|
1
|
Zhu W, Zhang Y and Wang Y: Immunotherapy
strategies and prospects for acute lung injury: Focus on immune
cells and cytokines. Front Pharmacol. 13:11033092022. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
Bellani G, Laffey JG, Pham T, Fan E,
Brochard L, Esteban A, Gattinoni L, van Haren F, Larsson A, McAuley
DF, et al: Epidemiology, patterns of care, and mortality for
patients with acute respiratory distress syndrome in intensive care
units in 50 countries. JAMA. 315:788–800. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
Hsieh PC, Wu YK, Yang MC, Su WL, Kuo CY
and Lan CC: Deciphering the role of damage-associated molecular
patterns and inflammatory responses in acute lung injury. Life Sci.
305:1207822022. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
Mokrá D: Acute lung injury-from
pathophysiology to treatment. Physiol Res. 69:S353–S366.
2020.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Mokra D, Mikolka P, Kosutova P and Mokry
J: Corticosteroids in acute lung injury: The dilemma continues. Int
J Mol Sci. 20:47652019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Wang F, Chen M, Ma J, Wang C, Wang J, Xia
H, Zhang D and Yao S: Integrating bulk and single-cell sequencing
reveals the phenotype-associated cell subpopulations in
sepsis-induced acute lung injury. Front Immunol. 13:9817842022.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Lendeckel U, Venz S and Wolke C:
Macrophages: Shapes and functions. ChemTexts. 8:122022. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Johnston LK, Rims CR, Gill SE, McGuire JK
and Manicone AM: Pulmonary macrophage subpopulations in the
induction and resolution of acute lung injury. Am J Respir Cell Mol
Biol. 47:417–426. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Dang W, Tao Y, Xu X, Zhao H, Zou L and Li
Y: The role of lung macrophages in acute respiratory distress
syndrome. Inflamm Res. 71:1417–1432. 2022. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Wang Z and Wang Z: The role of macrophages
polarization in sepsis-induced acute lung injury. Front Immunol.
14:12094382023. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Cheng P, Li S and Chen H: Macrophages in
lung injury, repair, and fibrosis. Cells. 10:4362021. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Aribindi K, Lim M, Lakshminrusimha S and
Albertson T: Investigational pharmacological agents for the
treatment of ARDS. Expert Opin Investig Drugs. 33:243–277. 2024.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Vichare R and Janjic JM:
Macrophage-targeted nanomedicines for ARDS/ALI: Promise and
potential. Inflammation. 45:2124–2141. 2022. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Booz GW, Altara R, Eid AH, Wehbe Z, Fares
S, Zaraket H, Habeichi NJ and Zouein FA: Macrophage responses
associated with COVID-19: A pharmacological perspective. Eur J.
887:1735472020.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Panahi Y, Gorabi AM, Talaei S, Beiraghdar
F, Akbarzadeh A, Tarhriz V and Mellatyar H: An overview on the
treatments and prevention against COVID-19. Virol J. 20:232023.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
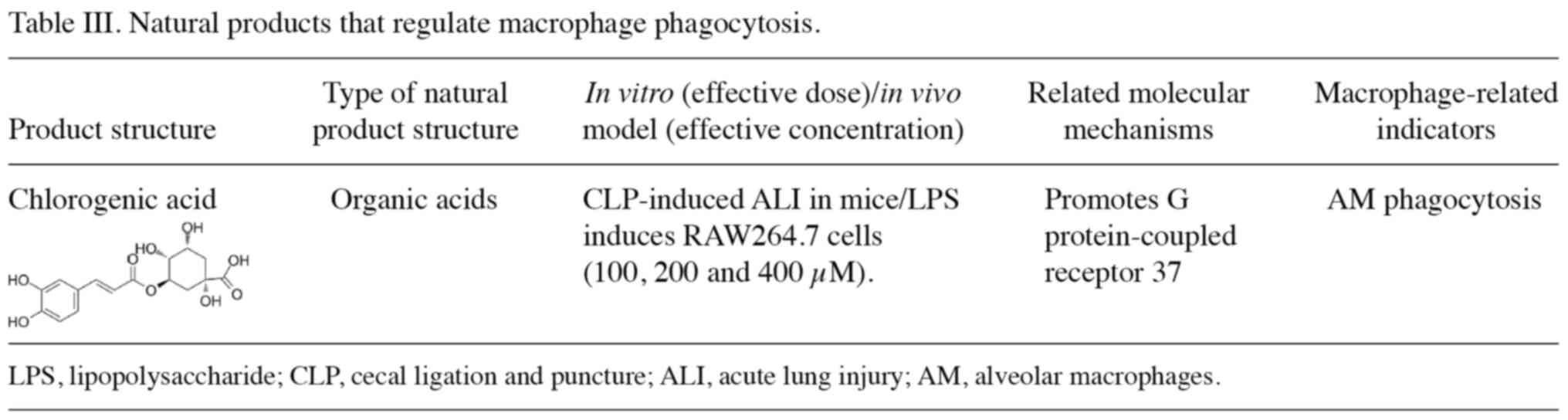
|
16
|
Matera MG, Rogliani P, Bianco A and
Cazzola M: Pharmacological management of adult patients with acute
respiratory distress syndrome. Expert Opin Pharmacother.
