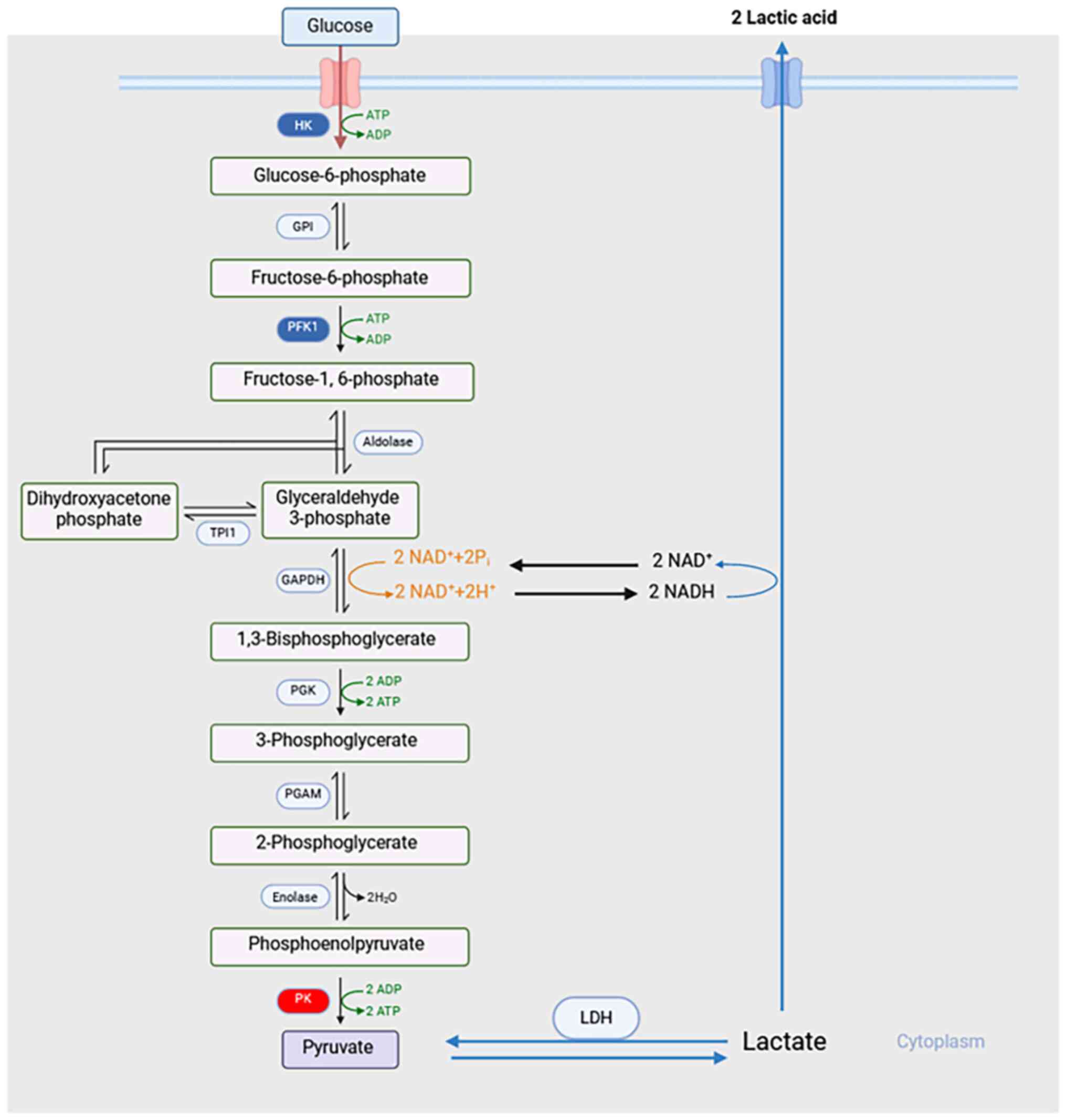
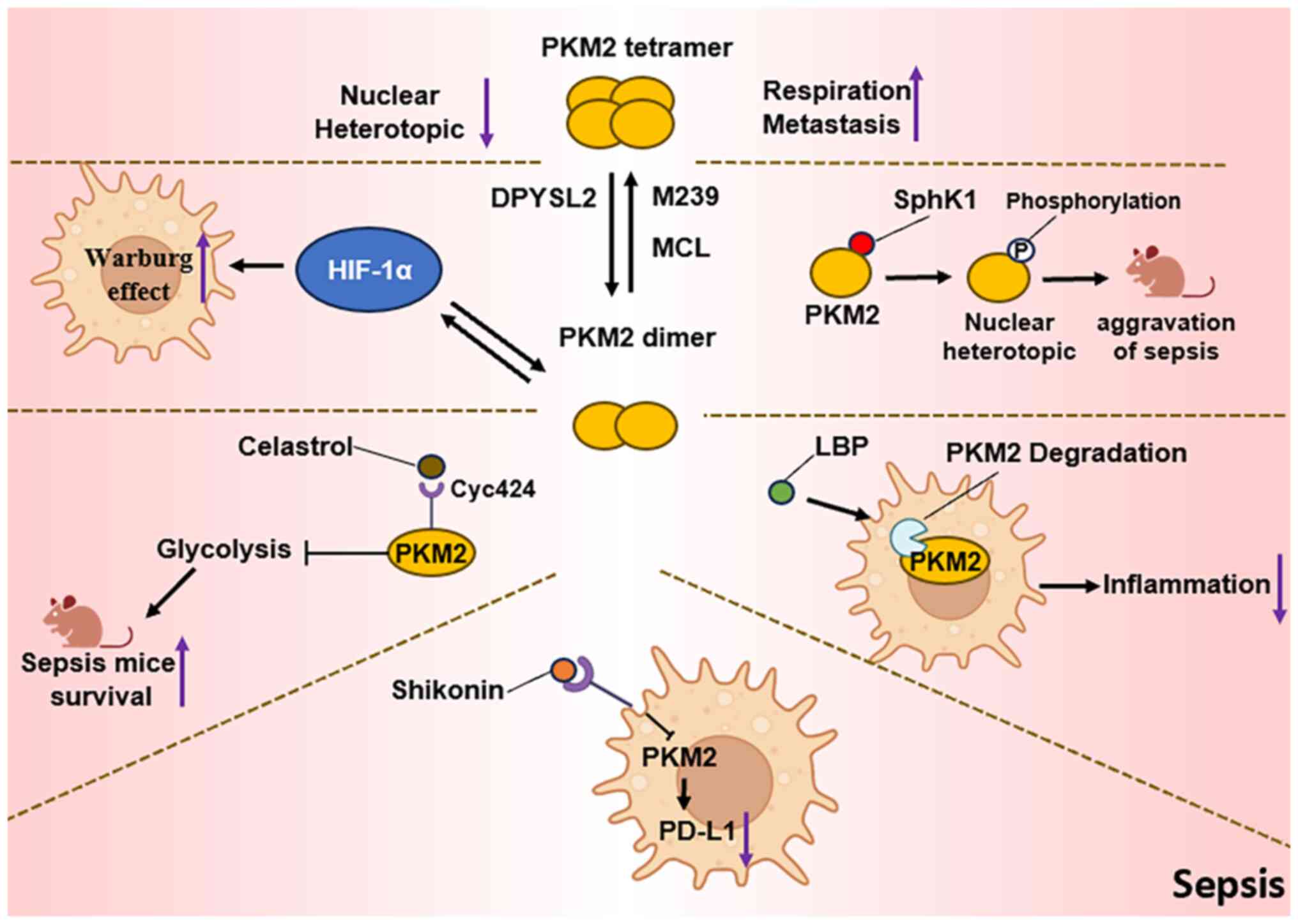
|
1
|
Stanski NL and Wong HR: Prognostic and
predictive enrichment in sepsis. Nat Rev Nephrol. 16:20–31. 2020.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
Rudd KE, Johnson SC, Agesa KM, Shackelford
KA, Tsoi D, Kievlan DR, Colombara DV, Ikuta KS, Kissoon N, Finfer
S, et al: Global, regional, and national sepsis incidence and
mortality, 1990–2017: Analysis for the global burden of disease
study. Lancet. 395:200–211. 2020. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
Huang M, Cai S and Su J: The pathogenesis
of sepsis and potential therapeutic targets. Int J Mol Sci.
