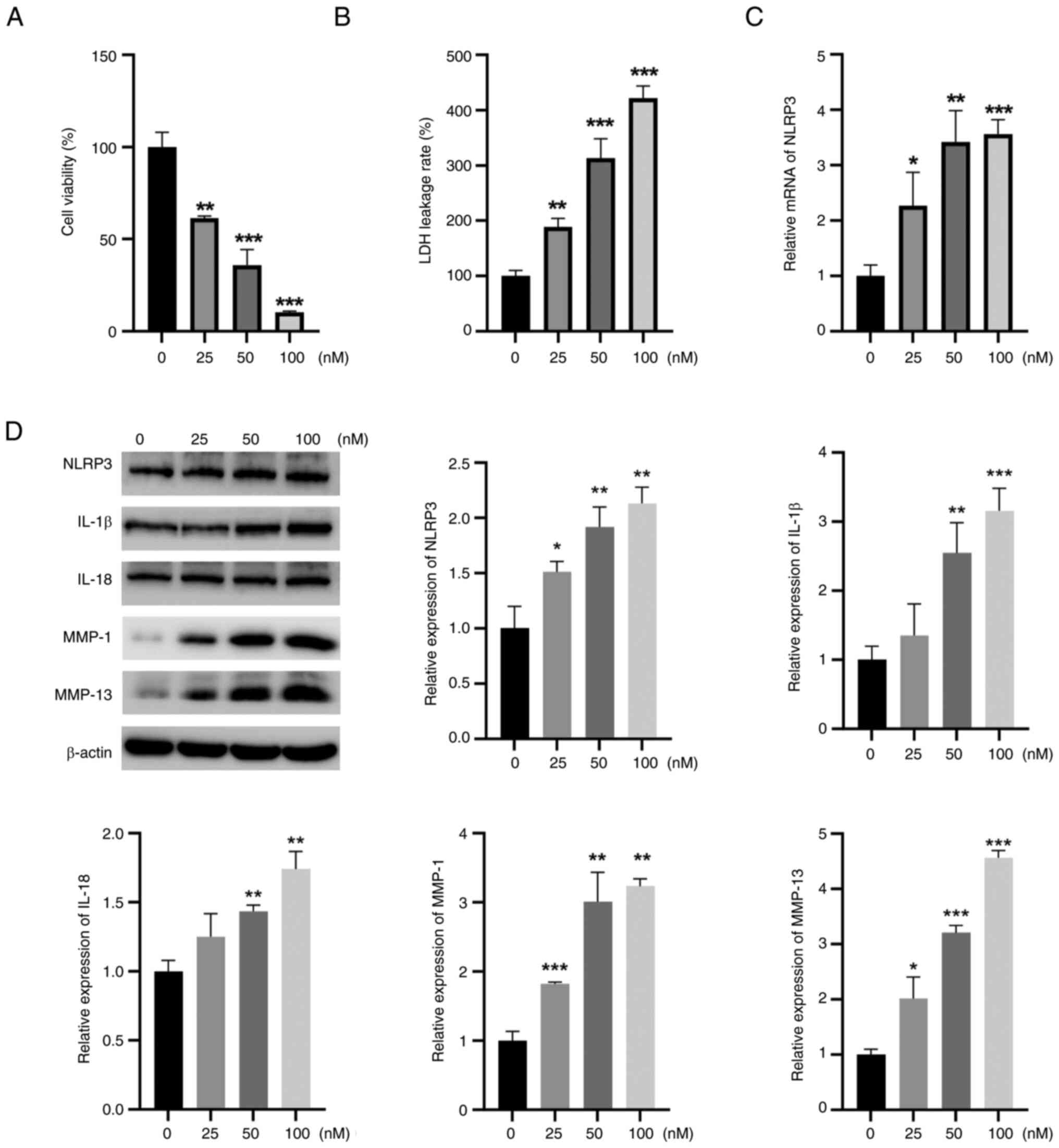 | Figure 2.TBTC induces chondrocyte damage in
rats. (A) Cell Counting Kit-8 results showed that TBTC reduced rat
chondrocyte viability in a concentration-dependent manner. (B) TBTC
significantly increased LDH leakage from rat chondrocytes. (C)
Reverse transcription-quantitative PCR results revealed that TBTC
elevated NLRP3 mRNA expression levels. (D) Western blot analysis
results revealed that TBTC upregulated the protein expression
levels of NLRP3, IL-1β, IL-18, MMP-1 and MMP-13 in rat
chondrocytes. *P<0.05, **P<0.01, ***P<0.001 vs. Con. Con,
control; IL, interleukin; LDH, lactate dehydrogenase; MMP, matrix
metalloproteinase; NLRP3, NLR family pyrin domain containing 3;
TBTC, tributyltin chloride. |
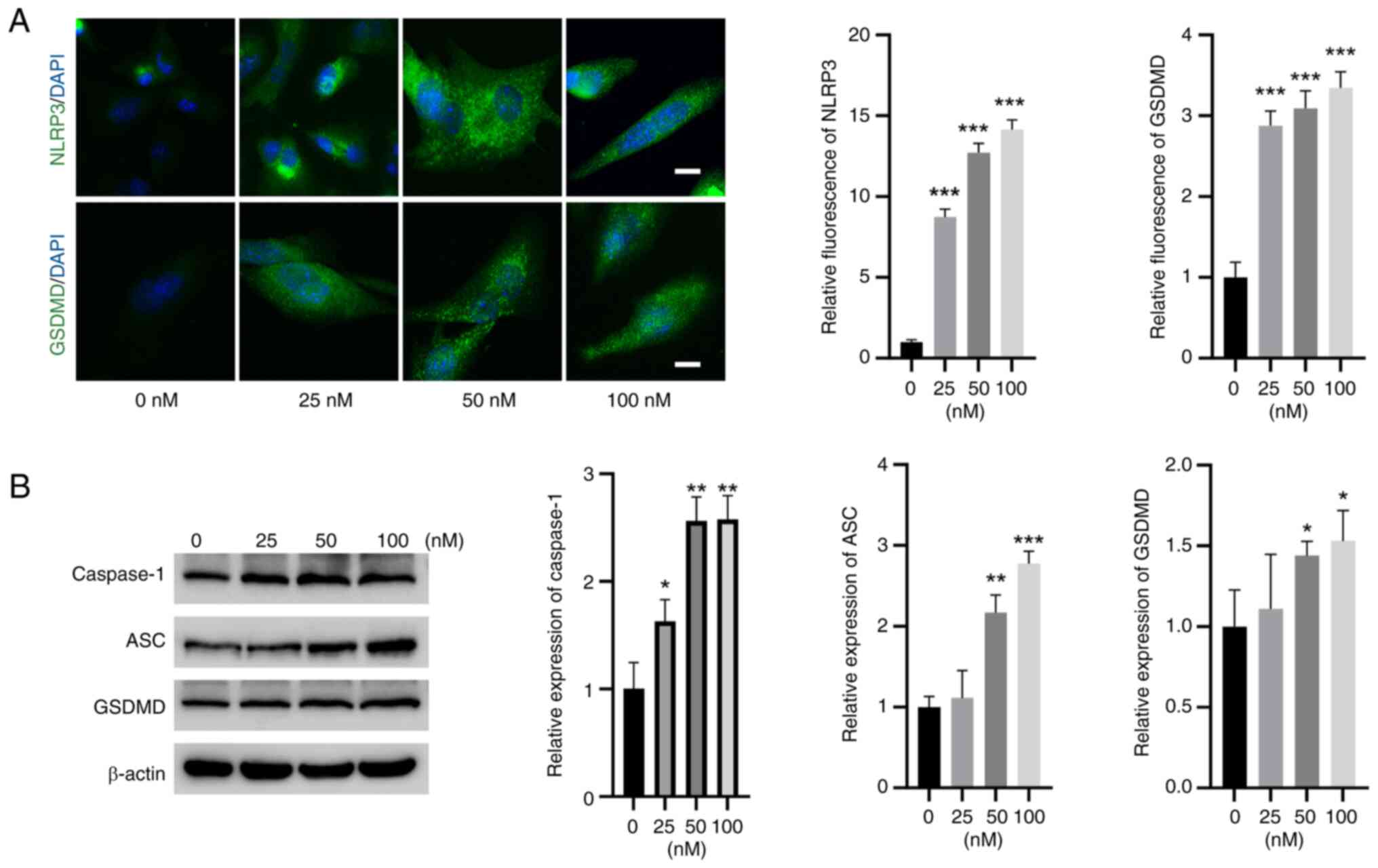
TBTC activates NLRP3 and caspase-1
signaling in rat chondrocytes
IF experiments revealed that the expression of NLRP3
and GSDMD was significantly greater in rat chondrocytes in the TBTC
groups than that in the control group (Fig. 3A). Moreover, western blot analysis
revealed that the expression levels of caspase-1, ASC and GSDMD
were significantly elevated in the TBTC groups compared with those
in the control group (Fig. 3B),
indicating the induction of pyroptosis by TBTC in rat
chondrocytes.
TBTC induces rat chondrocyte
pyroptosis through the activation of NLRP3 signaling
To further verify whether TBTC induces rat
chondrocyte pyroptosis via NLRP3, cells were transfected with a
siRNA specifically targeting NLRP3. The siRNA targeting NLRP3
effectively inhibited NLRP3 expression compared with NC group
(Fig. 4A). Compared with that in
the TBTC group, the LDH leakage rate was significantly decreased in
the si-NLRP3 + TBTC group (Fig.
4B). Moreover, the expression levels of pyroptosis-related
proteins, including caspase-1, ASC and GSDMD, were significantly
reduced in the si-NLRP3 + TBTC group than those in the TBTC group
(Fig. 4C). These results suggested
that TBTC induced rat chondrocyte pyroptosis by activating NLRP3
signaling.