21:2169–2183. 2020. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
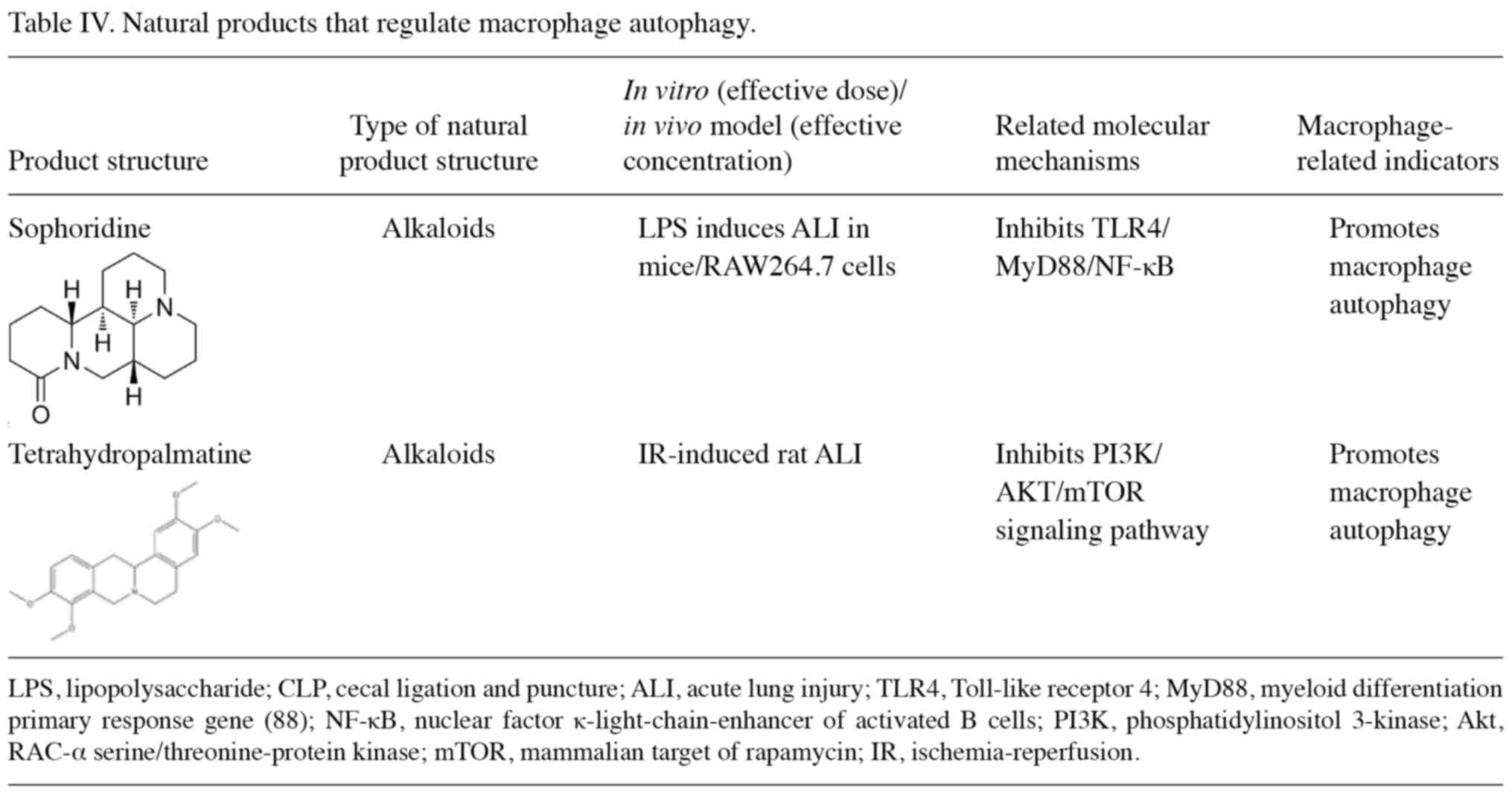
17
|
Lang FM, Lee KMC, Teijaro JR, Becher B and
Hamilton JA: GM-CSF-based treatments in COVID-19: Reconciling
opposing therapeutic approaches. Nat Rev Immunol. 20:507–514. 2020.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
Li S, Feng T, Zhang Y, Shi Q, Wang W, Ren
J, Shen G, Gu H, Luo C and Li Y: Lianhua Qingwen protects
LPS-induced acute lung injury by promoting M2 macrophage
infiltration. J Ethnopharmacol. 320:1174672024. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
Liang X and Liu JX: Role of macrophage
polarization in pulmonary diseases and intervention of traditional
Chinese medicines. Zhongguo Zhong Yao Za Zhi. 49:334–343. 2024.(In
Chinese). PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
Dong J, Liu W, Liu W, Wen Y, Liu Q, Wang
H, Xiang G, Liu Y and Hao H: Acute lung injury: A view from the
perspective of necroptosis. Inflamm Res. 73:997–1018. 2024.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
Qin Y, Li W, Liu J, Wang F, Zhou W, Xiao
L, Zhou P, Wu F, Chen X, Xu S, et al: Andrographolide ameliorates
sepsis-induced acute lung injury by promoting autophagy in alveolar
macrophages via the RAGE/PI3K/AKT/mTOR pathway. Int
Immunopharmacol. 139:1127192024. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22
|
Ma J, Wang J, Wang J, Zhou J, Jiang C,
Chen W, Zhang X, Pan J, Zhu J and Chen M: Araloside A alleviates
sepsis-induced acute lung injury via PHD2/HIF-1α in macrophages.
