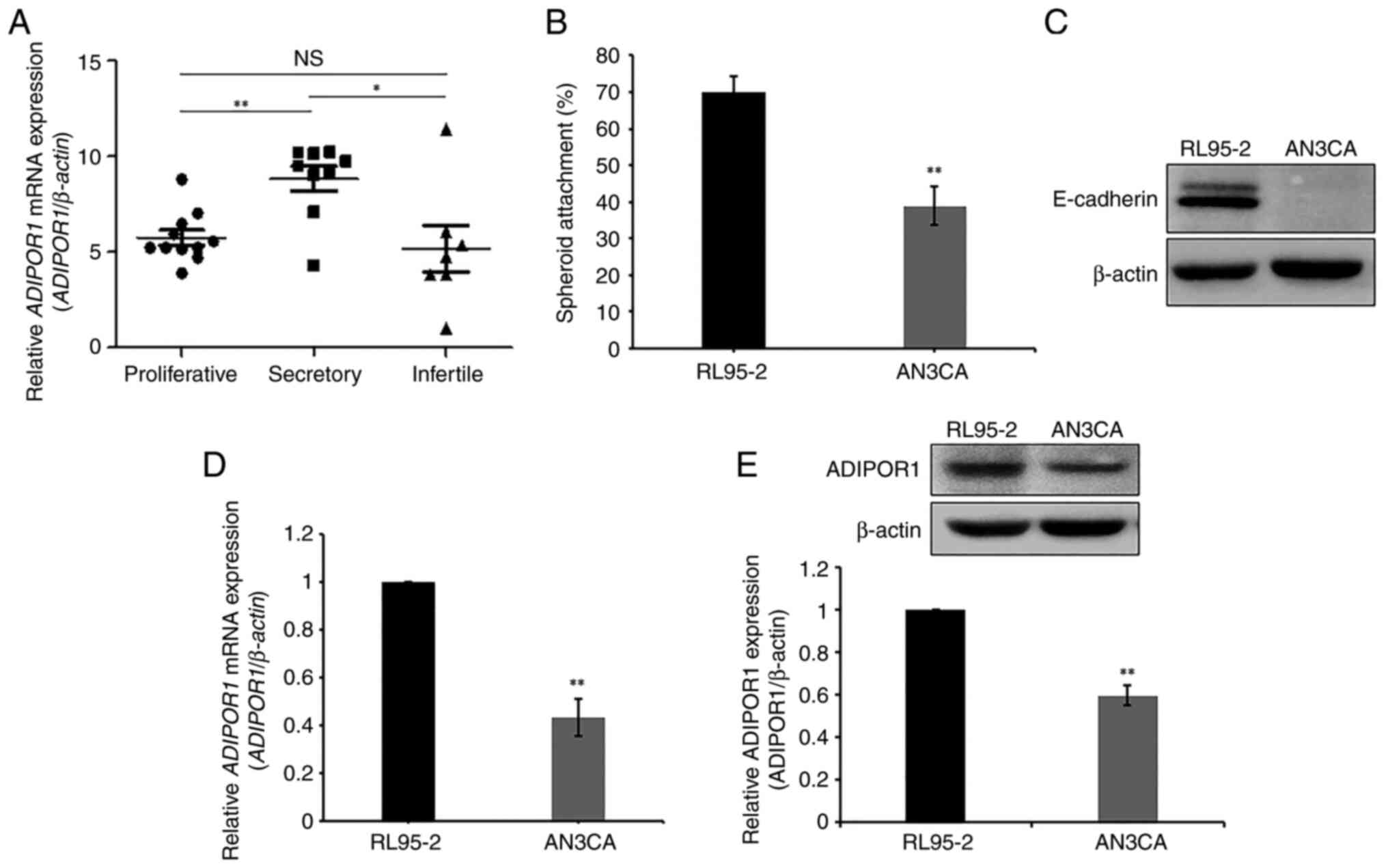
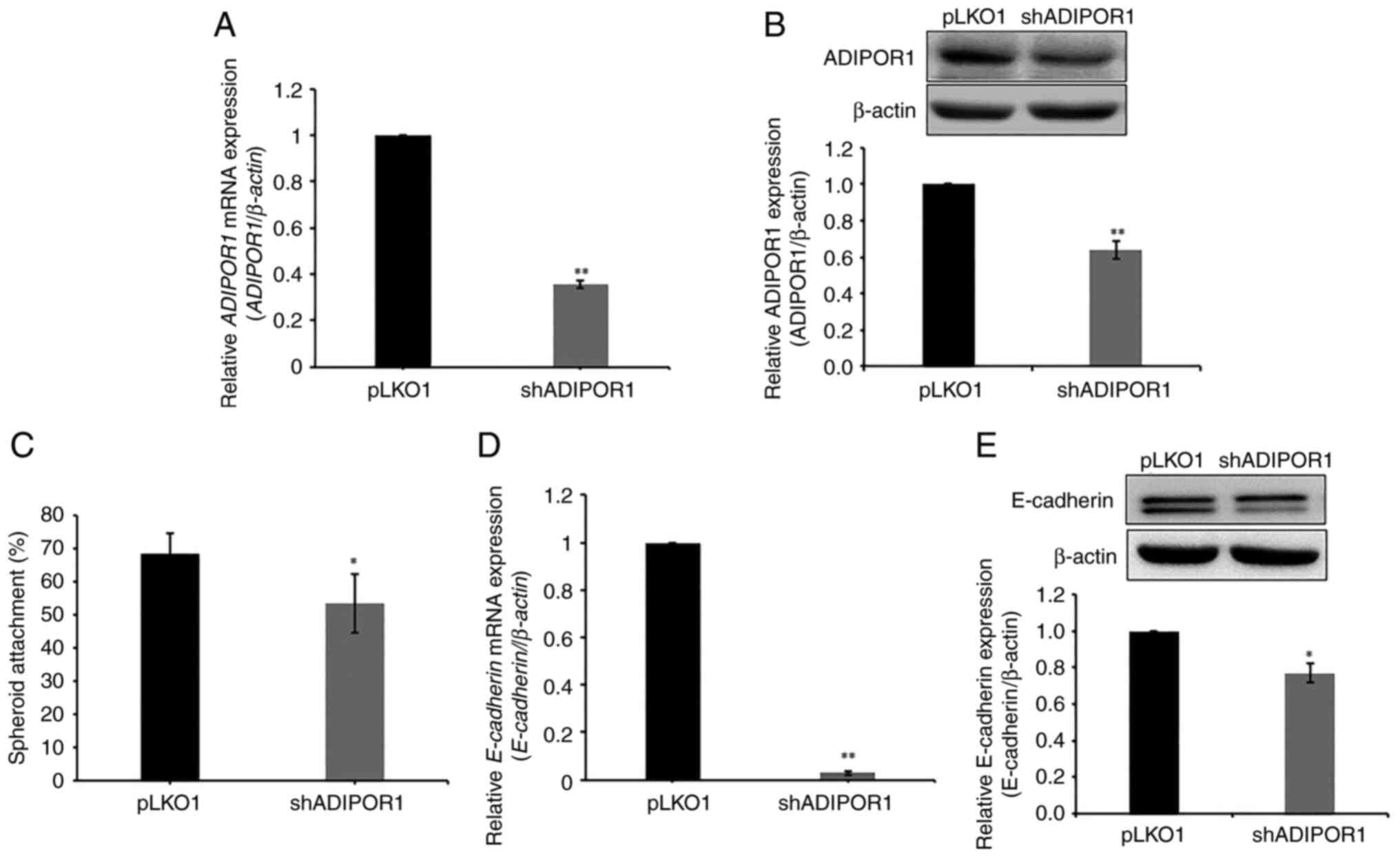
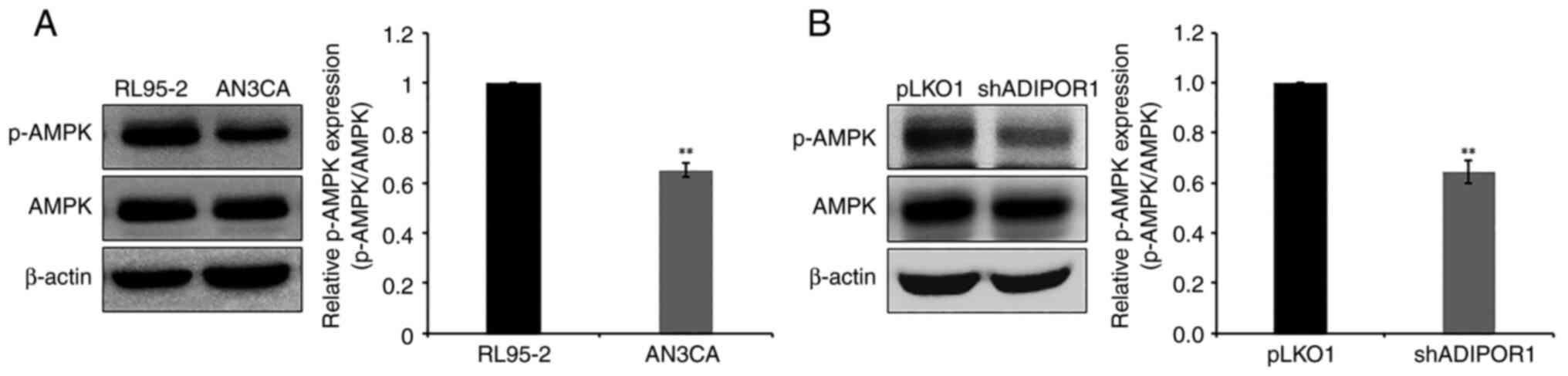
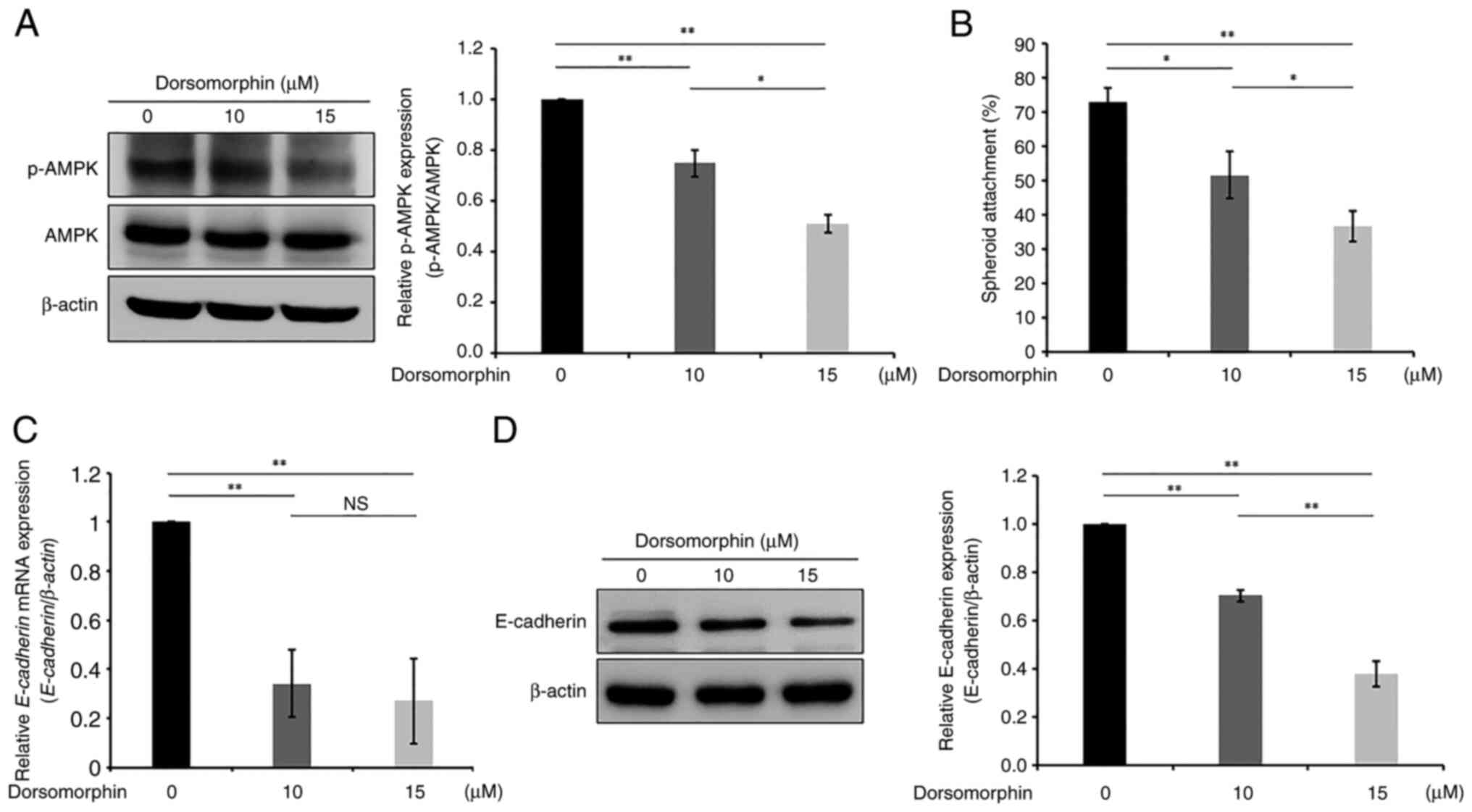
|
1
|
Achache H and Revel A: Endometrial
receptivity markers, the journey to successful embryo implantation.
Hum Reprod Update. 12:731–746. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
Nguyen TMD: Adiponectin: Role in
physiology and pathophysiology. Int J Prev Med. 11:1362020.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
