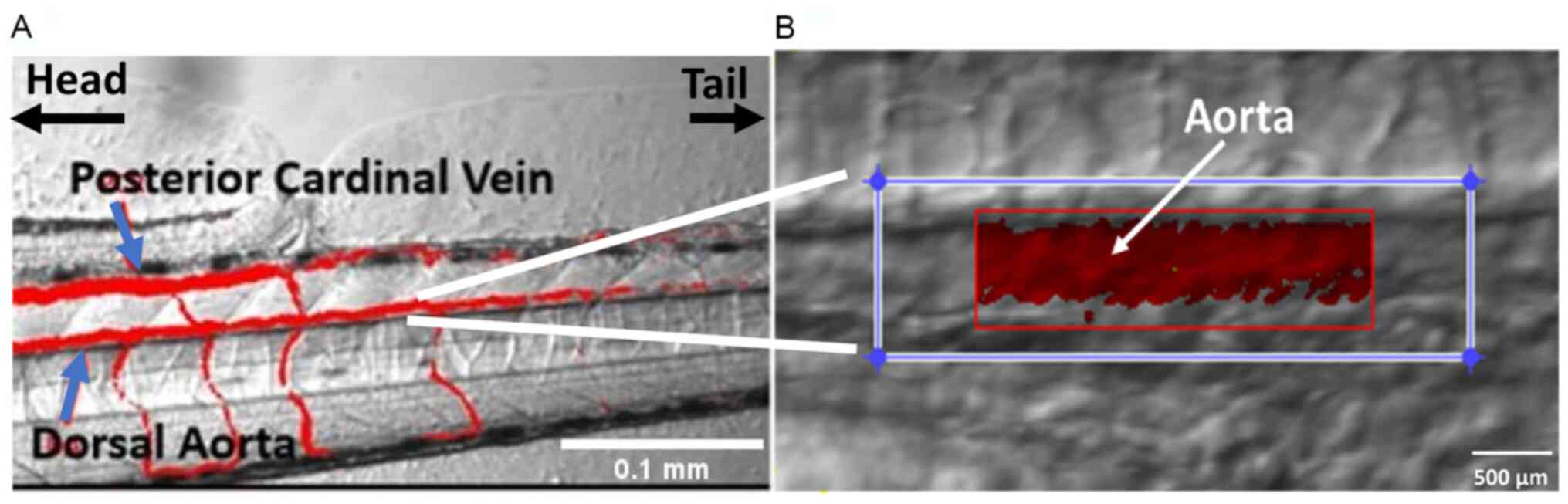
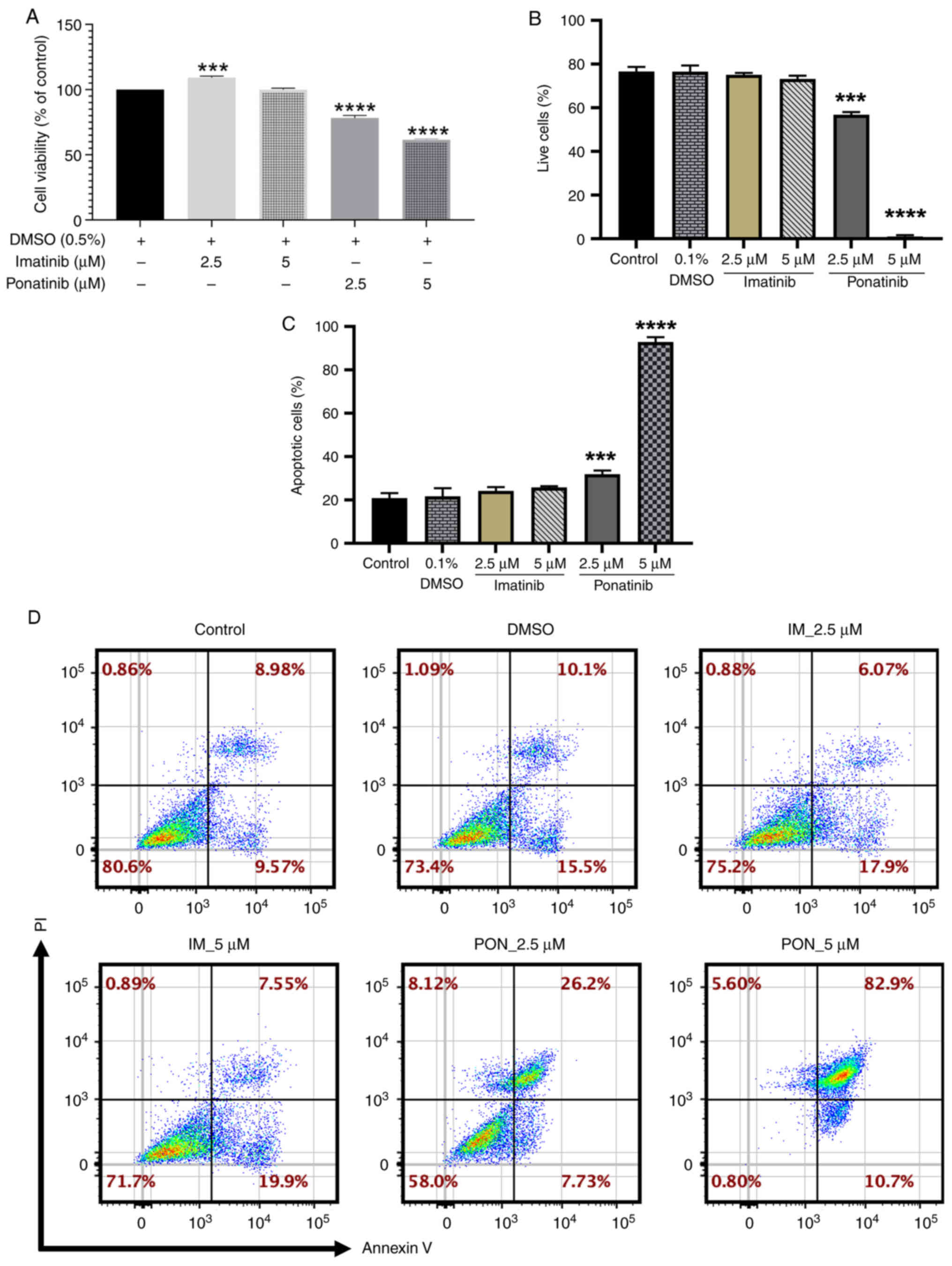
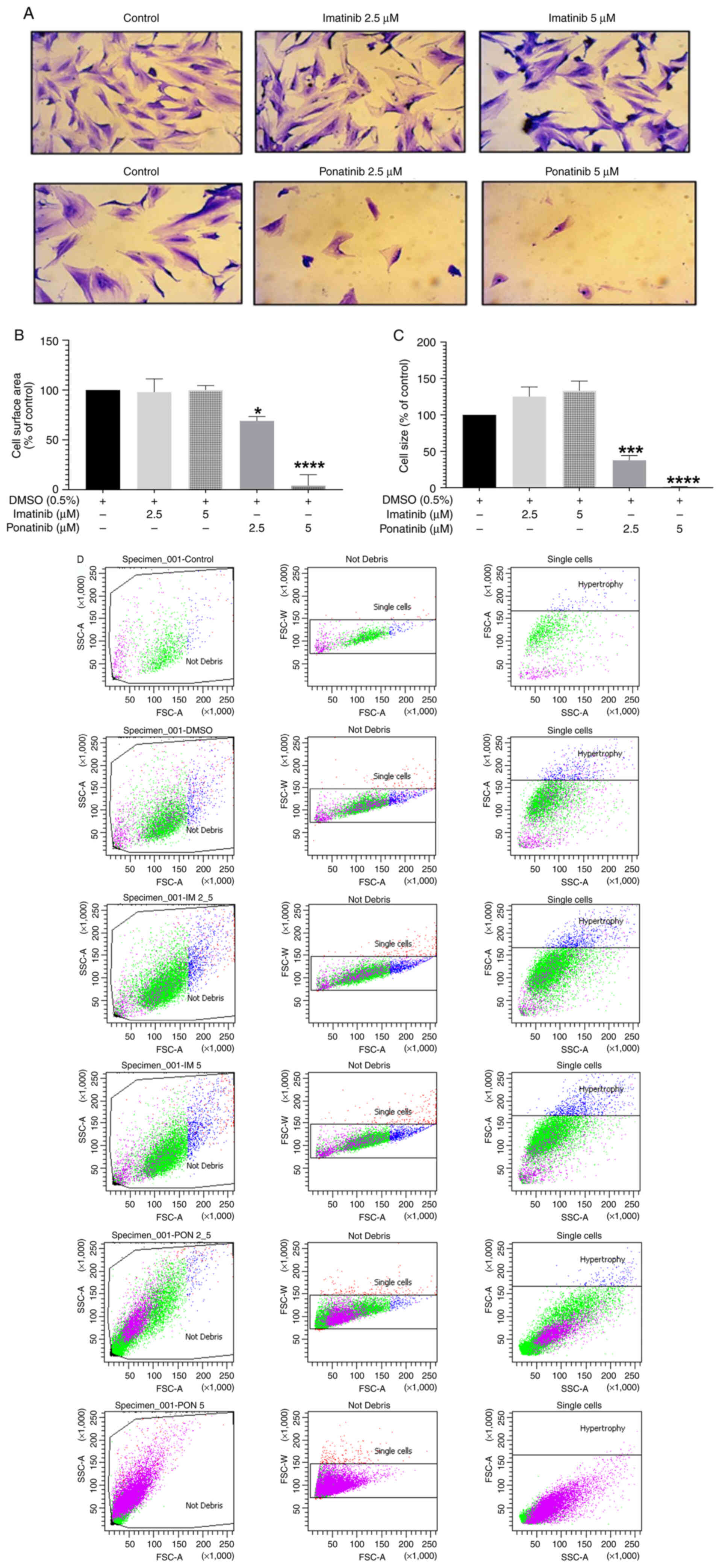
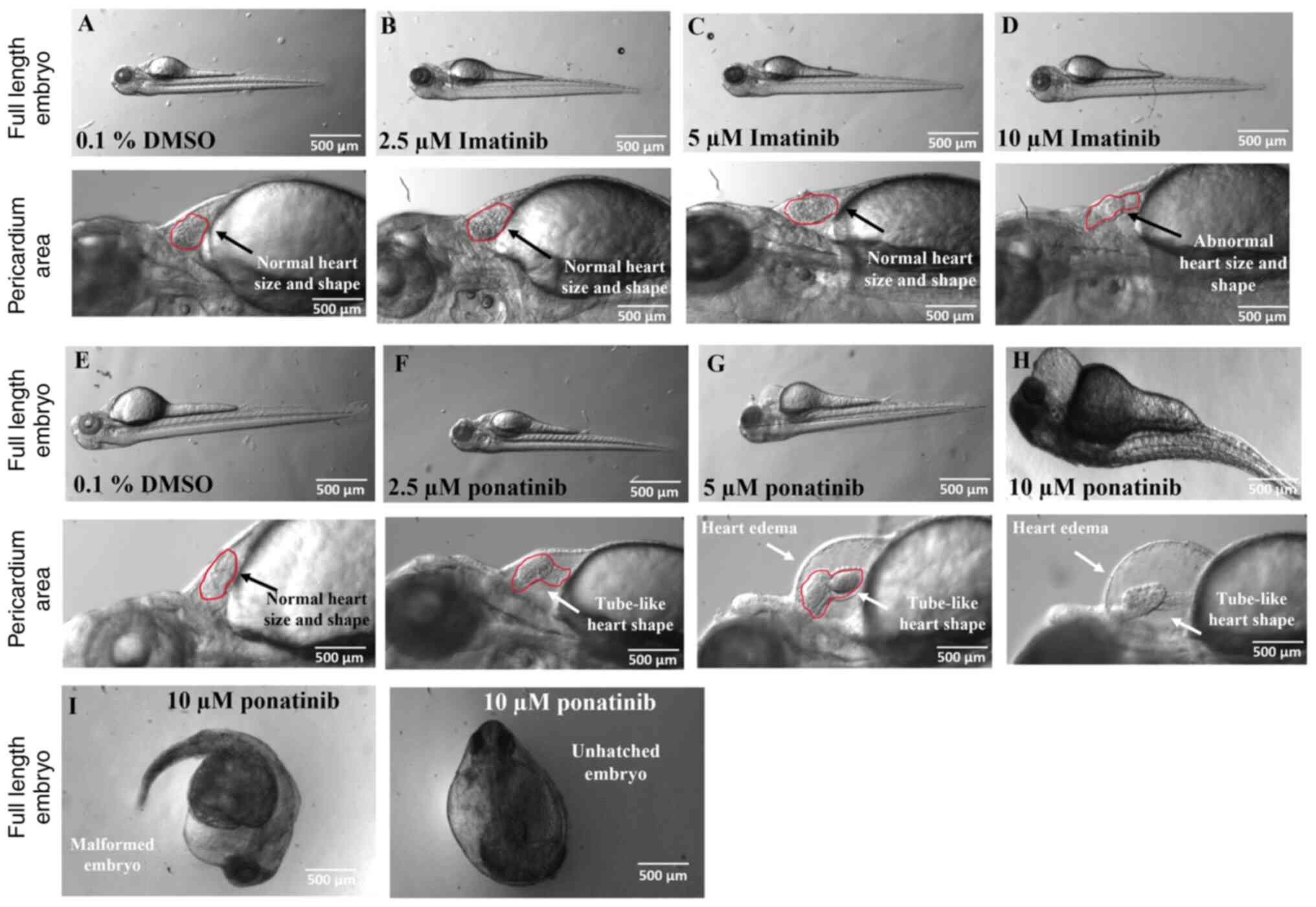
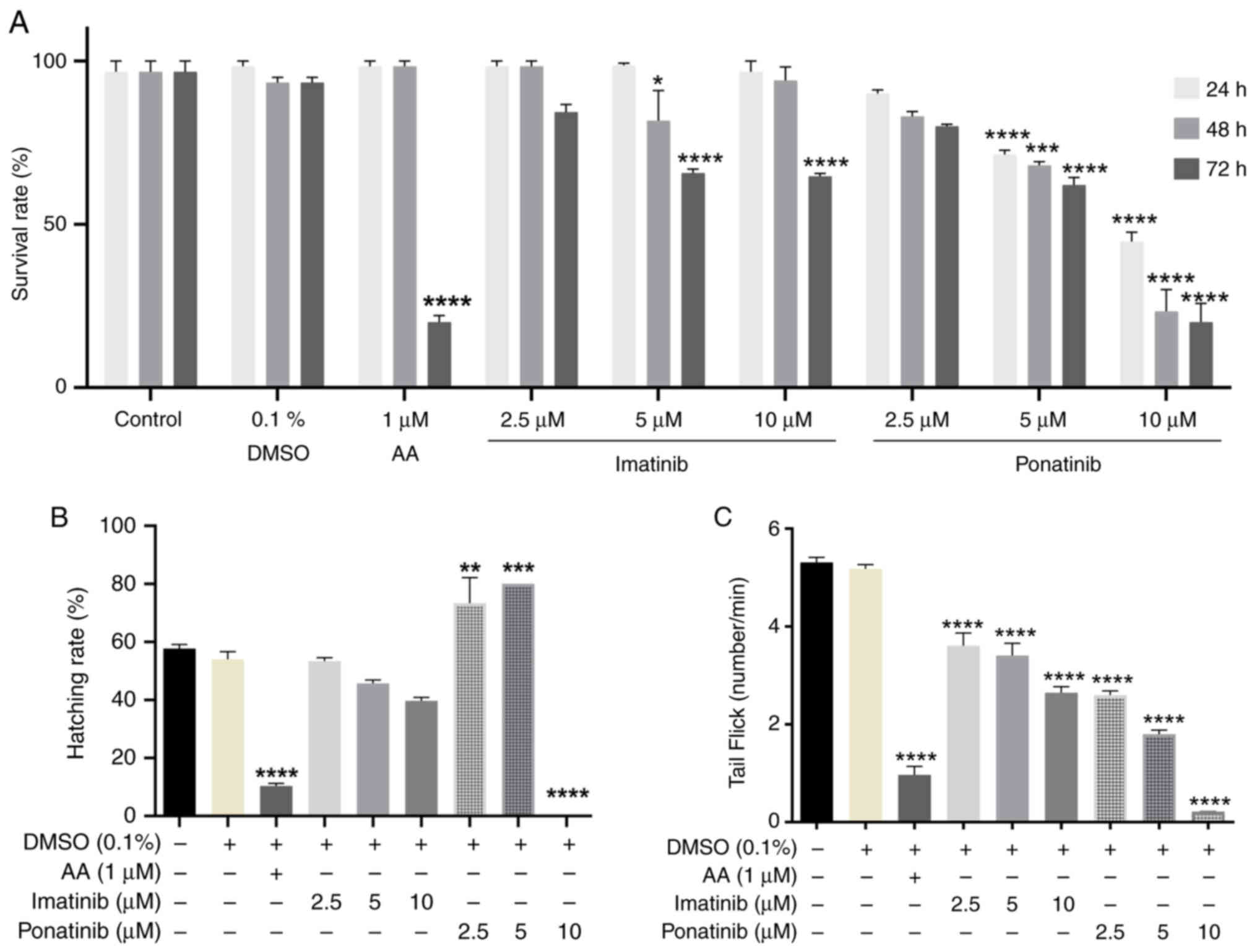
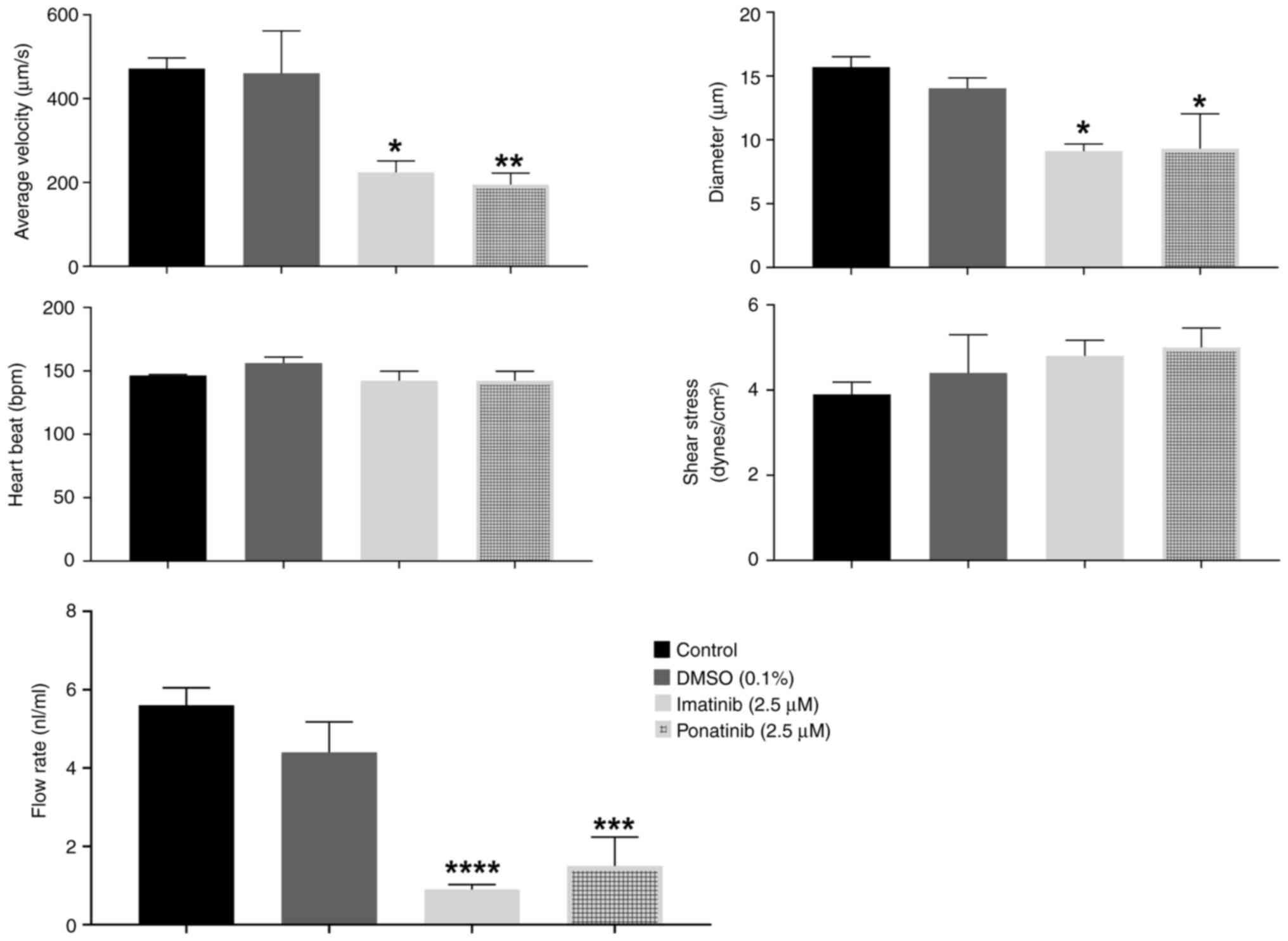