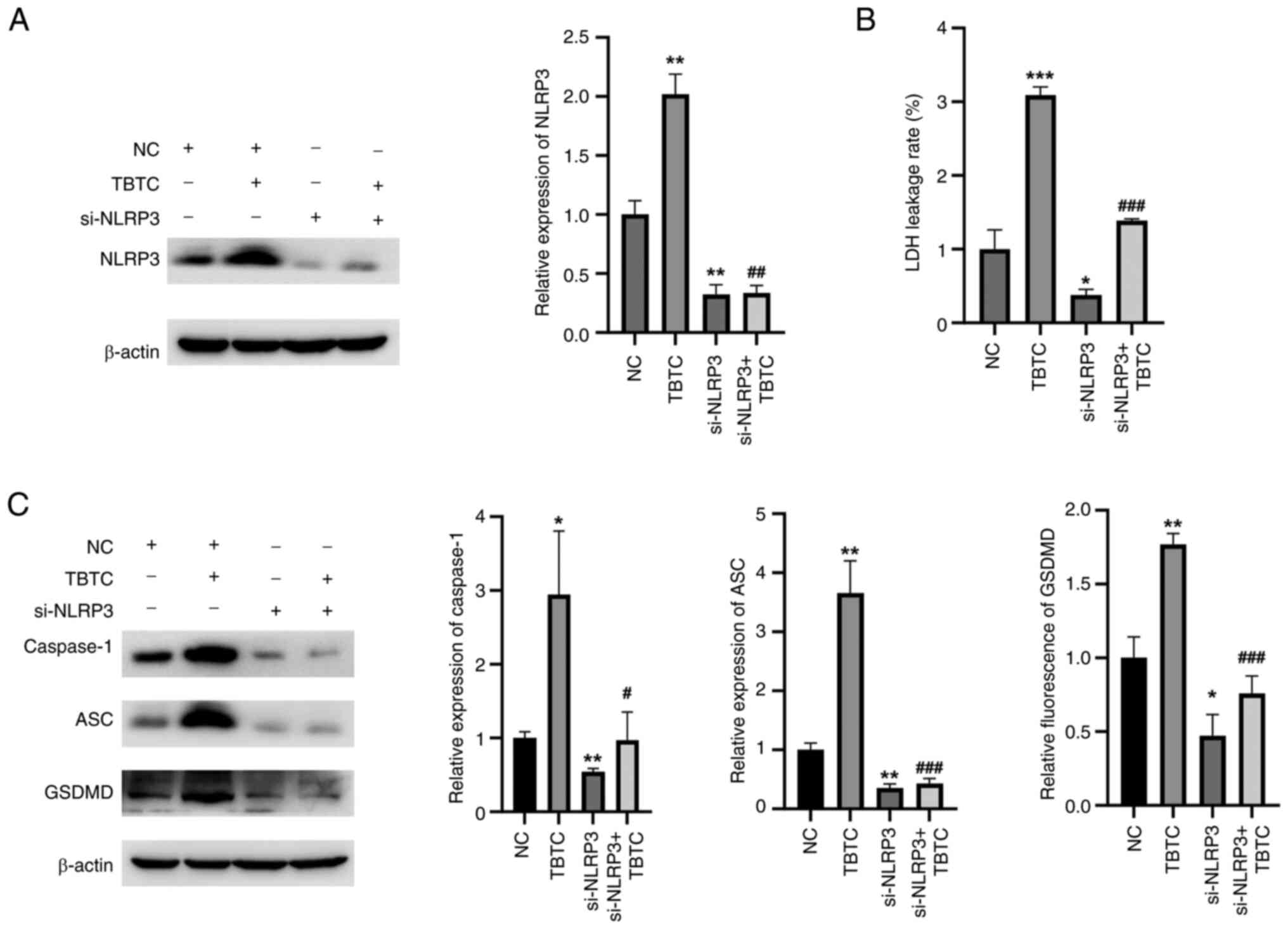 | Figure 4.TBTC induces rat chondrocyte
pyroptosis by activating NLRP3 signaling. (A) Western blot analysis
revealed that si-NLRP3 could effectively inhibit the protein
expression levels of NLRP3 in rat chondrocytes compared with that
of the negative control. (B) Knockdown of NLRP3 inhibited the
TBTC-induced increase in LDH leakage. (C) Compared with TBTC
treatment, silencing NLRP3 reduced the expression levels of
pyroptosis-related proteins. *P<0.05, **P<0.01, ***P<0.001
vs. NC; #P<0.05, ##P<0.01,
###P<0.001 vs. TBTC. ASC, PYD and CARD domain
containing; Con. Con, control; GSDMD, gasdermin D; LDH, lactate
dehydrogenase; NC, negative control; NLRP3, NLR family pyrin domain
containing 3; si, small interfering; TBTC, tributyltin
chloride. |
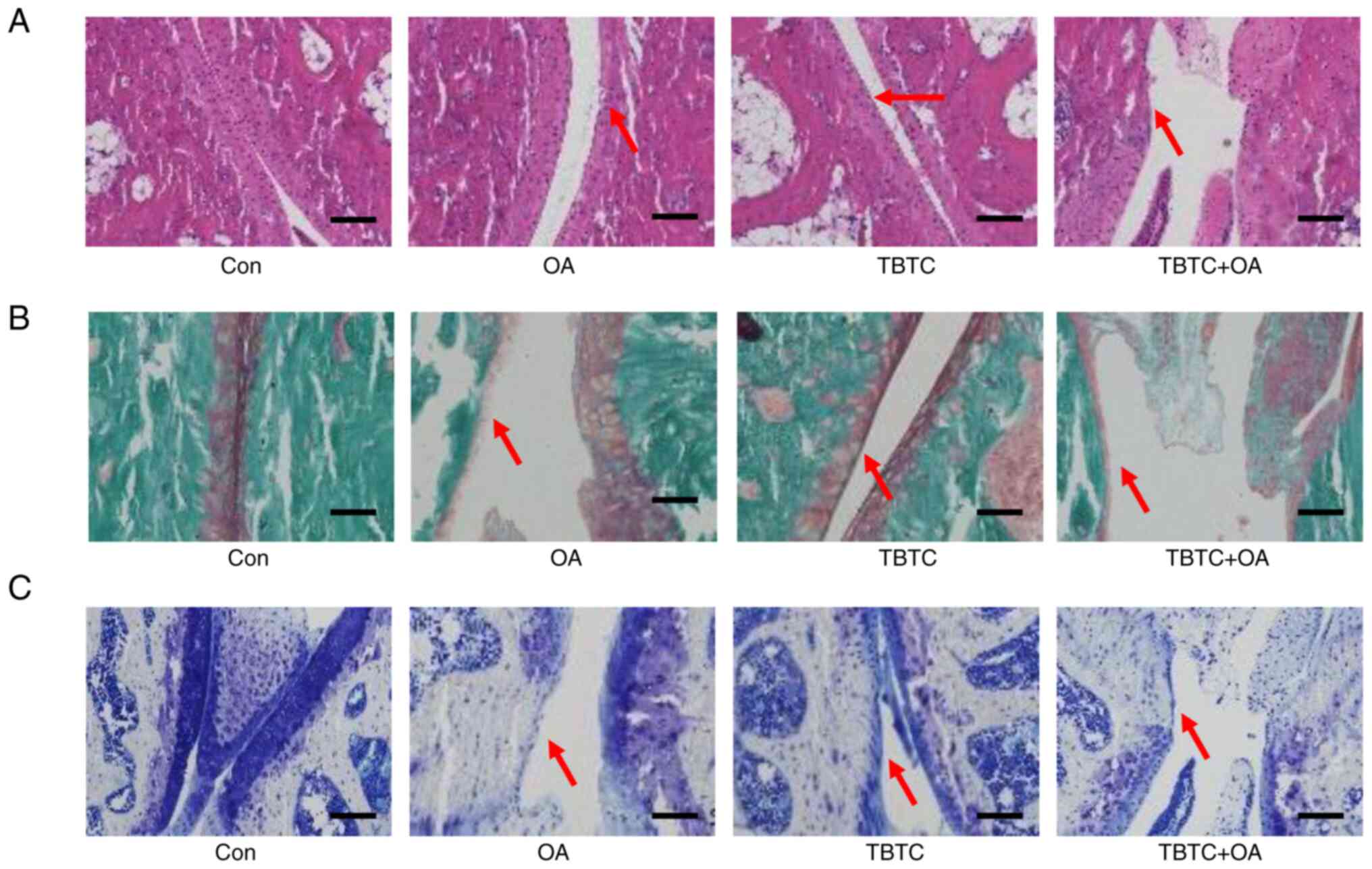
TBTC enhances cartilage damage in the
joints of mice from the OA group
H&E staining showed that in the cartilage of the
control group, the cell nuclei were dark blue, the cytoplasm and
cartilage matrix were pink, and the coloring was homogeneous; the
surface of the cartilage was smooth and flat, and was arranged
parallel to the surface of the joint (Fig. 5A). In the OA group, the surface of
the cartilage was rough, the integrity of the cartilage was
disrupted, and the surface cartilage exhibited fibrotic
degeneration and defects. In the TBTC-treated group, the cartilage
surface also showed some defects. Moreover, the integrity of the
cartilage was markedly disrupted, and the cartilage defects were