Phytomedicine. 135:1560892024. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23
|
Wang WT, Zhang YY, Li ZR, Li JM, Deng HS,
Li YY, Yang HY, Lau CC, Yao YJ, Pan HD, et al: Syringic acid
attenuates acute lung injury by modulating macrophage polarization
in LPS-induced mice. Phytomedicine. 129:1555912024. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24
|
Helou DG, Quach C, Hurrell BP, Li X, Li M,
Akbari A, Shen S, Shafiei-Jahani P and Akbari O: LAIR-1 limits
macrophage activation in acute inflammatory lung injury. Mucosal
Immunol. 16:788–800. 2023. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
25
|
Short KR, Kroeze EJBV, Fouchier RAM and
Kuiken T: Pathogenesis of influenza-induced acute respiratory
distress syndrome. Lancet Infect Dis. 14:57–69. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
26
|
Luo M, Zhao F, Cheng H, Su M and Wang Y:
Macrophage polarization: An important role in inflammatory
diseases. Front Immunol. 15:13529462024. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
27
|
Liu C, Xiao K and Xie L: Advances in the
regulation of macrophage polarization by mesenchymal stem cells and
implications for ALI/ARDS treatment. Front Immunol. 13:9281342022.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
28
|
Chen X, Tang J, Shuai W, Meng J, Feng J
and Han Z: Macrophage polarization and its role in the pathogenesis
of acute lung injury/acute respiratory distress syndrome. Inflamm
Res. 69:883–895. 2020. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
29
|
Wang L, Wang D, Zhang T, Ma Y, Tong X and
Fan H: The role of immunometabolism in macrophage polarization and
its impact on acute lung injury/acute respiratory distress
syndrome. Front Immunol. 14:11175482023. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
30
|
Murray PJ, Allen JE, Biswas SK, Fisher EA,
Gilroy DW, Goerdt S, Gordon S, Hamilton JA, Ivashkiv LB, Lawrence
T, et al: Macrophage activation and polarization: Nomenclature and
experimental guidelines. Immunity. 41:14–20. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
31
|
Aggarwal NR, King LS and D'alessio FR:
Diverse macrophage populations mediate acute lung inflammation and
resolution. Am J Physiol Lung Cell Mol Physiol. 306:L709–L725.
2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
32
|
Fukui S, Iwamoto N, Takatani A, Igawa T,
Shimizu T, Umeda M, Nishino A, Horai Y, Hirai Y, Koga T, et al: M1
and M2 monocytes in rheumatoid arthritis: A contribution of
imbalance of M1/M2 monocytes to osteoclastogenesis. Front Immunol.
8:19582017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
33
|
Shi C and Pamer EG: Monocyte recruitment
during infection and inflammation. Nat Rev Immunol. 11:762–774.
2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
34
|
Wang J, Li Q, Qiu Y and Lu H: COVID-19:
Imbalanced cell-mediated immune response drives to immunopathology.
Emerg Microbes Infect. 11:2393–2404. 2022. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
35
|
Jiao Y, Zhang T, Zhang C, Ji H, Tong X,
Xia R, Wang W, Ma Z and Shi X: Exosomal miR-30d-5p of neutrophils
induces M1 macrophage polarization and primes macrophage pyroptosis
in sepsis-related acute lung injury. Crit Care. 25:3562021.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
36
|
Li Z, Pan H, Yang J, Chen D, Wang Y, Zhang
H and Cheng Y: Xuanfei Baidu formula alleviates impaired
mitochondrial dynamics and activated NLRP3 inflammasome by
repressing NF-κB and MAPK pathways in LPS-induced ALI and
inflammation models. Phytomedicine. 108:1545452023. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
37
|
Liang P, Wang L, Yang S, Pan X, Li J,
Zhang Y, Liang Y, Li J and Zhou B: 5-Methoxyflavone alleviates
LPS-mediated lung injury by promoting Nrf2-mediated the suppression
of NOX4/TLR4 axis in bronchial epithelial cells and M1 polarization
in macrophages. J Inflamm (Lond). 19:242022. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
38
|
Bu C, Wang R, Wang Y, Lu B, He S and Zhao
X: Taraxasterol inhibits hyperactivation of macrophages to
alleviate the sepsis-induced inflammatory response of ARDS rats.
Cell Biochem Biophys. 80:763–770. 2022. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
39
|
Fang H, Chen J, Luo J, Hu J, Wang D, Lv L
and Zhang W: Abietic acid attenuates sepsis-induced lung injury by
inhibiting nuclear factor kappa-light-chain-enhancer of activated B
cells (NF-κB) pathway to inhibit M1 macrophage polarization. Exp
Anim. 71:481–490. 2022. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
40
|
Wang L and Zhao M: Suppression of NOD-like
receptor protein 3 inflammasome activation and macrophage M1
polarization by hederagenin contributes to attenuation of
sepsis-induced acute lung injury in rats. Bioengineered.