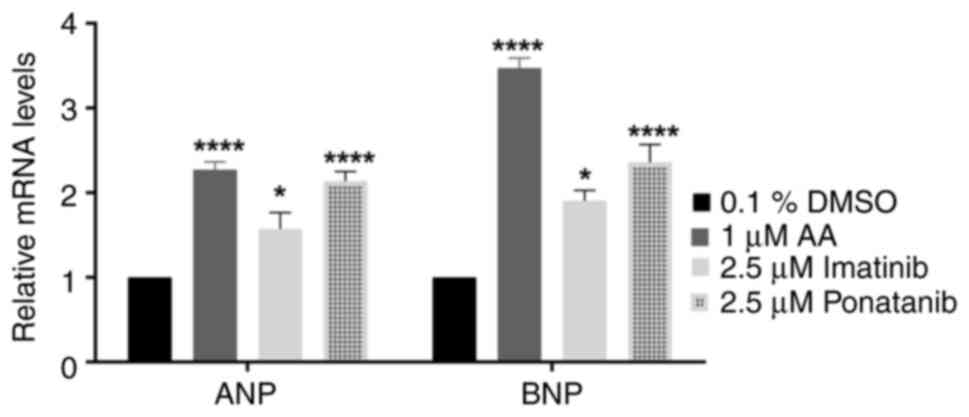
|
1
|
Heron MP and Anderson RN: National Center
for Health Statistics: Changes in the leading cause of death:
recent patterns in heart disease and cancer mortality. US
Department of Health and Human Services, Centers for Disease
Control and Prevention. National Center for Health Statistics;
Hyattsville, MD: 2016
|
|
2
|
Hochhaus A and Kantarjian H: The
development of dasatinib as a treatment for chronic myeloid
leukemia (CML): From initial studies to application in newly
diagnosed patients. J Cancer Res Clin Oncol. 139:1971–1984. 2013.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
López-Otín C and Hunter T: The regulatory
crosstalk between kinases and proteases in cancer. Nat Rev Cancer.
