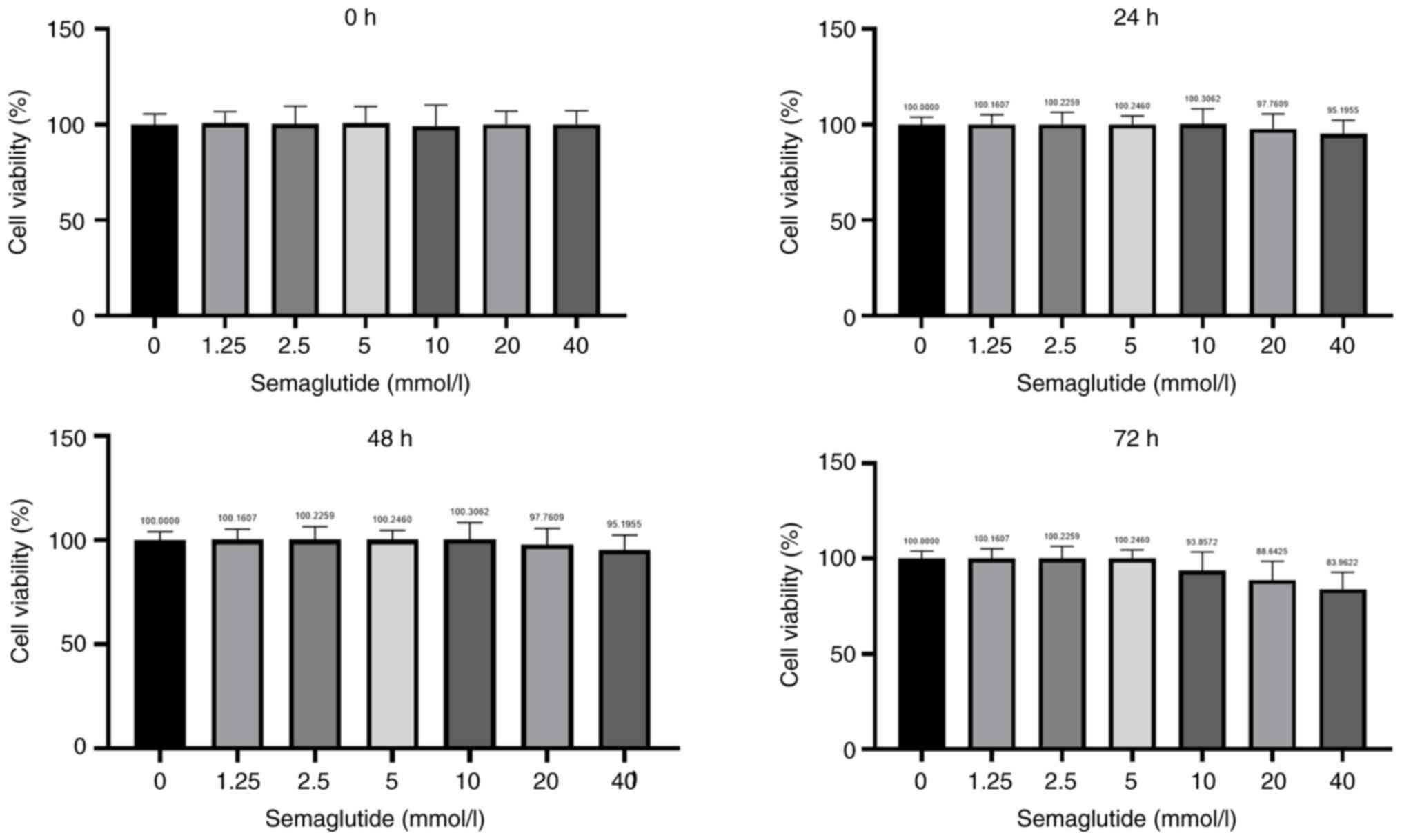
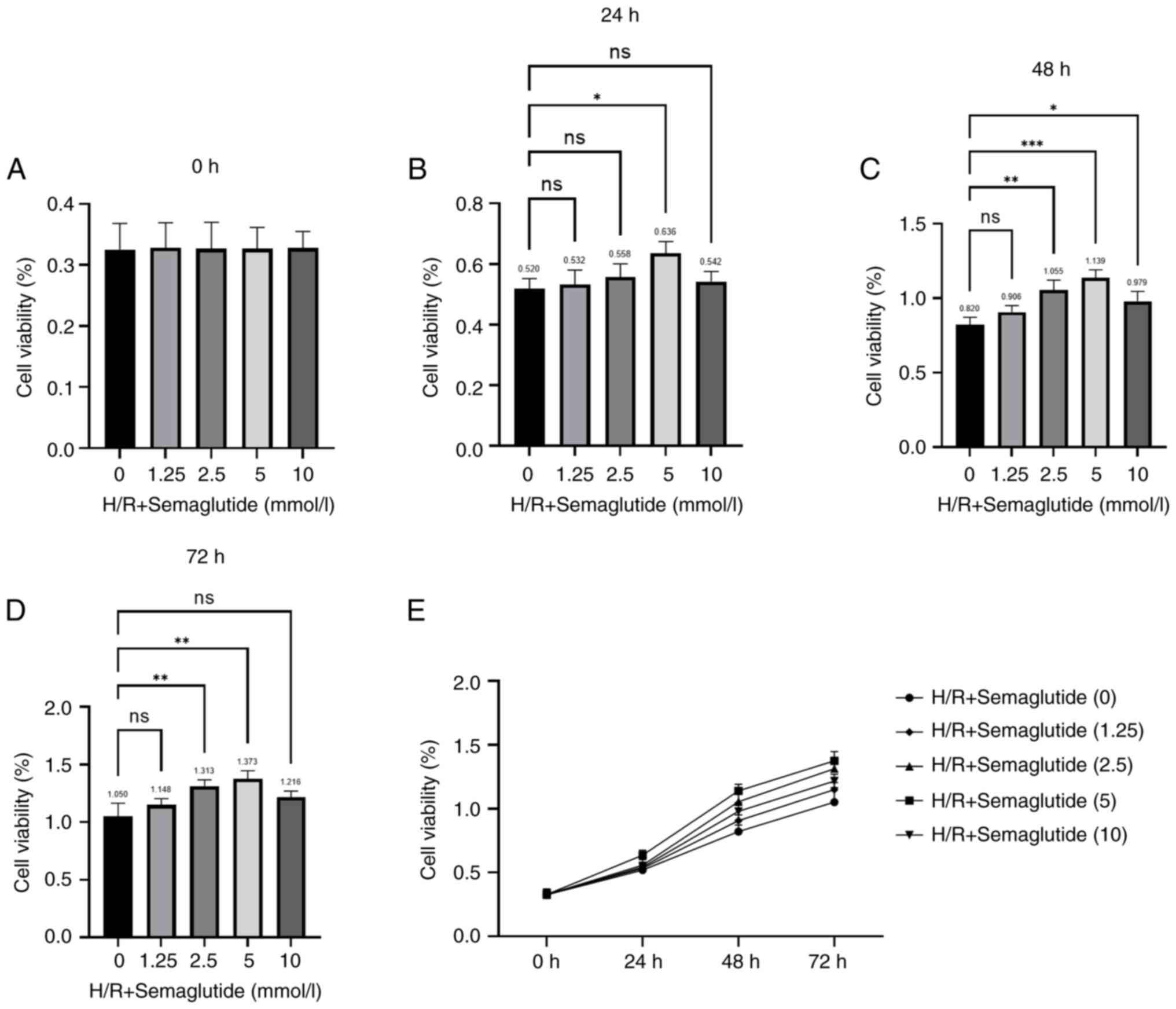
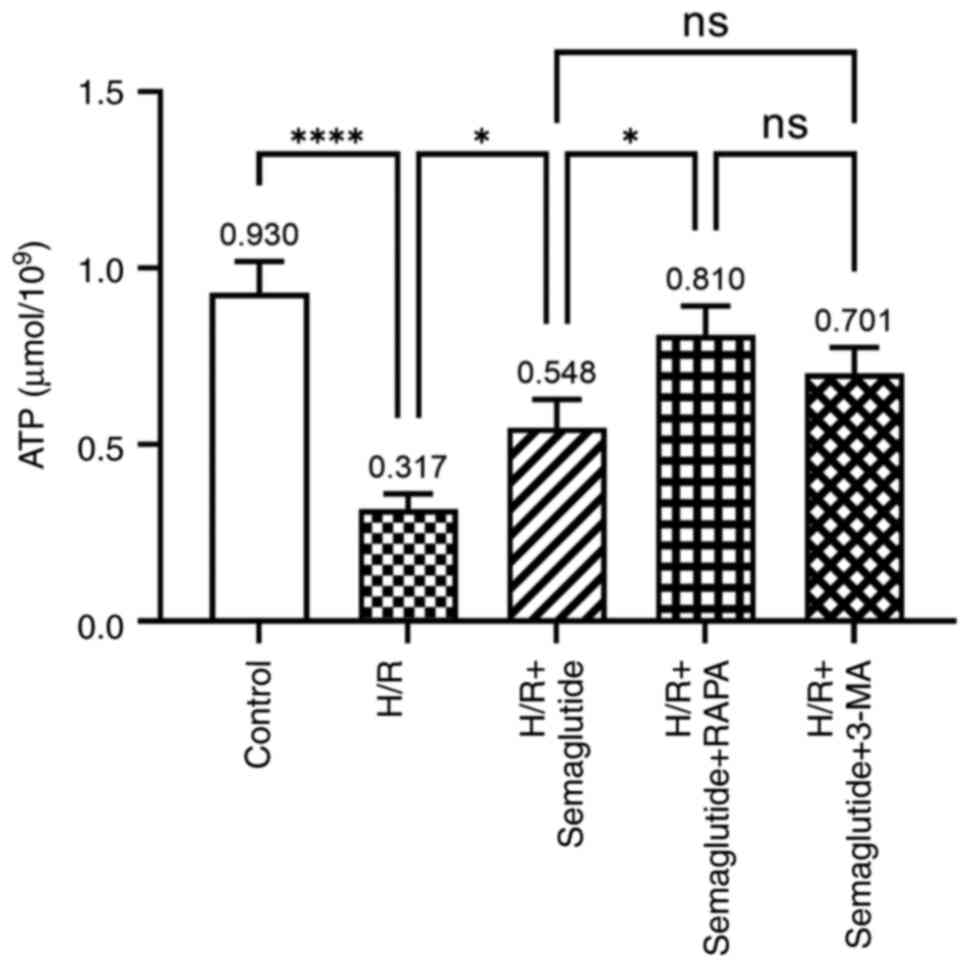
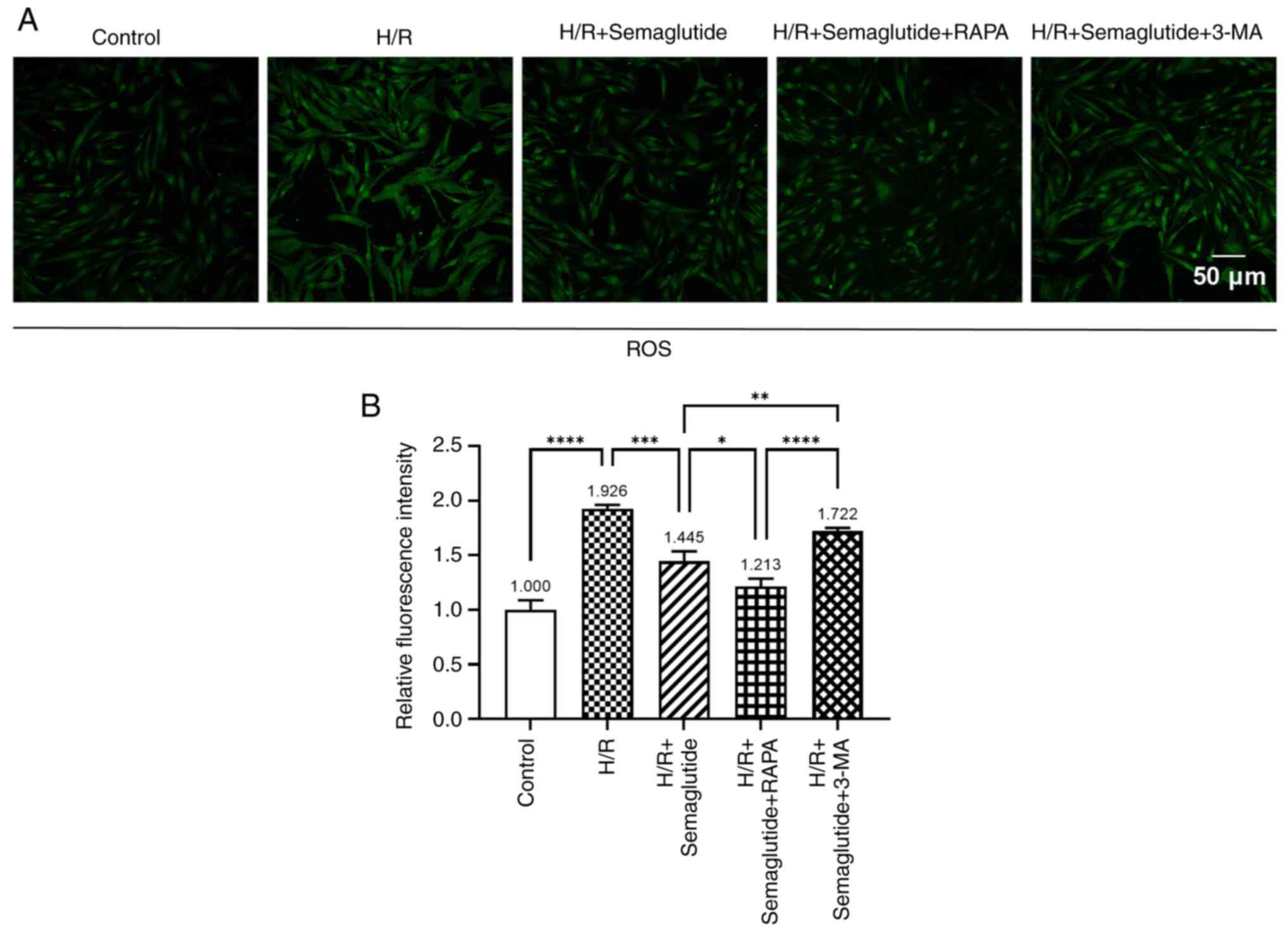
|
1
|
Yetgin T, Manintveld OC, Boersma E,
Kappetein AP, van Geuns RJ, Zijlstra F, Duncker DJ and van der
Giessen WJ: Remote ischemic conditioning in percutaneous coronary
intervention and coronary artery bypass grafting. Circ J.
76:2392–2404. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
Xu Y, Tang C, Tan S, Duan J, Tian H and
