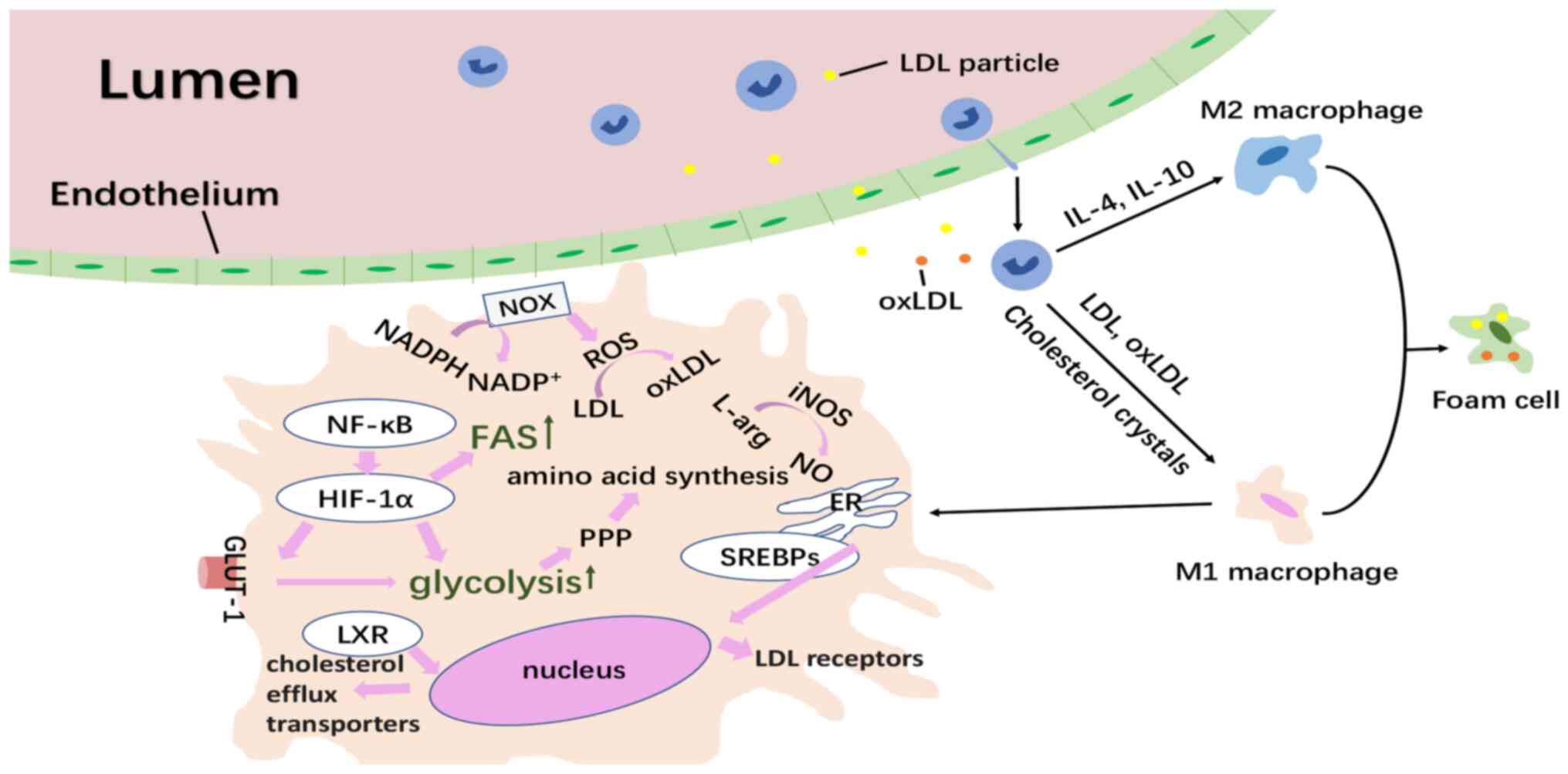
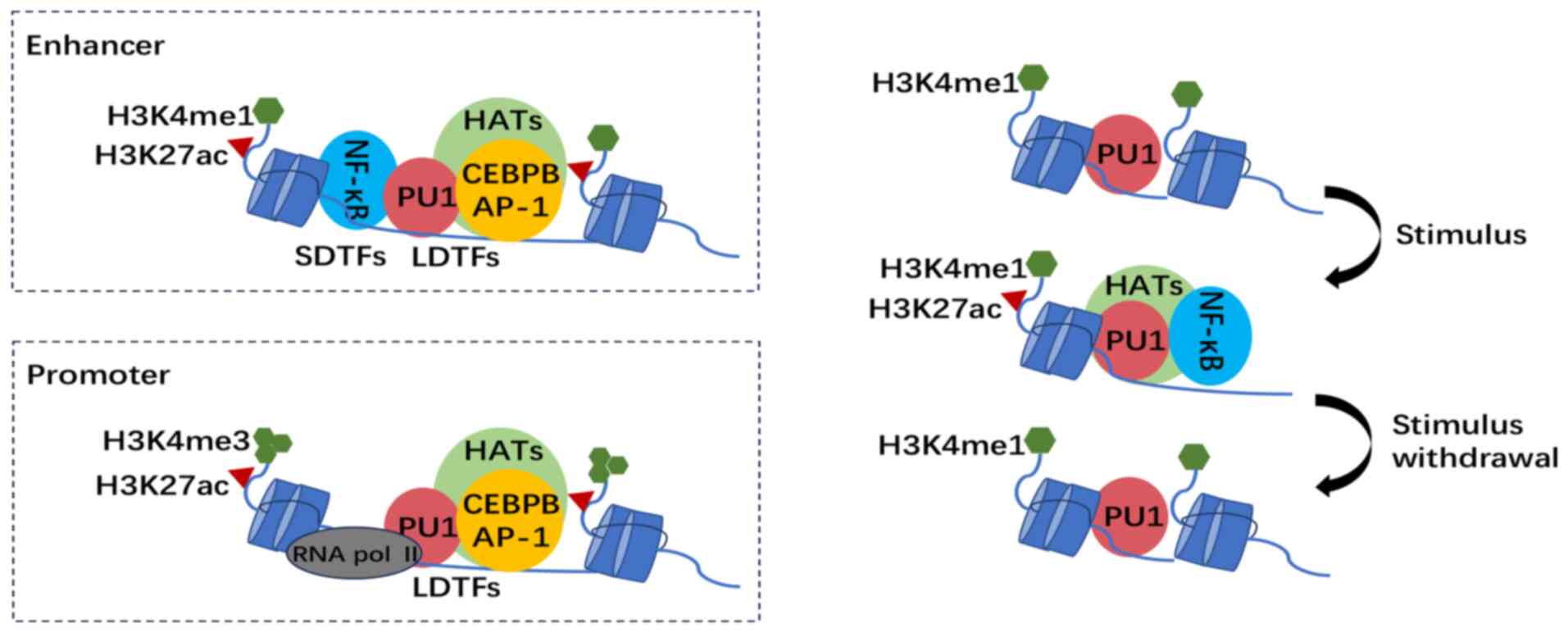
|
1
|
Libby P: The changing landscape of
atherosclerosis. Nature. 592:524–533. 2021. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
Boren J, Chapman MJ, Krauss RM, Packard
CJ, Bentzon JF, Binder CJ, Daemen MJ, Demer LL, Hegele RA, Nicholls
SJ, et al: Low-density lipoproteins cause atherosclerotic
cardiovascular disease: Pathophysiological, genetic, and
therapeutic insights: A consensus statement from the european
atherosclerosis society consensus panel. Eur Heart J. 41:2313–2330.
2020. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
Zhu Y, Xian X, Wang Z, Bi Y, Chen Q, Han
X, Tang D and Chen R: Research progress on the relationship between
atherosclerosis and inflammation. Biomolecules. 8:802018.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
Moore KJ, Sheedy FJ and Fisher EA:
Macrophages in atherosclerosis: A dynamic balance. Nat Rev Immunol.
13:709–721. 2013. View
Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Netea MG, Quintin J and van der Meer JW:
Trained immunity: A memory for innate host defense. Cell Host
Microbe. 9:355–361. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Netea MG: Training innate immunity: The
changing concept of immunological memory in innate host defence.
Eur J Clin Invest. 43:881–884. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Dominguez-Andres J, Santos JC, Bekkering
S, Mulder WJM, van der Meer JWM, Riksen NP, Joosten LAB and Netea
MG: Trained immunity: Adaptation within innate immune mechanisms.