10:278–292. 2010. View
Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
Ségaliny AI, Tellez-Gabriel M, Heymann MF
and Heymann D: Receptor tyrosine kinases: Characterisation,
mechanism of action and therapeutic interests for bone cancers. J
Bone Oncol. 4:1–12. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Zhang N and Li Y: Receptor tyrosine
kinases: Biological functions and anticancer targeted therapy.
MedComm (2020). 4:e4462023.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Chen Y, McAndrews KM and Kalluri R:
Clinical and therapeutic relevance of cancer-associated
fibroblasts. Nat Rev Clin Oncol. 18:792–804. 2021. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
K Bhanumathy K, Balagopal A, Vizeacoumar
FS, Vizeacoumar FJ, Freywald A and Giambra V: Protein tyrosine
kinases: Their roles and their targeting in leukemia. Cancers
(Basel). 13:1842021. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Paul MK and Mukhopadhyay AK: Tyrosine
kinase-role and significance in cancer. Int J Med Sci. 1:101–115.
2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Petrelli A and Giordano S: From single- to
multi-target drugs in cancer therapy: When aspecificity becomes an
advantage. Curr Med Chem. 15:422–432. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Jabbour E and Kantarjian H: Chronic
myeloid leukemia: 2018 Update on diagnosis, therapy and monitoring.
Am J Hematol. 93:442–459. 2018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Bukowski RM: Third generation tyrosine
kinase inhibitors and their development in advanced renal cell
carcinoma. Front Oncol. 2:132012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Stasi I and Cappuzzo F: Second generation
tyrosine kinase inhibitors for the treatment of metastatic
non-small-cell lung cancer. Transl Respir Med. 2:22014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Yewale C, Baradia D, Vhora I, Patil S and
Misra A: Epidermal growth factor receptor targeting in cancer: A
review of trends and strategies. Biomaterials. 34:8690–8707. 2013.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Segaliny A, Tellez-Gabriel M, Heymann MF
and Heymann D: Receptor tyrosine kinases: Characterisation,
mechanism of action and therapeutic interests for bone cancers. J
Bone Oncol. 4:1–12. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Yang Y, Li S, Wang Y, Zhao Y and Li Q:
Protein tyrosine kinase inhibitor resistance in malignant tumors:
Molecular mechanisms and future perspective. Signal Transduct
Target Ther. 7:3292022. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Moslehi JJ: Cardiovascular toxic effects
of targeted cancer therapies. N Engl J Med. 375:1457–1467. 2016.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Kerkelä R, Grazette L, Yacobi R, Iliescu
C, Patten R, Beahm C, Walters B, Shevtsov S, Pesant S, Clubb FJ, et
al: Cardiotoxicity of the cancer therapeutic agent imatinib
mesylate. Nat Med. 12:908–916. 2006. View
Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
Sayegh N, Yirerong J, Agarwal N, Addison
D, Fradley M, Cortes J, Weintraub NL, Sayed N, Raval G and Guha A:
Cardiovascular toxicities associated with tyrosine kinase
inhibitors. Curr Cardiol Rep. 25:269–280. 2023. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
Kantarjian H, Shah NP, Hochhaus A, Cortes
J, Shah S, Ayala M, Moiraghi B, Shen Z, Mayer J, Pasquini R, et al:
Dasatinib versus imatinib in newly diagnosed chronic-phase chronic
myeloid leukemia. N Engl J Med. 362:2260–2270. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
Montani D, Bergot E, Günther S, Savale L,
Bergeron A, Bourdin A, Bouvaist H, Canuet M, Pison C, Macro M, et
al: Pulmonary arterial hypertension in patients treated by
dasatinib. Circulation. 125:2128–2137. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
Cortes JE, Kim DW, Pinilla-Ibarz J, le
Coutre P, Paquette R, Chuah C, Nicolini FE, Apperley JF, Khoury HJ,
Talpaz M, et al: A phase 2 trial of ponatinib in Philadelphia
chromosome-positive leukemias. N Engl J Med. 369:1783–1796. 2013.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22
|
Dorer DJ, Knickerbocker RK, Baccarani M,
Cortes JE, Hochhaus A, Talpaz M and Haluska FG: Impact of dose
intensity of ponatinib on selected adverse events: Multivariate
analyses from a pooled population of clinical trial patients. Leuk
Res. 48:84–91. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23
|
Korashy HM, Al-Suwayeh HA, Maayah ZH,
Ansari MA, Ahmad SF and Bakheet SA: Mitogen-activated protein
kinases pathways mediate the sunitinib-induced hypertrophy in rat
cardiomyocyte H9c2 cells. Cardiovasc Toxicol. 15:41–51. 2015.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24
|
Zhao Y, Xue T, Yang X, Zhu H, Ding X, Lou
L, Lu W, Yang B and He Q: Autophagy plays an important role in
sunitinib- mediated cell death in H9c2 cardiac muscle cells.