more pronounced in the TBTC + OA group (Fig. 5A). The results of Safranin O-Fast
Green staining showed that the cartilage matrix was intact in the
control group, as evidenced by proteoglycans stained in red, and by
fibers, the subchondral bone cortex and trabeculae stained in green
(Fig. 5B). In the OA and TBTC
groups, the cartilage matrix exhibited some degree of disruption,
as evidenced by reduced proteoglycan coloration. In the TBTC + OA
group, the reduction in proteoglycan coloring was further
exacerbated (Fig. 5B). Toluidine
blue staining also revealed greater articular cartilage
degeneration in the mice from the OA and TBTC groups than in those
from the control group (Fig. 5C).
This cartilage degeneration was more pronounced in the mice from
the TBTC + OA group (Fig. 5C).
These results suggested that TBTC enhanced articular cartilage
degeneration in a mouse model of OA.
TBTC enhances the NLRP3-mediated
inflammatory response and pyroptosis in OA mouse bone joints
The present study then examined the effects of TBTC
on cartilage tissue damage in mice. The results revealed that the
protein expression levels of NLRP3, IL-1β, IL-18, MMP-1 and MMP-13
were significantly greater in the OA and TBTC groups than those in
the control group (Fig. 6A).
Similarly, the proteins were also upregulated in the TBTC + OA
group (Fig. 6A). The expression
levels of pyroptosis-related proteins were also detected. Notably,
the expression levels of the pyroptosis-related proteins caspase-1,
ASC and GSDMD were significantly greater in the OA and TBTC groups
than those in the control group (Fig.
