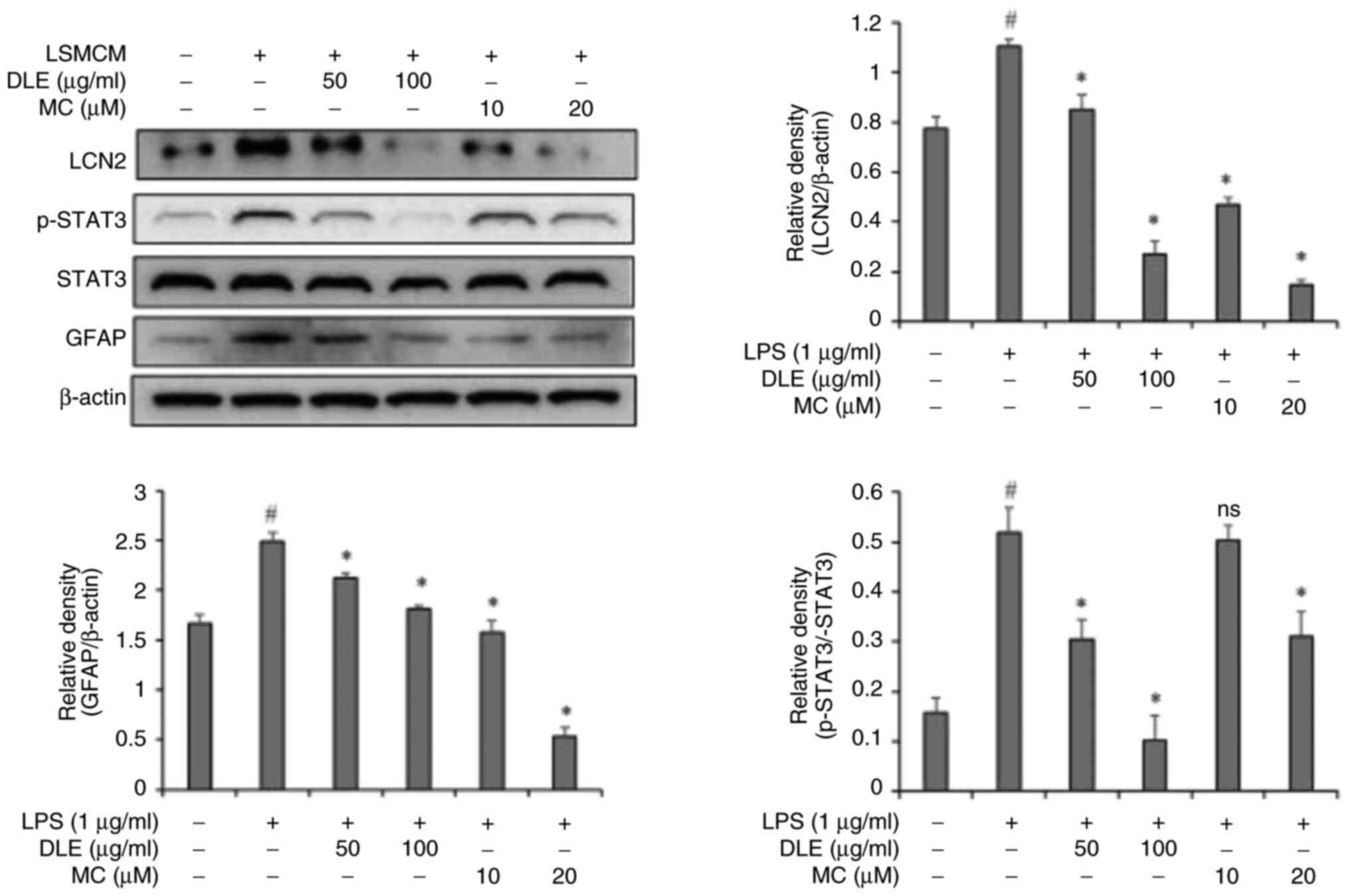
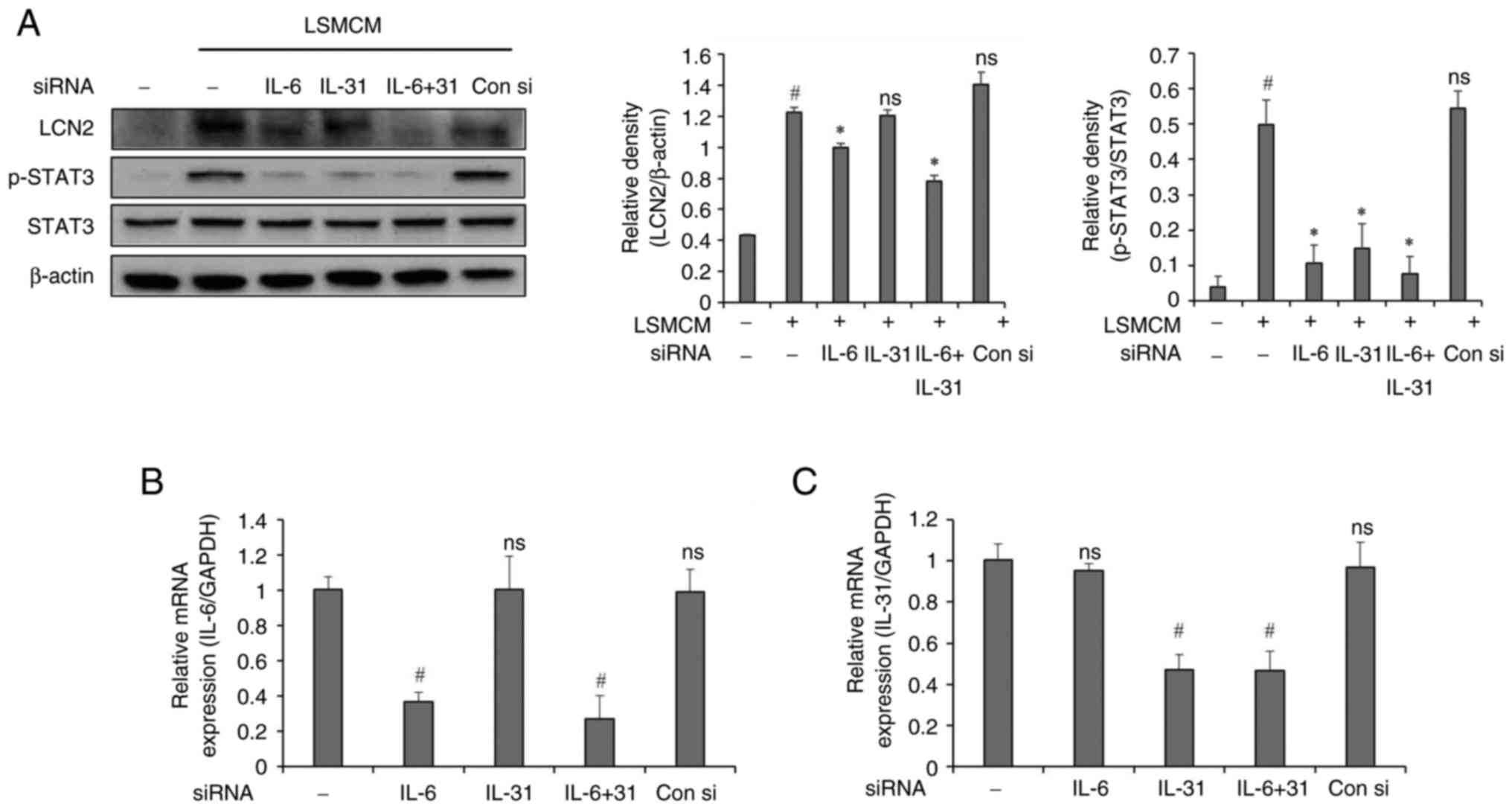
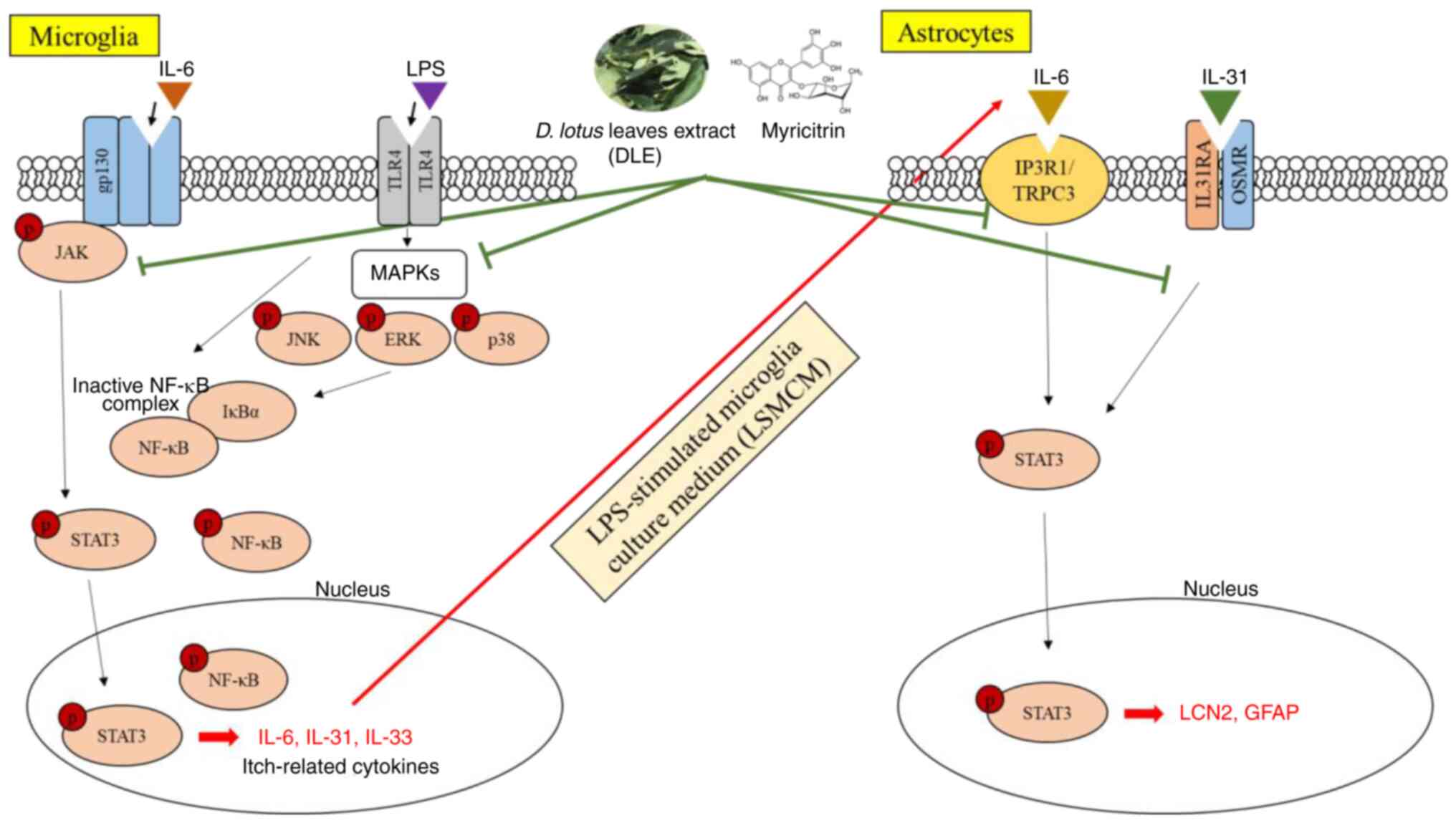
|
1
|
Bourane S, Duan B, Koch SC, Dalet A, Britz
O, Garcia-Campmany L, Kim E, Cheng L, Ghosh A, Ma Q and Goulding M:
Gate control of mechanical itch by a subpopulation of spinal cord
interneurons. Science. 350:550–554. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
Patel T and Yosipovitch G: Therapy of
pruritus. Expert Opin Pharmacother. 11:1673–1682. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
Lay M and Dong X: Neural mechanisms of
itch. Annu Rev Neurosci. 43:187–205. 2020. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
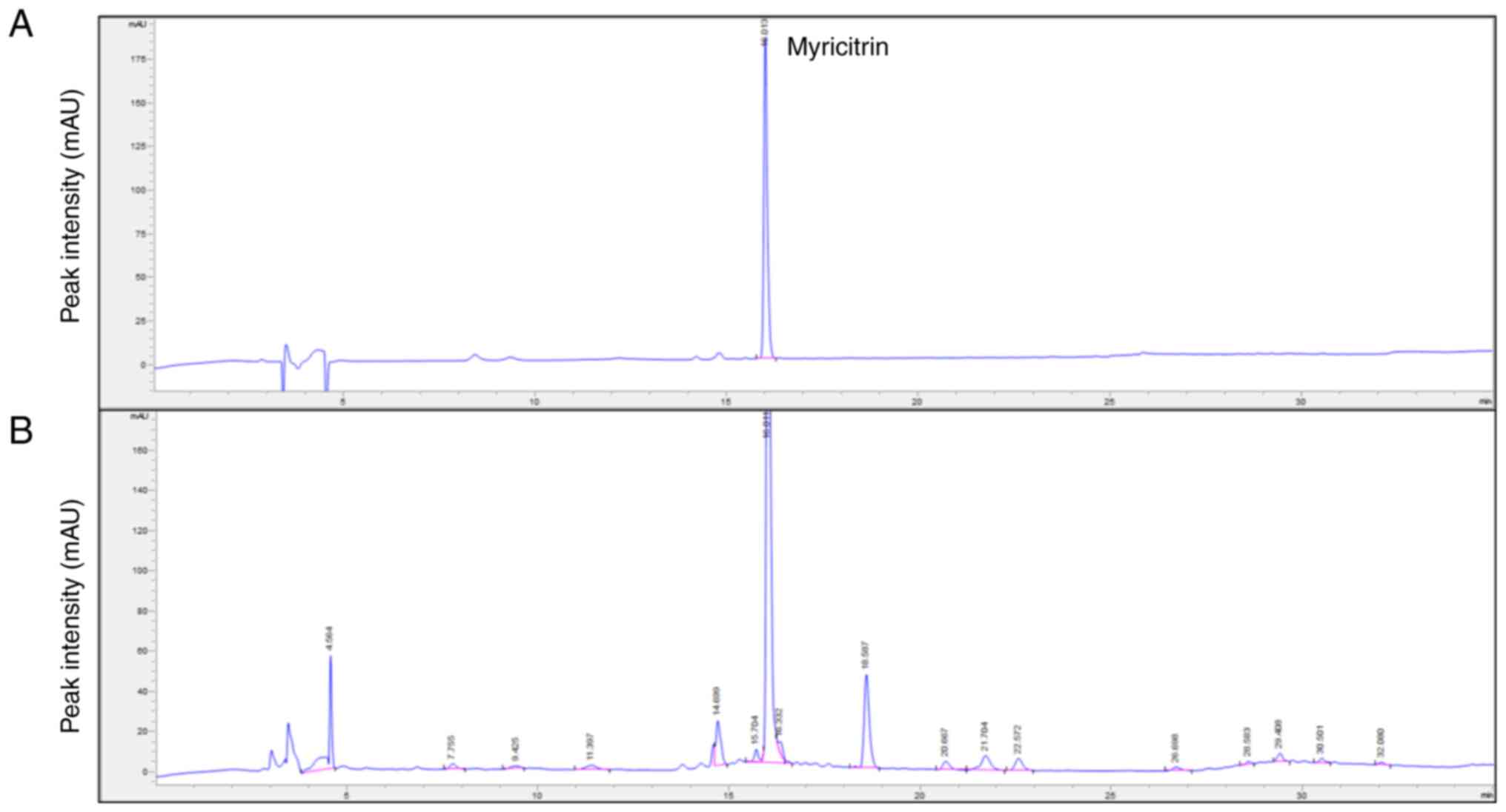
Sun YG and Chen ZF: A gastrin-releasing
peptide receptor mediates the itch sensation in the spinal cord.