Physiol Rev. 103:313–346. 2023. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Netea MG, Joosten LA, Latz E, Mills KH,
Natoli G, Stunnenberg HG, O'Neill LA and Xavier RJ: Trained
immunity: A program of innate immune memory in health and disease.
Science. 352:aaf10982016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Naik S, Larsen SB, Gomez NC, Alaverdyan K,
Sendoel A, Yuan S, Polak L, Kulukian A, Chai S and Fuchs E:
Inflammatory memory sensitizes skin epithelial stem cells to tissue
damage. Nature. 550:475–480. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
van den Burg HA and Takken FL: Does
chromatin remodeling mark systemic acquired resistance? Trends
Plant Sci. 14:286–294. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Foster SL, Hargreaves DC and Medzhitov R:
Gene-specific control of inflammation by TLR-induced chromatin
modifications. Nature. 447:972–978. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Lim AI, McFadden T, Link VM, Han SJ,
Karlsson RM, Stacy A, Farley TK, Lima-Junior DS, Harrison OJ, Desai
JV, et al: Prenatal maternal infection promotes tissue-specific
immunity and inflammation in offspring. Science. 373:eabf30022021.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Li Y, Chen Y, Cai G, Ni Q, Geng Y, Wang T,
Bao C, Ruan X, Wang H and Sun W: Roles of trained immunity in the
pathogenesis of periodontitis. J Periodontal Res. 58:864–873. 2023.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Wendeln AC, Degenhardt K, Kaurani L,
Gertig M, Ulas T, Jain G, Wagner J, Häsler LM, Wild K, Skodras A,
et al: Innate immune memory in the brain shapes neurological
disease hallmarks. Nature. 556:332–338. 2018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Bekkering S, Quintin J, Joosten LA, van
der Meer JW, Netea MG and Riksen NP: Oxidized low-density
lipoprotein induces long-term proinflammatory cytokine production
and foam cell formation via epigenetic reprogramming of monocytes.
Arterioscler Thromb Vasc Biol. 34:1731–1718. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Riksen NP, Bekkering S, Mulder WJM and
Netea MG: Trained immunity in atherosclerotic cardiovascular
disease. Nat Rev Cardiol. 20:799–811. 2023. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Shirai T, Nazarewicz RR, Wallis BB, Yanes
RE, Watanabe R, Hilhorst M, Tian L, Harrison DG, Giacomini JC,
Assimes TL, et al: The glycolytic enzyme PKM2 bridges metabolic and
inflammatory dysfunction in coronary artery disease. J Exp Med.
213:337–354. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
Mitroulis I, Hajishengallis G and Chavakis
T: Bone marrow inflammatory memory in cardiometabolic disease and
inflammatory comorbidities. Cardiovasc Res. 119:2801–2812. 2023.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
Kleinnijenhuis J, Quintin J, Preijers F,
Joosten LA, Jacobs C, Xavier RJ, van der Meer JW, van Crevel R and
Netea MG: BCG-induced trained immunity in NK cells: Role for
non-specific protection to infection. Clin Immunol. 155:213–219.
2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
Moorlag SJCFM, Rodriguez-Rosales YA,
Gillard J, Fanucchi S, Theunissen K, Novakovic B, de Bont CM,
Negishi Y, Fok ET, Kalafati L, et al: BCG vaccination induces
long-term functional reprogramming of human neutrophils. Cell Rep.
33:1083872020. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
Hole CR, Wager CML, Castro-Lopez N,
Campuzano A, Cai H, Wozniak KL, Wang Y and Wormley FL Jr: Induction
of memory-like dendritic cell responses in vivo. Nat Commun.