20:53762019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
Rocheteau P, Chatre L, Briand D, Mebarki
M, Jouvion G, Bardon J, Crochemore C, Serrani P, Lecci PP, Latil M,
et al: Sepsis induces long-term metabolic and mitochondrial muscle
stem cell dysfunction amenable by mesenchymal stem cell therapy.
Nat Commun. 6:101452015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Zhu CL, Wang Y, Liu Q, Li HR, Yu CM, Li P,
Deng XM and Wang JF: Dysregulation of neutrophil death in sepsis.
Front Immunol. 13:9639552022. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Zou S, Jie H, Han X and Wang J: The role
of neutrophil extracellular traps in sepsis and sepsis-related
acute lung injury. Int Immunopharmacol. 124:1104362023. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Chaplin DD: Overview of the immune
response. J Allergy Clin Immunol. 125 (Suppl 2):S3–S23. 2010.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Wasyluk W and Zwolak A: Metabolic
alterations in sepsis. J Clin Med. 10:24122021. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Xiao M, Liu D, Xu Y, Mao W and Li W: Role
of PFKFB3-driven glycolysis in sepsis. Ann Med. 55:1278–1289. 2023.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Zlacká J and Zeman M: Glycolysis under
circadian control. Int J Mol Sci. 22:136662021. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Li X, Yang Y, Zhang B, Lin X, Fu X, An Y,
Zou Y, Wang JX, Wang Z and Yu T: Lactate metabolism in human health
and disease. Signal Transduct Target Ther. 7:3052022. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Chen X, Sun N, Li R, Sang X, Li X, Zhao J,
Han J, Yang J and Ikezoe T: Targeting HLA-F suppresses the
proliferation of glioma cells via a reduction in hexokinase
2-dependent glycolysis. Int J Biol Sci. 17:1263–1276. 2021.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Yuan Y, Fan G, Liu Y, Liu L, Zhang T, Liu
P, Tu Q, Zhang X, Luo S, Yao L, et al: The transcription factor
KLF14 regulates macrophage glycolysis and immune function by
inhibiting HK2 in sepsis. Cell Mol Immunol. 19:504–515. 2022.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Zheng Z, Ma H, Zhang X, Tu F, Wang X, Ha
T, Fan M, Liu L, Xu J, Yu K, et al: Enhanced glycolytic metabolism
contributes to cardiac dysfunction in polymicrobial sepsis. J
Infect Dis. 215:1396–1406. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Bar-Or D, Carrick M, Tanner A II, Lieser
MJ, Rael LT and Brody E: Overcoming the Warburg effect: Is it the
key to survival in sepsis? J Crit Care. 43:197–201. 2018.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Wang X, Wang Z and Tang D: Aerobic
exercise improves LPS-induced sepsis via regulating the Warburg
effect in mice. Sci Rep. 11:177722021. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Zhu S, Guo Y, Zhang X, Liu H, Yin M, Chen
X and Peng C: Pyruvate kinase M2 (PKM2) in cancer and cancer
therapeutics. Cancer Lett. 503:240–248. 2021. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
Alquraishi M, Puckett DL, Alani DS,
Humidat AS, Frankel VD, Donohoe DR, Whelan J and Bettaieb A:
Pyruvate kinase M2: A simple molecule with complex functions. Free
Radic Biol Med. 143:176–192. 2019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
Gupta V and Bamezai RN: Human pyruvate
kinase M2: A multifunctional protein. Protein Sci. 19:2031–2044.
2010. View
Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
Swint-Kruse L, Dougherty LL, Page B, Wu T,
O'Neil PT, Prasannan CB, Timmons C, Tang Q, Parente DJ, Sreenivasan
S, et al: PYK-SubstitutionOME: An integrated database containing
allosteric coupling, ligand affinity and mutational, structural,
pathological, bioinformatic and computational information about
pyruvate kinase isozymes. Database (Oxford). 2023:baad0302023.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
Buneeva O, Kopylov A, Gnedenko O,
Medvedeva M, Veselovsky A, Ivanov A, Zgoda V and Medvedev A:
Proteomic profiling of mouse brain pyruvate kinase binding
proteins: A hint for moonlighting functions of PKM1? Int J Mol Sci.