Yang Y: Cardioprotective effect of isorhamnetin against myocardial
ischemia reperfusion (I/R) injury in isolated rat heart through
attenuation of apoptosis. J Cell Mol Med. 24:6253–6262. 2020.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
Wang A, Zhang H, Liang Z, Xu K, Qiu W,
Tian Y, Guo H, Jia J, Xing E, Chen R, et al: U0126 attenuates
ischemia/reperfusion-induced apoptosis and autophagy in myocardium
through MEK/ERK/EGR-1 pathway. Eur J Pharmacol. 788:280–285. 2016.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
Dong Y, Undyala VV, Gottlieb RA, Mentzer
RM Jr and Przyklenk K: Autophagy: Definition, molecular machinery,
and potential role in myocardial ischemia-reperfusion injury. J
Cardiovasc Pharmacol Ther. 15:220–230. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Mokhtari B and Badalzadeh R: Protective
and deleterious effects of autophagy in the setting of myocardial
ischemia/reperfusion injury: An overview. Mol Biol Rep.
49:11081–11099. 2022. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Onishi M, Yamano K, Sato M, Matsuda N and
Okamoto K: Molecular mechanisms and physiological functions of
mitophagy. EMBO J. 40:e1047052021. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Turkieh A, El Masri Y, Pinet F and
Dubois-Deruy E: Mitophagy regulation following myocardial
infarction. Cells. 11:1992022. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Gu J, Zhang T, Guo J, Chen K, Li H and
Wang J: PINK1 Activation and translocation to
mitochondria-associated membranes mediates mitophagy and protects
against hepatic ischemia/reperfusion injury. Shock. 54:783–793.