10:29552019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22
|
Sohrabi Y, Lagache SMM, Voges VC, Semo D,
Sonntag G, Hanemann I, Kahles F, Waltenberger J and Findeisen HM:
OxLDL-mediated immunologic memory in endothelial cells. J Mol Cell
Cardiol. 146:121–132. 2020. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23
|
Netea MG, Domínguez-Andrés J, Barreiro LB,
Chavakis T, Divangahi M, Fuchs E, Joosten LAB, van der Meer JWM,
Mhlanga MM, Mulder WJM, et al: Defining trained immunity and its
role in health and disease. Nat Rev Immunol. 20:375–388. 2020.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24
|
Bonetti J, Corti A, Lerouge L, Pompella A
and Gaucher C: Phenotypic modulation of macrophages and vascular
smooth muscle cells in atherosclerosis-nitro-redox
interconnections. Antioxidants (Basel). 10:5162021. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
25
|
Gordon S and Taylor PR: Monocyte and
macrophage heterogeneity. Nat Rev Immunol. 5:953–964. 2005.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
26
|
Duewell P, Kono H, Rayner KJ, Sirois CM,
Vladimer G, Bauernfeind FG, Abela GS, Franchi L, Nuñez G, Schnurr
M, et al: NLRP3 inflammasomes are required for atherogenesis and
activated by cholesterol crystals. Nature. 464:1357–1361. 2010.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
27
|
Chavez-Sanchez L, Garza-Reyes MG,
Espinosa-Luna JE, Chávez-Rueda K, Legorreta-Haquet MV and
Blanco-Favela F: The role of TLR2, TLR4 and CD36 in macrophage
activation and foam cell formation in response to oxLDL in humans.
Hum Immunol. 75:322–329. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
28
|
Hirose K, Iwabuchi K, Shimada K, Kiyanagi
T, Iwahara C, Nakayama H and Daida H: Different responses to
oxidized low-density lipoproteins in human polarized macrophages.
Lipids Health Dis. 10:12011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
29
|
Verreck FA, de Boer T, Langenberg DM,
Hoeve MA, Kramer M, Vaisberg E, Kastelein R, Kolk A, de
Waal-Malefyt R and Ottenhoff TH: Human IL-23-producing type 1
macrophages promote but IL-10-producing type 2 macrophages subvert
immunity to (myco)bacteria. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA. 101:4560–4565.
2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
30
|
Stein M, Keshav S, Harris N and Gordon S:
Interleukin 4 potently enhances murine macrophage mannose receptor
activity: A marker of alternative immunologic macrophage
activation. J Exp Med. 176:287–292. 1992. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
31
|
Gordon S: Alternative activation of
macrophages. Nat Rev Immunol. 3:23–35. 2003. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
32
|
Mosser DM and Edwards JP: Exploring the
full spectrum of macrophage activation. Nat Rev Immunol. 8:958–969.
2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
33
|
Jinnouchi H, Guo L, Sakamoto A, Torii S,
Sato Y, Cornelissen A, Kuntz S, Paek KH, Fernandez R, Fuller D, et
al: Diversity of macrophage phenotypes and responses in
atherosclerosis. Cell Mol Life Sci. 77:1919–1932. 2020. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
34
|
Chinetti-Gbaguidi G, Colin S and Staels B:
Macrophage subsets in atherosclerosis. Nat Rev Cardiol. 12:10–17.
2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
35
|
Kadl A, Meher AK, Sharma PR, Lee MY, Doran
AC, Johnstone SR, Elliott MR, Gruber F, Han J, Chen W, et al:
Identification of a novel macrophage phenotype that develops in
response to atherogenic phospholipids via Nrf2. Circ Res.
107:737–746. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
36
|
Stoger JL, Gijbels MJ, van der Velden S,
Manca M, van der Loos CM, Biessen EA, Daemen MJ, Lutgens E and de
Winther MP: Distribution of macrophage polarization markers in
human atherosclerosis. Atherosclerosis. 225:461–468. 2012.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
37
|
Stewart CR, Stuart LM, Wilkinson K, van
Gils JM, Deng J, Halle A, Rayner KJ, Boyer L, Zhong R, Frazier WA,
et al: CD36 ligands promote sterile inflammation through assembly
of a Toll-like receptor 4 and 6 heterodimer. Nat Immunol.
11:155–161. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
38
|
Feig JE, Vengrenyuk Y, Reiser V, Wu C,
Statnikov A, Aliferis CF, Garabedian MJ, Fisher EA and Puig O:
Regression of atherosclerosis is characterized by broad changes in
the plaque macrophage transcriptome. PLoS One. 7:e397902012.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
39
|
O'Neill LA, Kishton RJ and Rathmell J: A
guide to immunometabolism for immunologists. Nat Rev Immunol.
