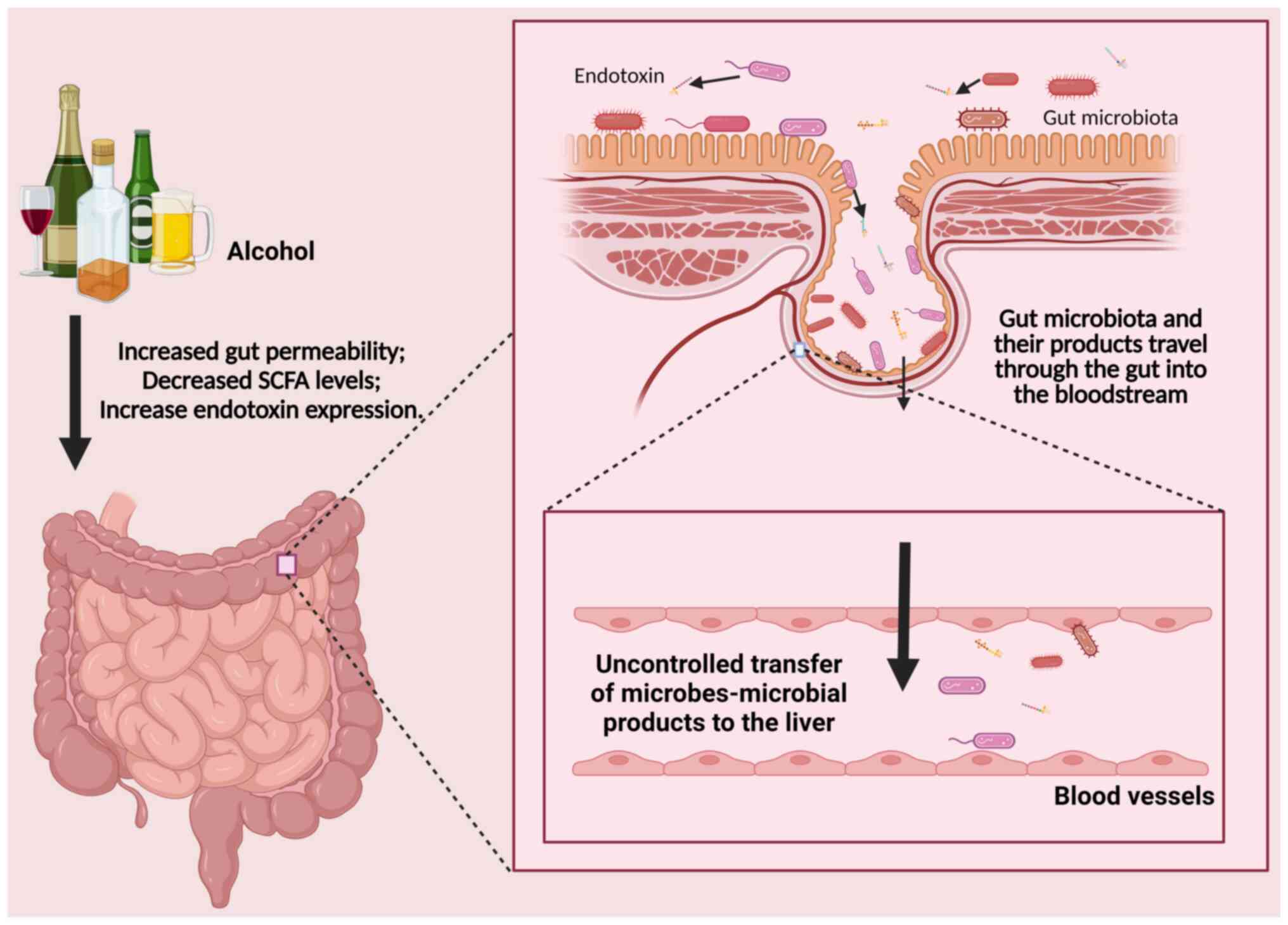
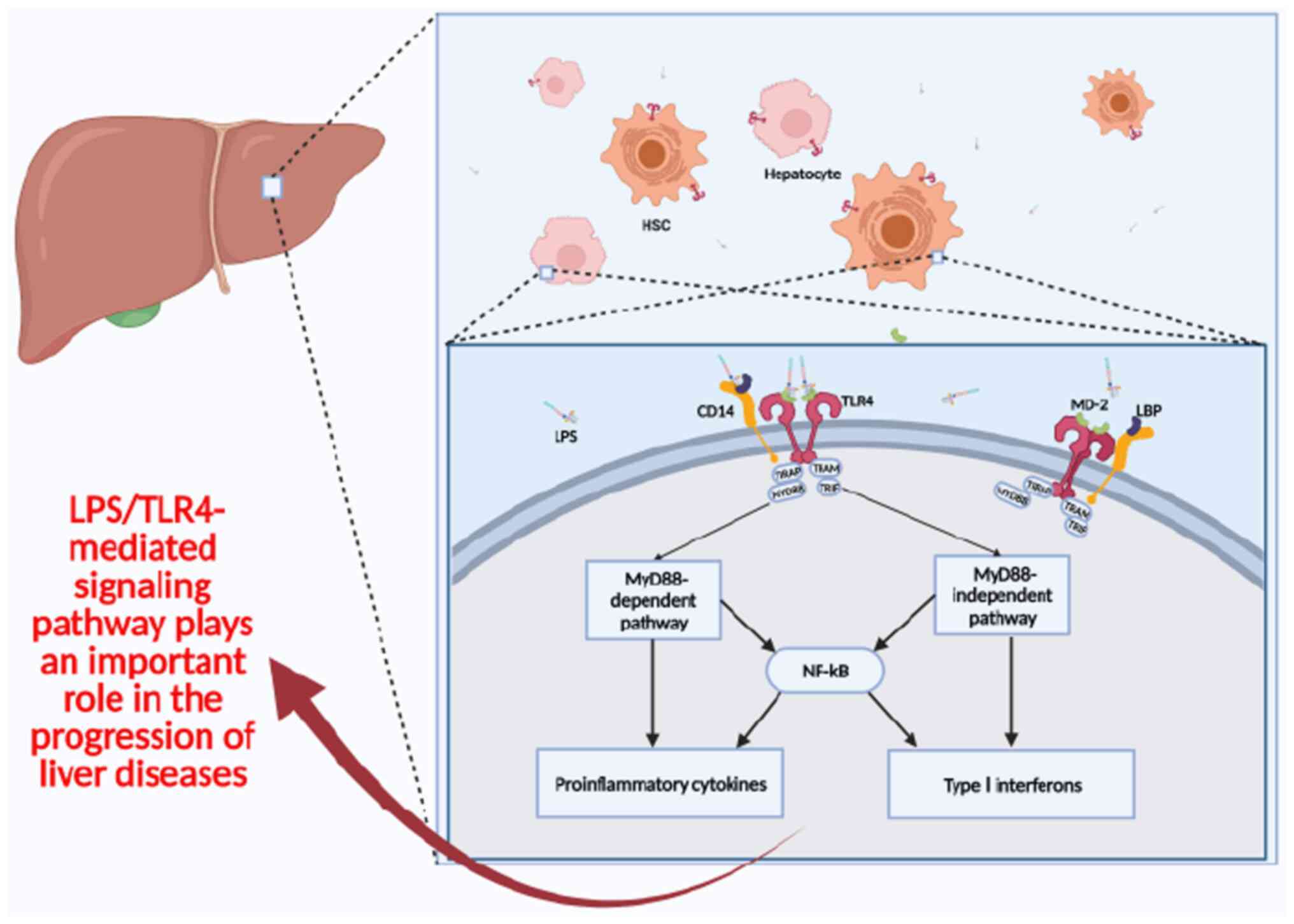
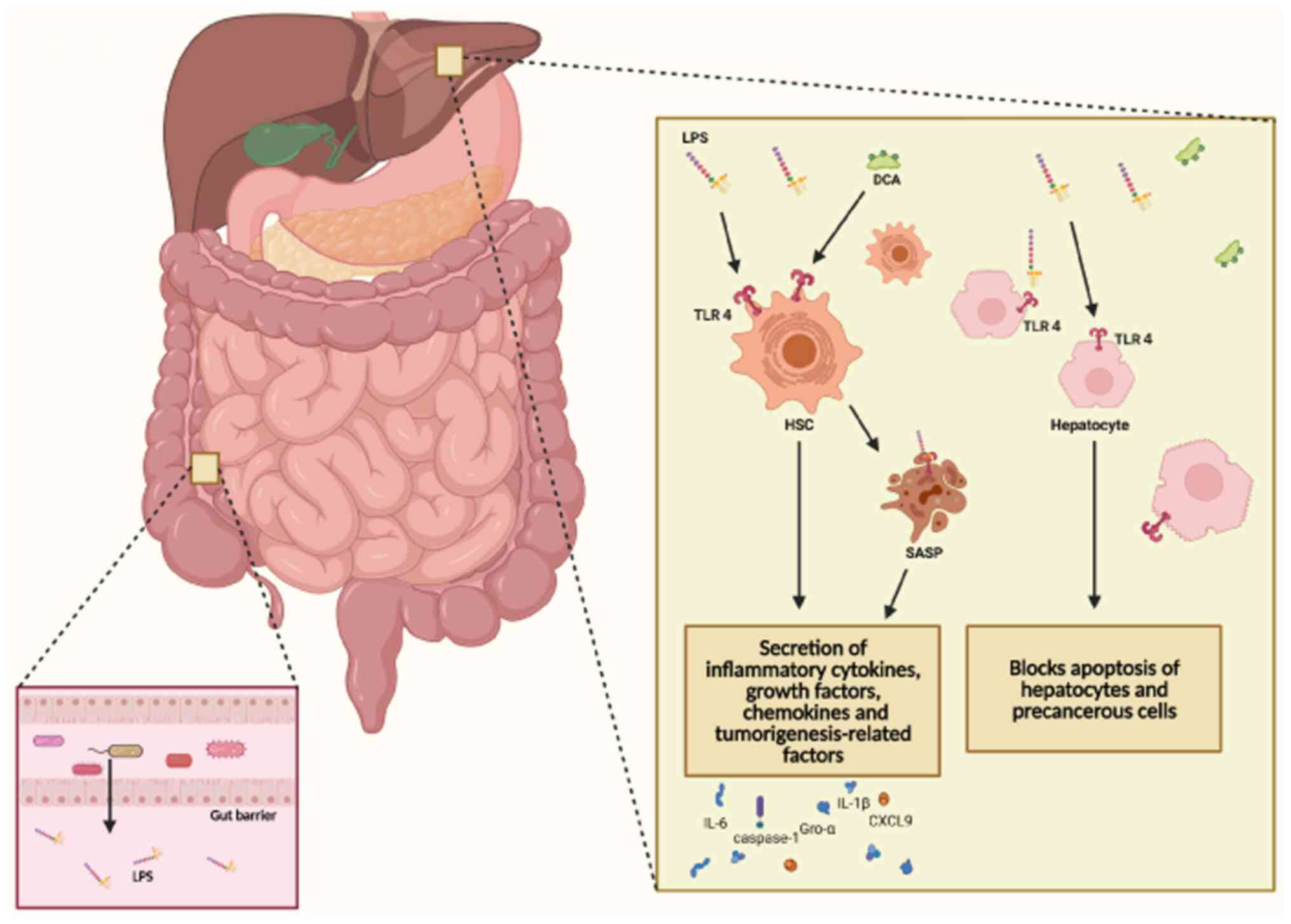
|
1
|
Adak A and Khan MR: An insight into gut
microbiota and its functionalities. Cell Mol Life Sci. 76:473–493.
2019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
Woodruff AW, Salih SY, de Savigny D, Baya
EI, Shah AI and Dafalla AA: Toxocariasis in the Sudan. Ann Trop Med
Parasitol. 75:559–561. 1981. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
Fan Y and Pedersen O: Gut microbiota in
human metabolic health and disease. Nat Rev Microbiol. 19:55–71.
2021. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
Wiest R, Albillos A, Trauner M, Bajaj JS
and Jalan R: Targeting the gut-liver axis in liver disease. J
Hepatol. 67:1084–1103. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Milosevic I, Vujovic A, Barac A, Djelic M,
Korac M, Radovanovic Spurnic A, Gmizic I, Stevanovic O, Djordjevic
V, Lekic N, et al: Gut-Liver axis, gut microbiota, and its
modulation in the management of liver diseases: A review of the
literature. Int J Mol Sci. 20:3952019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Kim ER, Park JS, Kim JH, Oh JY, Oh IJ,
Choi DH, Lee YS, Park IS, Kim S, Lee DH, et al: A GLP-1/GLP-2
receptor dual agonist to treat NASH: Targeting the gut-liver axis
and microbiome. Hepatology. 75:1523–1538. 2022. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Song Q, Zhang X, Liu W, Wei H, Liang W,
Zhou Y, Ding Y, Ji F, Ho-Kwan Cheung A, Wong N and Yu J:
Bifidobacterium pseudolongum-generated acetate suppresses
non-alcoholic fatty liver disease-associated hepatocellular
carcinoma. J Hepatol. 79:1352–1365. 2023. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Bertocchi A, Carloni S, Ravenda PS,
Bertalot G, Spadoni I, Lo Cascio A, Gandini S, Lizier M, Braga D,
Asnicar F, et al: Gut vascular barrier impairment leads to
intestinal bacteria dissemination and colorectal cancer metastasis
to liver. Cancer Cell. 39:708–724.e11. 2021. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Hu X, Chen F, Jia L, Long A, Peng Y, Li X,
Huang J, Wei X, Fang X, Gao Z, et al: A gut-derived hormone
regulates cholesterol metabolism. Cell. 187:1685–700.e18. 2024.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Kuang J, Wang J, Li Y, Li M, Zhao M, Ge K,
Zheng D, Cheung KCP, Liao B, Wang S, et al: Hyodeoxycholic acid
alleviates non-alcoholic fatty liver disease through modulating the
gut-liver axis. Cell Metab. 35:1752–1766.e8. 2023. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Sheng Z, Xu J, Li F, Yuan Y, Peng X, Chen
S, Zhou R and Huang W: The RING-domain E3 ubiquitin ligase RNF146
promotes cardiac hypertrophy by suppressing the LKB1/AMPK signaling
pathway. Exp Cell Res. 410:1129542022. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Goto J, Otaki Y, Watanabe T, Kobayashi Y,
Aono T, Watanabe K, Wanezaki M, Kutsuzawa D, Kato S, Tamura H, et
al: HECT (Homologous to the E6-AP Carboxyl Terminus)-Type ubiquitin
E3 ligase ITCH attenuates cardiac hypertrophy by suppressing the
Wnt/β-catenin signaling pathway. Hypertension. 76:1868–1878. 2020.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Broquetas T and Carrion JA: Past, present,
