|
1
|
Dorri M, Hashemitabar S and Hosseinzadeh
H: Cinnamon (Cinnamomum zeylanicum) as an antidote or a
protective agent against natural or chemical toxicities: A review.
Drug Chem Toxicol. 41:338–351. 2018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
Mishra A, Bhatti R, Singh A and Singh
Ishar MP: Ameliorative effect of the cinnamon oil from
Cinnamomum zeylanicum upon early stage diabetic nephropathy.
Planta medica. 76:412–417. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
Ustaoglu E, Turkoglu Z, Ulgen OA, Caytemel
C and Agirgol S: Anti-inflammatory effect of cinnamaldehyde in a
mouse model of 2,4-dinitrofluorobenzene-induced atopic dermatitis.
Indian J Dermatol. 68:170–177. 2023. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
Tanaka Y, Uchi H and Furue M: Antioxidant
cinnamaldehyde attenuates UVB-induced photoaging. J Dermatol Sci.
96:151–158. 2019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Ding Y, Qiu L, Zhao G, Xu J and Wang S:
Influence of cinnamaldehyde on viral myocarditis in mice. Am J Med
Sci. 340:114–120. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Friedman M: Chemistry, antimicrobial
mechanisms, and antibiotic activities of cinnamaldehyde against
pathogenic bacteria in animal feeds and human foods. J Agric Food
Chem. 65:10406–10423. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
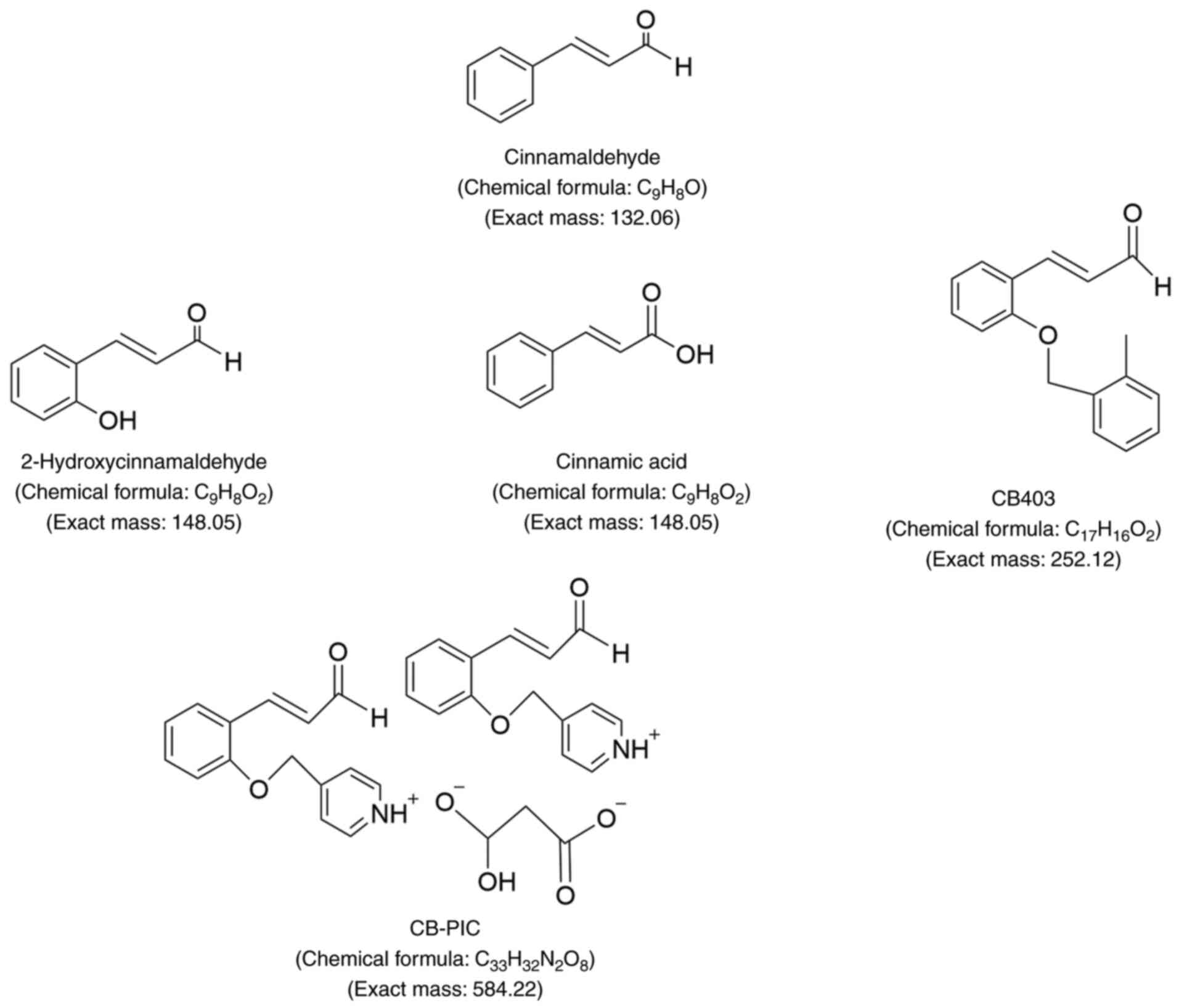
|
|
7
|
Huang J, Wang S, Luo X, Xie Y and Shi X:
Cinnamaldehyde reduction of platelet aggregation and thrombosis in
rodents. Thromb Res. 119:337–342. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Subash Babu P, Prabuseenivasan S and
Ignacimuthu S: Cinnamaldehyde-a potential antidiabetic agent.
Phytomedicine. 14:15–22. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Tung YT, Huang CC, Ho ST, Kuo YH, Lin CC,
Lin CT and Wu JH: Bioactive phytochemicals of leaf essential oils
of Cinnamomum osmophloeum prevent
lipopolysaccharide/D-galactosamine (LPS/D-GalN)-induced acute
hepatitis in mice. J Agric Food Chem. 59:8117–8123. 2011.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Guo X, Sun W, Huang L, Wu L, Hou Y, Qin L