Toxicol Appl Pharmacol. 248:20–27. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
25
|
Will Y, Dykens JA, Nadanaciva S, Hirakawa
B, Jamieson J, Marroquin LD, Hynes J, Patyna S and Jessen BA:
Effect of the multitargeted tyrosine kinase inhibitors imatinib,
dasatinib, sunitinib, and sorafenib on mitochondrial function in
isolated rat heart mitochondria and H9c2 cells. Toxicol Sci.
106:153–161. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
26
|
Talbert DR, Doherty KR, Trusk PB, Moran
DM, Shell SA and Bacus S: A multi-parameter in vitro screen in
human stem cell-derived cardiomyocytes identifies ponatinib-induced
structural and functional cardiac toxicity. Toxicol Sci.
143:147–155. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
27
|
Doherty KR, Wappel RL, Talbert DR, Trusk
PB, Moran DM, Kramer JW, Brown AM, Shell SA and Bacus S:
Multi-parameter in vitro toxicity testing of crizotinib, sunitinib,
erlotinib, and nilotinib in human cardiomyocytes. Toxicol Appl
Pharmacol. 272:245–255. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
28
|
French KJ, Coatney RW, Renninger JP, Hu
CX, Gales TL, Zhao S, Storck LM, Davis CB, McSurdy-Freed J, Chen E
and Frazier KS: Differences in effects on myocardium and
mitochondria by angiogenic inhibitors suggest separate mechanisms
of cardiotoxicity. Toxicol Pathol. 38:691–702. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
29
|
Pembrey RS, Marshall KC and Schneider RP:
Cell surface analysis techniques: What do cell preparation
protocols do to cell surface properties? Appl Environ Microbiol.
65:2877–2894. 1999. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
30
|
Prabhu KS, Siveen KS, Kuttikrishnan S,
Iskandarani A, Tsakou M, Achkar IW, Therachiyil L, Krishnankutty R,
Parray A, Kulinski M, et al: Targeting of X-linked inhibitor of
apoptosis protein and PI3-kinase/AKT signaling by embelin
suppresses growth of leukemic cells. PLoS One. 12:e01808952017.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
31
|
Khan AQ, Siveen KS, Prabhu KS,
Kuttikrishnan S, Akhtar S, Shaar A, Raza A, Mraiche F, Dermime S
and Uddin S: Curcumin-mediated degradation of S-phase kinase
protein 2 induces cytotoxic effects in human
papillomavirus-positive and negative squamous carcinoma cells.
Front Oncol. 8:3992018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
32
|
Westerfield M: The zebrafish book: A guide
for the laboratory use of zebrafish (Danio rerio). 4th edition.
University of Oregon Press; Eugene: 2000, http://zfin. org/zf_info/zfbook/zfbk.html
|
|
33
|
Kimmel CB, Ballard WW, Kimmel SR, Ullmann
B and Schilling TF: Stages of embryonic development of the
zebrafish. Dev Dyn. 203:253–310. 1995. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
34
|
Benslimane FM, Zakaria ZZ, Shurbaji S,
Abdelrasool MKA, Al-Badr MAHI, Al Absi ESK and Yalcin HC: Cardiac
function and blood flow hemodynamics assessment of zebrafish (Danio
rerio) using high-speed video microscopy. Micron. 136:1028762020.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
35
|
Yalcin HC, Amindari A, Butcher JT, Althani
A and Yacoub M: Heart function and hemodynamics analysis for
zebrafish embryos. Dev Dyn. 246:868–880. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
36
|
Benslimane FM, Alser M, Zakaria ZZ, Sharma
A, Abdelrahman HA and Yalcin HC: Adaptation of a mice doppler
echocardiography platform to measure cardiac flow velocities for
embryonic chicken and adult zebrafish. Front Bioeng Biotechnol.
7:962019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
37
|
Rao X, Huang X, Zhou Z and Lin X: An
improvement of the 2ˆ(−delta delta CT) method for quantitative
real-time polymerase chain reaction data analysis. Biostat
Bioinforma Biomath. 3:71–85. 2013.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
38
|
Huang CC, Chen PC, Huang CW and Yu J:
Aristolochic acid induces heart failure in zebrafish embryos that
is mediated by inflammation. Toxicol Sci. 100:486–494. 2007.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
39
|
Narumanchi S, Wang H, Perttunen S,
Tikkanen I, Lakkisto P and Paavola J: Zebrafish heart failure
models. Front Cell Dev Biol. 9:6625832021. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
40
|
Januzzi JL Jr: Natriuretic peptides as
biomarkers in heart failure. J Investig Med. 61:950–955. 2013.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
41
|
Wickramasinghe CD, Nguyen KL, Watson KE,
Vorobiof G and Yang EH: Concepts in cardio-oncology: Definitions,
mechanisms, diagnosis and treatment strategies of cancer
therapy-induced cardiotoxicity. Future Oncol. 12:855–870. 2016.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
42
|
Dolci A, Dominici R, Cardinale D, Sandri
MT and Panteghini M: Biochemical markers for prediction of
chemotherapy-induced cardiotoxicity: Systematic review of the
literature and recommendations for use. Am J Clin Pathol.