13:7262–7276. 2022. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
41
|
Zheng L, Su J, Zhang Z, Jiang L, Wei J, Xu
X and Lv S: Salidroside regulates inflammatory pathway of alveolar
macrophages by influencing the secretion of miRNA-146a exosomes by
lung epithelial cells. Sci Rep. 10:207502020. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
42
|
Cai YC, Huang Q, Wei XL, Mei RH, Sa LN and
Hu XL: Effects of salidroside on the secretion of inflammatory
mediators induced by lipopolysaccharide in the co-culture of rat
alveolar macrophages and type II alveolar epithelial cells. Sheng
Li Xue Bao. 71:575–580. 2019.(In Chinese). PubMed/NCBI
|
|
43
|
Feng H, Zhang D, Yin Y, Kang J and Zheng
R: Salidroside ameliorated the pulmonary inflammation induced by
cigarette smoke via mitigating M1 macrophage polarization by
JNK/c-Jun. Phytother Res. 37:4251–4264. 2023. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
44
|
Li X, Xiao C, Yuan J, Chen X, Li Q and
Shen F: Rhein-attenuates LPS-induced acute lung injury via
targeting NFATc1/Trem2 axis. Inflamm Res. 72:1237–1255. 2023.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
45
|
Wang W, Wang Z, Yang X, Song W, Chen P,
Gao Z, Wu J and Huang F: Rhein ameliorates septic lung injury and
intervenes in macrophage metabolic reprogramming in the
inflammatory state by sirtuin 1. Life Sci. 310:1211152022.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
46
|
Wu X, Yao J, Hu Q, Kang H, Miao Y, Zhu L,
Li C, Zhao X, Li J, Wan M and Tang W: Emodin ameliorates acute
pancreatitis-associated lung injury through inhibiting the alveolar
macrophages pyroptosis. Front Pharmacol. 13:8730532022. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
47
|
Hu Q, Yao J, Wu X, Li J, Li G, Tang W, Liu
J and Wan M: Emodin attenuates severe acute pancreatitis-associated
acute lung injury by suppressing pancreatic exosome-mediated
alveolar macrophage activation. Acta Pharm Sin B. 12:3986–4003.
2022. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
48
|
Wang S, Liu J, Dong J, Fan Z, Wang F, Wu
P, Li X, Kou R and Chen F: Allyl methyl trisulfide protected
against LPS-induced acute lung injury in mice via inhibition of the
NF-κB and MAPK pathways. Front Pharmacol. 13:9198982022. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
49
|
Zhuo Y, Li D, Cui L, Li C, Zhang S, Zhang
Q, Zhang L, Wang X and Yang L: Treatment with
3,4-dihydroxyphenylethyl alcohol glycoside ameliorates
sepsis-induced ALI in mice by reducing inflammation and regulating
M1 polarization. Biomed Pharmacother. 116:1090122019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
50
|
Mantovani A, Biswas SK, Galdiero MR, Sica
A and Locati M: Macrophage plasticity and polarization in tissue
repair and remodelling. J Pathol. 229:176–185. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
51
|
Yadav S, Priya A, Borade DR and
Agrawal-Rajput R: Macrophage subsets and their role: Co-relation
with colony-stimulating factor-1 receptor and clinical relevance.
Immunol Res. 71:130–152. 2022. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
52
|
Shapouri-Moghaddam A, Mohammadian S,
Vazini H, Taghadosi M, Esmaeili SA, Mardani F, Seifi B, Mohammadi
A, Afshari JT and Sahebkar A: Macrophage plasticity, polarization,
and function in health and disease. J Cell Physiol. 233:6425–6440.
2018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
53
|
Liang L, Xu W, Shen A, Fu X, Cen H, Wang
S, Lin Z, Zhang L, Lin F and Zhang X: Inhibition of YAP1 activity
ameliorates acute lung injury through promotion of M2 macrophage
polarization. MedComm (2020). 4:e2932023. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
54
|
Jiang R, Xu J, Zhang Y, Zhu X, Liu J and
Tan Y: Ligustrazine alleviate acute lung injury through suppressing
pyroptosis and apoptosis of alveolar macrophages. Front Pharmacol.