2020. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Leiter LA, Bain SC, Bhatt DL, Buse JB,
Mazer CD, Pratley RE, Rasmussen S, Ripa MS, Vrazic H and Verma S:
The effect of glucagon-like peptide-1 receptor agonists liraglutide
and semaglutide on cardiovascular and renal outcomes across
baseline blood pressure categories: Analysis of the LEADER and
SUSTAIN 6 trials. Diabetes Obes Metab. 22:1690–1695. 2020.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Nauck MA and Quast DR: Cardiovascular
safety and benefits of semaglutide in patients with type 2
Diabetes: Findings from SUSTAIN 6 and PIONEER 6. Front Endocrinol
(Lausanne). 12:6455662021. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Ryan DH, Lingvay I, Colhoun HM, Deanfield
J, Emerson SS, Kahn SE, Kushner RF, Marso S, Plutzky J,
Brown-Frandsen K, et al: Semaglutide effects on cardiovascular
outcomes in people with overweight or obesity (SELECT) rationale
and design. Am Heart J. 229:61–69. 2020. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Lin K, Wang A, Zhai C, Zhao Y, Hu H, Huang
D, Zhai Q, Yan Y and Ge J: Semaglutide protects against
diabetes-associated cardiac inflammation via Sirt3-dependent RKIP
pathway. Br J Pharmacol. Dec 22–2024.doi: 10.1111/bph.17327 (Epub
ahead of print). View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
13
|
Blundell J, Finlayson G, Axelsen M, Flint
A, Gibbons C, Kvist T and Hjerpsted JB: Effects of once-weekly
semaglutide on appetite, energy intake, control of eating, food
preference and body weight in subjects with obesity. Diabetes Obes
Metab. 19:1242–1251. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Zhu Q, Luo Y, Wen Y, Wang D, Li J and Fan
Z: Semaglutide inhibits ischemia/reperfusion-induced cardiomyocyte
apoptosis through activating PKG/PKCε/ERK1/2 pathway. Biochem
Biophys Res Commun. 647:1–8. 2023. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Ouyang M, Lu J, Ding Q, Qin T, Peng C and
Guo Q: Knockdown of long non-coding RNA PVT1 protects human AC16
cardiomyocytes from hypoxia/reoxygenation-induced apoptosis and
autophagy by regulating miR-186/Beclin-1 axis. Gene.
754:1447752020. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Yan X and Hou J: miR-22 host gene enhances
nuclear factor-kappa B activation to aggravate hypoxia-induced
injury in AC16 Cardiomyocytes. Cell Transplant.
30:9636897219903232021. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Yu CJ, Xia F, Ruan L, Hu SP, Zhu WJ and
Yang K: Circ_0004771 promotes Hypoxia/Reoxygenation induced
Cardiomyocyte injury via activation of mitogen-activated protein
kinase signaling pathway. Int Heart J. 64:1125–1132. 2023.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
Davidson MM, Nesti C, Palenzuela L, Walker
WF, Hernandez E, Protas L, Hirano M and Isaac ND: Novel cell lines
derived from adult human ventricular cardiomyocytes. J Mol Cell
Cardiol. 39:133–147. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
Sun K, Chen M, Kong X, Hou W, Xu Z and Liu
L: Cardiac-specific Suv39h1 knockout ameliorates high-fat diet
induced diabetic cardiomyopathy via regulating Hmox1 transcription.
Life Sci. 360:1232582025. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
Li Z, Zhao J, Li H, Li Y and Lin C:
Catalpol protects AC16 cells from hypoxia/reoxygenation injury by
regulating the miR-22-3p/DPP4 axis. J Biochem Mol Toxicol.