130:688–695. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
43
|
Pai VB and Nahata MC: Cardiotoxicity of
chemotherapeutic agents: Incidence, treatment and prevention. Drug
Saf. 22:263–302. 2000. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
44
|
Albini A, Pennesi G, Donatelli F,
Cammarota R, De Flora S and Noonan DM: Cardiotoxicity of anticancer
drugs: The need for cardio-oncology and cardio-oncological
prevention. J Natl Cancer Inst. 102:14–25. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
45
|
Sheng CC, Amiri-Kordestani L, Palmby T,
Force T, Hong CC, Wu JC, Croce K, Kim G and Moslehi J: 21st Century
cardio-oncology: Identifying cardiac safety signals in the era of
personalized medicine. JACC Basic Transl Sci. 1:386–398. 2016.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
46
|
Cortes JE, Kim DW, Pinilla-Ibarz J, Le
Coutre P, Paquette R, Chuah C, Nicolini FE, Apperley JF, Khoury HJ,
Talpaz M, et al: Long-term follow-up of ponatinib efficacy and
safety in the phase 2 PACE trial. Blood. 124:31352014. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
47
|
Sayed-Ahmed MM, Alrufaiq BI, Alrikabi A,
Abdullah ML, Hafez MM and Al-Shabanah OA: Carnitine supplementation
attenuates sunitinib-induced inhibition of AMP-activated protein
kinase downstream signals in cardiac tissues. Cardiovasc Toxicol.
19:344–356. 2019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
48
|
Jin Y, Xu Z, Yan H, He Q, Yang X and Luo
P: A comprehensive review of clinical cardiotoxicity incidence of
FDA-approved small-molecule kinase inhibitors. Front Pharmacol.
11:8912020. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
49
|
Moslehi JJ and Deininger M: Tyrosine
kinase inhibitor-associated cardiovascular toxicity in chronic
myeloid leukemia. J Clin Oncol. 33:4210–4218. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
50
|
Shah RR and Morganroth J: Update on
cardiovascular safety of tyrosine kinase inhibitors: With a special
focus on QT interval, left ventricular dysfunction and overall
risk/benefit. Drug Saf. 38:693–710. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
51
|
Cortes JE, Kim DW, Pinilla-Ibarz J, le
Coutre P, Paquette R, Chuah C, Nicolini FE, Apperley JF, Khoury HJ,
Talpaz M, et al: Long-term follow-up of ponatinib efficacy and
safety in the phase 2 PACE trial. Blood. 124:31352014. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
52
|
Zordoky BN and El-Kadi AOS: H9c2 cell line
is a valuable in vitro model to study the drug metabolizing enzymes
in the heart. J Pharmacol Toxicol Methods. 56:317–322. 2007.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
53
|
Watkins SJ, Borthwick GM and Arthur HM:
The H9C2 cell line and primary neonatal cardiomyocyte cells show
similar hypertrophic responses in vitro. In Vitro Cell Dev Biol
Anim. 47:125–131. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
54
|
Witek P, Korga A, Burdan F, Ostrowska M,
Nosowska B, Iwan M and Dudka J: The effect of a number of H9C2 rat
cardiomyocytes passage on repeatability of cytotoxicity study
results. Cytotechnology. 68:2407–2415. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
55
|
Kobuszewska A, Tomecka E, Zukowski K,
Jastrzebska E, Chudy M, Dybko A, Renaud P and Brzozka Z:
Heart-on-a-Chip: An investigation of the influence of static and
perfusion conditions on cardiac (H9C2) cell proliferation,
morphology, and alignment. SLAS Technol. 22:536–546. 2017.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
56
|
Bouleftour W, Mery B, Rowinski E, Rivier
C, Daguenet E and Magne N: Cardio-oncology preclinical models: A
comprehensive review. Anticancer Res. 41:5355–5364. 2021.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
57
|
Khan FR and Alhewairini SS: Zebrafish
(Danio rerio) as a model organism. Curr Trends Cancer manage.
27:3–18. 2018.
|
|
58
|
Lane S, More LA and Asnani A: Zebrafish
models of cancer therapy-induced cardiovascular toxicity. J
Cardiovasc Dev Dis. 8:82021.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
59
|
Al-Thani HF, Shurbaji S, Zakaria ZZ, Hasan
MH, Goracinova K, Korashy HM and Yalcin HC: Reduced cardiotoxicity
of ponatinib-loaded PLGA-PEG-PLGA nanoparticles in zebrafish
xenograft model. Materials (Basel). 15:39602022. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
60
|
Suleiman M: The role of P90 ribosomal S6
kinase and autophagy in sunitinib and ponatinib-induced
cardiotoxicity. 2019.
|
|
61
|
Lekes D, Szadvari I, Krizanova O, Lopusna
K, Rezuchova I, Novakova M, Novakova Z, Parak T and Babula P:
Nilotinib induces ER stress and cell death in H9c2 cells. Physiol
Res. 65 (Suppl 4):S505–S514. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
62
|
Wang H, Wang Y, Li J, He Z, Boswell SA,
Chung M, You F and Han S: Three tyrosine kinase inhibitors cause
cardiotoxicity by inducing endoplasmic reticulum stress and
inflammation in cardiomyocytes. BMC Med. 21:1472023. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
63
|
Lamore SD, Kohnken RA, Peters MF and
Kolaja KL: Cardiovascular toxicity induced by kinase inhibitors:
Mechanisms and preclinical approaches. Chem Res Toxicol.
33:125–136. 2020. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
64
|
Sun S, Qin J, Liao W, Gao X, Shang Z, Luo
D and Xiong S: Mitochondrial dysfunction in cardiotoxicity induced
by BCR-ABL1 tyrosine kinase inhibitors-underlying mechanisms,
detection, potential therapies. Cardiovasc Toxicol. 23:233–254.