16:553–565. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
40
|
Stienstra R, Netea-Maier RT, Riksen NP,
Joosten LAB and Netea MG: Specific and complex reprogramming of
cellular metabolism in myeloid cells during innate immune
responses. Cell Metab. 26:142–156. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
41
|
Groh L, Keating ST, Joosten LAB, Netea MG
and Riksen NP: Monocyte and macrophage immunometabolism in
atherosclerosis. Semin Immunopathol. 40:203–214. 2018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
42
|
Cheng SC, Quintin J, Cramer RA, Shepardson
KM, Saeed S, Kumar V, Giamarellos-Bourboulis EJ, Martens JH, Rao
NA, Aghajanirefah A, et al: mTOR- and HIF-1α-mediated aerobic
glycolysis as metabolic basis for trained immunity. Science.
345:12506842014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
43
|
Tawakol A, Singh P, Mojena M,
Pimentel-Santillana M, Emami H, MacNabb M, Rudd JH, Narula J,
Enriquez JA, Través PG, et al: HIF-1α and PFKFB3 mediate a tight
relationship between proinflammatory activation and anerobic
metabolism in atherosclerotic macrophages. Arterioscler Thromb Vasc
Biol. 35:1463–1471. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
44
|
Bekkering S, van den Munckhof I, Nielen T,
Lamfers E, Dinarello C, Rutten J, de Graaf J, Joosten LA, Netea MG,
Gomes ME and Riksen NP: Innate immune cell activation and
epigenetic remodeling in symptomatic and asymptomatic
atherosclerosis in humans in vivo. Atherosclerosis. 254:228–236.
2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
45
|
Riksen NP and Netea MG: Immunometabolic
control of trained immunity. Mol Aspects Med. 77:1008972021.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
46
|
Tannahill GM, Curtis AM, Adamik J,
Palsson-McDermott EM, McGettrick AF, Goel G, Frezza C, Bernard NJ,
Kelly B, Foley NH, et al: Succinate is an inflammatory signal that
induces IL-1β through HIF-1α. Nature. 496:238–242. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
47
|
Jha AK, Huang SC, Sergushichev A,
Lampropoulou V, Ivanova Y, Loginicheva E, Chmielewski K, Stewart
KM, Ashall J, Everts B, et al: Network integration of parallel
metabolic and transcriptional data reveals metabolic modules that
regulate macrophage polarization. Immunity. 42:419–430. 2015.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
48
|
Benit P, Letouzé E, Rak M, Aubry L,
Burnichon N, Favier J, Gimenez-Roqueplo AP and Rustin P:
Unsuspected task for an old team: Succinate, fumarate and other
Krebs cycle acids in metabolic remodeling. Biochim Biophys Acta.
1837:1330–1337. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
49
|
Saeed S, Quintin J, Kerstens HH, Rao NA,
Aghajanirefah A, Matarese F, Cheng SC, Ratter J, Berentsen K, van
der Ent MA, et al: Epigenetic programming of monocyte-to-macrophage
differentiation and trained innate immunity. Science.
345:12510862014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
50
|
Tall AR and Yvan-Charvet L: Cholesterol,
inflammation and innate immunity. Nat Rev Immunol. 15:104–116.
2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
51
|
Khokha R, Murthy A and Weiss A:
Metalloproteinases and their natural inhibitors in inflammation and
immunity. Nat Rev Immunol. 13:649–665. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
52
|
Ito A, Hong C, Rong X, Zhu X, Tarling EJ,
Hedde PN, Gratton E, Parks J and Tontonoz P: LXRs link metabolism
to inflammation through Abca1-dependent regulation of membrane
composition and TLR signaling. Elife. 4:e080092015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
53
|
Thomas DG, Doran AC, Fotakis P, Westerterp
M, Antonson P, Jiang H, Jiang XC, Gustafsson JÅ, Tabas I and Tall
AR: LXR suppresses inflammatory gene expression and neutrophil
migration through cis-repression and cholesterol efflux. Cell Rep.