and Liu T: Effect of cinnamaldehyde on glucose metabolism and
vessel function. Med Sci Monit. 23:3844–3853. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Kuru Bektaşoğlu P, Koyuncuoğlu T, Demir D,
Sucu G, Akakın D, Peker Eyüboğlu İ, Yüksel M, Çelikoğlu E, Yeğen BÇ
and Gürer B: Neuroprotective effect of cinnamaldehyde on secondary
brain injury after traumatic brain injury in a rat model. World
Neurosurg. 153:e392–e402. 2021. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Kwon HK, Hwang JS, So JS, Lee CG, Sahoo A,
Ryu JH, Jeon WK, Ko BS, Lee SH, Park ZY and Im SH: Cinnamon extract
induces tumor cell death through inhibition of NFkappaB and AP1.
BMC Cancer. 10:3922010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Nile A, Shin J, Shin J, Park GS, Lee S,
Lee JH, Lee KW, Kim BG, Han SG, Saini RK and Oh JW:
Cinnamaldehyde-Rich cinnamon extract induces cell death in colon
cancer cell lines HCT 116 and HT-29. Int J Mol Sci. 24:81912023.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Zhou Z, Wang C, Bai J, Zeng Z, Yang X, Wei
B and Yang Z: Cinnamaldehyde-modified chitosan hybrid nanoparticles
for DOX delivering to produce synergistic anti-tumor effects. Front
Bioeng Biotechnol. 10:9680652022. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Fang Q, Xu X, Yang L, Xue Y, Cheng X, Wang
X and Tang R: Self-assembled 5-fluorouracil-cinnamaldehyde
nanodrugs for greatly improved chemotherapy in vivo. J Biomater
Appl. 36:592–604. 2021. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Wang Z, Yao J, Guan Z, Wu H, Cheng H, Yan
G and Tang R: pH-triggered small molecule Nano-prodrugs emulsified
from tryptamine-cinnamaldehyde twin drug for targeted synergistic
glioma therapy. Colloids Surf B Biointerfaces. 207:1120522021.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Wang Q, Jia X, Li X, He M, Hao JN, Guan M,
Mao Y, Cao Y, Dai B and Li Y: One-pot fabrication of a
polydopamine-based nanoplatform for GSH triggered trimodal
ROS-amplification for cancer therapy. Biomater Sci. 10:4208–4217.