and future of long-term treatment for hepatitis B virus. World J
Gastroenterol. 29:3964–3983. 2023. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Frenette C, Mendiratta-Lala M, Salgia R,
Wong RJ, Sauer BG and Pillai A: ACG clinical guideline: Focal liver
lesions. Am J Gastroenterol. 119:1235–1271. 2024. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
European Association for the Study of the
Liver (EASL); European Association for the Study of Diabetes
(EASD); European Association for the Study of Obesity (EASO) and
the European Association for the Study of the Liver (EASL), .
EASL-EASD-EASO Clinical Practice Guidelines on the management of
metabolic dysfunction-associated steatotic liver disease (MASLD). J
Hepatol. 81:492–542. 2024. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Forrest EH, Atkinson SR, Richardson P,
Masson S, Ryder S, Thursz MR and Allison M: ACG clinical guideline
for alcoholic liver disease: The MELD threshold for corticosteroid
treatment has yet to be established. Am J Gastroenterol.
114:175–176. 2019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Dai JJ, Zhang YF and Zhang ZH: Global
trends and hotspots of treatment for nonalcoholic fatty liver
disease: A bibliometric and visualization analysis (2010–2023).
World J Gastroenterol. 29:5339–5360. 2023. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
Suddle A, Reeves H, Hubner R, Marshall A,
Rowe I, Tiniakos D, Hubscher S, Callaway M, Sharma D, See TC, et
al: British Society of Gastroenterology guidelines for the
management of hepatocellular carcinoma in adults. Gut.
73:1235–1268. 2024. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
Zhou Q, Li B and Li J: DLL4-Notch
signalling in acute-on-chronic liver failure: State of the art and
perspectives. Life Sci. 317:1214382023. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
Conde de la Rosa L, Garcia-Ruiz C, Vallejo
C, Baulies A, Nuñez S, Monte MJ, Marin JJG, Baila-Rueda L, Cenarro
A, Civeira F, et al: STARD1 promotes NASH-driven HCC by sustaining
the generation of bile acids through the alternative mitochondrial
pathway. J Hepatol. 74:1429–1441. 2021. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
Bernsmeier C, Singanayagam A, Patel VC,
Wendon J and Antoniades CG: Immunotherapy in the treatment and
prevention of infection in acute-on-chronic liver failure.
Immunotherapy. 7:641–654. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22
|
Wulf J, Guckenberger M, Haedinger U,
Oppitz U, Mueller G, Baier K and Flentje M: Stereotactic
radiotherapy of primary liver cancer and hepatic metastases. Acta
Oncol. 45:838–847. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23
|
Devarbhavi H, Asrani SK, Arab JP, Nartey
YA, Pose E and Kamath PS: Global burden of liver disease: 2023
update. J Hepatol. 79:516–537. 2023. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24
|
Taha G, Ezra L and Abu-Freha N: Hepatitis
C elimination: Opportunities and challenges in 2023. Viruses.
15:14132023. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
25
|
Hsu YC, Huang DQ and Nguyen MH: Global
burden of hepatitis B virus: Current status, missed opportunities
and a call for action. Nat Rev Gastroenterol Hepatol. 20:524–537.