12:6805122021. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
55
|
Zhou W, Hong J, Liu T, Li M, Jin H and
Wang X: Polygonatum polysaccharide regulates macrophage
polarization and improves LPS-Induced acute lung injury through
TLR4-MAPK/NF-κB pathway. Can Respir J. 2022:1–11. 2022. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
56
|
Liu JH, Cao L, Zhang CH, Li C, Zhang ZH
and Wu Q: Dihydroquercetin attenuates lipopolysaccharide-induced
acute lung injury through modulating FOXO3-mediated NF-κB signaling
via miR-132-3p. Pulm Pharmacol Ther. 64:1019342020. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
57
|
Li C, Liu J, Zhang C, Cao L, Zou F and
Zhang Z: Dihydroquercetin (DHQ) ameliorates LPS-induced acute lung
injury by regulating macrophage M2 polarization through
IRF4/miR-132-3p/FBXW7 axis. Pulm Pharmacol Ther. 83:1022492023.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
58
|
Zhang Y, Song D, Peng Z, Wang R, Li K, Ren
H, Sun X, Du N and Tang SC: Anisodamine enhances macrophage M2
polarization through suppressing G9a-mediated interferon regulatory
factor 4 silencing to alleviate lipopolysaccharide-induced acute
lung injury. J Pharmacol Exp Ther. 381:247–256. 2022. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
59
|
Wang Y, Wang X, Zhang L and Zhang R:
Alleviation of acute lung injury in rats with sepsis by resveratrol
via the phosphatidylinositol 3-Kinase/Nuclear factor-erythroid 2
related factor 2/Heme oxygenase-1 (PI3K/Nrf2/HO-1) pathway. Med Sci
Monit. 24:3604–3611. 2018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
60
|
Zhu X, Liu Q, Wang M, Liang M, Yang X, Xu
X, Zou H and Qiu J: Activation of Sirt1 by resveratrol inhibits
TNF-α induced inflammation in fibroblasts. PLoS One. 6:e270812011.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
61
|
Misawa T, Saitoh T, Kozaki T, Park S,
Takahama M and Akira S: Resveratrol inhibits the acetylated
α-tubulin-mediated assembly of the NLRP3-inflammasome. Int Immunol.
27:425–434. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
62
|
Hu L, Chen Z, Li L, Jiang Z and Zhu L:
Resveratrol decreases CD45+CD206− subtype
macrophages in LPS-induced murine acute lung injury by SOCS3
signalling pathway. J Cell Mol Med. 23:8101–8113. 2019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
63
|
Li QR, Tan SR, Yang L, He W, Chen L, Shen
FX, Wang Z and Wang HF: Mechanism of chlorogenic acid in alveolar
macrophage polarization in Klebsiella pneumoniae-induced pneumonia.
J Leukoc Biol. 112:9–21. 2022. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
64
|
Pan MH, Lai CS, Wang YJ and Ho CT:
Acacetin suppressed LPS-induced up-expression of iNOS and COX-2 in
murine macrophages and TPA-induced tumor promotion in mice. Biochem
Pharmacol. 72:1293–1303. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
65
|
Chang B, Wang Z, Cheng H, Xu T, Chen J, Wu
W, Li Y and Zhang Y: Acacetin protects against sepsis-induced acute
lung injury by facilitating M2 macrophage polarization via
TRAF6/NF-κB/COX2 axis. Innate Immun. 30:11–20. 2023. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
66
|
Qiao X, Wang H, He Y, Song D, Altawil A,
Wang Q and Yin Y: Grape seed proanthocyanidin ameliorates
LPS-induced acute lung injury by modulating M2a macrophage
polarization via the TREM2/PI3K/Akt pathway. Inflammation.
46:2147–2164. 2023. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
67
|
Wen H, Lu D, Chen H, Zhu Y, Xie Q, Zhang Z
and Wu Z: Tetrahydropalmatine induces the polarization of M1
macrophages to M2 to relieve limb ischemia-reperfusion-induced lung
injury via inhibiting the TLR4/NF-κB/NLRP3 signaling pathway. Drug
Dev Res. 83:1362–1372. 2022. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
68
|
Wu YX, Jiang FJ, Liu G, Wang YY, Gao ZQ,
Jin SH, Nie YJ, Chen D, Chen JL and Pang QF: Dehydrocostus lactone
attenuates methicillin-resistant staphylococcus aureus-induced
inflammation and acute lung injury via modulating macrophage
polarization. Int J Mol Sci. 22:97542021. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
69
|
Xie K, Chai YS, Lin SH, Xu F and Wang CJ:
Luteolin regulates the differentiation of regulatory T cells and
activates IL-10-dependent macrophage polarization against acute
lung injury. J Immunol Res. 2021:1–12. 2021. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
70
|
Yang L, Zhang YM, Guo MN, Zhang H, Zhu XY,
Xu C and Liu YJ: Matrine attenuates lung injury by modulating
macrophage polarization and suppressing apoptosis. J Surg Res.
281:264–274. 2023. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
71
|
Ye Z, Wang P, Feng G, Wang Q, Liu C, Lu J,
Chen J and Liu P: Cryptotanshinone attenuates LPS-induced acute
lung injury by regulating metabolic reprogramming of macrophage.
Front Med (Lausanne). 9:10754652022. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
72
|
Zhang J, Wang C, Wang H, Li X, Xu J and Yu
K: Loganin alleviates sepsis-induced acute lung injury by
regulating macrophage polarization and inhibiting NLRP3
inflammasome activation. Int Immunopharmacol. 95:1075292021.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
73
|
Zhao JY, Pu J, Fan J, Feng XY, Xu JW,
Zhang R and Shang Y: Tanshinone IIA prevents acute lung injury by
regulating macrophage polarization. J Integr Med. 20:274–280. 2022.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
74
|
Ying ZH, Li HM, Yu WY and Yu CH: Iridin
prevented against lipopolysaccharide-induced inflammatory responses
of macrophages via inactivation of PKM2-mediated glycolytic
pathways. J Inflamm Res. 14:341–354. 2021. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
75
|
Zhao L, Zhang M, Liu YW, Tan Y, Yin J,
Chen Y, Chen D and Ni B: Sinomenine alleviates
lipopolysaccharide-induced acute lung injury via a
PPARβ/δ-dependent mechanism. Eur J Pharmacol. 953:1758382023.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
76
|
Gao WJ, Liu JX, Xie Y, Luo P, Liu ZQ, Liu
L and Zhou H: Suppression of macrophage migration by
down-regulating Src/FAK/P130Cas activation contributed to the
anti-inflammatory activity of sinomenine. Pharmacol Res.