2022. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
Tu Y, Xiao X, Dong Y, Li J, Liu Y, Zong Q
and Yuan Y: Cinnamaldehyde-based poly(thioacetal): A ROS-awakened
self-amplifying degradable polymer for enhanced cancer
immunotherapy. Biomaterials. 289:1217952022. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
Peters MM and Caldwell J: Studies on
trans-cinnamaldehyde. 1. The influence of dose size and sex on its
disposition in the rat and mouse. Food Chem Toxicol. 32:869–876.
1994. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
Hong SH, Ismail IA, Kang SM, Han DC and
Kwon BM: Cinnamaldehydes in cancer chemotherapy. Phytother Res.
30:754–767. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
Zhang LQ, Zhang ZG, Fu Y and Xu Y:
Research progress of trans-cinnamaldehyde pharmacological effects.
Zhongguo Zhong Yao Za Zhi. 40:4568–4572. 2015.(In Chinese).
PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22
|
Zinn S, Betz T, Medcraft C and Schnell M:
Structure determination of trans-cinnamaldehyde by broadband
microwave spectroscopy. Phys Chem Chem Phys. 17:16080–16085. 2015.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23
|
Bickers D, Calow P, Greim H, Hanifin JM,
Rogers AE, Saurat JH, Sipes IG, Smith RL and Tagami H; RIFM expert
panel, : A toxicologic and dermatologic assessment of cinnamyl
alcohol, cinnamaldehyde and cinnamic acid when used as fragrance
ingredients. Food Chem Toxicol. 43:799–836. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24
|
Vasconcelos NG, Croda J and Simionatto S:
Antibacterial mechanisms of cinnamon and its constituents: A
review. Microb Pathog. 120:198–203. 2018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
25
|
Zhao H, Xie Y, Yang Q, Cao Y, Tu H, Cao W
and Wang S: Pharmacokinetic study of cinnamaldehyde in rats by
GC-MS after oral and intravenous administration. J Pharm Biomed
Anal. 89:150–157. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
26
|
Zhao H, Yang Q, Xie Y, Sun J, Tu H, Cao W
and Wang S: Simultaneous determination of cinnamaldehyde and its
metabolite in rat tissues by gas chromatography-mass spectrometry.
Biomed Chromatogr. 29:182–187. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
27
|
Zhao H, Yuan J, Yang Q, Xie Y, Cao W and
Wang S: Cinnamaldehyde in a novel intravenous submicrometer
emulsion: Pharmacokinetics, tissue distribution, antitumor
efficacy, and toxicity. J Agric Food Chem. 63:6386–6392. 2015.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
28
|
Alqahtani MS, Kazi M, Alsenaidy MA and
Ahmad MZ: Advances in oral drug delivery. Front Pharmacol.
12:6184112021. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
29
|
Wu L, Meng Y, Xu Y and Chu X: Improved
uptake and bioavailability of cinnamaldehyde via solid lipid
nanoparticles for oral delivery. Pharm Dev Technol. 27:1038–1048.
2022. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
30
|
Liu L, Cao W, Xia M, Tian C, Wu W, Cai Y
and Chu X: Self-Emulsifying drug delivery system enhances tissue
distribution of cinnamaldehyde by altering the properties of the
mucus layer. AAPS PharmSciTech. 23:2612022. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
31
|
Cai Y, Liu L, Xia M, Tian C, Wu W, Dong B
and Chu X: SEDDS facilitate cinnamaldehyde crossing the mucus
barrier: The perspective of mucus and Caco-2/HT29 co-culture
models. Int J Pharm. 614:1214612022. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
32
|
Dong B, Chen J, Cai Y, Wu W and Chu X: In
vitro and in vivo evaluation of cinnamaldehyde Microemulsion-Mucus
interaction. J Food Biochem. 46:e143072022. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
33
|
Bray F, Laversanne M, Sung H, Ferlay J,
Siegel RL, Soerjomataram I and Jemal A: Global cancer statistics
2022: GLOBOCAN estimates of incidence and mortality worldwide for
36 cancers in 185 countries. CA Cancer J Clin. 74:229–263. 2024.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
34
|
Bray F, Laversanne M, Weiderpass E and
Soerjomataram I: The ever-increasing importance of cancer as a
leading cause of premature death worldwide. Cancer. 127:3029–3030.