24:76342023. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22
|
Du D, Liu C, Qin M, Zhang X, Xi T, Yuan S,
Hao H and Xiong J: Metabolic dysregulation and emerging
therapeutical targets for hepatocellular carcinoma. Acta Pharm Sin
B. 12:558–580. 2022. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23
|
Battisti UM, Gao C, Akladios F, Kim W,
Yang H, Bayram C, Bolat I, Kiliclioglu M, Yuksel N, Tozlu OO, et
al: Ellagic acid and its metabolites as potent and selective
allosteric inhibitors of liver pyruvate kinase. Nutrients.
15:5772023. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24
|
Zhang S, Liao Z, Li S and Luo Y:
Non-metabolic enzyme function of PKM2 in hepatocellular carcinoma:
A review. Medicine (Baltimore). 102:e355712023. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
25
|
Yang X, Li C and Chen Y: Phosphoserine
aminotransferase 1: A metabolic enzyme target of cancers. Curr
Cancer Drug Targets. 23:171–186. 2023. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
26
|
Noguchi T, Inoue H and Tanaka T: The M1-
and M2-type isozymes of rat pyruvate kinase are produced from the
same gene by alternative RNA splicing. J Biol Chem.
261:13807–13812. 1986. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
27
|
Dombrauckas JD, Santarsiero BD and Mesecar
AD: Structural basis for tumor pyruvate kinase M2 allosteric
regulation and catalysis. Biochemistry. 44:9417–9429. 2005.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
28
|
Prakasam G, Iqbal MA, Bamezai RNK and
Mazurek S: Posttranslational modifications of pyruvate kinase M2:
Tweaks that benefit cancer. Front Oncol. 8:222018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
29
|
Yang YC, Cheng TY, Huang SM, Su CY, Yang
PW, Lee JM, Chen CK, Hsiao M, Hua KT and Kuo ML: Cytosolic PKM2
stabilizes mutant EGFR protein expression through regulating
HSP90-EGFR association. Oncogene. 35:3387–3398. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
30
|
Liu WR, Tian MX, Yang LX, Lin YL, Jin L,
Ding ZB, Shen YH, Peng YF, Gao DM, Zhou J, et al: PKM2 promotes
metastasis by recruiting myeloid-derived suppressor cells and
indicates poor prognosis for hepatocellular carcinoma. Oncotarget.
6:846–861. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
31
|
Chaneton B and Gottlieb E: Rocking cell
metabolism: Revised functions of the key glycolytic regulator PKM2
in cancer. Trends Biochem Sci. 37:309–316. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
32
|
Bailleul J, Ruan Y, Abdulrahman L, Scott
AJ, Yazal T, Sung D, Park K, Hoang H, Nathaniel J, Chu FI, et al:
M2 isoform of pyruvate kinase rewires glucose metabolism during
radiation therapy to promote an antioxidant response and
glioblastoma radioresistance. Neuro Oncol. 25:1989–2000. 2023.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
33
|
Liu Z, Le Y, Chen H, Zhu J and Lu D: Role
of PKM2-mediated immunometabolic reprogramming on development of
cytokine storm. Front Immunol. 12:7485732021. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
34
|
Luo W, Hu H, Chang R, Zhong J, Knabel M,
O'Meally R, Cole RN, Pandey A and Semenza GL: Pyruvate kinase M2 is
a PHD3-stimulated coactivator for hypoxia-inducible factor 1. Cell.
145:732–744. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
35
|
Malla A, Gupta S and Sur R: Glycolytic
enzymes in non-glycolytic web: Functional analysis of the key
players. Cell Biochem Biophys. Jan 9–2024.(Epub ahead of print).