Nature. 448:700–703. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
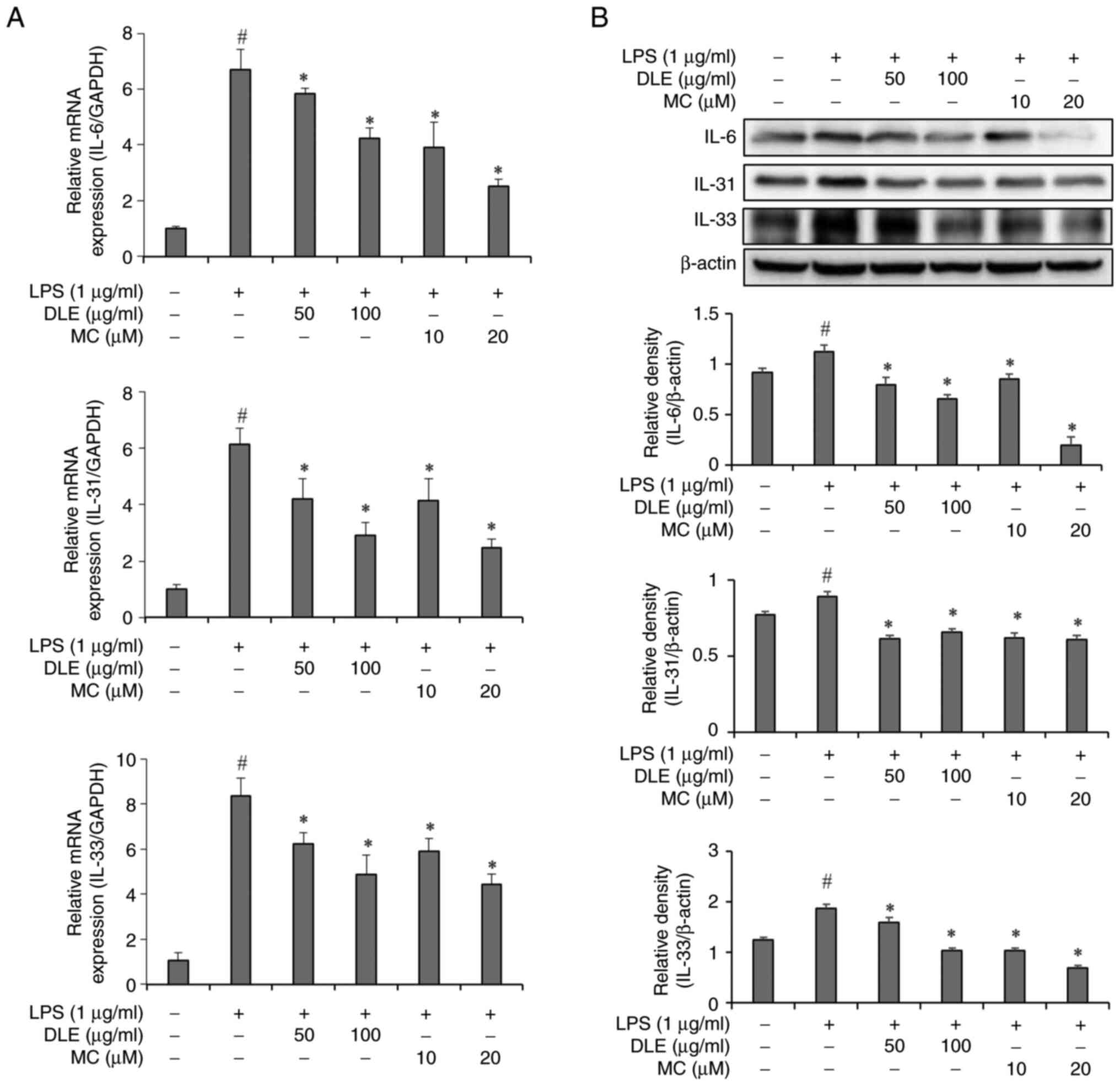
|
5
|
Colonna M and Butovsky O: Microglia
function in the central nervous system during health and
neurodegeneration. Annu Rev Immunol. 35:441–468. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
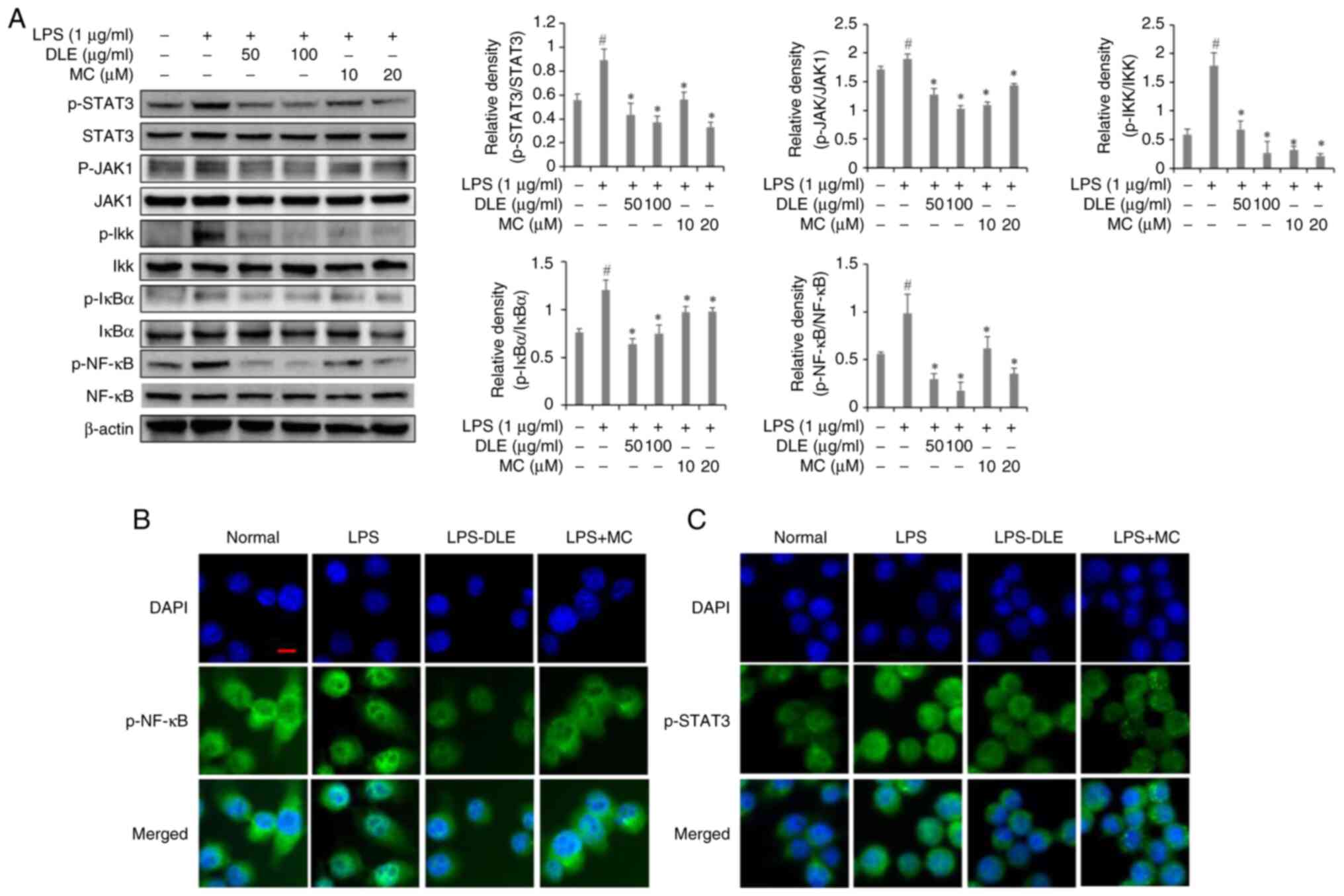
|
|
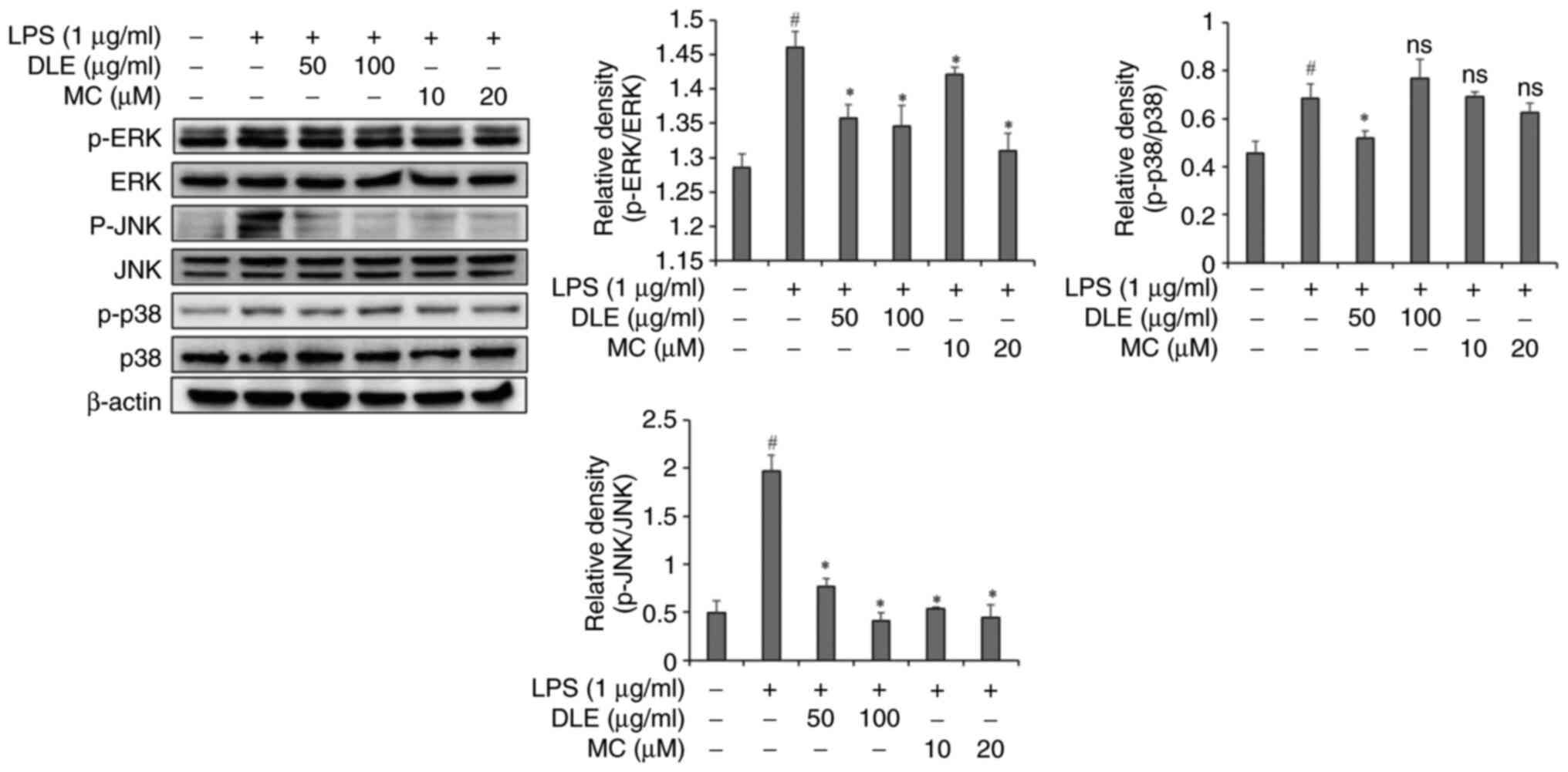
6
|
Muzio L, Viotti A and Martino G: Microglia
in neuroinflammation and neurodegeneration: From understanding to
therapy. Front Neurosci. 15:7420652021. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Tjalkens RB, Popichak KA and Kirkley KA:
Inflammatory activation of microglia and astrocytes in manganese
neurotoxicity. Adv Neurobiol. 18:159–181. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Yang Y, Mou B, Zhang QR, Zhao HX, Zhang
JY, Yun X, Xiong MT, Liu Y, Liu YU, Pan H, et al: Microglia are
involved in regulating histamine-dependent and non-dependent itch
transmissions with distinguished signal pathways. Glia.
71:2541–2558. 2023. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Liu X, Wang Y, Zeng Y, Wang D, Wen Y, Fan
L, He Y, Zhang J, Sun W, Liu Y and Tao A: Microglia-neuron
interactions promote chronic itch via the NLRP3-IL-1β-GRPR axis.
Allergy. 78:1570–1584. 2023. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Herculano-Houzel S: The glia/neuron ratio:
How it varies uniformly across brain structures and species and
what that means for brain physiology and evolution. Glia.