167:1055132021. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
77
|
Yi L, Luo JF, Xie BB, Liu JX, Wang JY, Liu
L, Wang PX, Zhou H and Dong Y: α7 nicotinic acetylcholine receptor
is a novel mediator of sinomenine anti-inflammation effect in
macrophages stimulated by lipopolysaccharide. Shock. 44:188–195.
2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
78
|
Zhi YK, Li J, Yi L, Zhu RL, Luo JF, Shi
QP, Bai SS, Li YW, Du Q, Cai JZ, et al: Sinomenine inhibits
macrophage M1 polarization by downregulating α7nAChR via a feedback
pathway of α7nAChR/ERK/Egr-1. Phytomedicine. 100:1540502022.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
79
|
Guo R, Wang H and Cui N: Autophagy
regulation on pyroptosis: Mechanism and medical implication in
sepsis. Mediators Inflamm. 2021:99250592021. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
80
|
Shi J, Gao W and Shao F: Pyroptosis:
Gasdermin-mediated programmed necrotic cell death. Trends Biochem
Sci. 42:245–254. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
81
|
Wei T, Zhang C and Song Y: Molecular
mechanisms and roles of pyroptosis in acute lung injury. Chin Med J
(Engl). 135:2417–2426. 2022. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
82
|
Tang Y, Yu Y, Li R, Tao Z, Zhang L, Wang
X, Qi X, Li Y, Meng T, Qu H, et al: Phenylalanine promotes alveolar
macrophage pyroptosis via the activation of CaSR in ARDS. Front
Immunol. 14:11141292023. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
83
|
Wu DD, Pan PH, Liu B, Su XL, Zhang LM, Tan
HY, Cao Z, Zhou ZR, Li HT, Li HS, et al: Inhibition of alveolar
macrophage pyroptosis reduces lipopolysaccharide-induced acute lung
injury in mice. Chin Med J (Engl). 128:2638–2645. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
84
|
Liu Y, Zhang Y, Feng Q, Liu Q, Xie J, Li
H, Yang F, Liu X, Gao W, Bai X, et al: GPA peptide attenuates
sepsis-induced acute lung injury in mice via inhibiting oxidative
stress and pyroptosis of alveolar macrophage. Oxid Med Cell Longev.
2021:1–12. 2021. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
85
|
Li H, Li Y, Song C, Hu Y, Dai M, Liu B and
Pan P: Neutrophil extracellular traps augmented alveolar macrophage
pyroptosis via AIM2 inflammasome activation in LPS-induced
ALI/ARDS. J Inflamm Res. 14:4839–4858. 2021. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
86
|
Hsu CG, Chávez CL, Zhang C, Sowden M, Yan
C and Berk BC: The lipid peroxidation product 4-hydroxynonenal
inhibits NLRP3 inflammasome activation and macrophage pyroptosis.
Cell Death Differ. 29:1790–1803. 2022. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
87
|
Liu Y, Zhang Y, You G, Zheng D, He Z, Guo
W, Antonina K, Shukhrat Z, Ding B, Zan J and Zhang Z: Tangeretin
attenuates acute lung injury in septic mice by inhibiting
ROS-mediated NLRP3 inflammasome activation via regulating
PLK1/AMPK/DRP1 signaling axis. Inflamm Res. 73:47–63. 2024.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
88
|
Wang X, Wu FP, Huang YR, Li HD, Cao XY,
You Y, Meng ZF, Sun KY and Shen XY: Matrine suppresses NLRP3
inflammasome activation via regulating PTPN2/JNK/SREBP2 pathway in
sepsis. Phytomedicine. 109:1545742023. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
89
|
Liu Y, Yang H, Zhu F, Ouyang Y and Pan P:
Inhibition of STAT3 phosphorylation by colchicine regulates NLRP3
activation to alleviate sepsis-induced acute lung injury.
Inflammopharmacology. 31:2007–2021. 2023. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
90
|
Yuan Y, Liao Q, Xue M, Shi Y, Rong L, Song
Z, Tong Z, Zheng W, Zhu Q, Cui X and Tao Z: Shufeng jiedu capsules
alleviate lipopolysaccharide-induced acute lung inflammatory injury
via activation of GPR18 by verbenalin. Cell Physiol Biochem.