2021. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
35
|
Zheng RS, Chen R, Han BF, Wang SM, Li L,
Sun KX, Zeng HM, Wei WW and He J: Cancer incidence and mortality in
China, 2022. Zhonghua Zhong Liu Za Zhi. 46:221–231. 2024.(In
Chinese). PubMed/NCBI
|
|
36
|
Luo G, Zhang Y, Etxeberria J, Arnold M,
Cai X, Hao Y and Zou H: Projections of lung cancer incidence by
2035 in 40 countries worldwide: Population-based study. JMIR Public
Health Surveill. 9:e436512023. View
Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
37
|
Imai T, Yasuhara K, Tamura T, Ueda M,
Hirose M and Mitsumori K: Inhibitory effects of cinnamaldehyde on
4-(methylnitrosamino)-1-(3-pyridyl)-1-butanone-induced lung
carcinogenesis in rasH2 mice. Cancer Lett. 175:9–16. 2002.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
38
|
Meng M, Geng S, Du Z, Yao J, Zheng Y, Li
Z, Zhang Z, Li J, Duan Y and Du G: Berberine and cinnamaldehyde
together prevent lung carcinogenesis. Oncotarget. 8:76385–76397.
2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
39
|
Tian F, Yu CT, Ye WD and Wang Q:
Cinnamaldehyde induces cell apoptosis mediated by a novel circular
RNA hsa_circ_0043256 in non-small cell lung cancer. Biochem Biophys
Res Commun. 493:1260–1266. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
40
|
Wu C, Zhuang Y, Jiang S, Tian F, Teng Y,
Chen X, Zheng P, Liu S, Zhou J, Wu J, et al: Cinnamaldehyde induces
apoptosis and reverses epithelial-mesenchymal transition through
inhibition of Wnt/β-catenin pathway in non-small cell lung cancer.
Int J Biochem Cell Biol. 84:58–74. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
41
|
Park J and Baek SH: Combination therapy
with cinnamaldehyde and hyperthermia induces apoptosis of A549
Non-Small cell lung carcinoma cells via regulation of reactive
oxygen species and mitogen-activated protein kinase family. Int J
Mol Sci. 21:62292020. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
42
|
Chen R, Wu J, Lu C, Yan T, Qian Y, Shen H,
Zhao Y, Wang J, Kong P and Zhang X: Systematic Transcriptome
analysis reveals the inhibitory function of cinnamaldehyde in
non-small cell lung cancer. Front Pharmacol. 11:6110602020.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
43
|
Qu R, Ma Y, Zhang Z and Fu W: Increasing
burden of colorectal cancer in China. Lancet Gastroenterol Hepatol.
7:7002022. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
44
|
Sargent DJ, Wieand HS, Haller DG, Gray R,
Benedetti JK, Buyse M, Labianca R, Seitz JF, O'Callaghan CJ,
Francini G, et al: Disease-free survival versus overall survival as
a primary end point for adjuvant colon cancer studies: Individual
patient data from 20,898 patients on 18 randomized trials. J Clin
Oncol. 23:8664–8670. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
45
|
Jeong HW, Han DC, Son KH, Han MY, Lim JS,
Ha JH, Lee CW, Kim HM, Kim HC and Kwon BM: Antitumor effect of the
cinnamaldehyde derivative CB403 through the arrest of cell cycle
progression in the G2/M phase. Biochem Pharmacol. 65:1343–1350.
2003. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
46
|
Lee CW, Lee SH, Lee JW, Ban JO, Lee SY,
Yoo HS, Jung JK, Moon DC, Oh KW and Hong JT:
2-hydroxycinnamaldehyde inhibits SW620 colon cancer cell growth
through AP-1 inactivation. J Pharmacol Sci. 104:19–28. 2007.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
47
|
Cho SY, Lee HJ, Lee HJ, Jung DB, Kim H,
Sohn EJ, Kim B, Jung JH, Kwon BM and Kim SH: Activation of
AMP-Activated protein kinase α and extracelluar signal-regulated
kinase mediates CB-PIC-Induced apoptosis in hypoxic SW620
colorectal cancer cells. Evid Based Complement Alternat Med.