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
36
|
Liang N, Mi L, Li J, Li T, Chen J, Dionigi
G, Guan H and Sun H: Pan-cancer analysis of the oncogenic and
prognostic role of PKM2: A potential target for survival and
immunotherapy. Biomed Res Int. 2023:33751092023. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
37
|
Palsson-McDermott EM, Curtis AM, Goel G,
Lauterbach MAR, Sheedy FJ, Gleeson LE, van den Bosch MWM, Quinn SR,
Domingo-Fernandez R, Johnston DGW, et al: Pyruvate kinase M2
regulates hif-1alpha activity and IL-1beta induction and is a
critical determinant of the Warburg effect in LPS-activated
macrophages. Cell Metab. 21:3472015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
38
|
Yang W, Zheng Y, Xia Y, Ji H, Chen X, Guo
F, Lyssiotis CA, Aldape K, Cantley LC and Lu Z: ERK1/2-dependent
phosphorylation and nuclear translocation of PKM2 promotes the
Warburg effect. Nat Cell Biol. 14:1295–1304. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
39
|
Shirai T, Nazarewicz RR, Wallis BB, Yanes
RE, Watanabe R, Hilhorst M, Tian L, Harrison DG, Giacomini JC,
Assimes TL, et al: The glycolytic enzyme PKM2 bridges metabolic and
inflammatory dysfunction in coronary artery disease. J Exp Med.
213:337–354. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
40
|
Lv L, Li D, Zhao D, Lin R, Chu Y, Zhang H,
Zha Z, Liu Y, Li Z, Xu Y, et al: Acetylation targets the M2 isoform
of pyruvate kinase for degradation through chaperone-mediated
autophagy and promotes tumor growth. Mol Cell. 42:719–730. 2011.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
41
|
Chhipa AS and Patel S: Targeting pyruvate
kinase muscle isoform 2 (PKM2) in cancer: What do we know so far?
Life Sci. 280:1196942021. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
42
|
Palsson-McDermott EM and O'Neill LA: The
Warburg effect then and now: From cancer to inflammatory diseases.
Bioessays. 35:965–973. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
43
|
Karnovsky ML: The metabolism of
leukocytes. Semin Hematol. 5:156–165. 1968.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
44
|
Kelly B and O'Neill LA: Metabolic
reprogramming in macrophages and dendritic cells in innate
immunity. Cell Res. 25:771–784. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
45
|
Palmer CS, Ostrowski M, Balderson B,
Christian N and Crowe SM: Glucose metabolism regulates T cell
activation, differentiation, and functions. Front Immunol. 6:12015.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
46
|
Jakubzick CV, Randolph GJ and Henson PM:
Monocyte differentiation and antigen-presenting functions. Nat Rev
Immunol. 17:349–362. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
47
|
Hu X, Wan X, Diao Y, Shen Z, Zhang Z, Wang
P, Hu D, Wang X, Yan W, Yu C, et al: Fibrinogen-like protein 2
regulates macrophage glycolytic reprogramming by directly targeting
PKM2 and exacerbates alcoholic liver injury. Int Immunopharmacol.
124:1109572023. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
48
|
Zhou S, Lan Y, Li Y, Li Z, Pu J and Wei L:
Hypoxic tumor-derived exosomes induce M2 macrophage polarization
via PKM2/AMPK to promote lung cancer progression. Cell Transplant.
31:96368972211069982022. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
49
|
Zheng YW, Wang M, Xie JW, Chen R, Wang XT,
He Y, Yang TC, Liu LL and Lin LR: Recombinant Treponema pallidum
protein Tp47 promoted the phagocytosis of macrophages by activating
NLRP3 inflammasome induced by PKM2-dependent glycolysis. J Eur Acad
Dermatol Venereol. 37:2067–2079. 2023. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
50
|
Zheng XQ, Li Z, Meng QQ, Li W, Li QL, Xie
L, Xiao Y, Xu QY and Chen YY: Treponema pallidum recombinant
protein Tp47 activates NOD-like receptor family protein 3
inflammasomes in macrophages via glycolysis. Int Immunopharmacol.