50:629–639. 2018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
91
|
Yang L, Liu T, Zhuo Y, Li D, Li D, Liu J,
Gao H, Zhang L, Lin J and Wang X: Verbenalin alleviates acute lung
injury induced by sepsis and IgG immune complex through GPR18
receptor. Cell Signal. 109:1107682023. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
92
|
Chen LL, Song C, Zhang Y, Li Y, Zhao YH,
Lin FY, Han DD, Dai MH, Li W and Pan PH: Quercetin protects against
LPS-induced lung injury in mice via SIRT1-mediated suppression of
PKM2 nuclear accumulation. Eur J Pharmacol. 936:1753522022.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
93
|
Zhong C, Yang J, Deng K, Lang X, Zhang J,
Li M, Qiu L, Zhong G and Yu J: Tiliroside attenuates NLRP3
inflammasome activation in macrophages and protects against acute
lung injury in mice. Molecules. 28:75272023. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
94
|
Xu HW, Li WF, Hong SS, Shao JJ, Chen JH,
Chattipakorn N, Wu D, Luo W and Liang G: Tabersonine, a natural
NLRP3 inhibitor, suppresses inflammasome activation in macrophages
and attenuate NLRP3-driven diseases in mice. Acta Pharmacol Sin.
44:1252–1261. 2023. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
95
|
Shao JJ, Li WF, Sun JF, Zhuang ZS, Min JL,
Long XH, Wu GJ, Xu HW and Liang G: Britannin as a novel NLRP3
inhibitor, suppresses inflammasome activation in macrophages and
alleviates NLRP3-related diseases in mice. Acta Pharmacol Sin.
45:803–814. 2024. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
96
|
Yang F, Ye XJ, Chen MY, Li HC, Wang YF,
Zhong MY, Zhong CS, Zeng B, Xu LH, He XH and Ouyang DY: Inhibition
of NLRP3 inflammasome activation and pyroptosis in macrophages by
taraxasterol is associated with its regulation on mTOR signaling.
Front Immunol. 12:6326062021. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
97
|
Jang WY, Kim MY and Cho JY: Antioxidant,
anti-inflammatory, anti-menopausal, and anti-cancer effects of
lignans and their metabolites. Int J Mol Sci. 23:154822022.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
98
|
Zhang S, Yang L, Hu D, He S, Cui L, Zhao
J, Zhuo Y, Zhang L and Wang X: Syringaresinol alleviates IgG immune
complex induced acute lung injury via activating PPARγ and
suppressing pyroptosis. Int Immunopharmacol 124(Pt B). 1110712023.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
99
|
Li W, Xu H, Shao J, Chen J, Lin Y, Zheng
Z, Wang Y, Luo W and Liang G: Discovery of alantolactone as a
naturally occurring NLRP3 inhibitor to alleviate NLRP3-driven
inflammatory diseases in mice. Br J Pharmacol. 180:1634–1647. 2023.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
100
|
Liu C, Zhou Y, Tu Q, Yao L, Li J and Yang
Z: Alpha-linolenic acid pretreatment alleviates NETs-induced
alveolar macrophage pyroptosis by inhibiting pyrin inflammasome
activation in a mouse model of sepsis-induced ALI/ARDS. Front
Immunol. 14:11466122023. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
101
|
Weavers H, Evans IR, Martin P and Wood W:
Corpse engulfment generates a molecular memory that primes the
macrophage inflammatory response. Cell. 165:1658–1671. 2016.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
102
|
Sun D, Zhang G, Xie M, Wang Y, Liang X, Tu
M, Su Z and Zeng R: Softness enhanced macrophage-mediated therapy
of inhaled apoptotic-cell-inspired nanosystems for acute lung
injury. J Nanobiotechnology. 21:1722023. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
103
|
Leventis PA and Grinstein S: The
distribution and function of phosphatidylserine in cellular
membranes. Ann Rev Biophysics. 39:407–427. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
104
|
Banerjee S, Friggeri A, Liu G and Abraham
E: The C-terminal acidic tail is responsible for the inhibitory
effects of HMGB1 on efferocytosis. J Leukoc Biol. 88:973–979. 2010.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
105
|
Mahida RY, Scott A, Parekh D, Lugg ST,
Hardy RS, Lavery GG, Matthay MA, Naidu B, Perkins GD and Thickett
DR: Acute respiratory distress syndrome is associated with impaired
alveolar macrophage efferocytosis. Eur Respir J. 58:21008292021.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
106
|
Mahida RY, Lax S, Bassford CR, Scott A,
Parekh D, Hardy RS, Naidu B, Matthay MA, Stewart PM, Cooper MC, et
al: Impaired alveolar macrophage 11β-hydroxysteroid dehydrogenase
type 1 reductase activity contributes to increased pulmonary
inflammation and mortality in sepsis-related ARDS. Front Immunol.
14:11598312023. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
107
|
Martín-Vicente P, López-Martínez C and
Albaiceta GM: The last-minute redemption of inflammatory cells in
lung repair. Eur Respir J. 59:21030002022. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
108
|
Nepal S, Tiruppathi C, Tsukasaki Y,
Farahany J, Mittal M, Rehman J, Prockop DJ and Malik AB: STAT6
induces expression of Gas6 in macrophages to clear apoptotic
neutrophils and resolve inflammation. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA.
116:16513–16518. 2019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
109
|
Jiang T, Xia Y, Wang W, Zhao J, Liu W, Liu
S, Shi S, Li B, He X and Jin Y: Apoptotic bodies inhibit
inflammation by PDL1-PD1-mediated macrophage metabolic
reprogramming. Cell Prolif. 57:e135312023. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
110
|
Wang Y, Zhang W, Xu Y, Wu D, Gao Z, Zhou
J, Qian H, He B and Wang G: Extracellular HMGB1 impairs
macrophage-mediated efferocytosis by suppressing the
Rab43-controlled cell surface transport of CD91. Front Immunol.