2013:9743132013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
48
|
Yun M, Lee D, Park MN, Kim EO, Sohn EJ,
Kwon BM and Kim SH: Cinnamaldehyde derivative (CB-PIC) sensitizes
chemo-resistant cancer cells to drug-induced apoptosis via
suppression of MDR1 and its upstream STAT3 and AKT signalling. Cell
Physiol Biochem. 35:1821–1830. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
49
|
Yu C, Liu SL, Qi MH and Zou X:
Cinnamaldehyde/chemotherapeutic Agents interaction and
drug-metabolizing genes in colorectal cancer. Mol Med Rep.
9:669–676. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
50
|
Long M, Tao S, Rojo de la Vega M, Jiang T,
Wen Q, Park SL, Zhang DD and Wondrak GT: Nrf2-dependent suppression
of azoxymethane/dextran sulfate sodium-induced colon carcinogenesis
by the cinnamon-derived dietary factor cinnamaldehyde. Cancer Prev
Res (Phila). 8:444–454. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
51
|
Dong P, Konno Y, Watari H, Hosaka M,
Noguchi M and Sakuragi N: The impact of microRNA-mediated PI3K/AKT
signaling on epithelial-mesenchymal transition and cancer stemness
in endometrial cancer. J Transl Med. 12:2312014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
52
|
Li J, Teng Y, Liu S, Wang Z, Chen Y, Zhang
Y, Xi S, Xu S, Wang R and Zou X: Cinnamaldehyde affects the
biological behavior of human colorectal cancer cells and induces
apoptosis via inhibition of the PI3K/Akt signaling pathway. Oncol
Rep. 35:1501–1510. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
53
|
Zhang W, Lei W, Shen F, Wang M, Li L and
Chang J: Cinnamaldehyde induces apoptosis and enhances
anti-colorectal cancer activity via covalent binding to HSPD1.
Phytother Res. Apr 22–2023.doi: 10.1002/ptr.7840 (Epub ahead of
print). View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
54
|
Nguyen HA and Kim SA:
2′-Hydroxycinnamaldehyde induces apoptosis through HSF1-mediated
BAG3 expression. Int J Oncol. 50:283–289. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
55
|
Wu CE, Zhuang YW, Zhou JY, Liu SL, Wang RP
and Shu P: Cinnamaldehyde enhances apoptotic effect of oxaliplatin
and reverses epithelial-mesenchymal transition and stemnness in
hypoxic colorectal cancer cells. Exp Cell Res. 383:1115002019.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
56
|
Kosari F, Taheri M, Moradi A, Hakimi Alni
R and Alikhani MY: Evaluation of cinnamon extract effects on clbB
gene expression and biofilm formation in Escherichia coli strains
isolated from colon cancer patients. BMC Cancer. 20:2672020.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
57
|
Petrocelli G, Farabegoli F, Valerii MC,
Giovannini C, Sardo A and Spisni E: Molecules present in plant
essential oils for prevention and treatment of colorectal cancer
(CRC). Molecules. 26:8852021. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
58
|
Wani KD, Kadu BS, Mansara P, Gupta P,
Deore AV, Chikate RC, Poddar P, Dhole SD and Kaul-Ghanekar R:
Synthesis, characterization and in vitro study of biocompatible
cinnamaldehyde functionalized magnetite nanoparticles (CPGF Nps)
for hyperthermia and drug delivery applications in breast cancer.