126:1112042024. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
51
|
Zhao P, Han SN, Arumugam S, Yousaf MN, Qin
Y, Jiang JX, Torok NJ, Chen Y, Mankash MS, Liu J, et al: Digoxin
improves steatohepatitis with differential involvement of liver
cell subsets in mice through inhibition of PKM2 transactivation. Am
J Physiol Gastrointest Liver Physiol. 317:G387–G397. 2019.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
52
|
Zhao K, Wang X, Zhao D, Lin Q, Zhang Y and
Hu Y: lncRNA HITT inhibits lactate production by repressing PKM2
oligomerization to reduce tumor growth and macrophage polarization.
Research (Wash D C). 2022:98549042022.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
53
|
Zhu J and Paul WE: CD4 T cells: Fates,
functions, and faults. Blood. 112:1557–1569. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
54
|
Bettencourt IA and Powell JD: Targeting
metabolism as a novel therapeutic approach to autoimmunity,
inflammation, and transplantation. J Immunol. 198:999–1005. 2017.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
55
|
Pearce EL and Pearce EJ: Metabolic
pathways in immune cell activation and quiescence. Immunity.
38:633–643. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
56
|
Angiari S, Runtsch MC, Sutton CE,
Palsson-McDermott EM, Kelly B, Rana N, Kane H, Papadopoulou G,
Pearce EL, Mills KHG and O'Neill LAJ: Pharmacological activation of
pyruvate kinase M2 inhibits CD4+ T cell pathogenicity
and suppresses autoimmunity. Cell Metab. 31:391–405.e8. 2020.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
57
|
Jiang S: Tetrameric PKM2 activation Curbs
CD4+ T cell overactivation. Trends Endocrinol Metab.
31:393–395. 2020. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
58
|
Damasceno LEA, Prado DS, Veras FP, Fonseca
MM, Toller-Kawahisa JE, Rosa MH, Públio GA, Martins TV, Ramalho FS,
Waisman A, et al: PKM2 promotes Th17 cell differentiation and
autoimmune inflammation by fine-tuning STAT3 activation. J Exp Med.
217:e201906132020. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
59
|
Moreno-Fernandez ME, Giles DA, Oates JR,
Chan CC, Damen MSMA, Doll JR, Stankiewicz TE, Chen X, Chetal K,
Karns R, et al: PKM2-dependent metabolic skewing of hepatic Th17
cells regulates pathogenesis of non-alcoholic fatty liver disease.
Cell Metab. 33:1187–1204.e9. 2021. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
60
|
Chen C, Zhang W, Zhou T, Liu Q, Han C,
Huang Z, Chen S, Mei Q, Zhang C, Zhang K, et al: Vitamin B5 rewires
Th17 cell metabolism via impeding PKM2 nuclear translocation. Cell
Rep. 41:1117412022. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
61
|
Walls JF, Subleski JJ, Palmieri EM,
Gonzalez-Cotto M, Gardiner CM, McVicar DW and Finlay DK: Metabolic
but not transcriptional regulation by PKM2 is important for natural
killer cell responses. Elife. 9:e591662020. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
62
|
Jin X, Zhang W, Wang Y, Liu J, Hao F, Li
Y, Tian M, Shu H, Dong J, Feng Y and Wei M: Pyruvate kinase M2
promotes the activation of dendritic cells by enhancing IL-12p35
expression. Cell Rep. 31:1076902020. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
63
|
Guak H, Al Habyan S, Ma EH, Aldossary H,
Al-Masri M, Won SY, Ying T, Fixman ED, Jones RG, McCaffrey LM and
Krawczyk CM: Glycolytic metabolism is essential for CCR7
oligomerization and dendritic cell migration. Nat Commun.
9:24632018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
64
|
Deng J, Lü S, Liu H, Liu B, Jiang C, Xu Q,
Feng J and Wang X: Homocysteine activates B cells via regulating
PKM2-dependent metabolic reprogramming. J Immunol. 198:170–183.
2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
65
|
Wang L, Tang D and Zhang P: Changes of
serum pyruvate kinase M2 level in patients with sepsis and its
clinical value. Infect Drug Resist. 16:6437–6449. 2023. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
66
|
Yang L, Xie M, Yang M, Yu Y, Zhu S, Hou W,
Kang R, Lotze MT, Billiar TR, Wang H, et al: PKM2 regulates the
Warburg effect and promotes HMGB1 release in sepsis. Nat Commun.