2023. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
26
|
Hernandez-Evole H, Jimenez-Esquivel N,
Pose E and Bataller R: Alcohol-associated liver disease:
Epidemiology and management. Ann Hepatol. 29:1011622024. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
27
|
Julien J, Ayer T, Bethea ED, Tapper EB and
Chhatwal J: Projected prevalence and mortality associated with
alcohol-related liver disease in the USA, 2019–40: A modelling
study. Lancet Public Health. 5:e316–e23. 2020. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
28
|
McGlynn KA, Petrick JL and El-Serag HB:
Epidemiology of hepatocellular carcinoma. Hepatology. 73 (Suppl
1):S4–S13. 2021. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
29
|
Collins SL, Stine JG, Bisanz JE, Okafor CD
and Patterson AD: Bile acids and the gut microbiota: Metabolic
interactions and impacts on disease. Nat Rev Microbiol. 21:236–247.
2023. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
30
|
Taranto MP, Perez-Martinez G and Font de
Valdez G: Effect of bile acid on the cell membrane functionality of
lactic acid bacteria for oral administration. Res Microbiol.
157:720–725. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
31
|
Han B, Lv X, Liu G, Li S, Fan J, Chen L,
Huang Z, Lin G, Xu X, Huang Z, et al: Gut microbiota-related bile
acid metabolism-FXR/TGR5 axis impacts the response to
anti-α4β7-integrin therapy in humanized mice with colitis. Gut
Microbes. 15:22321432023. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
32
|
Liu HM, Chang ZY, Yang CW, Chang HH and
Lee TY: Farnesoid X receptor agonist GW4064 protects
lipopolysaccharide-induced intestinal epithelial barrier function
and colorectal tumorigenesis signaling through the
αKlotho/βKlotho/FGFs pathways in mice. Int J Mol Sci. 24:169322023.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
33
|
Ploton M, Mazuy C, Gheeraert C, Dubois V,
Berthier A, Dubois-Chevalier J, Maréchal X, Bantubungi K, Diemer H,
Cianférani S, et al: The nuclear bile acid receptor FXR is a PKA-
and FOXA2-sensitive activator of fasting hepatic gluconeogenesis. J
Hepatol. 69:1099–1109. 2018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
34
|
Cao Y, Xiao Y, Zhou K, Yan J, Wang P, Yan
W and Cai W: FXR agonist GW4064 improves liver and intestinal
pathology and alters bile acid metabolism in rats undergoing small
intestinal resection. Am J Physiol Gastrointest Liver Physiol.
317:G108–G115. 2019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
35
|
Yan Y, Sha Y, Huang X, Yuan W, Wu F, Hong
J, Fang S, Huang B, Hu C, Wang B and Zhang X: Roux-en-Y gastric
bypass improves metabolic conditions in association with increased
serum bile acids level and hepatic Farnesoid X receptor expression
in a T2DM rat model. Obes Surg. 29:2912–2922. 2019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
36
|
Watanabe M, Houten SM, Mataki C,
Christoffolete MA, Kim BW, Sato H, Messaddeq N, Harney JW, Ezaki O,
Kodama T, et al: Bile acids induce energy expenditure by promoting
intracellular thyroid hormone activation. Nature. 439:484–489.
2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
37
|
Zietak M and Kozak LP: Bile acids induce
uncoupling protein 1-dependent thermogenesis and stimulate energy
expenditure at thermoneutrality in mice. Am J Physiol Endocrinol
Metab. 310:E346–E354. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
38
|
Van Treuren W and Dodd D: Microbial
contribution to the human metabolome: Implications for health and
disease. Annu Rev Pathol. 15:345–369. 2020. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
39
|
Cornell RP: Restriction of gut-derived
endotoxin impairs DNA synthesis for liver regeneration. Am J
Physiol. 249:R563–R569. 1985.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
40
|
Nolan JP: The role of intestinal endotoxin
in liver injury: A long and evolving history. Hepatology.
52:1829–1835. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
41
|
Liu H, Xi Q, Tan S, Qu Y, Meng Q, Zhang Y,
Cheng Y and Wu G: The metabolite butyrate produced by gut
microbiota inhibits cachexia-associated skeletal muscle atrophy by
regulating intestinal barrier function and macrophage polarization.
Int Immunopharmacol. 124:1110012023. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
42
|
Tang G, Du Y, Guan H, Jia J, Zhu N, Shi Y,
Rong S and Yuan W: Butyrate ameliorates skeletal muscle atrophy in
diabetic nephropathy by enhancing gut barrier function and
FFA2-mediated PI3K/Akt/mTOR signals. Br J Pharmacol. 179:159–178.
2022. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
43
|
Meena AS, Shukla PK, Bell B, Giorgianni F,
Caires R, Fernández-Peña C, Beranova S, Aihara E, Montrose MH,
Chaib M, et al: TRPV6 channel mediates alcohol-induced gut barrier
dysfunction and systemic response. Cell Rep. 39:1109372022.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
44
|
Dominguez-Bello MG, Godoy-Vitorino F,
Knight R and Blaser MJ: Role of the microbiome in human
development. Gut. 68:1108–1114. 2019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
45
|
Han YH, Onufer EJ, Huang LH, Sprung RW,
Davidson WS, Czepielewski RS, Wohltmann M, Sorci-Thomas MG, Warner
BW and Randolph GJ: Enterically derived high-density lipoprotein
restrains liver injury through the portal vein. Science.
373:eabe67292021. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
46
|
Gomaa EZ: Human gut microbiota/microbiome
in health and diseases: A review. Antonie Van Leeuwenhoek.
113:2019–2040. 2020. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
47
|
Robles-Alonso V and Guarner F: Progress in
the knowledge of the intestinal human microbiota. Nutr Hosp.
28:553–557. 2013.(In Spanish). PubMed/NCBI
|
|
48
|
Charlet R, Bortolus C, Barbet M, Sendid B
and Jawhara S: A decrease in anaerobic bacteria promotes Candida
glabrata overgrowth while β-glucan treatment restores the gut
microbiota and attenuates colitis. Gut Pathog. 10:502018.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
49
|
Charlet R, Pruvost Y, Tumba G, Istel F,
Poulain D, Kuchler K, Sendid B and Jawhara S: Remodeling of the
Candida glabrata cell wall in the gastrointestinal tract affects
the gut microbiota and the immune response. Sci Rep. 8:33162018.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
50
|
Bertin Y, Girardeau JP, Chaucheyras-Durand
F, Lyan B, Pujos-Guillot E, Harel J and Martin C:
Enterohaemorrhagic Escherichia coli gains a competitive advantage
by using ethanolamine as a nitrogen source in the bovine intestinal
content. Environ Microbiol. 13:365–377. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
51
|
Ma HD, Zhao ZB, Ma WT, Liu QZ, Gao CY, Li
L, Wang J, Tsuneyama K, Liu B, Zhang W, et al: Gut microbiota
translocation promotes autoimmune cholangitis. J Autoimmun.
95:47–57. 2018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
52
|
Shao T, Zhao C, Li F, Gu Z, Liu L, Zhang
L, Wang Y, He L, Liu Y, Liu Q, et al: Intestinal HIF-1α deletion
exacerbates alcoholic liver disease by inducing intestinal
dysbiosis and barrier dysfunction. J Hepatol. 69:886–895. 2018.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
53
|
Giuffre M, Campigotto M, Campisciano G,
Comar M and Croce LS: A story of liver and gut microbes: How does
the intestinal flora affect liver disease? A review of the
literature. Am J Physiol Gastrointest Liver Physiol. 318:G889–G906.
2020. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
54
|
Bellot P, Frances R and Such J:
Pathological bacterial translocation in cirrhosis: Pathophysiology,
diagnosis and clinical implications. Liver Int. 33:31–39. 2013.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
55
|
Giorgio V, Miele L, Principessa L,
Ferretti F, Villa MP, Negro V, Grieco A, Alisi A and Nobili V:
Intestinal permeability is increased in children with non-alcoholic
fatty liver disease, and correlates with liver disease severity.
Dig Liver Dis. 46:556–560. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
56
|
Miele L, Valenza V, La Torre G, Montalto
M, Cammarota G, Ricci R, Mascianà R, Forgione A, Gabrieli ML,
Perotti G, et al: Increased intestinal permeability and tight
junction alterations in nonalcoholic fatty liver disease.
Hepatology. 49:1877–1887. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
57
|
Rao R: Endotoxemia and gut barrier
dysfunction in alcoholic liver disease. Hepatology. 50:638–644.
2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
58
|
Sewell GW and Kaser A: Interleukin-23 in
the pathogenesis of inflammatory bowel disease and implications for
therapeutic intervention. J Crohns Colitis. 16 (Suppl 2):ii3–ii19.
2022. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
59
|
Sokol H, Leducq V, Aschard H, Pham HP,
Jegou S, Landman C, Cohen D, Liguori G, Bourrier A, Nion-Larmurier
I, et al: Fungal microbiota dysbiosis in IBD. Gut. 66:1039–1048.