PLoS One. 9:e1073152014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
59
|
Rad SK, Kanthimathi MS, Abd Malek SN, Lee
GS, Looi CY and Wong WF: Cinnamomum cassia suppresses Caspase-9
through stimulation of AKT1 in MCF-7 cells but not in MDA-MB-231
cells. PLoS One. 10:e01452162015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
60
|
Chiang YF, Chen HY, Huang KC, Lin PH and
Hsia SM: Dietary antioxidant trans-cinnamaldehyde reduced
Visfatin-induced breast cancer progression: In vivo and in vitro
study. Antioxidants (Basel, Switzerland). 8:6252019.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
61
|
Liu Y, An T, Wan D, Yu B, Fan Y and Pei X:
Targets and mechanism used by cinnamaldehyde, the main active
ingredient in cinnamon, in the treatment of breast cancer. Front
Pharmacol. 11:5827192020. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
62
|
Kubatka P, Kello M, Kajo K, Samec M, Jasek
K, Vybohova D, Uramova S, Liskova A, Sadlonova V, Koklesova L, et
al: Chemopreventive and therapeutic efficacy of Cinnamomum
zeylanicum L. bark in experimental breast carcinoma:
Mechanistic in vivo and in vitro analyses. Molecules. 25:13992020.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
63
|
Dong K, Zhao ZZ, Kang J, Lin LR, Chen WT,
Liu JX, Wu XL and Lu TL: Cinnamaldehyde and Doxorubicin Co-Loaded
graphene oxide wrapped mesoporous silica nanoparticles for enhanced
MCF-7 cell apoptosis. Int J Nanomedicine. 15:10285–10304. 2020.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
64
|
Kuo YT, Liu CH, Wong SH, Pan YC and Lin
LT: Small molecules baicalein and cinnamaldehyde are potentiators
of measles virus-induced breast cancer oncolysis. Phytomedicine.
89:1536112021. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
65
|
Schuster C, Wolpert N, Moustaid-Moussa N
and Gollahon LS: Combinatorial effects of the natural products
arctigenin, chlorogenic acid, and cinnamaldehyde commit oxidation
assassination on breast cancer cells. Antioxidants (Basel).
11:5912022. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
66
|
Yao P, Wang X, Wang Q, Dai Q, Peng Y, Yuan
Q, Mou N, Lv S, Weng B, Wang Y and Sun F: Cyclic RGD-functionalized
pH/ROS Dual-responsive nanoparticle for targeted breast cancer
therapy. Pharmaceutics. 15:18272023. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
67
|
Taniguchi H: Liver cancer 2.0. Int J Mol
Sci. 24:172752023. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
68
|
Wu SJ, Ng LT and Lin CC: Effects of
vitamin E on the cinnamaldehyde-induced apoptotic mechanism in
human PLC/PRF/5 cells. Clin Exp Pharmacol Physiol. 31:770–776.
2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
69
|
Moon EY, Lee MR, Wang AG, Lee JH, Kim HC,
Kim HM, Kim JM, Kwon BM and Yu DY: Delayed occurrence of
H-ras12V-induced hepatocellular carcinoma with long-term treatment
with cinnamaldehydes. Eur J Pharmacol. 530:270–275. 2006.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
70
|
Huang TC, Chung YL, Wu ML and Chuang SM:
Cinnamaldehyde enhances Nrf2 nuclear translocation to upregulate
phase II detoxifying enzyme expression in HepG2 cells. J Agric Food
Chem. 59:5164–5171. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
71
|
Ng LT and Wu SJ: Antiproliferative
activity of cinnamomum cassia constituents and effects of
pifithrin-alpha on their apoptotic signaling pathways in Hep G2
cells. Evid Based Complement Alternat Med. 2011:4921482011.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
72
|
Lin LT, Tai CJ, Chang SP, Chen JL, Wu SJ
and Lin CC: Cinnamaldehyde-induced apoptosis in human hepatoma
PLC/PRF/5 cells involves the mitochondrial death pathway and is
sensitive to inhibition by cyclosporin A and z-VAD-fmk. Anticancer
Agents Med Chem. 13:1565–1574. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
73
|
Perng DS, Tsai YH, Cherng J, Kuo CW, Shiao
CC and Cherng JM: Discovery of a novel anti-cancer agent targeting
both topoisomerase I and II in hepatocellular carcinoma Hep 3B
cells in vitro and in vivo: Cinnamomum verum component
2-methoxycinnamaldehyde. J Drug Target. 24:624–634. 2016.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
74
|
Aly SM, Fetaih HA, Hassanin AAI,
Abomughaid MM and Ismail AA: Protective effects of garlic and
cinnamon oils on hepatocellular carcinoma in albino rats. Anal Cell
Pathol (Amst). 2019:98954852019.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
75
|
Kim H, Lee HJ, Sim DY, Park JE, Ahn CH,
Park SY, Jang E, Kim B and Kim SH: The antitumor effect of
cinnamaldehyde derivative CB-PIC in hepatocellular carcinoma cells
via inhibition of pyruvate and STAT3 signaling. Int J Mol Sci.