5:44362014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
67
|
Li S, Xue X, Zhang H, Jiang L, Zhang Y,
Zhu X and Wang Y: Inhibition of sphingosine kinase 1 attenuates
LPS-induced acute lung injury by suppressing endothelial cell
pyroptosis. Chem Biol Interact. 390:1108682024. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
68
|
Ni L, Lin B, Shen M, Li C, Hu L, Fu F,
Chen L, Yang J and Shi D: PKM2 deficiency exacerbates gram-negative
sepsis-induced cardiomyopathy via disrupting cardiac calcium
homeostasis. Cell Death Discov. 8:4962022. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
69
|
Zhang Q, Luo P, Xia F, Tang H, Chen J,
Zhang J, Liu D, Zhu Y, Liu Y, Gu L, et al: Capsaicin ameliorates
inflammation in a TRPV1-independent mechanism by inhibiting
PKM2-LDHA-mediated Warburg effect in sepsis. Cell Chem Biol.
29:1248–1259.e6. 2022. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
70
|
Ding H, Wang JJ, Zhang XY, Yin L and Feng
T: Lycium barbarum polysaccharide antagonizes LPS-induced
inflammation by altering the glycolysis and differentiation of
macrophages by triggering the degradation of PKM2. Biol Pharm Bull.
44:379–388. 2021. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
71
|
Yuan L, Wang Y, Chen Y, Chen X, Li S and
Liu X: Shikonin inhibits immune checkpoint PD-L1 expression on
macrophage in sepsis by modulating PKM2. Int Immunopharmacol.
121:1104012023. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
72
|
Zhao X, Wu X, Si Y, Xie J, Wang L, Liu S,
Duan C, Wang Q, Wu D, Wang Y, et al: D-DI/PLT can be a prognostic
indicator for sepsis. PeerJ. 11:e159102023. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
73
|
Fu G, Deng M, Neal MD, Billiar TR and
Scott MJ: Platelet-monocyte aggregates: Understanding mechanisms
and functions in sepsis. Shock. 55:156–166. 2021. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
74
|
Greco E, Lupia E, Bosco O, Vizio B and
Montrucchio G: Platelets and multi-organ failure in sepsis. Int J
Mol Sci. 18:22002017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
75
|
Nayak MK, Ghatge M, Flora GD, Dhanesha N,
Jain M, Markan KR, Potthoff MJ, Lentz SR and Chauhan AK: The
metabolic enzyme pyruvate kinase M2 regulates platelet function and
arterial thrombosis. Blood. 137:1658–1668. 2021. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
76
|
Zu XL and Guppy M: Cancer metabolism:
Facts, fantasy, and fiction. Biochem Biophys Res Commun.
313:459–465. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
77
|
Zhou Y, Guo Y and Tam KY: Targeting
glucose metabolism to develop anticancer treatments and therapeutic
patents. Expert Opin Ther Pat. 32:441–453. 2022. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
78
|
Zhao M, Wei F, Sun G, Wen Y, Xiang J, Su
F, Zhan L, Nian Q, Chen Y and Zeng J: Natural compounds targeting
glycolysis as promising therapeutics for gastric cancer: A review.
Front Pharmacol. 13:10043832022. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
79
|
Shan W, Zhou Y and Tam KY: The development
of small-molecule inhibitors targeting hexokinase 2. Drug Discov
Today. 27:2574–2585. 2022. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
80
|
Xu JQ, Fu YL, Zhang J, Zhang KY, Ma J,
Tang JY, Zhang ZW and Zhou ZY: Targeting glycolysis in non-small
cell lung cancer: Promises and challenges. Front Pharmacol.
13:10373412022. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
81
|
Zuo J, Tang J, Lu M, Zhou Z, Li Y, Tian H,
Liu E, Gao B, Liu T and Shao P: Glycolysis rate-limiting enzymes:
Novel potential regulators of rheumatoid arthritis pathogenesis.
Front Immunol. 12:7797872021. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|