36:e230342022. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
Peng CL, Jiang N, Zhao JF, Liu K, Jiang W
and Cao PG: Metformin relieves H/R-induced cardiomyocyte injury
through miR-19a/ACSL axis-possible therapeutic target for
myocardial I/R injury. Toxicol Appl Pharmacol. 414:1154082021.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22
|
Chang YF, Zhang D, Hu WM, Liu DX and Li L:
Semaglutide-mediated protection against Aβ correlated with
enhancement of autophagy and inhibition of apotosis. J Clin
Neurosci. 81:234–239. 2020. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23
|
Wu L, Zhan Y and Wang Y: Semaglutide may
ameliorate fibrosis and inhibit epithelial-mesenchymal transition
in intrauterine adhesion models. Int J Mol Sci. 25:61962024.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24
|
Li Y, Zhou Y, Pei H and Li D: Disruption
of BACH1 protects AC16 Cardiomyocytes against
hypoxia/reoxygenation-evoked injury by diminishing CDKN3
transcription. Cardiovasc Toxicol. 24:1105–1115. 2024. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
25
|
Bajaj HS, Al-Jabri B and Verma S:
Glucagon-like peptide-1 receptor agonists and cardiovascular
protection in type 2 diabetes: A pathophysiology-based review of
clinical implications. Curr Opin Cardiol. 33:665–675. 2018.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
26
|
Yao H, Zhang A, Li D, Wu Y, Wang CZ, Wan
JY and Yuan CS: Comparative effectiveness of GLP-1 receptor
agonists on glycaemic control, body weight, and lipid profile for
type 2 diabetes: Systematic review and network meta-analysis. BMJ.
384:e0764102024. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
27
|
Marx N, Husain M, Lehrke M, Verma S and
Sattar N: GLP-1 receptor agonists for the reduction of
atherosclerotic cardiovascular risk in patients with type 2
diabetes. Circulation. 146:1882–1894. 2022. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
28
|
Kristensen SL, Rørth R, Jhund PS, Docherty
KF, Sattar N, Preiss D, Køber L, Petrie MC and McMurray JJV:
Cardiovascular, mortality, and kidney outcomes with GLP-1 receptor
agonists in patients with type 2 diabetes: A systematic review and
meta-analysis of cardiovascular outcome trials. Lancet Diabetes
Endocrinol. 7:776–785. 2019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
29
|
Marso SP, Daniels GH, Brown-Frandsen K,
Kristensen P, Mann JF, Nauck MA, Nissen SE, Pocock S, Poulter NR,
Ravn LS, et al: Liraglutide and cardiovascular outcomes in type 2
diabetes. N Engl J Med. 375:311–322. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
30
|
Gerstein HC, Colhoun HM, Dagenais GR, Diaz
R, Lakshmanan M, Pais P, Probstfield J, Riesmeyer JS, Riddle MC,
Rydén L, et al: Dulaglutide and cardiovascular outcomes in type 2
diabetes (REWIND): A double-blind, randomized placebo-controlled
trial. Lancet. 394:121–130. 2019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
31
|
Williams TC and Stewart E: Semaglutide and
cardiovascular outcomes in patients with type 2 diabetes. N Engl J
Med. 376:8912017.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
32
|
Aroda VR, Ahmann A, Cariou B, Chow F,
Davies MJ, Jódar E, Mehta R, Woo V and Lingvay I: Comparative
efficacy, safety, and cardiovascular outcomes with once-weekly
subcutaneous semaglutide in the treatment of type 2 diabetes:
Insights from the SUS TAIN 1–7 trials. Diabetes Metab. 45:409–418.
2019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
33
|
Davies M, Færch L, Jeppesen OK, Pakseresht
A, Pedersen SD, Perreault L, Rosenstock J, Shimomura I, Viljoen A,
Wadden TA, et al: Semaglutide 2·4 mg once a week in adults with
overweight or obesity, and type 2 diabetes (STEP 2): A randomised,
double-blind, double-dummy, placebo-controlled, phase 3 trial.
Lancet. 397:971–984. 2021. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
34
|
Li A, Su X, Hu S and Wang Y: Efficacy and
safety of oral semaglutide in type 2 diabetes mellitus: A
systematic review and meta-analysis. Diabetes Res Clin Pract.
198:1106052023. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
35
|
Pan X, Yue L, Ban J, Ren L and Chen S:
Effects of semaglutide on cardiac protein expression and cardiac
function of obese mice. J Inflamm Res. 15:6409–6425. 2022.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
36
|
Li Q, Tuo X, Li B, Deng Z, Qiu Y and Xie
H: Semaglutide attenuates excessive exercise-induced myocardial
injury by inhibiting oxidative stress and inflammation in rats.