23:64612022. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
76
|
Han L, Mei J, Ma J, Wang F, Gu Z, Li J,
Zhang Z, Zeng Y, Lou X, Yao X, et al: Cinnamaldehyde induces
endogenous apoptosis of the prostate cancer-associated fibroblasts
via interfering the Glutathione-associated mitochondria function.
Med Oncol. 37:912020. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
77
|
Mei J, Ma J, Xu Y, Wang Y, Hu M, Ma F, Qin
Z, Xue R and Tao N: Cinnamaldehyde treatment of prostate
cancer-associated fibroblasts prevents their inhibitory effect on T
cells through Toll-Like receptor 4. Drug Des Devel Ther.
14:3363–3372. 2020. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
78
|
Zhang X, Linder S and Bazzaro M: Drug
development targeting the ubiquitin-proteasome system (UPS) for the
treatment of human cancers. Cancers (Basel). 12:9022020. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
79
|
Concannon CG, Koehler BF, Reimertz C,
Murphy BM, Bonner C, Thurow N, Ward MW, Villunger A, Strasser A,
Kögel D and Prehn JH: Apoptosis induced by proteasome inhibition in
cancer cells: Predominant role of the p53/PUMA pathway. Oncogene.
26:1681–1692. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
80
|
Gopalakrishnan S and Ismail A: Aromatic
monophenols from cinnamon bark act as proteasome inhibitors by
upregulating ER stress, suppressing FoxM1 expression, and inducing
apoptosis in prostate cancer cells. Phytother Res. 35:5781–5794.
2021. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
81
|
Gopalakrishnan S, Dhaware M, Sudharma AA,
Mullapudi SV, Siginam SR, Gogulothu R, Mir IA and Ismail A:
Chemopreventive effect of cinnamon and its bioactive compounds in a
rat model of premalignant prostate carcinogenesis. Cancer Prev Res
(Phila). 16:139–151. 2023. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
82
|
Moon KH and Pack MY: Cytotoxicity of
cinnamic aldehyde on leukemia L1210 cells. Drug Chem Toxicol.
6:521–535. 1983. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
83
|
Ka H, Park HJ, Jung HJ, Choi JW, Cho KS,
Ha J and Lee KT: Cinnamaldehyde induces apoptosis by ROS-mediated
mitochondrial permeability transition in human promyelocytic
leukemia HL-60 cells. Cancer Lett. 196:143–152. 2003. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
84
|
Zhang JH, Liu LQ, He YL, Kong WJ and Huang
SA: Cytotoxic effect of trans-cinnamaldehyde on human leukemia K562
cells. Acta Pharmacol Sin. 31:861–866. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
85
|
Schoene NW, Kelly MA, Polansky MM and
Anderson RA: A polyphenol mixture from cinnamon targets p38 MAP
kinase-regulated signaling pathways to produce G2/M arrest. J Nutr
Biochem. 20:614–620. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
86
|
Liu LQ, Liu ZL, Wang X, Cui HY, Jin MD,
Wang DY and Huang SA: Mechanism of cinnamic aldehyde-inducing
apoptosis of chronic myeloid Leukemic cells in vitro. Zhongguo Shi
Yan Xue Ye Xue Za Zhi. 19:617–620. 2011.(In Chinese). PubMed/NCBI
|
|
87
|
Kim JE, Son JE, Jeong H, Joon Kim D, Seo
SK, Lee E, Lim TG, Kim JR, Chen H, Bode AM, et al: A Novel
Cinnamon-Related natural product with Pim-1 inhibitory activity
inhibits leukemia and skin cancer. Cancer Res. 75:2716–2728. 2015.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
88
|
Cui Q, Wang JQ, Assaraf YG, Ren L, Gupta
P, Wei L, Ashby CR Jr, Yang DH and Chen ZS: Modulating ROS to
overcome multidrug resistance in cancer. Drug Resist Updat.