6B). These proteins were also increased in the TBTC + OA group
(Fig. 6B). These results confirmed
that TBTC could increase the NLRP3-mediated inflammatory response
and pyroptosis, thereby promoting osteoarticular injury in
mice.
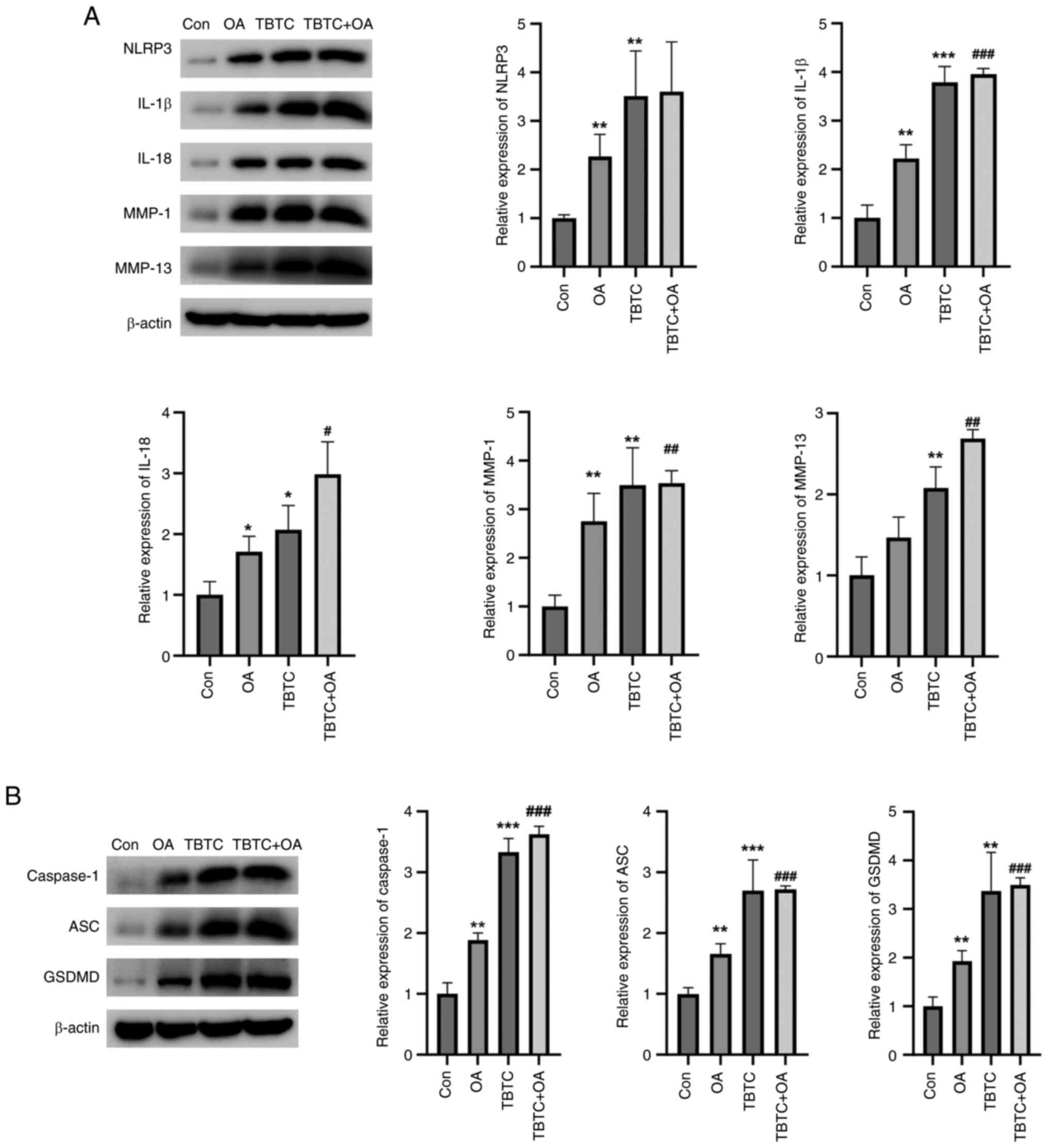 | Figure 6.TBTC enhances the NLRP3-mediated
inflammatory response and cellular pyroptosis in mouse OA. (A) TBTC
increased the protein expression levels of NLRP3, IL-1β, IL-18,
MMP-1 and MMP-13. (B) TBTC increased the expression levels of the
pyroptosis-related proteins caspase-1, ASC and GSDMD in mouse
osteoarticular tissues. *P<0.05, **P<0.01, ***P<0.001 vs.
Con; #P<0.05, ##P<0.01,
###P<0.001 vs. OA. Con. ASC, PYD and CARD domain
containing; Con, control; GSDMD, gasdermin D; IL, interleukin; MMP,
matrix metalloproteinase; OA, osteoarthritis; TBTC, tributyltin
chloride. |
Discussion
TBT is a synthetic metal compound and an important
industrial raw material that is widely used as a stabilizer for
plastic products, a pesticide, a fungicide, and an anticorrosive
and antifouling coating for ships and boats (18). In the past 20 years, TBT has
entered the environment, particularly the marine environment, in
large quantities, resulting in widespread pollution of the oceans
(18). TBT pollution has attracted
the attention of a number of countries worldwide, and some
countries have begun to take measures to limit the use of TBT.
