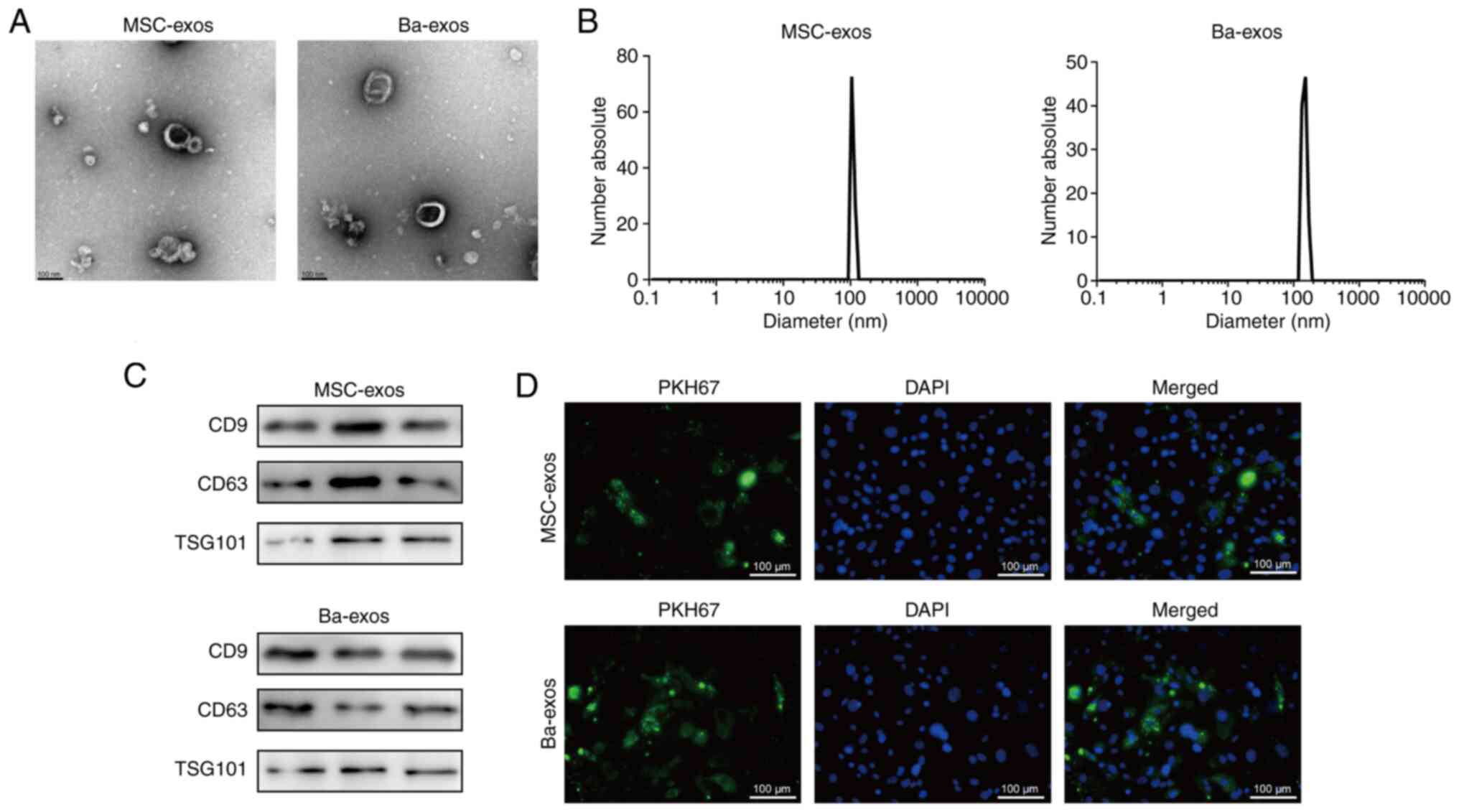
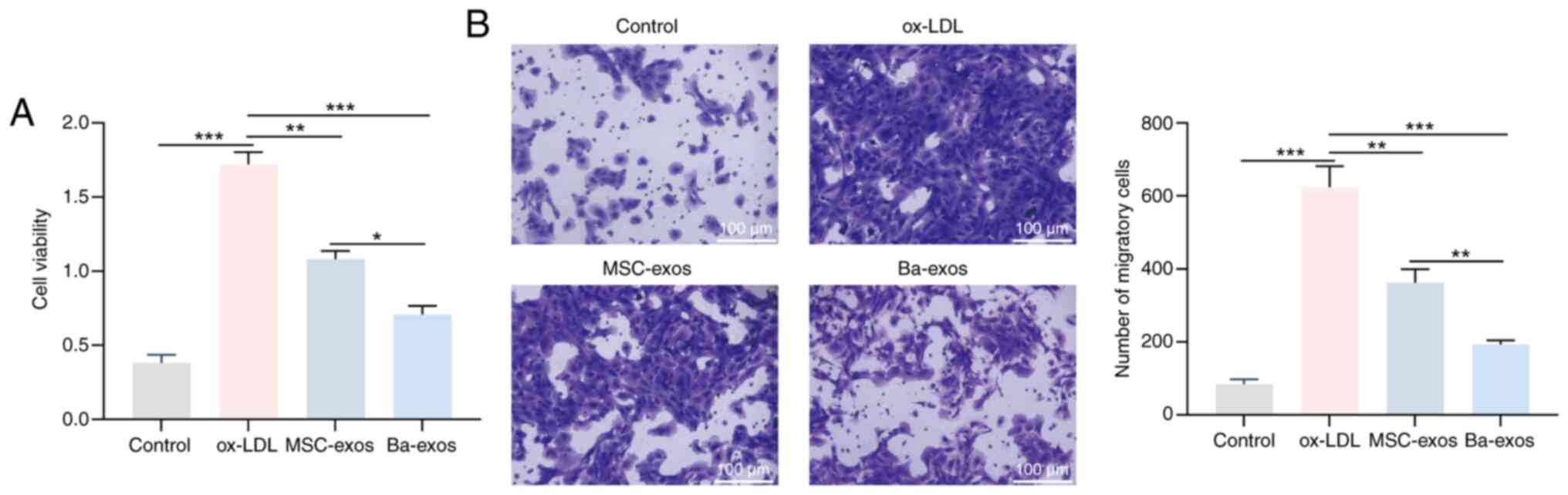
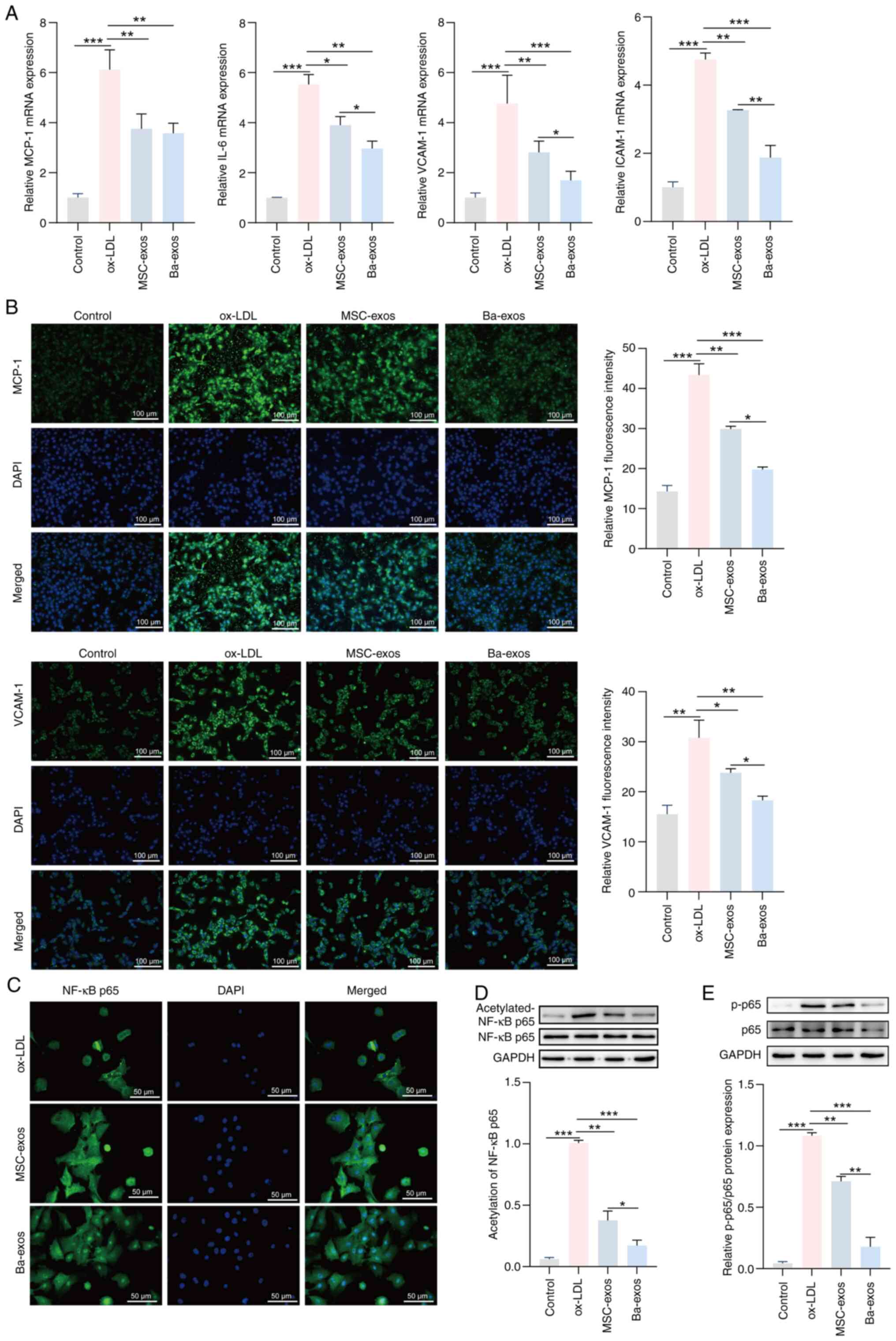
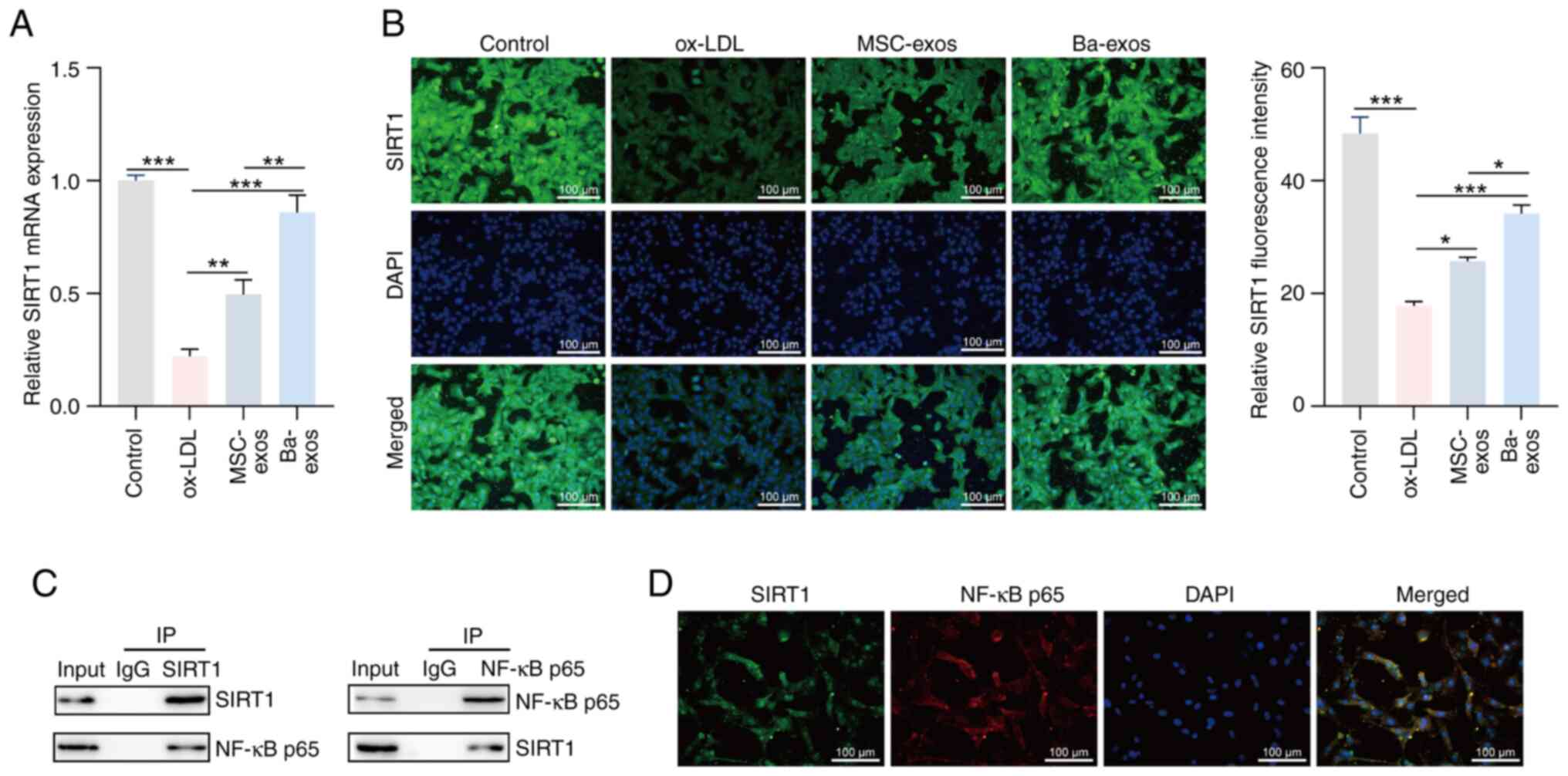
|
1
|
Fan J and Watanabe T: Atherosclerosis:
Known and unknown. Pathol Int. 72:151–160. 2022. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
Falk E: Pathogenesis of atherosclerosis. J
Am Coll Cardiol. 47 (8 Suppl):C7–C12. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
Arnett DK, Blumenthal RS, Albert MA,
Buroker AB, Goldberger ZD, Hahn EJ, Himmelfarb CD, Khera A,
Lloyd-Jones D, McEvoy JW, et al: 2019 ACC/AHA guideline on the
primary prevention of cardiovascular disease: A report of the
american college of cardiology/American heart association task
force on clinical practice guidelines. Circulation. 140:e596–e646.