2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
60
|
Ng SC, Benjamin JL, McCarthy NE, Hedin CR,
Koutsoumpas A, Plamondon S, Price CL, Hart AL, Kamm MA, Forbes A,
et al: Relationship between human intestinal dendritic cells, gut
microbiota, and disease activity in Crohn's disease. Inflamm Bowel
Dis. 17:2027–2037. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
61
|
Coccia M, Harrison OJ, Schiering C,
Asquith MJ, Becher B, Powrie F and Maloy KJ: IL-1β mediates chronic
intestinal inflammation by promoting the accumulation of IL-17A
secreting innate lymphoid cells and CD4(+) Th17 cells. J Exp Med.
209:1595–1609. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
62
|
Ma TY, Boivin MA, Ye D, Pedram A and Said
HM: Mechanism of TNF-{alpha} modulation of Caco-2 intestinal
epithelial tight junction barrier: Role of myosin light-chain
kinase protein expression. Am J Physiol Gastrointest Liver Physiol.
288:G422–G430. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
63
|
He WQ, Wang J, Sheng JY, Zha JM, Graham WV
and Turner JR: Contributions of myosin light chain kinase to
regulation of epithelial paracellular permeability and mucosal
homeostasis. Int J Mol Sci. 21:9932020. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
64
|
Chotikatum S, Naim HY and El-Najjar N:
Inflammation induced ER stress affects absorptive intestinal
epithelial cells function and integrity. Int Immunopharmacol.
55:336–344. 2018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
65
|
Kinoshita N, Hiroi T, Ohta N, Fukuyama S,
Park EJ and Kiyono H: Autocrine IL-15 mediates intestinal
epithelial cell death via the activation of neighboring
intraepithelial NK cells. J Immunol. 169:6187–6192. 2002.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
66
|
Rohr M, Narasimhulu CA, Keewan E, Hamid S
and Parthasarathy S: The dietary peroxidized lipid, 13-HPODE,
promotes intestinal inflammation by mediating granzyme B secretion
from natural killer cells. Food Funct. 11:9526–9534. 2020.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
67
|
Yasuda K, Nakanishi K and Tsutsui H:
Interleukin-18 in health and disease. Int J Mol Sci. 19:6492019.
View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
68
|
Woznicki JA, Saini N, Flood P, Rajaram S,
Lee CM, Stamou P, Skowyra A, Bustamante-Garrido M, Regazzoni K,
Crawford N, et al: TNF-α synergises with IFN-γ to induce
caspase-8-JAK1/2-STAT1-dependent death of intestinal epithelial
cells. Cell Death Dis. 12:8642021. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
69
|
Chang JT: Pathophysiology of inflammatory
bowel diseases. N Engl J Med. 383:2652–2664. 2020. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
70
|
Romagnani S: Lymphokine production by
human T cells in disease states. Annu Rev Immunol. 12:227–257.
1994. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
71
|
Fort MM, Cheung J, Yen D, Li J, Zurawski
SM, Lo S, Menon S, Clifford T, Hunte B, Lesley R, et al: IL-25
induces IL-4, IL-5, and IL-13 and Th2-associated pathologies in
vivo. Immunity. 15:985–995. 2001. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
72
|
Lin Y, Li B, Yang X, Liu T, Shi T, Deng B,
Zhang Y, Jia L, Jiang Z and He R: Non-hematopoietic STAT6 induces
epithelial tight junction dysfunction and promotes intestinal
inflammation and tumorigenesis. Mucosal Immunol. 12:1304–1315.
2019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
73
|
Ceponis PJ, Botelho F, Richards CD and
McKay DM: Interleukins 4 and 13 increase intestinal epithelial
permeability by a phosphatidylinositol 3-kinase pathway. Lack of
evidence for STAT 6 involvement. J Biol Chem. 275:29132–29137.
2000. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
74
|
He L, Liu T, Shi Y, Tian F, Hu H, Deb DK,
Bissonnette M and Li YC: Gut epithelial Vitamin D receptor
regulates Microbiota-dependent mucosal inflammation by suppressing
intestinal epithelial cell apoptosis. Endocrinology. 159:967–979.
2018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
75
|
Lee SH, Kwon JE and Cho ML: Immunological
pathogenesis of inflammatory bowel disease. Intest Res. 16:26–42.
2018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
76
|
Wang X, Ni J, You Y, Feng G, Zhang S, Bao
W, Hou H, Li H, Liu L, Zheng M, et al: SNX10-mediated LPS sensing
causes intestinal barrier dysfunction via a caspase-5-dependent
signaling cascade. EMBO J. 40:e1080802021. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
77
|
Li Q, Rempel JD, Yang J and Minuk GY: The
effects of Pathogen-associated molecular patterns on peripheral
blood monocytes in patients with Non-alcoholic fatty liver disease.
J Clin Exp Hepatol. 12:808–817. 2022. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
78
|
Nakamoto N and Kanai T: Role of toll-like
receptors in immune activation and tolerance in the liver. Front
Immunol. 5:2212014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
79
|
Szabo G, Dolganiuc A and Mandrekar P:
Pattern recognition receptors: A contemporary view on liver
diseases. Hepatology. 44:287–298. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
80
|
Kesar V and Odin JA: Toll-like receptors
and liver disease. Liver Int. 34:184–196. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
81
|
Hardin PE: From biological clock to
biological rhythms. Genome Biol. 1:REVIEWS10232000. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
82
|
Jouffe C, Weger BD, Martin E, Atger F,
Weger M, Gobet C, Ramnath D, Charpagne A, Morin-Rivron D, Powell
EE, et al: Disruption of the circadian clock component BMAL1
elicits an endocrine adaption impacting on insulin sensitivity and
liver disease. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA. 119:e22000831192022.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
83
|
Kinouchi K and Sassone-Corsi P: Metabolic
rivalry: Circadian homeostasis and tumorigenesis. Nat Rev Cancer.
20:645–661. 2020. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
84
|
Nassan M and Videnovic A: Circadian
rhythms in neurodegenerative disorders. Nat Rev Neurol. 18:7–24.
2022. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
85
|
Song S, Tien CL, Cui H, Basil P, Zhu N,
Gong Y, Li W, Li H, Fan Q, Min Choi J, et al: Myocardial
Rev-erb-mediated diurnal metabolic rhythm and obesity paradox.
Circulation. 145:448–464. 2022. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
86
|
Choi H, Rao MC and Chang EB: Gut
microbiota as a transducer of dietary cues to regulate host
circadian rhythms and metabolism. Nat Rev Gastroenterol Hepatol.
18:679–689. 2021. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
87
|
Heddes M, Altaha B, Niu Y, Reitmeier S,
Kleigrewe K, Haller D and Kiessling S: The intestinal clock drives
the microbiome to maintain gastrointestinal homeostasis. Nat
Commun. 13:60682022. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
88
|
Thaiss CA, Zeevi D, Levy M,
Zilberman-Schapira G, Suez J, Tengeler AC, Abramson L, Katz MN,
Korem T, Zmora N, et al: Transkingdom control of microbiota diurnal
oscillations promotes metabolic homeostasis. Cell. 159:514–529.
2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
89
|
Backhed F, Ding H, Wang T, Hooper LV, Koh
GY, Nagy A, Semenkovich CF and Gordon JI: The gut microbiota as an
environmental factor that regulates fat storage. Proc Natl Acad Sci
USA. 101:15718–15723. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
90
|
Rabot S, Membrez M, Bruneau A, Gerard P,
Harach T, Moser M, Raymond F, Mansourian R and Chou CJ: Germ-free
C57BL/6J mice are resistant to high-fat-diet-induced insulin
resistance and have altered cholesterol metabolism. FASEB J.
24:4948–4959. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
91
|
Zhang X, Coker OO, Chu ES, Fu K, Lau HCH,
Wang YX, Chan AWH, Wei H, Yang X, Sung JJY and Yu J: Dietary
cholesterol drives fatty liver-associated liver cancer by
modulating gut microbiota and metabolites. Gut. 70:761–774. 2021.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
92
|
Wang B, Kong Q, Li X, Zhao J, Zhang H,
Chen W and Wang G: A High-fat diet increases gut microbiota
biodiversity and energy expenditure due to nutrient difference.
Nutrients. 12:31972020. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
93
|
Turnbaugh PJ, Ley RE, Mahowald MA, Magrini
V, Mardis ER and Gordon JI: An Obesity-associated gut microbiome
with increased capacity for energy harvest. Nature. 444:1027–1031.
2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
94
|
Riva A, Borgo F, Lassandro C, Verduci E,
Morace G, Borghi E and Berry D: Pediatric obesity is associated
with an altered gut microbiota and discordant shifts in Firmicutes
populations. Environ Microbiol. 19:95–105. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
95
|
Palmnas-Bedard MSA, Costabile G, Vetrani
C, Aberg S, Hjalmarsson Y, Dicksved J, Riccardi G and Landberg R:
The human gut microbiota and glucose metabolism: A scoping review
of key bacteria and the potential role of SCFAs. Am J Clin Nutr.