Studies have shown that TBT not only has endocrine-disrupting
effects on organisms and causes reproductive toxicity, but also
affects the nervous and immune systems (15,19,20).
A previous study revealed that TBTC reduces the bone mineral
density in the rat femoral epiphysis by inhibiting Wnt/β-catenin
signaling, which in turn disrupts the homeostasis between
osteogenesis and adipogenesis (21). However, the effects of TBTC on
chondrocytes are still poorly understood.
To the best of our knowledge, for the first time,
the present study revealed that TBTC decreased the survival of rat
chondrocytes in a concentration-dependent manner. In addition, TBTC
increased the leakage rate of LDH, an important indicator of
pyroptosis. Cellular pyroptosis is a type of lytic and
inflammatory-dependent programmed cell death that leads to the
cytolysis and release of inflammatory mediators (IL-1β and IL-18),
which then cause tissue damage (4,6,22).
Chung et al (23) reported
that 0.01–0.5 µM TBT induced senescence of human articular
chondrocytes in vitro. Their results showed that 10 nM TBT
reduced human chondrocyte viability and promoted elevated
expression of inflammatory factors, but with no statistically
significant difference. By contrast, 100 nM TBT significantly
induced human chondrocyte senescence and inflammatory responses.
Notably, pyroptosis is very similar to apoptosis, but some aspects
are markedly different from apoptosis because this death phenomenon
is dependent on pro-inflammatory caspase-1. Based on the
relationship between pyroptosis and inflammation, a low
concentration (25 nM) of TBTC was selected to ensure that it
induced an inflammatory response, as well as a high concentration
(100 nM) of TBTC, and an intermediate concentration (50 nM) of
TBTC. The results revealed that the protein expression levels of
IL-1β, IL-18, MMP-1 and MMP-13 were significantly increased in rat
chondrocytes after TBTC treatment, indicating that TBTC may induce
the release of inflammatory mediators in rat chondrocytes by
activating the NLRP3 inflammasome.
Inflammation caused by activation of the NLRP3
inflammasome is the basis of numerous diseases, such as breast
cancer and acute liver injury (6,24,25).
Once activated, NLRP3 interacts with the adaptor ASC, which
subsequently causes the activation of caspase-1 (6). GSDMD, a member of the GSDM family, is
cleaved by caspase-1 and releases the N-terminal structural domain,
which oligomerizes at the plasma membrane and forms a pore for the
release of substrates, such as IL-1β and IL-18 (22,26).
Caspase-1-mediated cellular death serves a role in the regulation
of various diseases, such as cancer, cardiac hypertrophy and
neurological disorders (27–29).
In addition, caspase-1 deficiency reduces arthropathic changes in
chronic arthritis (30). In the
present study, in rat chondrocytes, TBTC was able to increase the
expression levels of caspase-1, GSDMD and ASC. To further validate
that TBTC activates the upregulation of inflammatory factors in
chondrocytes and triggers pyroptosis through activation of the
NLRP3 inflammasome, chondrocytes were transfected with a siRNA
specifically targeting NLRP3. The results showed that silencing
NLRP3 effectively reversed TBTC-mediated increases in the
expression of caspase-1, GSDMD and ASC. Therefore, it was
hypothesized that TBTC enhanced the expression of the inflammatory
factors IL-1β and IL-18 through upregulation of the NLRP3/caspase-1
pyroptosis pathway, causing further expansion of the inflammatory
response.
OA is a progressive joint disease, and drugs
currently used in the clinic, such as acetaminophen and
nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs, can alleviate pain but cannot
cure the disease (9). The NLRP3
inflammasome has been shown to be associated with the pathogenesis
of various arthritic diseases by stimulating inflammatory mediators
and degradative enzymes (9,31).
It has previously been reported that the NLRP3 inflammasome serves
an important role in inflammation and apoptosis of fibroblast-like
synoviocytes, suggesting that the NLRP3 inflammasome is involved in
the progression of OA (32,33).
Since TBTC can activate the NLRP3 inflammasome-mediated
inflammatory response and cellular pyroptosis in chondrocytes, the
present study aimed to assess whether TBTC can aggravate the
progression of OA. To evaluate this, a mouse model of OA was
constructed and the mice were treated with TBTC. Chung et al
(23) reported that 5 and 25
µg/kg/day TBTC induced mouse articular cartilage aging in
vivo. This previous study revealed that 25 µg/kg/day TBTC
significantly induced aging of joints in mice; however, at 5
µg/kg/day, there was no significant senescence of articular
cartilage in mice, but the inflammatory response showed an
increased trend. The reason why a high dose of TBTC was not used in
the present study is that 25 µg/kg/day TBT induced chondrocyte
senescence, which itself causes senescence-associated secretory
phenotype. Unlike the aforementioned study, the present study did
not consider whether TBTC induced chondrocyte senescence, but
instead the present study explored the effects of TBTC on mouse OA.
Therefore a dose slightly higher than 5 µg/kg/day was used to
ensure that it enhanced the inflammatory response without inducing
senescence, thus providing insight into whether TBTC worsened OA.