2023. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
65
|
Méry B, Guy JB, Vallard A, Espenel S,
Ardail D, Rodriguez-Lafrasse C, Rancoule C and Magné N: In vitro
cell death determination for drug discovery: A landscape review of
real issues. J Cell Death. 10:11796707176912512017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
66
|
Yussman MG, Toyokawa T, Odley A, Lynch RA,
Wu G, Colbert MC, Aronow BJ, Lorenz JN and Dorn GW II:
Mitochondrial death protein Nix is induced in cardiac hypertrophy
and triggers apoptotic cardiomyopathy. Nat Med. 8:725–730. 2002.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
67
|
Kostin S, Pool L, Elsässer A, Hein S,
Drexler HC, Arnon E, Hayakawa Y, Zimmermann R, Bauer E, Klövekorn
WP and Schaper J: Myocytes die by multiple mechanisms in failing
human hearts. Circ Res. 92:715–724. 2003. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
68
|
Tham YK, Bernardo BC, Ooi JY, Weeks KL and
McMullen JR: Pathophysiology of cardiac hypertrophy and heart
failure: Signaling pathways and novel therapeutic targets. Arch
Toxicol. 89:1401–1438. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
69
|
Ghasemi M, Turnbull T, Sebastian S and
Kempson I: The MTT assay: Utility, limitations, pitfalls, and
interpretation in bulk and single-cell analysis. Int J Mol Sci.
22:128272021. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
70
|
Rai Y, Pathak R, Kumari N, Sah DK, Pandey
S, Kalra N, Soni R, Dwarakanath BS and Bhatt AN: Mitochondrial
biogenesis and metabolic hyperactivation limits the application of
MTT assay in the estimation of radiation induced growth inhibition.
Sci Rep. 8:15312018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
71
|
van Meerloo J, Kaspers GJ and Cloos J:
Cell sensitivity assays: The MTT assay. Methods Mol Biol.
731:237–245. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
72
|
Yu T, Cao J, Alaa Eddine M, Moustafa M,
Mock A, Erkut C, Abdollahi A, Warta R, Unterberg A, Herold-Mende C
and Jungwirth G: Receptor-tyrosine kinase inhibitor ponatinib
inhibits meningioma growth in vitro and in vivo. Cancers (Basel).
13:58982021. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
73
|
Ghasemi M, Liang S, Luu QM and Kempson I:
The MTT assay: A method for error minimization and interpretation
in measuring cytotoxicity and estimating cell viability. Methods
Mol Biol. 2644:15–33. 2023. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
74
|
Gustafson D, Fish JE, Lipton JH and Aghel
N: Mechanisms of cardiovascular toxicity of BCR-ABL1 tyrosine
kinase inhibitors in chronic myelogenous leukemia. Curr Hematol
Malig Rep. 15:20–30. 2020. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
75
|
Loren CP, Aslan JE, Rigg RA, Nowak MS,
Healy LD, Gruber A, Druker BJ and McCarty OJ: The BCR-ABL inhibitor
ponatinib inhibits platelet immunoreceptor tyrosine-based
activation motif (ITAM) signaling, platelet activation and
aggregate formation under shear. Thromb Res. 135:155–160. 2015.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
76
|
Menyhárt O, Harami-Papp H, Sukumar S,
Schäfer R, Magnani L, de Barrios O and Győrffy B: Guidelines for
the selection of functional assays to evaluate the hallmarks of
cancer. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1866:300–319. 2016.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
77
|
Wang X, Xia Y, Liu L, Liu M, Gu N, Guang H
and Zhang F: Comparison of MTT assay, flow cytometry, and RT-PCR in
the evaluation of cytotoxicity of five prosthodontic materials. J
Biomed Mater Res B Appl Biomater. 95:357–364. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
78
|
Yurinskaya V, Aksenov N, Moshkov A, Model
M, Goryachaya T and Vereninov A: A comparative study of U937 cell
size changes during apoptosis initiation by flow cytometry, light
scattering, water assay and electronic sizing. Apoptosis.
22:1287–1295. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
79
|
Chen L, Zhao L, Samanta A, Mahmoudi SM,
Buehler T, Cantilena A, Vincent RJ, Girgis M, Breeden J, Asante S,
et al: STAT3 balances myocyte hypertrophy vis-à-vis autophagy in
response to Angiotensin II by modulating the AMPKα/mTOR axis. PLoS
One. 12:e01798352017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
80
|
Hasinoff BB, Patel D and Wu X: The
myocyte-damaging effects of the BCR-ABL1-targeted tyrosine kinase
inhibitors increase with potency and decrease with specificity.
Cardiovasc Toxicol. 17:297–306. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
81
|
Hoyberghs J, Bars C, Ayuso M, Van Ginneken
C, Foubert K and Van Cruchten S: DMSO concentrations up to 1% are
safe to be used in the zebrafish embryo developmental toxicity
assay. Front Toxicol. 3:8040332021. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
82
|
OECD, . OECD guidelines for the testing of
chemicals. Oecd. 1994.
|
|
83
|
Jaballah M, Mohamed IA, Alemrayat B,
Al-Sulaiti F, Mlih M and Mraiche F: Na+/H+ exchanger isoform 1
induced cardiomyocyte hypertrophy involves activation of p90
ribosomal s6 kinase. PLoS One. 10:e01222302015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
84
|
Yamaguchi N, Chakraborty A, Pasek DA,
Molkentin JD and Meissner G: Dysfunctional ryanodine receptor and
cardiac hypertrophy: Role of signaling molecules. Am J Physiol
Heart Circ Physiol. 300:H2187–H2195. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|