Takemura Y, Osuga Y, Yamauchi T, Kobayashi
M, Harada M, Hirata T, Morimoto C, Hirota Y, Yoshino O, Koga K, et
al: Expression of adiponectin receptors and its possible
implication in the human endometrium. Endocrinology. 147:3203–3210.
2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
Takemura Y, Osuga Y, Harada M, Hirata T,
Koga K, Morimoto C, Hirota Y, Yoshino O, Yano T and Taketani Y:
Serum adiponectin concentrations are decreased in women with
endometriosis. Hum Reprod. 20:3510–3513. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Cheng L, Shi H, Jin Y, Li X, Pan J, Lai Y,
Lin Y, Jin Y, Roy G, Zhao A and Li F: Adiponectin deficiency leads
to female subfertility and ovarian dysfunctions in mice.
Endocrinology. 157:4875–4887. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Yamauchi T, Kamon J, Ito Y, Tsuchida A,
Yokomizo T, Kita S, Sugiyama T, Miyagishi M, Hara K, Tsunoda M, et
al: Cloning of adiponectin receptors that mediate antidiabetic
metabolic effects. Nature. 423:762–769. 2003. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Yamauchi T, Nio Y, Maki T, Kobayashi M,
Takazawa T, Iwabu M, Okada-Iwabu M, Kawamoto S, Kubota N, Kubota T,
et al: Targeted disruption of AdipoR1 and AdipoR2 causes abrogation
of adiponectin binding and metabolic actions. Nat Med. 13:332–339.
2007. View
Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Dos Santos E, Serazin V, Morvan C, Torre
A, Wainer R, de Mazancourt P and Dieudonné MN: Adiponectin and
leptin systems in human endometrium during window of implantation.