116:862–874. 2022. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
96
|
Dunn R, Wetten A, McPherson S and Donnelly
MC: Viral hepatitis in 2021: The challenges remaining and how we
should tackle them. World J Gastroenterol. 28:76–95. 2022.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
97
|
Zhao X and Guo S: Methods for visualizing
intracellular organelles. J Vis Exp. Mar 3–2023.doi:
10.3791/64966.
|
|
98
|
Zhao W, Ma L, Cai C and Gong X: Caffeine
Inhibits NLRP3 inflammasome activation by suppressing MAPK/NF-κB
and A2aR signaling in LPS-induced THP-1 macrophages. Int J Biol
Sci. 15:1571–1581. 2019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
99
|
Chou HH, Chien WH, Wu LL, Cheng CH, Chung
CH, Horng JH, Ni YH, Tseng HT, Wu D, Lu X, et al: Age-related
immune clearance of hepatitis B virus infection requires the
establishment of gut microbiota. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA.
112:2175–2180. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
100
|
Chauhan A, Kumar R, Sharma S, Mahanta M,
Vayuuru SK, Nayak B and Kumar S: Shalimar: Fecal microbiota
transplantation in Hepatitis B e antigen-positive chronic Hepatitis
B patients: A pilot study. Dig Dis Sci. 66:873–880. 2021.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
101
|
Huang H, Ren Z, Gao X, Hu X, Zhou Y, Jiang
J, Lu H, Yin S, Ji J, Zhou L and Zheng S: Integrated analysis of
microbiome and host transcriptome reveals correlations between gut
microbiota and clinical outcomes in HBV-related hepatocellular
carcinoma. Genome Med. 12:1022020. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
102
|
Preveden T, Scarpellini E, Milic N, Luzza
F and Abenavoli L: Gut microbiota changes and chronic hepatitis C
virus infection. Expert Rev Gastroenterol Hepatol. 11:813–819.
2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
103
|
Shen Y, Wu SD, Chen Y, Li XY, Zhu Q,
Nakayama K, Zhang WQ, Weng CZ, Zhang J, Wang HK, et al: Alterations
in gut microbiome and metabolomics in chronic hepatitis B
infection-associated liver disease and their impact on peripheral
immune response. Gut Microbes. 15:21550182023. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
104
|
Wei X, Yan X, Zou D, Yang Z, Wang X, Liu
W, Wang S, Li X, Han J, Huang L and Yuan J: Abnormal fecal
microbiota community and functions in patients with hepatitis B
liver cirrhosis as revealed by a metagenomic approach. BMC
Gastroenterol. 13:1752013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
105
|
Bajaj JS, Liu EJ, Kheradman R, Fagan A,
Heuman DM, White M, Gavis EA, Hylemon P, Sikaroodi M and Gillevet
PM: Fungal dysbiosis in cirrhosis. Gut. 67:1146–1154. 2018.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
106
|
Aly AM, Adel A, El-Gendy AO, Essam TM and
Aziz RK: Gut microbiome alterations in patients with stage 4
hepatitis C. Gut Pathog. 8:422016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
107
|
Luther J, Khan S, Gala MK, Kedrin D,
Sridharan G, Goodman RP, Garber JJ, Masia R, Diagacomo E, Adams D,
et al: Hepatic gap junctions amplify alcohol liver injury by
propagating cGAS-mediated IRF3 activation. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA.
117:11667–11673. 2020. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
108
|
Jophlin LL, Singal AK, Bataller R, Wong
RJ, Sauer BG, Terrault NA and Shah VH: ACG clinical guideline:
Alcohol-associated liver disease. Am J Gastroenterol. 119:30–54.
2024. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
109
|
Huang DQ, Mathurin P, Cortez-Pinto H and
Loomba R: Global epidemiology of alcohol-associated cirrhosis and
HCC: Trends, projections and risk factors. Nat Rev Gastroenterol
Hepatol. 20:37–49. 2023. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
110
|
Singal AK, Bataller R, Ahn J, Kamath PS
and Shah VH: ACG clinical guideline: Alcoholic liver disease. Am J
Gastroenterol. 113:175–194. 2018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
111
|
Acharya C and Bajaj JS: Gut Microbiota and
complications of liver disease. Gastroenterol Clin North Am.
46:155–169. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
112
|
Dubinkina VB, Tyakht AV, Odintsova VY,
Yarygin KS, Kovarsky BA, Pavlenko AV, Ischenko DS, Popenko AS,
Alexeev DG, Taraskina AY, et al: Links of gut microbiota
composition with alcohol dependence syndrome and alcoholic liver
disease. Microbiome. 5:1412017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
113
|
Blaak EE, Canfora EE, Theis S, Frost G,
Groen AK, Mithieux G, Nauta A, Scott K, Stahl B, van Harsselaar J,
et al: Short chain fatty acids in human gut and metabolic health.
Benef Microbes. 11:411–455. 2020. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
114
|
Wang Z, Zhang X, Zhu L, Yang X, He F, Wang
T, Bao T, Lu H, Wang H and Yang S: Inulin alleviates inflammation
of alcoholic liver disease via SCFAs-inducing suppression of M1 and
facilitation of M2 macrophages in mice. Int Immunopharmacol.
78:1060622020. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
115
|
Yang X, He F, Zhang Y, Xue J, Li K, Zhang
X, Zhu L, Wang Z, Wang H and Yang S: Inulin ameliorates alcoholic
liver disease via suppressing LPS-TLR4-mpsi axis and modulating gut
microbiota in mice. Alcohol Clin Exp Res. 43:411–424. 2019.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
116
|
Deng M, Qu F, Chen L, Liu C, Zhang M, Ren
F, Guo H, Zhang H, Ge S, Wu C and Zhao L: SCFAs alleviated
steatosis and inflammation in mice with NASH induced by MCD. J
Endocrinol. 245:425–437. 2020. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
117
|
Mundi MS, Velapati S, Patel J, Kellogg TA,
Abu Dayyeh BK and Hurt RT: Evolution of NAFLD and its management.
Nutr Clin Pract. 35:72–84. 2020. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
118
|
Aron-Wisnewsky J, Warmbrunn MV, Nieuwdorp
M and Clement K: Metabolism and metabolic disorders and the
microbiome: The intestinal microbiota associated with obesity,
lipid metabolism, and metabolic health-pathophysiology and
therapeutic strategies. Gastroenterology. 160:573–599. 2021.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
119
|
Canfora EE, Meex RCR, Venema K and Blaak
EE: Gut microbial metabolites in obesity, NAFLD and T2DM. Nat Rev
Endocrinol. 15:261–273. 2019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
120
|
Kolodziejczyk AA, Zheng D, Shibolet O and
Elinav E: The role of the microbiome in NAFLD and NASH. EMBO Mol
Med. 11:e93022019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
121
|
Henao-Mejia J, Elinav E, Jin C, Hao L,
Mehal WZ, Strowig T, Thaiss CA, Kau AL, Eisenbarth SC, Jurczak MJ,
et al: Inflammasome-mediated dysbiosis regulates progression of
NAFLD and obesity. Nature. 482:179–185. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
122
|
Zhong S, Li L, Liang N, Zhang L, Xu X,
Chen S and Yin H: Acetaldehyde dehydrogenase 2 regulates HMG-CoA
reductase stability and cholesterol synthesis in the liver. Redox
Biol. 41:1019192021. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
123
|
Inokuchi S, Tsukamoto H, Park E, Liu ZX,
Brenner DA and Seki E: Toll-like receptor 4 mediates
alcohol-induced steatohepatitis through bone marrow-derived and
endogenous liver cells in mice. Alcohol Clin Exp Res. 35:1509–1518.
2011.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
124
|
Bogatyrev SR, Rolando JC and Ismagilov RF:
Self-reinoculation with fecal flora changes microbiota density and
composition leading to an altered bile-acid profile in the mouse
small intestine. Microbiome. 8:192020. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
125
|
Ma C, Han M, Heinrich B, Fu Q, Zhang Q,
Sandhu M, Agdashian D, Terabe M, Berzofsky JA, Fako V, et al: Gut
microbiome-mediated bile acid metabolism regulates liver cancer via
NKT cells. Science. 360:eaan59312018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
126
|
Endo H, Niioka M, Kobayashi N, Tanaka M
and Watanabe T: Butyrate-producing probiotics reduce nonalcoholic
fatty liver disease progression in rats: New insight into the
probiotics for the gut-liver axis. PLoS One. 8:e633882013.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
127
|
Ma YY, Li L, Yu CH, Shen Z, Chen LH and Li
YM: Effects of probiotics on nonalcoholic fatty liver disease: A
meta-analysis. World J Gastroenterol. 19:6911–6918. 2013.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
128
|
Kirpich IA, Solovieva NV, Leikhter SN,
Shidakova NA, Lebedeva OV, Sidorov PI, Bazhukova TA, Soloviev AG,
Barve SS, McClain CJ and Cave M: Probiotics restore bowel flora and
improve liver enzymes in human alcohol-induced liver injury: A
pilot study. Alcohol. 42:675–682. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
129
|
Schuppan D and Afdhal NH: Liver cirrhosis.