25:3774–3785. e42018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
54
|
Ghisletti S, Huang W, Ogawa S, Pascual G,
Lin ME, Willson TM, Rosenfeld MG and Glass CK: Parallel
SUMOylation-dependent pathways mediate gene- and signal-specific
transrepression by LXRs and PPARgamma. Mol Cell. 25:57–70. 2007.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
55
|
Bories G, Colin S, Vanhoutte J, Derudas B,
Copin C, Fanchon M, Daoudi M, Belloy L, Haulon S, Zawadzki C, et
al: Liver X receptor activation stimulates iron export in human
alternative macrophages. Circ Res. 113:1196–1205. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
56
|
Spann NJ, Garmire LX, McDonald JG, Myers
DS, Milne SB, Shibata N, Reichart D, Fox JN, Shaked I, Heudobler D,
et al: Regulated accumulation of desmosterol integrates macrophage
lipid metabolism and inflammatory responses. Cell. 151:138–152.
2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
57
|
Zhang X, McDonald JG, Aryal B,
Canfrán-Duque A, Goldberg EL, Araldi E, Ding W, Fan Y, Thompson BM,
Singh AK, et al: Desmosterol suppresses macrophage inflammasome
activation and protects against vascular inflammation and
atherosclerosis. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA. 118:e21076821182021.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
58
|
Endo-Umeda K, Kim E, Thomas DG, Liu W, Dou
H, Yalcinkaya M, Abramowicz S, Xiao T, Antonson P, Gustafsson JÅ,
et al: Myeloid LXR (Liver X Receptor) deficiency induces
inflammatory gene expression in foamy macrophages and accelerates
atherosclerosis. Arterioscler Thromb Vasc Biol. 42:719–731. 2022.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
59
|
Ecker J, Liebisch G, Englmaier M, Grandl
M, Robenek H and Schmitz G: Induction of fatty acid synthesis is a
key requirement for phagocytic differentiation of human monocytes.
Proc Natl Acad Sci USA. 107:7817–7822. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
60
|
Rong S, Cortés VA, Rashid S, Anderson NN,
McDonald JG, Liang G, Moon YA, Hammer RE and Horton JD: Expression
of SREBP-1c requires SREBP-2-mediated generation of a sterol ligand
for LXR in livers of mice. Elife. 6:e250152017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
61
|
Im SS, Yousef L, Blaschitz C, Liu JZ,
Edwards RA, Young SG, Raffatellu M and Osborne TF: Linking lipid
metabolism to the innate immune response in macrophages through
sterol regulatory element binding protein-1a. Cell Metab.
13:540–549. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
62
|
Arts RJ, Novakovic B, Horst RT, Carvalho
A, Bekkering S, Lachmandas E, Rodrigues F, Silvestre R, Cheng SC,
Wang SY, et al: Glutaminolysis and fumarate accumulation integrate
immunometabolic and epigenetic programs in trained immunity. Cell
Metab. 24:807–819. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
63
|
Huang SC, Everts B, Ivanova Y, O'Sullivan
D, Nascimento M, Smith AM, Beatty W, Love-Gregory L, Lam WY,
O'Neill CM, et al: Cell-intrinsic lysosomal lipolysis is essential
for alternative activation of macrophages. Nat Immunol. 15:846–855.
2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
64
|
Van den Bossche J, O'Neill LA and Menon D:
Macrophage immunometabolism: Where are we (Going)? Trends Immunol.
38:395–406. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
65
|
Malandrino MI, Fucho R, Weber M,
Calderon-Dominguez M, Mir JF, Valcarcel L, Escoté X, Gómez-Serrano
M, Peral B, Salvadó L, et al: Enhanced fatty acid oxidation in
adipocytes and macrophages reduces lipid-induced triglyceride
accumulation and inflammation. Am J Physiol Endocrinol Metab.
308:E756–E769. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
66
|
Feingold KR, Shigenaga JK, Kazemi MR,
McDonald CM, Patzek SM, Cross AS, Moser A and Grunfeld C:
Mechanisms of triglyceride accumulation in activated macrophages. J
Leukoc Biol. 92:829–839. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
67
|
Schneider JG, Yang Z, Chakravarthy MV,
Lodhi IJ, Wei X, Turk J and Semenkovich CF: Macrophage fatty-acid
synthase deficiency decreases diet-induced atherosclerosis. J Biol
Chem. 285:23398–23409. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
68
|
Bostrom P, Magnusson B, Svensson PA,
Wiklund O, Borén J, Carlsson LM, Ståhlman M, Olofsson SO and Hultén
LM: Hypoxia converts human macrophages into triglyceride-loaded
foam cells. Arterioscler Thromb Vasc Biol. 26:1871–1876. 2006.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
69
|
Freigang S, Ampenberger F, Weiss A,
Kanneganti TD, Iwakura Y, Hersberger M and Kopf M: Fatty
acid-induced mitochondrial uncoupling elicits
inflammasome-independent IL-1α and sterile vascular inflammation in
atherosclerosis. Nat Immunol. 14:1045–1053. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
70
|
Rath M, Müller I, Kropf P, Closs EI and
Munder M: Metabolism via Arginase or nitric oxide synthase: Two
competing arginine pathways in macrophages. Front Immunol.