Fertil Steril. 97:771–778.e771. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Riek U, Scholz R, Konarev P, Rufer A,
Suter M, Nazabal A, Ringler P, Chami M, Müller SA, Neumann D, et
al: Structural properties of AMP-activated protein kinase:
Dimerization, molecular shape, and changes upon ligand binding. J
Biol Chem. 283:18331–18343. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Ross FA, MacKintosh C and Hardie DG:
AMP-activated protein kinase: A cellular energy sensor that comes
in 12 flavours. FEBS J. 283:2987–3001. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Griffiths RM, Pru CA, Behura SK, Cronrath
AR, McCallum ML, Kelp NC, Winuthayanon W, Spencer TE and Pru JK:
AMPK is required for uterine receptivity and normal responses to
steroid hormones. Reproduction. 159:707–717. 2020. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Qi Y, Wang X, Hou S, Wu Z, Xu X and Pang
C: Intracavitary physiotherapy combined with acupuncture mediated
AMPK/mTOR signalling to improve endometrial receptivity in patients
with thin endometrium. Eur J Obstet Gynecol Reprod Biol. 277:32–41.
2022. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Carey EA, Albers RE, Doliboa SR, Hughes M,
Wyatt CN, Natale DR and Brown TL: AMPK knockdown in placental
trophoblast cells results in altered morphology and function. Stem
Cells Dev. 23:2921–2930. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Waker CA, Albers RE, Pye RL, Doliboa SR,
Wyatt CN, Brown TL and Mayes DA: AMPK knockdown in placental
labyrinthine progenitor cells results in restriction of critical
energy resources and terminal differentiation failure. Stem Cells
Dev. 26:808–817. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Jha RK, Titus S, Saxena D, Kumar PG and
Laloraya M: Profiling of E-cadherin, beta-catenin and Ca(2+) in
embryo-uterine interactions at implantation. FEBS Lett.
580:5653–5660. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Giannini A, D'Oria O, Corrado G, Bruno V,
Sperduti I, Bogani G, Laganà AS, Chiantera V, Caserta D and Vizza
E: The role of L1CAM as predictor of poor prognosis in stage I
endometrial cancer: A systematic review and meta-analysis. Arch
Gynecol Obstet. 309:789–799. 2024. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Vizza E, Bruno V, Cutillo G, Mancini E,
Sperduti I, Patrizi L, Certelli C, Zampa A, Giannini A and Corrado
G: Prognostic role of the removed vaginal cuff and its correlation
with L1CAM in low-risk endometrial adenocarcinoma. Cancers (Basel).
14:342021. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
Noyes RW, Hertig AT and Rock J: Reprint
of: Dating the endometrial biopsy. Fertil Steril. 112:e93–e115.
2019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
Livak KJ and Schmittgen TD: Analysis of
relative gene expression data using real-time quantitative PCR and
the 2(−Delta Delta C(T)) method. Methods. 25:402–408. 2001.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
Yu SL, Kang Y, Jeong DU, Lee DC, Jeon HJ,
Kim TH, Lee SK, Han AR, Kang J and Park SR: The miR-182-5p/NDRG1
axis controls endometrial receptivity through the
NF-κB/ZEB1/E-cadherin pathway. Int J Mol Sci. 23:123032022.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
Rahnama F, Thompson B, Steiner M, Shafiei
F, Lobie PE and Mitchell MD: Epigenetic regulation of E-cadherin
controls endometrial receptivity. Endocrinology. 150:1466–1472.
2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22
|
Yi Y, Chen D, Ao J, Zhang W, Yi J, Ren X,
Fei J, Li F, Niu M, Chen H, et al: Transcriptional suppression of
AMPKα1 promotes breast cancer metastasis upon oncogene activation.