Lancet. 371:838–851. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
130
|
Quiroz-Aldave JE, Gamarra-Osorio ER,
Durand-Vasquez MDC, Rafael-Robles LDP, Gonzales-Yovera JG,
Quispe-Flores MA, Concepción-Urteaga LA, Román-González A,
Paz-Ibarra J and Concepción-Zavaleta MJ: From liver to hormones:
The endocrine consequences of cirrhosis. World J Gastroenterol.
30:1073–1095. 2024. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
131
|
Horn P and Tacke F: Metabolic
reprogramming in liver fibrosis. Cell Metab. 36:1439–1455. 2024.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
132
|
Yang X, Li Q, Liu W, Zong C, Wei L, Shi Y
and Han Z: Mesenchymal stromal cells in hepatic fibrosis/cirrhosis:
From pathogenesis to treatment. Cell Mol Immunol. 20:583–599. 2023.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
133
|
Iredale JP, Thompson A and Henderson NC:
Extracellular matrix degradation in liver fibrosis: Biochemistry
and regulation. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1832:876–883. 2013.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
134
|
Bataller R and Brenner DA: Liver fibrosis.
J Clin Invest. 115:209–218. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
135
|
Smith A, Baumgartner K and Bositis C:
Cirrhosis: Diagnosis and management. Am Fam Physician. 100:759–770.
2019.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
136
|
Tapper EB and Parikh ND: Diagnosis and
management of cirrhosis and its complications: A review. JAMA.
329:1589–1602. 2023. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
137
|
GBD 2019 Diseases and Injuries
Collaborators: Global burden of 369 diseases and injuries in 204
countries and territories, 1990–2019: A systematic analysis for the
Global Burden of Disease Study 2019. Lancet. 396:1204–1222. 2020.
View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
138
|
Asrani SK, Devarbhavi H, Eaton J and
Kamath PS: Burden of liver diseases in the world. J Hepatol.
70:151–171. 2019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
139
|
European Association for the Study of the
Liver. Electronic address, . simpleeasloffice@easloffice.eu
and European Association for the Study of the Liver: EASL clinical
practice guidelines on Acute-on-chronic liver failure. J Hepatol.
79:461–491. 2023. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
140
|
Gines P, Krag A, Abraldes JG, Sola E,
Fabrellas N and Kamath PS: Liver cirrhosis. Lancet. 398:1359–1376.
2021. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
141
|
Groschwitz KR and Hogan SP: Intestinal
barrier function: Molecular regulation and disease pathogenesis. J
Allergy Clin Immunol. 124:3–22. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
142
|
Nishimura N, Kaji K, Kitagawa K, Sawada Y,
Furukawa M, Ozutsumi T, Fujinaga Y, Tsuji Y, Takaya H, Kawaratani
H, et al: Intestinal permeability is a mechanical rheostat in the
pathogenesis of liver cirrhosis. Int J Mol Sci. 22:69212021.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
143
|
Trebicka J, Macnaughtan J, Schnabl B,
Shawcross DL and Bajaj JS: The microbiota in cirrhosis and its role
in hepatic decompensation. J Hepatol. 75 (Suppl 1):S67–S81. 2021.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
144
|
Benjamin J, Singla V, Arora I, Sood S and
Joshi YK: Intestinal permeability and complications in liver
cirrhosis: A prospective cohort study. Hepatol Res. 43:200–207.
2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
145
|
Shibamoto A, Kaji K, Nishimura N, Kubo T,
Iwai S, Tomooka F, Suzuki J, Tsuji Y, Fujinaga Y, Kawaratani H, et
al: Vitamin D deficiency exacerbates alcohol-related liver injury
via gut barrier disruption and hepatic overload of endotoxin. J
Nutr Biochem. 122:1094502023. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
146
|
Suk KT and Kim DJ: Gut microbiota: Novel
therapeutic target for nonalcoholic fatty liver disease. Expert Rev
Gastroenterol Hepatol. 13:193–204. 2019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
147
|
Albillos A, Lario M and Alvarez-Mon M:
Cirrhosis-associated immune dysfunction: Distinctive features and
clinical relevance. J Hepatol. 61:1385–1396. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
148
|
Fukui H: Role of gut dysbiosis in liver
diseases: What have we learned so far? Diseases. 7:582019.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
149
|
Camilleri M, Madsen K, Spiller R,
Greenwood-Van Meerveld B and Verne GN: Intestinal barrier function
in health and gastrointestinal disease. Neurogastroenterol Motil.
24:503–512. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
150
|
Ghosh S, Whitley CS, Haribabu B and Jala
VR: Regulation of intestinal barrier function by microbial
metabolites. Cell Mol Gastroenterol Hepatol. 11:1463–1482. 2021.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
151
|
Oh TG, Kim SM, Caussy C, Fu T, Guo J,
Bassirian S, Singh S, Madamba EV, Bettencourt R, Richards L, et al:
A universal Gut-microbiome-derived signature predicts cirrhosis.
Cell Metab. 32:878–888.e6. 2020. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
152
|
Chang CS, Chen GH, Lien HC and Yeh HZ:
Small intestine dysmotility and bacterial overgrowth in cirrhotic
patients with spontaneous bacterial peritonitis. Hepatology.
28:1187–1190. 1998. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
153
|
Corradi F, Brusasco C, Fernandez J, Vila
J, Ramirez MJ, Seva-Pereira T, Fernández-Varo G, Mosbah IB, Acevedo
J, Silva A, et al: Effects of pentoxifylline on intestinal
bacterial overgrowth, bacterial translocation and spontaneous
bacterial peritonitis in cirrhotic rats with ascites. Dig Liver
Dis. 44:239–244. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
154
|
Bajaj JS, Heuman DM, Hylemon PB, Sanyal
AJ, Puri P, Sterling RK, Luketic V, Stravitz RT, Siddiqui MS, Fuchs
M, et al: Randomised clinical trial: Lactobacillus GG modulates gut
microbiome, metabolome and endotoxemia in patients with cirrhosis.
Aliment Pharmacol Ther. 39:1113–1125. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
155
|
Bajaj JS, Kassam Z, Fagan A, Gavis EA, Liu
E, Cox IJ, Kheradman R, Heuman D, Wang J, Gurry T, et al: Fecal
microbiota transplant from a rational stool donor improves hepatic
encephalopathy: A randomized clinical trial. Hepatology.
66:1727–1738. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
156
|
Bajaj JS, Hylemon PB, Ridlon JM, Heuman
DM, Daita K, White MB, Monteith P, Noble NA, Sikaroodi M and
Gillevet PM: Colonic mucosal microbiome differs from stool
microbiome in cirrhosis and hepatic encephalopathy and is linked to
cognition and inflammation. Am J Physiol Gastrointest Liver
Physiol. 303:G675–G685. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
157
|
Chen Y, Yang F, Lu H, Wang B, Chen Y, Lei
D, Wang Y, Zhu B and Li L: Characterization of fecal microbial
communities in patients with liver cirrhosis. Hepatology.
54:562–572. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
158
|
Shen TD, Daniel SG, Patel S, Kaplan E,
Phung L, Lemelle-Thomas K, Chau L, Herman L, Trisolini C, Stonelake
A, et al: The Mucosally-adherent rectal microbiota contains
features unique to alcohol-related cirrhosis. Gut Microbes.
13:19877812021. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
159
|
Egger M, Horvath A, Pruller F, Fickert P,
Finkelman M, Kriegl L, Grønbaek H, Møller HJ, Prattes J, Krause R,
et al: Fungal translocation measured by serum 1,3-β-D-glucan
correlates with severity and outcome of liver cirrhosis-A pilot
study. Liver Int. 43:1975–1983. 2023. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
160
|
Saaoud F, Liu L, Xu K, Cueto R, Shao Y, Lu
Y, Sun Y, Snyder NW, Wu S, Yang L, et al: Aorta- and
liver-generated TMAO enhances trained immunity for increased
inflammation via ER stress/mitochondrial ROS/glycolysis pathways.
JCI Insight. 8:e1581832023. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
161
|
Pleguezuelo M, Benitez JM, Jurado J,
Montero JL and De la Mata M: Diagnosis and management of bacterial
infections in decompensated cirrhosis. World J Hepatol. 5:16–25.