2019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
Grundy SM, Stone NJ, Bailey AL, Beam C,
Birtcher KK, Blumenthal RS, Braun LT, de Ferranti S,
Faiella-Tommasino J, Forman DE, et al: 2018
AHA/ACC/AACVPR/AAPA/ABC/ACPM/ADA/AGS/APhA/ASPC/NLA/PCNA guideline
on the management of blood cholesterol: A report of the american
college of cardiology/American heart association task force on
clinical practice guidelines. Circulation. 139:e1082–e1143. 2019.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Collet JP, Thiele H, Barbato E, Barthélémy
O, Bauersachs J, Bhatt DL, Dendale P, Dorobantu M, Edvardsen T,
Folliguet T, et al: 2020 ESC guidelines for the management of acute
coronary syndromes in patients presenting without persistent
ST-segment elevation. Eur Heart J. 42:1289–1367. 2021. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Aprotosoaie AC, Costache AD and Costache
II: Therapeutic strategies and chemoprevention of atherosclerosis:
What do we know and where do we go? Pharmaceutics. 14:7222022.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Capodanno D, Alberts M and Angiolillo DJ:
Antithrombotic therapy for secondary prevention of atherothrombotic
events in cerebrovascular disease. Nat Rev Cardiol. 13:609–622.
2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Lan W, Petznick A, Heryati S, Rifada M and
Tong L: Nuclear factor-κB: central regulator in ocular surface
inflammation and diseases. Ocul Surf. 10:137–148. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Baker RG, Hayden MS and Ghosh S: NF-κB,
inflammation, and metabolic disease. Cell Metab. 13:11–22. 2011.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Lawrence T: The nuclear factor NF-kappaB
pathway in inflammation. Cold Spring Harb Perspect Biol.
1:a0016512009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Wang D, Yu X, Gao K, Li F, Li X, Pu H,
Zhang P, Guo S and Wang W: Sweroside alleviates pressure
overload-induced heart failure through targeting CaMKIIδ to inhibit
ROS-mediated NF-κB/NLRP3 in cardiomyocytes. Redox Biol.
74:1032232024. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Hao T, Fang W, Xu D, Chen Q, Liu Q, Cui K,
Cao X, Li Y, Mai K and Ai Q: Phosphatidylethanolamine alleviates
OX-LDL-induced macrophage inflammation by upregulating autophagy
and inhibiting NLRP1 inflammasome activation. Free Radic Biol Med.