62:1377–1391. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Grace PM, Hutchinson MR, Maier SF and
Watkins LR: Pathological pain and the neuroimmune interface. Nat
Rev Immunol. 14:217–231. 2014. View
Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Svensson CI and Brodin E: Spinal
astrocytes in pain processing: Non-neuronal cells as therapeutic
targets. Mol Interv. 10:25–38. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Shiratori-Hayashi M, Yamaguchi C, Eguchi
K, Shiraishi Y, Kohno K, Mikoshiba K, Inoue K, Nishida M and Tsuda
M: Astrocytic STAT3 activation and chronic itch require
IP3R1/TRPC-dependent Ca2+ signals in mice. J Allergy
Clin Immunol. 147:1341–1353. 2021. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Uddin G, Rauf A, Siddiqui BS, Muhammad N,
Khan A and Shah SUA: Anti-nociceptive, anti-inflammatory and
sedative activities of the extracts and chemical constituents of
Diospyros lotus L. Phytomedicine. 21:954–959. 2014.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Uddin G, Rauf A, Siddiqui B, Arfan M,
Rahman I and Khan I: Proximate chemical composition and
antimicrobial activities of fixed oils from Diospyros lotus
L. Med Chem. 3:282–285. 2013.
|
|
16
|
Yin H, Yan HH, Qin CQ, Li HR, Li X and Ren
DF: Protective effect of fermented Diospyros lotus L.
extracts against the high glucose-induced apoptosis of MIN6 cells.
J Food Biochem. 45:e136852021. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Loizzo MR, Said A, Tundis R, Hawas UW,
Rashed K and Menichini F, Frega NG and Menichini F: Antioxidant and
antiproliferative activity of Diospyros lotus L. extract and
isolated compounds. Plant Food Hum Nutr. 64:264–270. 2009.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
Cho BO, Che DN, Shin JY, Kang HJ, Kim JH,
Kim HY, Cho WG and Jang SI: Ameliorative effects of Diospyros
lotus leaf extract against UVB-induced skin damage in BALB/c
mice. Biomed Pharmacother. 95:264–274. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
Cho BO, Yin HH, Fang CZ, Kim SJ, Jeong SI
and Jang SI: Hepatoprotective effect of Diospyros lotus leaf
extract against acetaminophen-induced acute liver injury in mice.
Food Sci Biotechnol. 24:2205–2212. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
20
|
Che DN, Kang HJ, Cho BO, Shin JY and Jang
SI: Combined effects of Diospyros lotus leaf and grape stalk
extract in high-fat-diet-induced obesity in mice. Food Sci
Biotechnol. 28:1207–1215. 2019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
Cho BO, Che DN, Yin HH, Shin JY and Jang
SI: Diospyros lotus leaf and grapefruit stem extract
synergistically ameliorate atopic dermatitis-like skin lesion in
mice by suppressing infiltration of mast cells in skin lesions.
Biomed Pharmacother. 89:819–826. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22
|
Cho BO, Shin JY, Kim JS, Kim JS, Che DN,
Kang HJ, Kang HJ, Oh H, Kim YS and Jang SI: Enzyme-treated date
plum leave extract ameliorates atopic dermatitis-like skin lesion
in hairless mice. Asian Pac J Trop Biomed. 10:239–247. 2020.
View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
23
|
Shin JY, Cho BO, Park JH, Kang ES, Kim YS
and Jang SI: Diospyros lotus leaf extract and its main
component myricitrin regulate pruritus through the inhibition of
astrocyte activation. Exp Ther Med. 26:3232023. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24
|
Livak KJ and Schmittgen TD: Analysis of
relative gene expression data using real-time quantitative PCR and
the 2(−Delta Delta C(T)) method. Methods. 25:402–408. 2001.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
25
|
Zheng LT, Ryu GM, Kwon BM, Lee WH and Suk
K: Anti-inflammatory effects of catechols in
lipopolysaccharide-stimulated microglia cells: Inhibition of
microglial neurotoxicity. Eur J Pharmacol. 588:106–113. 2008.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
26
|
Rivest S: Regulation of innate immune
responses in the brain. Nat Rev Immunol. 9:429–439. 2009.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
27
|
Che DN, Cho BO, Kim JS, Shin JY, Kang HJ
and Jang SI: Effect of luteolin and apigenin on the production of
IL-31 and IL-33 in lipopolysaccharides-activated microglia cells
and their mechanism of action. Nutrients. 12:8112020. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
28
|
Storan ER, O'Gorman SM, McDonald ID and
Steinhoff M: Role of cytokines and chemokines in itch. Handb Exp
Pharmacol. 226:163–176. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
29
|
Keshari S, Sipayung AD, Hsieh CC, Su LJ,
Chiang YR, Chang HC, Yang WC, Chuang TH, Chen CL and Huang CM:
Il-6/P-Btk/P-Erk signaling mediates calcium phosphate-induced
pruritus. FASEB J. 33:12036–12046. 2019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
30
|
Shiratori-Hayashi M and Tsuda M: Spinal
glial cells in itch modulation. Pharmacol Res Perspect.
9:e007542021. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
31
|
Cevikbas F, Wang X, Akiyama T, Kempkes C,
Savinko T, Antal A, Kukova G, Buhl T, Ikoma A, Buddenkotte J, et
al: A sensory neuron-expressed IL-31 receptor mediates T helper
cell-dependent itch: Involvement of TRPV1 and TRPA1. J Allergy Clin
Immunol. 133:448–460. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
32
|
Yasuoka S, Kawanokuchi J, Parajuli B, Jin
S, Doi Y, Noda M, Sonobe Y, Takeuchi H, Mizuno T and Suzumura A:
Production and functions of IL-33 in the central nervous system.