Proc Natl Acad Sci USA. 117:8013–8021. 2020. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23
|
Messaoudi S, El Kasmi I, Bourdiec A,
Crespo K, Bissonnette L, Saint CL, Bissonnette F and Kadoch IJ: 15
years of transcriptomic analysis on endometrial receptivity: What
have we learnt? Fertil Res Pract. 5:92019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24
|
Rubin SC, Abdulkadir M, Lewis J,
Harutyunyan A, Hirani R and Grimes CL: Review of endometrial
receptivity array: A personalized approach to embryo transfer and
its clinical applications. J Pers Med. 13:7492023. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
25
|
Nien JK, Mazaki-Tovi S, Romero R, Erez O,
Kusanovic JP, Gotsch F, Pineles BL, Gomez R, Edwin S, Mazor M, et
al: Plasma adiponectin concentrations in non-pregnant, normal and
overweight pregnant women. J Perinat Med. 35:522–531. 2007.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
26
|
Pandey N, Kriplani A, Yadav RK, Lyngdoh BT
and Mahapatra SC: Peritoneal fluid leptin levels are increased but
adiponectin levels are not changed in infertile patients with
pelvic endometriosis. Gynecol Endocrinol. 26:843–849. 2010.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
27
|
Barbe A, Bongrani A, Mellouk N, Estienne
A, Kurowska P, Grandhaye J, Elfassy Y, Levy R, Rak A, Froment P and
Dupont J: Mechanisms of adiponectin action in fertility: An
overview from gametogenesis to gestation in humans and animal
models in normal and pathological conditions. Int J Mol Sci.
20:15262019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
28
|
Kadowaki T and Yamauchi T: Adiponectin and
adiponectin receptors. Endocr Rev. 26:439–451. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
29
|
Zhou L, Deepa SS, Etzler JC, Ryu J, Mao X,
Fang Q, Liu DD, Torres JM, Jia W, Lechleiter JD, et al: Adiponectin
activates AMP-activated protein kinase in muscle cells via
APPL1/LKB1-dependent and phospholipase
C/Ca2+/Ca2+/calmodulin-dependent protein kinase kinase-dependent
pathways. J Biol Chem. 284:22426–22435. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
30
|
Kim MW, Abid NB, Jo MH, Jo MG, Yoon GH and
Kim MO: Suppression of adiponectin receptor 1 promotes memory
dysfunction and Alzheimer's disease-like pathologies. Sci Rep.
7:124352017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
31
|
Nie L, Zhang LX, Wang YC, Long Y, Ma YD,
Liao LC, Dai XH, Cui ZH, Liu H, Wang ZQ, et al: Consistency and
synchronization of AMPK-glycogen in endometrial epithelial cells
are critical to the embryo implantation. Reproduction. 163:293–307.
2022. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
32
|
Kaufman MR and Brown TL: AMPK and
placental progenitor cells. Exp Suppl. 107:73–79. 2016.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
33
|
Konieczny P, Adamus T, Sułkowski M,
Skrzypek K and Majka M: Impact of AMPK on cervical carcinoma
progression and metastasis. Cell Death Dis. 14:432023. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
34
|
Dong Y, Hu H, Zhang X, Zhang Y, Sun X,
Wang H, Kan W, Tan MJ, Shi H, Zang Y and Li J: Phosphorylation of
PHF2 by AMPK releases the repressive H3K9me2 and inhibits cancer
metastasis. Signal Transduct Target Ther. 8:952023. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
35
|
Višnjić D, Lalić H, Dembitz V, Tomić B and
Smoljo T: AICAr, a widely used AMPK activator with important
AMPK-independent effects: A systematic review. Cells. 10:10952021.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
36
|
Turner ML, Cronin JG, Noleto PG and
Sheldon IM: Glucose availability and AMP-activated protein kinase
link energy metabolism and innate immunity in the bovine
endometrium. PLoS One. 11:e01514162016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
37
|
Lane SL, Houck JA, Doyle AS, Bales ES,
Lorca RA, Julian CG and Moore LG: AMP-activated protein kinase
activator AICAR attenuates hypoxia-induced murine fetal growth
restriction in part by improving uterine artery blood flow. J
Physiol. 598:4093–4105. 2020. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|