2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
162
|
Kim J, Ahn SW, Kim JY, Whon TW, Lim SK,
Ryu BH, Han NS, Choi HJ, Roh SW and Lee SH: Probiotic
Lactobacilli ameliorate alcohol-induced hepatic damage via
gut microbial alteration. Front Microbiol. 13:8692502022.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
163
|
Llovet JM, Pinyol R, Yarchoan M, Singal
AG, Marron TU, Schwartz M, Pikarsky E, Kudo M and Finn RS: Adjuvant
and neoadjuvant immunotherapies in hepatocellular carcinoma. Nat
Rev Clin Oncol. 21:294–311. 2024. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
164
|
Ding JH, Jin Z, Yang XX, Lou J, Shan WX,
Hu YX, Du Q, Liao QS, Xie R and Xu JY: Role of gut microbiota via
the gut-liver-brain axis in digestive diseases. World J
Gastroenterol. 26:6141–6162. 2020. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
165
|
Queipo-Ortuño MI, Boto-Ordóñez M, Murri M,
Gomez-Zumaquero JM, Clemente-Postigo M, Estruch R, Cardona Diaz F,
Andrés-Lacueva C and Tinahones FJ: Influence of red wine
polyphenols and ethanol on the gut microbiota ecology and
biochemical biomarkers. Am J Clin Nutr. 95:1323–1334. 2012.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
166
|
Mutlu E, Keshavarzian A, Engen P, Forsyth
CB, Sikaroodi M and Gillevet P: Intestinal dysbiosis: A possible
mechanism of alcohol-induced endotoxemia and alcoholic
steatohepatitis in rats. Alcohol Clin Exp Res. 33:1836–1846. 2009.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
167
|
Yan AW, Fouts DE, Brandl J, Starkel P,
Torralba M, Schott E, Tsukamoto H, Nelson KE, Brenner DA and
Schnabl B: Enteric dysbiosis associated with a mouse model of
alcoholic liver disease. Hepatology. 53:96–105. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
168
|
Mutlu EA, Gillevet PM, Rangwala H,
Sikaroodi M, Naqvi A, Engen PA, Kwasny M, Lau CK and Keshavarzian
A: Colonic microbiome is altered in alcoholism. Am J Physiol
Gastrointest Liver Physiol. 302:G966–G978. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
169
|
Boursier J, Mueller O, Barret M, Machado
M, Fizanne L, Araujo-Perez F, Guy CD, Seed PC, Rawls JF, David LA,
et al: The severity of nonalcoholic fatty liver disease is
associated with gut dysbiosis and shift in the metabolic function
of the gut microbiota. Hepatology. 63:764–775. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
170
|
Wang B, Jiang X, Cao M, Ge J, Bao Q, Tang
L, Chen Y and Li L: Altered fecal microbiota correlates with liver
biochemistry in nonobese patients with Non-alcoholic fatty liver
disease. Sci Rep. 6:320022016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
171
|
Singh DP, Khare P, Bijalwan V, Baboota RK,
Singh J, Kondepudi KK, Chopra K and Bishnoi M: Coadministration of
isomalto-oligosaccharides augments metabolic health benefits of
cinnamaldehyde in high fat diet fed mice. Biofactors. 43:821–835.
2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
172
|
Ponziani FR, Bhoori S, Castelli C,
Putignani L, Rivoltini L, Del Chierico F, Sanguinetti M, Morelli D,
Paroni Sterbini F, Petito V, et al: Hepatocellular carcinoma is
associated with gut microbiota profile and inflammation in
nonalcoholic fatty liver disease. Hepatology. 69:107–120. 2019.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
173
|
Sarangi AN, Goel A, Singh A, Sasi A and
Aggarwal R: Faecal bacterial microbiota in patients with cirrhosis
and the effect of lactulose administration. BMC Gastroenterol.
17:1252017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
174
|
Ren Z, Li A, Jiang J, Zhou L, Yu Z, Lu H,
Xie H, Chen X, Shao L, Zhang R, et al: Gut microbiome analysis as a
tool towards targeted non-invasive biomarkers for early
hepatocellular carcinoma. Gut. 68:1014–1023. 2019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
175
|
Schneider KM, Mohs A, Gui W, Galvez EJC,
Candels LS, Hoenicke L, Muthukumarasamy U, Holland CH, Elfers C,
Kilic K, et al: Imbalanced gut microbiota fuels hepatocellular
carcinoma development by shaping the hepatic inflammatory
microenvironment. Nat Commun. 13:39642022. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
176
|
Li Z, Zhang Y, Hong W, Wang B, Chen Y,
Yang P, Zhou J, Fan J, Zeng Z and Du S: Gut microbiota modulate
radiotherapy-associated antitumor immune responses against
hepatocellular carcinoma Via STING signaling. Gut Microbes.
14:21190552022. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
177
|
Thoen RU, Longo L, Leonhardt LC, Pereira
MHM, Rampelotto PH, Cerski CTS and Álvares-da-Silva MR: Alcoholic
liver disease and intestinal microbiota in an experimental model:
Biochemical, inflammatory, and histologic parameters. Nutrition.
106:1118882023. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
178
|
McMahan RH, Hulsebus HJ, Najarro KM, Giesy
LE, Frank DN and Kovacs EJ: Changes in gut microbiome correlate
with intestinal barrier dysfunction and inflammation following a
3-day ethanol exposure in aged mice. Alcohol. 107:136–143. 2023.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
179
|
Sangineto M, Grander C, Grabherr F, Mayr
L, Enrich B, Schwärzler J, Dallio M, Bukke VN, Moola A, Moschetta
A, et al: Recovery of Bacteroides thetaiotaomicron
ameliorates hepatic steatosis in experimental alcohol-related liver
disease. Gut Microbes. 14:20890062022. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
180
|
Day AW and Kumamoto CA: Gut microbiome
dysbiosis in alcoholism: Consequences for health and recovery.
Front Cell Infect Microbiol. 12:8401642022. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
181
|
Wang W, Li Q, Chai W, Sun C, Zhang T, Zhao
C, Yuan Y, Wang X, Liu H and Ye H: Lactobacillus paracasei
Jlus66 extenuate oxidative stress and inflammation via regulation
of intestinal flora in rats with non alcoholic fatty liver disease.
Food Sci Nutr. 7:2636–2646. 2019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
182
|
Safari Z and Gerard P: The links between
the gut microbiome and non-alcoholic fatty liver disease (NAFLD).
Cell Mol Life Sci. 76:1541–1558. 2019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
183
|
Ji Y, Yin Y, Li Z and Zhang W: Gut
Microbiota-derived components and metabolites in the progression of
non-alcoholic fatty liver disease (NAFLD). Nutrients. 11:17122019.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
184
|
Fang J, Yu CH, Li XJ, Yao JM, Fang ZY,
Yoon SH and Yu WY: Gut dysbiosis in nonalcoholic fatty liver
disease: Pathogenesis, diagnosis, and therapeutic implications.
Front Cell Infect Microbiol. 12:9970182022. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
185
|
Liu S and Yang X: Intestinal flora plays a
role in the progression of hepatitis-cirrhosis-liver cancer. Front
Cell Infect Microbiol. 13:11401262023. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
186
|
Lee NY and Suk KT: The role of the gut
microbiome in liver cirrhosis treatment. Int J Mol Sci. 22:1992020.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
187
|
Qin N, Yang F, Li A, Prifti E, Chen Y,
Shao L, Guo J, Le Chatelier E, Yao J, Wu L, et al: Alterations of
the human gut microbiome in liver cirrhosis. Nature. 513:59–64.
2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
188
|
Akkiz H: The gut microbiome and
hepatocellular carcinoma. J Gastrointest Cancer. 52:1314–1319.
2021. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
189
|
Schwabe RF and Greten TF: Gut microbiome
in HCC-mechanisms, diagnosis and therapy. J Hepatol. 72:230–238.
2020. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
190
|
Zhang S, Hou L and Sun Q: Correlation
analysis of intestinal flora and immune function in patients with
primary hepatocellular carcinoma. J Gastrointest Oncol.
13:1308–1316. 2022. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
191
|
Zhang HL, Yu LX, Yang W, Tang L, Lin Y, Wu
H, Zhai B, Tan YX, Shan L, Liu Q, et al: Profound impact of gut
homeostasis on chemically-induced pro-tumorigenic inflammation and
hepatocarcinogenesis in rats. J Hepatol. 57:803–812. 2012.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
192
|
Dapito DH, Mencin A, Gwak GY, Pradere JP,
Jang MK, Mederacke I, Caviglia JM, Khiabanian H, Adeyemi A,
Bataller R, et al: Promotion of hepatocellular carcinoma by the
intestinal microbiota and TLR4. Cancer Cell. 21:504–516. 2012.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
193
|
Mou WL, Chen SR, Wu ZT, Hu LH, Zhang JY,
Chang HJ, Zhou H and Liu Y: LPS-TLR4/MD-2-TNF-α signaling mediates
alcohol-induced liver fibrosis in rats. J Toxicol Pathol.