208:402–417. 2023. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Huang D, Gao W, Lu H, Qian JY and Ge JB:
Oxidized low-density lipoprotein stimulates dendritic cells
maturation via LOX-1-mediated MAPK/NF-κB pathway. Braz J Med Biol
Res. 54:e110622021. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Bian W, Jing X, Yang Z, Shi Z, Chen R, Xu
A, Wang N, Jiang J, Yang C, Zhang D, et al: Downregulation of
LncRNA NORAD promotes Ox-LDL-induced vascular endothelial cell
injury and atherosclerosis. Aging (Albany NY). 12:6385–6400. 2020.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Hwang JW, Yao H, Caito S, Sundar IK and
Rahman I: Redox regulation of SIRT1 in inflammation and cellular
senescence. Free Radic Biol Med. 61:95–110. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Stein S, Schäfer N, Breitenstein A, Besler
C, Winnik S, Lohmann C, Heinrich K, Brokopp CE, Handschin C,
Landmesser U, et al: SIRT1 reduces endothelial activation without
affecting vascular function in ApoE-/- mice. Aging (Albany NY).
2:353–360. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Yang Z, Li T, Wang C, Meng M, Tan S and
Chen L: Dihydromyricetin inhibits M1 macrophage polarization in
atherosclerosis by modulating miR-9-mediated SIRT1/NF-κB signaling
pathway. Mediators Inflamm. 2023:25475882023. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
Golpanian S, Wolf A, Hatzistergos KE and
Hare JM: Rebuilding the damaged heart: Mesenchymal stem cells,
cell-based therapy, and engineered heart tissue. Physiol Rev.
96:1127–1168. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
Ha DH, Kim HK, Lee J, Kwon HH, Park GH,
Yang SH, Jung JY, Choi H, Lee JH, Sung S, et al: Mesenchymal
stem/stromal cell-derived exosomes for immunomodulatory
therapeutics and skin regeneration. Cells. 9:11572020. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
Zhang N, Luo Y, Zhang H, Zhang F, Gao X
and Shao J: Exosomes derived from mesenchymal stem cells ameliorate
the progression of atherosclerosis in ApoE-/- mice via
FENDRR. Cardiovasc Toxicol. 22:528–544. 2022. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
Ma J, Chen L, Zhu X, Li Q, Hu L and Li H:
Mesenchymal stem cell-derived exosomal miR-21a-5p promotes M2
macrophage polarization and reduces macrophage infiltration to
attenuate atherosclerosis. Acta Biochim Biophys Sin (Shanghai).
53:1227–1236. 2021. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22
|
Hu C and Li L: Preconditioning influences
mesenchymal stem cell properties in vitro and in vivo. J Cell Mol
Med. 22:1428–1442. 2018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23
|
Liu X, Wang J, Wang P, Zhong L, Wang S,
Feng Q, Wei X and Zhou L: Hypoxia-pretreated mesenchymal stem
cell-derived exosomes-loaded low-temperature extrusion 3D-printed
implants for neural regeneration after traumatic brain injury in
canines. Front Bioeng Biotechnol. 10:10251382022. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24
|
Li T, Zhao Y, Cao Z, Shen Y, Chen J, Huang
X, Shao Z, Zeng Y, Chen Q, Yan X, et al: Exosomes Derived from
apelin-pretreated mesenchymal stem cells ameliorate sepsis-induced
myocardial dysfunction by alleviating cardiomyocyte pyroptosis via
delivery of miR-34a-5p. Int J Nanomedicine. 20:687–703. 2025.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
25
|
Zhu J, Wang J, Sheng Y, Zou Y, Bo L, Wang
F, Lou J, Fan X, Bao R, Wu Y, et al: Baicalin improves survival in
a murine model of polymicrobial sepsis via suppressing inflammatory
response and lymphocyte apoptosis. PLoS One. 7:e355232012.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
26
|
Motoo Y and Sawabu N: Antitumor effects of
saikosaponins, baicalin and baicalein on human hepatoma cell lines.