H&E staining revealed more severe cartilage destruction in the
OA + TBTC group than in the OA group, which was accompanied by
subchondral bone sclerosis, suggesting that TBTC aggravated
cartilage degeneration in the osteoarthritic joints in the OA
group. The results of Safranin O-Fast Green and toluidine blue
staining showed that the loss of proteoglycan staining was more
obvious in the OA + TBTC group than in the control group. These
results suggested that TBTC may reduce the amounts of collagen and
proteoglycans in articular cartilage tissue, which leads to
cartilage destruction and aggravates the progression of OA.
Consistent with the results of the in vitro study, TBTC
treatment further exacerbated the expression levels of
NLRP3-mediated inflammatory factors, as well as cellular
pyroptosis-related proteins in the joint tissues of mice from the
OA group, further confirming that the activation of NLRP3 by TBTC
exacerbated the inflammatory response and cartilage tissue damage
in the mice from the OA group.
In conclusion, to the best of our knowledge, the
present study revealed, for the first time, that TBTC exacerbated
the progression of OA in vivo by activating the NLRP3
inflammasome-mediated inflammatory response and cellular pyroptosis
in chondrocytes. Therefore, TBTC may cause damage to the articular
cartilage, and it is thus necessary to strictly control the use of
TBT.
Acknowledgements
Not applicable.
Funding
This work was supported by a grant from the Natural Science
Foundation of Jiangsu Province (grant no. JZ-2021-087).
Availability of data and materials
The data generated in the present study may be
requested from the corresponding author.
Authors' contributions
SX and RM designed the study, performed the
experiments, analyzed the data and provided final approval of the
version to be published. SX and RM confirm the authenticity of all
the raw data. Both authors read and approved the final version of
the manuscript.
Ethics approval and consent to
participate
The present study was approved by the Animal Ethics
Committee at Yangzhou University (approval no. YZ-ja986B; Yancheng,
China).
Patient consent for publication
Not applicable.
Competing interests
The authors declare that they have no competing
interests.
References
|
1
|
Abramoff B and Caldera FE: Osteoarthritis:
Pathology, diagnosis, and treatment options. Med Clin North Am.
104:293–311. 2020. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
Colletti A and Cicero AFG: Nutraceutical
approach to chronic osteoarthritis: From molecular research to
clinical evidence. Int J Mol Sci. 22:129202021. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
Hawker GA and King LK: The burden of
osteoarthritis in older adults. Clin Geriatr Med. 38:181–192. 2022.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
Yang J, Hu S, Bian Y, Yao J, Wang D, Liu
X, Guo Z, Zhang S and Peng L: Targeting cell death: Pyroptosis,
ferroptosis, apoptosis and necroptosis in osteoarthritis. Front
Cell Dev Biol. 9:7899482022. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Sharma BR and Kanneganti TD: NLRP3
inflammasome in cancer and metabolic diseases. Nat Immunol.
22:550–559. 2021. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Huang Y, Xu W and Zhou R: NLRP3
inflammasome activation and cell death. Cell Mol Immunol.
18:2114–2127. 2021. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Fu J and Wu H: Structural mechanisms of
NLRP3 inflammasome assembly and activation. Annu Rev Immunol.
41:301–316. 2023. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Chen Z, Zhong H, Wei J, Lin S, Zong Z,
Gong F, Huang X, Sun J, Li P, Lin H, et al: Inhibition of Nrf2/HO-1
signaling leads to increased activation of the NLRP3 inflammasome
in osteoarthritis. Arthritis Res Ther. 21:3002019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Li X, Mei W, Huang Z, Zhang L, Zhang L, Xu
B, Shi X, Xiao Y, Ma Z, Liao T, et al: Casticin suppresses
monoiodoacetic acid-induced knee osteoarthritis through inhibiting
HIF-1α/NLRP3 inflammasome signaling. Int Immunopharmacol.
86:1067452020. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Zu Y, Mu Y, Li Q, Zhang ST and Yan HJ:
Icariin alleviates osteoarthritis by inhibiting NLRP3-mediated
pyroptosis. J Orthop Surg Res. 14:3072019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Jin X, Dong X, Sun Y, Liu Z, Liu L and Gu
H: Dietary fatty acid regulation of the NLRP3 inflammasome via the
TLR4/NF-κB signaling pathway affects chondrocyte pyroptosis. Oxid
Med Cell Longev. 2022:37113712022. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Daigneault BW and de Agostini Losano JD:
Tributyltin chloride exposure to post-ejaculatory sperm reduces
motility, mitochondrial function and subsequent embryo development.
Reprod Fertil Dev. 34:833–843. 2022. View
Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Chen P, Song Y, Tang L, Zhong W, Zhang J,
Cao M, Chen J, Cheng G, Li H, Fan T, et al: Tributyltin chloride
(TBTCL) induces cell injury via dysregulation of endoplasmic
reticulum stress and autophagy in Leydig cells. J Hazard Mater.
448:1307852023. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Zhao C, Zhang Y, Suo A, Mu J and Ding D:
Toxicity of tributyltin chloride on haarder (Liza haematocheila)
after its acute exposure: Bioaccumulation, antioxidant defense,
histological, and transcriptional analyses. Fish Shellfish Immunol.