5:5322014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
71
|
Napoli C, de Nigris F, Williams-Ignarro S,
Pignalosa O, Sica V and Ignarro LJ: Nitric oxide and
atherosclerosis: An update. Nitric Oxide. 15:265–279. 2006.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
72
|
Luoma JS and Yla-Herttuala S: Expression
of inducible nitric oxide synthase in macrophages and smooth muscle
cells in various types of human atherosclerotic lesions. Virchows
Arch. 434:561–568. 1999. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
73
|
Esaki T, Hayashi T, Muto E, Yamada K,
Kuzuya M and Iguchi A: Expression of inducible nitric oxide
synthase in T lymphocytes and macrophages of cholesterol-fed
rabbits. Atherosclerosis. 128:39–46. 1997. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
74
|
Rom O, Grajeda-Iglesias C, Najjar M,
Abu-Saleh N, Volkova N, Dar DE, Hayek T and Aviram M:
Atherogenicity of amino acids in the lipid-laden macrophage model
system in vitro and in atherosclerotic mice: A key role for
triglyceride metabolism. J Nutr Biochem. 45:24–38. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
75
|
Wallace C and Keast D: Glutamine and
macrophage function. Metabolism. 41:1016–1020. 1992. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
76
|
Kuznetsova T, Prange KHM, Glass CK and de
Winther MPJ: Transcriptional and epigenetic regulation of
macrophages in atherosclerosis. Nat Rev Cardiol. 17:216–228. 2020.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
77
|
Conrath U: Molecular aspects of defence
priming. Trends Plant Sci. 16:524–531. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
78
|
van der Heijden C, Noz MP, Joosten LAB,
Netea MG, Riksen NP and Keating ST: Epigenetics and trained
immunity. Antioxid Redox Signal. 29:1023–1040. 2018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
79
|
Heintzman ND, Hon GC, Hawkins RD,
Kheradpour P, Stark A, Harp LF, Ye Z, Lee LK, Stuart RK, Ching CW,
et al: Histone modifications at human enhancers reflect global
cell-type-specific gene expression. Nature. 459:108–112. 2009.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
80
|
Rada-Iglesias A, Bajpai R, Swigut T,
Brugmann SA, Flynn RA and Wysocka J: A unique chromatin signature
uncovers early developmental enhancers in humans. Nature.
470:279–283. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
81
|
Ostuni R, Piccolo V, Barozzi I, Polletti
S, Termanini A, Bonifacio S, Curina A, Prosperini E, Ghisletti S
and Natoli G: Latent enhancers activated by stimulation in
differentiated cells. Cell. 152:157–171. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
82
|
Vento-Tormo R, Company C, Rodríguez-Ubreva
J, de la Rica L, Urquiza JM, Javierre BM, Sabarinathan R, Luque A,
Esteller M, Aran JM, et al: IL-4 orchestrates STAT6-mediated DNA
demethylation leading to dendritic cell differentiation. Genome
Biol. 17:42016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
83
|
Dekkers KF, Neele AE, Jukema JW, Heijmans
BT and de Winther MPJ: Human monocyte-to-macrophage differentiation
involves highly localized gain and loss of DNA methylation at
transcription factor binding sites. Epigenetics Chromatin.
12:342019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
84
|
Novakovic B, Habibi E, Wang SY, Arts RJW,
Davar R, Megchelenbrink W, Kim B, Kuznetsova T, Kox M, Zwaag J, et
al: β-glucan reverses the epigenetic state of LPS-induced
immunological tolerance. Cell. 167:1354–1368. e142016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
85
|
Zaret KS and Mango SE: Pioneer
transcription factors, chromatin dynamics, and cell fate control.