35:193–203. 2022. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
194
|
Yu LX, Yan HX, Liu Q, Yang W, Wu HP, Dong
W, Tang L, Lin Y, He YQ, Zou SS, et al: Endotoxin accumulation
prevents carcinogen-induced apoptosis and promotes liver
tumorigenesis in rodents. Hepatology. 52:1322–1333. 2010.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
195
|
Yoshimoto S, Loo TM, Atarashi K, Kanda H,
Sato S, Oyadomari S, Iwakura Y, Oshima K, Morita H, Hattori M, et
al: Obesity-induced gut microbial metabolite promotes liver cancer
through senescence secretome. Nature. 499:97–101. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
196
|
Nguyen PT, Kanno K, Pham QT, Kikuchi Y,
Kakimoto M, Kobayashi T, Otani Y, Kishikawa N, Miyauchi M, Arihiro
K, et al: Senescent hepatic stellate cells caused by deoxycholic
acid modulates malignant behavior of hepatocellular carcinoma. J
Cancer Res Clin Oncol. 146:3255–3268. 2020. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
197
|
Vaughn BP, Rank KM and Khoruts A: Fecal
microbiota transplantation: Current status in treatment of gi and
liver disease. Clin Gastroenterol Hepatol. 17:353–361. 2019.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
198
|
Routy B, Lenehan JG, Miller WH Jr, Jamal
R, Messaoudene M, Daisley BA, Hes C, Al KF, Martinez-Gili L,
Punčochář M, et al: Fecal microbiota transplantation plus anti-PD-1
immunotherapy in advanced melanoma: A phase I trial. Nat Med.
29:2121–2132. 2023. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
199
|
Belvoncikova P, Maronek M and Gardlik R:
Gut dysbiosis and fecal microbiota transplantation in autoimmune
diseases. Int J Mol Sci. 23:107292022. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
200
|
Borody TJ, Eslick GD and Clancy RL: Fecal
microbiota transplantation as a new therapy: From Clostridioides
difficile infection to inflammatory bowel disease, irritable bowel
syndrome, and colon cancer. Curr Opin Pharmacol. 49:43–51. 2019.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
201
|
Burz SD, Monnoye M, Philippe C, Farin W,
Ratziu V, Strozzi F, Paillarse JM, Chêne L, Blottière HM and Gérard
P: Fecal microbiota transplant from human to mice gives insights
into the role of the gut microbiota in non-alcoholic fatty liver
disease (NAFLD). Microorganisms. 9:1992021. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
202
|
Purohit A, Alam MJ, Kandiyal B, Shalimar
Das B and Banerjee SK: Gut microbiome and non-alcoholic fatty liver
disease. Prog Mol Biol Transl Sci. 191:187–206. 2022. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
203
|
Brandt LJ and Aroniadis OC: An overview of
fecal microbiota transplantation: Techniques, indications, and
outcomes. Gastrointest Endosc. 78:240–249. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
204
|
Persky SE and Brandt LJ: Treatment of
recurrent Clostridium difficile-associated diarrhea by
administration of donated stool directly through a colonoscope. Am
J Gastroenterol. 95:3283–3285. 2000. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
205
|
Michailidis L, Currier AC, Le M and
Flomenhoft DR: Adverse events of fecal microbiota transplantation:
A meta-analysis of high-quality studies. Ann Gastroenterol.
34:802–814. 2021.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
206
|
Allegretti JR, Kassam Z, Mullish BH,
Chiang A, Carrellas M, Hurtado J, Marchesi JR, McDonald JAK,
Pechlivanis A, Barker GF, et al: Effects of fecal microbiota
transplantation with oral capsules in obese patients. Clin
Gastroenterol Hepatol. 18:855–863.e2. 2020. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
207
|
Yang J, Tang X, Liang Z, Chen M and Sun L:
Taurocholic acid promotes hepatic stellate cell activation via
S1PR2/p38 MAPK/YAP signaling under cholestatic conditions. Clin Mol
Hepatol. 29:465–481. 2023. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
208
|
Mancinelli R, Ceci L, Kennedy L, Francis
H, Meadows V, Chen L, Carpino G, Kyritsi K, Wu N, Zhou T, et al:
The effects of Taurocholic acid on biliary damage and liver
fibrosis are mediated by calcitonin-gene-related peptide signaling.
Cells. 11:15912022. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
209
|
Uyttebroek S, Chen B, Onsea J, Ruythooren
F, Debaveye Y, Devolder D, Spriet I, Depypere M, Wagemans J,
Lavigne R, et al: Safety and efficacy of phage therapy in
difficult-to-treat infections: A systematic review. Lancet Infect
Dis. 22:e208–e220. 2022. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
210
|
Federici S, Kredo-Russo S, Valdes-Mas R,
Kviatcovsky D, Weinstock E, Matiuhin Y, Silberberg Y, Atarashi K,
Furuichi M, Oka A, et al: Targeted suppression of human
IBD-associated gut microbiota commensals by phage consortia for
treatment of intestinal inflammation. Cell. 185:2879–2898.e24.
2022. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
211
|
Duan Y, Young R and Schnabl B:
Bacteriophages and their potential for treatment of
gastrointestinal diseases. Nat Rev Gastroenterol Hepatol.
19:135–144. 2022. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
212
|
Shuwen H and Kefeng D: Intestinal phages
interact with bacteria and are involved in human diseases. Gut
Microbes. 14:21137172022. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
213
|
Duan Y, Llorente C, Lang S, Brandl K, Chu
H, Jiang L, White RC, Clarke TH, Nguyen K, Torralba M, et al:
Bacteriophage targeting of gut bacterium attenuates alcoholic liver
disease. Nature. 575:505–511. 2019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
214
|
Fujiki J and Schnabl B: Phage therapy:
Targeting intestinal bacterial microbiota for the treatment of
liver diseases. JHEP Rep. 5:1009092023. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
215
|
Gong X, Geng H, Yang Y, Zhang S, He Z, Fan
Y, Yin F, Zhang Z and Chen GQ: Metabolic engineering of commensal
bacteria for gut butyrate delivery and dissection of host-microbe
interaction. Metab Eng. 80:94–106. 2023. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
216
|
Anand AC and Acharya SK: The story of
ammonia in liver disease: An unraveling continuum. J Clin Exp
Hepatol. 14:1013612024. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
217
|
Kurtz CB, Millet YA, Puurunen MK,
Perreault M, Charbonneau MR, Isabella VM, Kotula JW, Antipov E,
Dagon Y, Denney WS, et al: An engineered E. coli Nissle
improves hyperammonemia and survival in mice and shows
dose-dependent exposure in healthy humans. Sci Transl Med.
11:eaau79752019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
218
|
Yu M, Hu S, Tang B, Yang H and Sun D:
Engineering Escherichia coli Nissle 1917 as a microbial
chassis for therapeutic and industrial applications. Biotechnol
Adv. 67:1082022023. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
219
|
Lynch JP, Goers L and Lesser CF: Emerging
strategies for engineering Escherichia coli Nissle
1917-based therapeutics. Trends Pharmacol Sci. 43:772–786. 2022.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
220
|
Husted AS, Trauelsen M, Rudenko O, Hjorth
SA and Schwartz TW: GPCR-mediated signaling of metabolites. Cell
Metab. 25:777–796. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
221
|
Akiba Y and Kaunitz JD: Duodenal luminal
chemosensing; acid, ATP, and nutrients. Curr Pharm Des.
20:2760–2765. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
222
|
Kokorovic A, Cheung GW, Breen DM, Chari M,
Lam CK and Lam TK: Duodenal mucosal protein kinase C-δ regulates
glucose production in rats. Gastroenterology. 141:1720–1727. 2011.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
223
|
van Baar ACG, Beuers U, Wong K, Haidry R,
Costamagna G, Hafedi A, Deviere J, Ghosh SS, Lopez-Talavera JC,
Rodriguez L, et al: Endoscopic duodenal mucosal resurfacing
improves glycaemic and hepatic indices in type 2 diabetes: 6-month
multicentre results. JHEP Rep. 1:429–437. 2019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
224
|
de Oliveira GHP, de Moura DTH, Funari MP,
McCarty TR, Ribeiro IB, Bernardo WM, Sagae VMT, Freitas JR Jr,
Souza GMV and de Moura EGH: Metabolic effects of endoscopic
duodenal mucosal resurfacing: A systematic review and
Meta-analysis. Obes Surg. 31:1304–1312. 2021. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
225
|
Shamseddeen H, Vuppalanchi R and Gromski
MA: Duodenal mucosal resurfacing for nonalcoholic fatty liver
disease. Clin Liver Dis (Hoboken). 20:166–169. 2022. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
226
|
Condello G and Chen CY: Minireview:
Current status of endoscopic duodenal mucosal resurfacing. Obes Res
Clin Pract. 14:504–507. 2020. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
227
|
Mingrone G, van Baar AC, Deviere J,
Hopkins D, Moura E, Cercato C, Rajagopalan H, Lopez-Talavera JC,
White K, Bhambhani V, et al: Safety and efficacy of hydrothermal
duodenal mucosal resurfacing in patients with type 2 diabetes: The
randomised, double-blind, sham-controlled, multicentre REVITA-2
feasibility trial. Gut. 71:254–264. 2022. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
228
|
Hadefi A, Verset L, Pezzullo M, Rosewick
N, Degre D, Gustot T, Moreno C, Devière J and Trépo E: Endoscopic
duodenal mucosal resurfacing for nonalcoholic steatohepatitis
(NASH): A pilot study. Endosc Int Open. 9:E1792–E1800. 2021.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|