41:1–25. 2018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
89
|
Farokhzad OC and Langer R: Impact of
nanotechnology on drug delivery. ACS Nano. 3:16–20. 2009.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
90
|
Liou GY and Storz P: Reactive oxygen
species in cancer. Free Radic Res. 44:479–496. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
91
|
Dong K, Yang C, Yan Y, Wang P, Sun Y, Wang
K, Lu T, Chen Q, Zhang Y, Xing J and Dong Y: Investigation of the
intracellular oxidative stress amplification, safety and anti-tumor
effect of a kind of novel redox-responsive micelle. J Mater Chem B.
6:1105–1117. 2018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
92
|
Bansal A and Simon MC: Glutathione
metabolism in cancer progression and treatment resistance. J Cell
Biol. 217:2291–2298. 2018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
93
|
Liu Q, Ding X, Xu X, Lai H, Zeng Z, Shan
T, Zhang T, Chen M, Huang Y, Huang Z, et al: Tumor-targeted
hyaluronic acid-based oxidative stress nanoamplifier with ROS
generation and GSH depletion for antitumor therapy. Int J Biol
Macromol. 207:771–783. 2022. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
94
|
Bai Y, Wang R, Wang X, Duan X, Yan X, Liu
C and Tian W: Hyaluronic acid coated Nano-particles for
H2O2-elevation augmented Photo-/Chemodynamic
therapy. Int J Biol Macromol. 245:1255232023. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
95
|
National Toxicology Program, . NTP
toxicology and carcinogenesis studies of trans-cinnamaldehyde (CAS
No. 14371-10-9) in F344/N rats and B6C3F1 mice (feed studies). Natl
Toxicol Program Tech Rep Ser. 2004:1–281. 2004.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
96
|
Hooth MJ, Sills RC, Burka LT, Haseman JK,
Witt KL, Orzech DP, Fuciarelli AF, Graves SW, Johnson JD and Bucher
JR: Toxicology and carcinogenesis studies of microencapsulated
trans-cinnamaldehyde in rats and mice. Food Chem Toxicol.
42:1757–1768. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
97
|
Anand P, Murali KY, Tandon V, Murthy PS
and Chandra R: Insulinotropic effect of cinnamaldehyde on
transcriptional regulation of pyruvate kinase, phosphoenolpyruvate
carboxykinase, and GLUT4 translocation in experimental diabetic
rats. Chem Biol Interact. 186:72–81. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
98
|
Kiwamoto R, Ploeg D, Rietjens IM and Punt
A: Dose-dependent DNA adduct formation by cinnamaldehyde and other
food-borne α,β-unsaturated aldehydes predicted by physiologically
based in silico modelling. Toxicol In Vitro. 31:114–125. 2016.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
99
|
Mao M, Zheng W, Deng B, Wang Y, Zhou D,
Shen L, Niku W and Zhang N: Cinnamaldehyde alleviates
doxorubicin-induced cardiotoxicity by decreasing oxidative stress
and ferroptosis in cardiomyocytes. PLoS One. 18:e02921242023.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
100
|
Abd El Salam ASG, Samaha MM and Abd
Elrazik NA: Cytoprotective effects of cinnamaldehyde and adipoRon
against cyclophosphamide-induced cardio-renal toxicity in rats:
Insights into oxidative stress, inflammation, and apoptosis. Int
Immunopharmacol. 124:1110442023. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
101
|
Bae WY, Choi JS, Kim JE and Jeong JW:
Cinnamic aldehyde suppresses hypoxia-induced angiogenesis via
inhibition of hypoxia-inducible factor-1α expression during tumor
progression. Biochem Pharmacol. 98:41–50. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
102
|
DeCaprio J and Kohl TO: Chromatin
Immunoprecipitation. Cold Spring Harbor Protocols. 2020:0986652020.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
103
|
Nakato R and Sakata T: Methods for
ChIP-seq analysis: A practical workflow and advanced applications.
Methods. 187:44–53. 2021. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
104
|
Hino S, Sato T and Nakao M: Chromatin
immunoprecipitation sequencing (ChIP-seq) for detecting histone
modifications and modifiers. Methods Mol Biol. 2577:55–64. 2023.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
105
|
Kumar P, Kiran S, Saha S, Su Z, Paulsen T,
Chatrath A, Shibata Y, Shibata E and Dutta A: ATAC-seq identifies
thousands of extrachromosomal circular DNA in cancer and cell
lines. Sci Adv. 6:eaba24892020. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|