130:501–511. 2022. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Horie Y, Yamagishi T, Shintaku Y, Iguchi T
and Tatarazako N: Effects of tributyltin on early life-stage,
reproduction, and gonadal sex differentiation in Japanese medaka
(Oryzias latipes). Chemosphere. 203:418–425. 2018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Pitcher T, Sousa-Valente J and Malcangio
M: The monoiodoacetate model of osteoarthritis pain in the mouse. J
Vis Exp. 537462016.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Livak KJ and Schmittgen TD: Analysis of
relative gene expression data using real-time quantitative PCR and
the 2(−Delta Delta C(T)) method. Methods. 25:402–408. 2001.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
Barbosa KL, Dettogni RS, da Costa CS,
Gastal EL, Raetzman LT, Flaws JA and Graceli JB: Tributyltin and
the female hypothalamic-pituitary-gonadal disruption. Toxicol Sci.
186:179–189. 2022. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
de Araújo JFP, Podratz PL, Merlo E,
Sarmento IV, da Costa CS, Niño OMS, Faria RA, Freitas Lima LC and
Graceli JB: Organotin exposure and vertebrate reproduction: A
review. Front Endocrinol (Lausanne). 9:642018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
Ximenes CF, Rodrigues SML, Podratz PL,
Merlo E, de Araújo JFP, Rodrigues LCM, Coitinho JB, Vassallo DV,
Graceli JB and Stefanon I: Tributyltin chloride disrupts aortic
vascular reactivity and increases reactive oxygen species
production in female rats. Environ Sci Pollut Res Int.
24:24509–24520. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
Yao W, Wei X, Guo H, Cheng D, Li H, Sun L,
Wang S, Guo D, Yang Y and Si J: Tributyltin reduces bone mineral
density by reprograming bone marrow mesenchymal stem cells in rat.
Environ Toxicol Pharmacol. 73:1032712020. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22
|
An S, Hu H, Li Y and Hu Y: Pyroptosis
plays a role in osteoarthritis. Aging Dis. 11:1146–1157. 2020.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23
|
Chung YP, Weng TI, Chan DC, Yang RS and
Liu SH: Low-dose tributyltin triggers human chondrocyte senescence
and mouse articular cartilage aging. Arch Toxicol. 97:547–559.
2023. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24
|
Faria SS, Costantini S, de Lima VCC, de
Andrade VP, Rialland M, Cedric R, Budillon A and Magalhães KG:
NLRP3 inflammasome-mediated cytokine production and pyroptosis cell
death in breast cancer. J Biomed Sci. 28:262021. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
25
|
Yu C, Chen P, Miao L and Di G: The role of
the NLRP3 inflammasome and programmed cell death in acute liver
injury. Int J Mol Sci. 24:30672023. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
26
|
Zhang L, Xing R, Huang Z, Zhang N, Zhang
L, Li X and Wang P: Inhibition of synovial macrophage pyroptosis
alleviates synovitis and fibrosis in knee osteoarthritis. Mediators
Inflamm. 2019:21659182019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
27
|
Li S, Sun Y, Song M, Song Y, Fang Y, Zhang
Q, Li X, Song N, Ding J, Lu M and Hu G:
NLRP3/caspase-1/GSDMD-mediated pyroptosis exerts a crucial role in
astrocyte pathological injury in mouse model of depression. JCI
Insight. 6:e1468522021. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
28
|
Yan H, Luo B, Wu X, Guan F, Yu X, Zhao L,
Ke X, Wu J and Yuan J: Cisplatin induces pyroptosis via activation
of MEG3/NLRP3/caspase-1/GSDMD pathway in triple-negative breast
cancer. Int J Biol Sci. 17:2606–2621. 2021. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
29
|
Wang F, Liang Q, Ma Y, Sun M, Li T, Lin L,
Sun Z and Duan J: Silica nanoparticles induce pyroptosis and
cardiac hypertrophy via ROS/NLRP3/Caspase-1 pathway. Free Radic
Biol Med. 182:171–181. 2022. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
30
|
Liu J, Jia S, Yang Y, Piao L, Wang Z, Jin
Z and Bai L: Exercise induced meteorin-like protects chondrocytes
against inflammation and pyroptosis in osteoarthritis by inhibiting
PI3K/Akt/NF-κB and NLRP3/caspase-1/GSDMD signaling. Biomed
Pharmacother. 158:1141182023. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
31
|
Zhang Y, Yan H, Jiang Y, Chen T, Ma Z, Li
F, Lin M, Xu Y, Zhang X, Zhang J and He H: Long non-coding RNA
IGF2-AS represses breast cancer tumorigenesis by epigenetically
regulating IGF2. Exp Biol Med (Maywood). 246:371–379. 2021.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
32
|
Sakalyte R, Denkovskij J, Bernotiene E,
Stropuviene S, Mikulenaite SO, Kvederas G, Porvaneckas N, Tutkus V,
Venalis A and Butrimiene I: The expression of inflammasomes NLRP1
and NLRP3, toll-like receptors, and vitamin D receptor in synovial
fibroblasts from patients with different types of knee arthritis.
Front Immunol. 12:7675122022. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
33
|
Zhao LR, Xing RL, Wang PM, Zhang NS, Yin
SJ, Li XC and Zhang L: NLRP1 and NLRP3 inflammasomes mediate
LPS/ATP-induced pyroptosis in knee osteoarthritis. Mol Med Rep.
17:5463–5469. 2018.PubMed/NCBI
|