Curr Opin Genet Dev. 37:76–81. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
86
|
Glass CK and Natoli G: Molecular control
of activation and priming in macrophages. Nat Immunol. 17:26–33.
2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
87
|
Schmidt SV, Krebs W, Ulas T, Xue J, Baßler
K, Günther P, Hardt AL, Schultze H, Sander J, Klee K, et al: The
transcriptional regulator network of human inflammatory macrophages
is defined by open chromatin. Cell Res. 26:151–170. 2016.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
88
|
Liu T, Zhang L, Joo D and Sun SC: NF-κB
signaling in inflammation. Signal Transduct Target Ther.
2:170232017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
89
|
Heinz S, Benner C, Spann N, Bertolino E,
Lin YC, Laslo P, Cheng JX, Murre C, Singh H and Glass CK: Simple
combinations of lineage-determining transcription factors prime
cis-regulatory elements required for macrophage and B cell
identities. Mol Cell. 38:576–589. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
90
|
Ghisletti S, Barozzi I, Mietton F,
Polletti S, De Santa F, Venturini E, Gregory L, Lonie L, Chew A,
Wei CL, et al: Identification and characterization of enhancers
controlling the inflammatory gene expression program in
macrophages. Immunity. 32:317–328. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
91
|
Fanucchi S, Fok ET, Dalla E, Shibayama Y,
Börner K, Chang EY, Stoychev S, Imakaev M, Grimm D, Wang KC, et al:
Immune genes are primed for robust transcription by proximal long
noncoding RNAs located in nuclear compartments. Nat Genet.
51:138–150. 2019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
92
|
Fanucchi S, Domínguez-Andrés J, Joosten
LAB, Netea MG and Mhlanga MM: The intersection of epigenetics and
metabolism in trained immunity. Immunity. 54:32–43. 2021.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
93
|
Colin S, Chinetti-Gbaguidi G and Staels B:
Macrophage phenotypes in atherosclerosis. Immunol Rev. 262:153–166.
2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
94
|
Cochain C, Vafadarnejad E, Arampatzi P,
Pelisek J, Winkels H, Ley K, Wolf D, Saliba AE and Zernecke A:
Single-cell RNA-seq reveals the transcriptional landscape and
heterogeneity of aortic macrophages in murine atherosclerosis. Circ
Res. 122:1661–1674. 2018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
95
|
Piccolo V, Curina A, Genua M, Ghisletti S,
Simonatto M, Sabò A, Amati B, Ostuni R and Natoli G: Opposing
macrophage polarization programs show extensive epigenomic and
transcriptional cross-talk. Nat Immunol. 18:530–540. 2017.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
96
|
Czimmerer Z, Daniel B, Horvath A, Rückerl
D, Nagy G, Kiss M, Peloquin M, Budai MM, Cuaranta-Monroy I, Simandi
Z, et al: The transcription factor STAT6 mediates direct repression
of inflammatory enhancers and limits activation of alternatively
polarized macrophages. Immunity. 48:75–90. e62018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
97
|
Neele AE, Van den Bossche J, Hoeksema MA
and de Winther MP: Epigenetic pathways in macrophages emerge as
novel targets in atherosclerosis. Eur J Pharmacol. 763:79–89. 2015.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
98
|
Mullican SE, Gaddis CA, Alenghat T, Nair
MG, Giacomin PR, Everett LJ, Feng D, Steger DJ, Schug J, Artis D
and Lazar MA: Histone deacetylase 3 is an epigenomic brake in
macrophage alternative activation. Genes Dev. 25:2480–2488. 2011.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
99
|
Hoeksema MA, Gijbels MJ, Van den Bossche
J, van der Velden S, Sijm A, Neele AE, Seijkens T, Stöger JL,
Meiler S, Boshuizen MC, et al: Targeting macrophage Histone
deacetylase 3 stabilizes atherosclerotic lesions. EMBO Mol Med.
6:1124–1132. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
100
|
Chistiakov DA, Kashirskikh DA, Khotina VA,
Grechko AV and Orekhov AN: Immune-inflammatory responses in
atherosclerosis: The role of myeloid cells. J Clin Med. 8:17982019.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|