Brain Res. 1385:8–17. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
33
|
Lawrence T: The nuclear factor NF-κB
pathway in inflammation. Cold Spring Harb Perspect Biol.
1:a0016512009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
34
|
Viatour P, Merville MP, Bours V and
Chariot A: Phosphorylation of NF-κB and IκB proteins: Implications
in cancer and inflammation. Trends Biochem Sci. 30:43–52. 2005.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
35
|
Park HY, Han MH, Park C, Jin CY, Kim GY,
Choi IW, Kim ND, Nam TJ, Kwon TK and Choi YH: Anti-inflammatory
effects of fucoidan through inhibition of NF-κB, MAPK and Akt
activation in lipopolysaccharide-induced BV2 microglia cells. Food
Chem Toxicol. 49:1745–1752. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
36
|
Kaminska B: MAPK signalling pathways as
molecular targets for anti-inflammatory therapy-from molecular
mechanisms to therapeutic benefits. Biochim Biophys Acta.
1754:253–262. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
37
|
Vermeulen L, De Wilde G, Van Damme P,
Berghe WV and Haegeman G: Transcriptional activation of the NF-κB
p65 subunit by mitogen-and stress-activated protein kinase-1
(MSK1). EMBO J. 22:1313–1324. 2003. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
38
|
Marrero MB, Venema VJ, He H, Caldwell RB
and Venema RC: Inhibition by the JAK/STAT pathway of IFNγ-and
LPS-stimulated nitric oxide synthase induction in vascular smooth
muscle cells. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 252:508–512. 1998.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
39
|
Samavati L, Rastogi R, Du W, Hüttemann M,
Fite A and Franchi L: STAT3 tyrosine phosphorylation is critical
for interleukin 1 beta and interleukin-6 production in response to
lipopolysaccharide and live bacteria. Mol Immunol. 46:1867–1877.
2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
40
|
Morris R, Kershaw NJ and Babon JJ: The
molecular details of cytokine signaling via the JAK/STAT pathway.
Protein Sci. 27:1984–2009. 2018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
41
|
Ren Y, Yue B, Ren G, Yu Z, Luo X, Sun A,
Zhang J, Han M, Wang Z and Dou W: Activation of PXR by
alantolactone ameliorates DSS-induced experimental colitis via
suppressing NF-κB signaling pathway. Sci Rep. 9:166362019.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
42
|
Pan S, Liu R, Wu X, Ma K, Luo W, Nie K,
Zhang C, Meng X, Tong T, Chen X, et al: LncRNA NEAT1 mediates
intestinal inflammation by regulating TNFRSF1B. Ann Transl Med.
9:7732021. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
43
|
Zhang Q, Putheti P, Zhou Q, Liu Q and Gao
W: Structures and biological functions of IL-31 and IL-31
receptors. Cytokine Growth Factor Rev. 19:347–356. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
44
|
Datsi A, Steinhoff M, Ahmad F, Alam M and
Buddenkotte J: Interleukin-31: The ‘itchy’ cytokine in inflammation
and therapy. Allergy. 76:2982–2997. 2021. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
45
|
Ceyzériat K, Abjean L, Carrillo-de Sauvage
MA, Haim LB and Escartin C: The complex STATes of astrocyte
reactivity: How are they controlled by the JAK–STAT3 pathway?
Neurosci. 330:205–218. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
46
|
Green D and Dong X: Supporting itch: A new
role for astrocytes in chronic itch. Nat Med. 21:841–842. 2015.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
47
|
Shiratori-Hayashi M, Koga K, Tozaki-Saitoh
H, Kohro Y, Toyonaga H, Yamaguchi C, Hasegawa A, Nakahara T,
Hachisuka J, Akira S, et al: STAT3-dependent reactive astrogliosis
in the spinal dorsal horn underlies chronic itch. Nat Med.
21:927–931. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
48
|
Nemmer JM, Kuchner M, Datsi A, Oláh P,
Julia V, Raap U and Homey B: Interleukin-31 signaling bridges the
gap between immune cells, the nervous system and epithelial
tissues. Front Med (Lausanne). 8:6390972021. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
49
|
Domitrović R, Rashed K, Cvijanović O,
Vladimir-Knežević S, Škoda M and Višnić A: Myricitrin exhibits
antioxidant, anti-inflammatory and antifibrotic activity in carbon
tetrachloride-intoxicated mice. Chem Biol Interact. 230:21–29.
2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
50
|
Shimosaki S, Tsurunaga Y, Itamura H and
Nakamura M: Anti-allergic effect of the flavonoid myricitrin from
Myrica rubra leaf extracts in vitro and in vivo. Nat Prod Res.
25:374–380. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
51
|
Qi S, Feng Z, Li Q, Qi Z and Zhang Y:
Myricitrin modulates NADPH oxidase-dependent ROS production to
inhibit endotoxin-mediated inflammation by blocking the JAK/STAT1
and NOX2/p47 phox pathways. Oxid Med Cell Longev. 2017:97387452017.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|