13:7676302022. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
111
|
Aderem A and Underhill DM: Mechanisms of
phagocytosis in macrophages. Annu Rev Immunol. 17:593–623. 1999.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
112
|
He F, Gao F, Cai N, Jiang M and Wu C:
Chlorogenic acid enhances alveolar macrophages phagocytosis in
acute respiratory distress syndrome by activating G protein-coupled
receptor 37 (GPR 37). Phytomedicine. 107:1544742022. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
113
|
Aman Y, Schmauck-Medina T, Hansen M,
Morimoto RI, Simon AK, Bjedov I, Palikaras K, Simonsen A, Johansen
T, Tavernarakis N, et al: Autophagy in healthy aging and disease.
Nat Aging. 1:634–650. 2021. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
114
|
Saha S, Panigrahi DP, Patil S and Bhutia
SK: Autophagy in health and disease: A comprehensive review. Biomed
Pharmacother. 104:485–495. 2018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
115
|
Wang K, Chen Y, Zhang P, Lin P, Xie N and
Wu M: Protective features of autophagy in pulmonary infection and
inflammatory diseases. Cells. 8:1232019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
116
|
Murray PJ: On macrophage diversity and
inflammatory metabolic timers. Nat Rev Immunol. 20:89–90. 2020.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
117
|
Liu C, Xiao K and Xie L: Progress in
preclinical studies of macrophage autophagy in the regulation of
ALI/ARDS. Front Immunol. 13:9227022022. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
118
|
Huang M, Yu Y, Tang X, Dong R, Li X, Li F,
Jin Y, Gong S, Wang X, Zeng Z, et al: 3-Hydroxybutyrate ameliorates
sepsis-associated acute lung injury by promoting autophagy through
the activation of GPR109α in macrophages. Biochem Pharmacol.
213:1156322023. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
119
|
Quach C, Helou DG, Li M, Hurrell BP,
Howard E, Shafiei-Jahani P, Soroosh P, Ou JJ, Razani B, Rehan V and
Akbari O: Enhancing autophagy in CD11c+ antigen-presenting cells as
a therapeutic strategy for acute respiratory distress syndrome.
Cell Rep. 42:1129902023. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
120
|
Qiu P, Liu Y, Chen K, Dong Y, Liu S and
Zhang J: Hydrogen-rich saline regulates the polarization and
apoptosis of alveolar macrophages and attenuates lung injury via
suppression of autophagy in septic rats. Ann Transl Med. 9:9742021.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
121
|
Liang J, Liu J, Tang Y, Peng Q, Zhang L,
Ma X, Xu N, Wei J and Han H: Sophoridine inhibits endotoxin-induced
acute lung injury by enhancing autophagy of macrophage and reducing
inflammation. J Leukoc Biol. 112:115–125. 2022. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
122
|
Wen H, Zhang H, Wang W and Li Y:
Tetrahydropalmatine protects against acute lung injury induced by
limb ischemia/reperfusion through restoring PI3K/AKT/mTOR-mediated
autophagy in rats. Pulm Pharmacol Ther. 64:1019472020. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
123
|
Tang D, Cao F, Yan C, Fang K, Ma J, Gao L,
Sun B and Wang G: Extracellular Vesicle/Macrophage axis: Potential
targets for inflammatory disease intervention. Front Immunol.
13:7054722022. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
124
|
Viola A, Munari F, Sánchez-Rodríguez R,
Scolaro T and Castegna A: The metabolic signature of macrophage
responses. Front Immunol. 10:14622019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
125
|
Feng Z, Jing Z, Li Q, Chu L, Jiang Y,
Zhang X, Yan L, Liu Y, Jiang J, Xu P, et al: Exosomal STIMATE
derived from type II alveolar epithelial cells controls metabolic
reprogramming of tissue-resident alveolar macrophages.
Theranostics. 13:991–1009. 2023. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
126
|
Zhong WJ, Liu T, Yang HH, Duan JX, Yang
JT, Guan XX, Xiong JB, Zhang YF, Zhang CY, Zhou Y and Guan CX:
TREM-1 governs NLRP3 inflammasome activation of macrophages by
firing up glycolysis in acute lung injury. Int J Biol Sci.
19:242–257. 2023. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
127
|
Breda CN, Davanzo GG, Basso PJ, Câmara NO
and Moraes-Vieira PMM: Mitochondria as central hub of the immune
system. Redox Biol. 26:1012552019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
128
|
Rosales C and Uribe-Querol E:
Phagocytosis: A fundamental process in immunity. Biomed Res Int.
2017:90428512017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
129
|
Meidaninikjeh S, Sabouni N, Marzouni HZ,
Bengar S, Khalili A and Jafari R: Monocytes and macrophages in
COVID-19: Friends and foes. Life Sci. 269:1190102021. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
130
|
Wang Z, Li S and Huang B: Alveolar
macrophages: Achilles' heel of SARS-CoV-2 infection. Signal
Transduct Target Ther. 7:2422022. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|