Life Sci. 250:1175312020. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
37
|
Fan P, Xie XH, Chen CH, Peng X, Zhang P,
Yang C and Wang YT: Molecular regulation mechanisms and
interactions between reactive oxygen species and mitophagy. DNA
Cell Biol. 38:10–22. 2019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
38
|
Hamacher-Brady A, Brady NR and Gottlieb
RA: Enhancing macroautophagy protects against ischemia/reperfusion
injury in cardiac myocytes. J Biol Chem. 281:29776–29787. 2006.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
39
|
Chen Y, Azad MB and Gibson SB: Superoxide
is the major reactive oxygen species regulating autophagy. Cell
Death Differ. 16:1040–1052. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
40
|
Lei S, Feng Y, Huang P, Chen B, Bao K, Wu
Q, Zhang H and Huang X: Ophiopogonin D'-induced mitophagy and
mitochondrial damage are associated with dysregulation of the
PINK1/Parkin signaling pathway in AC16 cells. Toxicology.
477:1532752022. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
41
|
Sciarretta S, Maejima Y, Zablocki D and
Sadoshima J: The role of autophagy in the heart. Annu Rev Physiol.
80:1–26. 2018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
42
|
Ashrafizadeh M, Ahmadi Z, Farkhondeh T and
Samarghandian S: Autophagy as a molecular target of quercetin
underlying its protective effects in human diseases. Arch Physiol
Biochem. 128:200–208. 2022. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
43
|
Przyklenk K, Dong Y, Undyala VV and
Whittaker P: Autophagy as a therapeutic target for
ischaemia/reperfusion injury? Concepts, controversies, and
challenges. Cardiovasc Res. 94:197–205. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
44
|
Sciarretta S, Yee D, Shenoy V, Nagarajan N
and Sadoshima J: The importance of autophagy in cardioprotection.
High Blood Press Cardiovasc Prev. 21:21–28. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
45
|
Nishida K, Taneike M and Otsu K: The role
of autophagic degradation in the heart. J Mol Cell Cardiol.
78:73–79. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
46
|
Carmichael PL and Peng S:
Doxorubicin-induced mitophagy and mitochondrial damage is
associated with dysregulation of the PINK1/parkin pathway. Toxicol
In Vitro. 51:1–10. 2018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
47
|
Quinn PMJ, Moreira PI, Ambrósio AF and
Alves CH: PINK1/PARKIN signalling in neurodegeneration and
neuroinflammation. Acta Neuropathol Commun. 8:1892020. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
48
|
Zhou P, Xie W, Meng X, Zhai Y, Dong X,
Zhang X, Sun G and Sun X: Notoginsenoside R1 ameliorates diabetic
retinopathy through PINK1-dependent activation of mitophagy. Cells.
8:2132019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
49
|
Jin C, Cao Y and Li Y: Bone mesenchymal
stem cells origin exosomes are effective against sepsis-induced
acute kidney injury in rat model. Int J Nanomedicine. 18:7745–7758.
2023. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
50
|
Bjørkøy G, Lamark T, Brech A, Outzen H,
Perander M, Overvatn A, Stenmark H and Johansen T: p62/SQSTM1 forms
protein aggregates degraded by autophagy and has a protective
effect on huntingtin-induced cell death. J Cell Biol. 171:603–614.
2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
51
|
Komatsu M, Kurokawa H, Waguri S, Taguchi
K, Kobayashi A, Ichimura Y, Sou YS, Ueno I, Sakamoto A, Tong KI, et
al: The selective autophagy substrate p62 activates the stress
responsive transcription factor Nrf2 through inactivation of Keap1.
Nat Cell Biol. 12:213–223. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
52
|
Zhang Y, Mun SR, Linares JF, Ahn J, Towers
CG, Ji CH, Fitzwalter BE, Holden MR, Mi W, Shi X, et al:
ZZ-dependent regulation of p62/SQSTM1 in autophagy. Nat Commun.
9:43732018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
53
|
Yang X, Zhang R, Nakahira K and Gu Z:
Mitochondrial DNA mutation, diseases, and nutrient-regulated
mitophagy. Annu Rev Nutr. 39:201–226. 2019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
54
|
McLean BA, Wong CK, Kabir MG and Drucker
DJ: Glucagon-like Peptide-1 receptor Tie2+ cells are essential for
the cardioprotective actions of liraglutide in mice with
experimental myocardial infarction. Mol Metab. 66:1016412022.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|