Cancer Lett. 86:91–95. 1994. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
27
|
Yu H, Chen B and Ren Q: Baicalin relieves
hypoxia-aroused H9c2 cell apoptosis by activating
Nrf2/HO-1-mediated HIF1α/BNIP3 pathway. Artif Cells Nanomed
Biotechnol. 47:3657–3663. 2019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
28
|
Chen Z, Pan X, Sheng Z, Yan G, Chen L and
Ma G: Baicalin suppresses the proliferation and migration of
Ox-LDL-VSMCs in atherosclerosis through upregulating miR-126-5p.
Biol Pharm Bull. 42:1517–1523. 2019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
29
|
Wu Y, Wang F, Fan L, Zhang W, Wang T, Du Y
and Bai X: Baicalin alleviates atherosclerosis by relieving
oxidative stress and inflammatory responses via inactivating the
NF-κB and p38 MAPK signaling pathways. Biomed Pharmacother.
97:1673–1679. 2018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
30
|
Yu M, Liu W, Li J, Lu J, Lu H, Jia W and
Liu F: Exosomes derived from atorvastatin-pretreated MSC accelerate
diabetic wound repair by enhancing angiogenesis via AKT/eNOS
pathway. Stem Cell Res Ther. 11:3502020. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
31
|
Livak KJ and Schmittgen TD: Analysis of
relative gene expression data using real-time quantitative PCR and
the 2(-Delta Delta C(T)) method. Methods. 25:402–408. 2001.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
32
|
Kong P, Cui ZY, Huang XF, Zhang DD, Guo RJ
and Han M: Inflammation and atherosclerosis: Signaling pathways and
therapeutic intervention. Signal Transduct Target Ther. 7:1312022.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
33
|
Zhang W, Yan C, Xiao Y, Sun Y, Lin Y, Li Q
and Cai W: Sulfasalazine induces autophagy inhibiting neointimal
hyperplasia following carotid artery injuries in mice. Front Bioeng
Biotechnol. 11:11997852023. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
34
|
Zheng Z, Bian Y, Zhang Y, Ren G and Li G:
Metformin activates AMPK/SIRT1/NF-κB pathway and induces
mitochondrial dysfunction to drive caspase3/GSDME-mediated cancer
cell pyroptosis. Cell Cycle. 19:1089–1104. 2020. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
35
|
He B, Nie Q, Wang F, Han Y, Yang B, Sun M,
Fan X, Ye Z, Liu P and Wen J: Role of pyroptosis in atherosclerosis
and its therapeutic implications. J Cell Physiol. 236:7159–7175.
2021. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
36
|
Groenen AG, Halmos B, Tall AR and
Westerterp M: Cholesterol efflux pathways, inflammation, and
atherosclerosis. Crit Rev Biochem Mol Biol. 56:426–439. 2021.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
37
|
Lotfy A, AboQuella NM and Wang H:
Mesenchymal stromal/stem cell (MSC)-derived exosomes in clinical
trials. Stem Cell Res Ther. 14:662023. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
38
|
Xiong J, Hu H, Guo R, Wang H and Jiang H:
Mesenchymal stem cell exosomes as a new strategy for the treatment
of diabetes complications. Front Endocrinol (Lausanne).
12:6462332021. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
39
|
Guo M, Yin Z, Chen F and Lei P:
Mesenchymal stem cell-derived exosome: A promising alternative in
the therapy of Alzheimer's disease. Alzheimers Res Ther.
12:1092020. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
40
|
Chen W, Lin F, Feng X, Yao Q, Yu Y, Gao F,
Zhou J, Pan Q, Wu J, Yang J, et al: MSC-derived exosomes attenuate
hepatic fibrosis in primary sclerosing cholangitis through
inhibition of Th17 differentiation. Asian J Pharm Sci.
19:1008892024.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
41
|
Liu J, Ren L, Li S, Li W, Zheng X, Yang Y,
Fu W, Yi J, Wang J and Du G: The biology, function, and
applications of exosomes in cancer. Acta Pharm Sin B. 11:2783–2797.
2021. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
42
|
Jiang Y, Yu M, Song ZF, Wei ZY, Huang J
and Qian HY: Targeted delivery of mesenchymal stem cell-derived
bioinspired exosome-mimetic nanovesicles with platelet membrane
fusion for atherosclerotic treatment. Int J Nanomedicine.
19:2553–2571. 2024. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
43
|
Liu S, Fan M, Xu JX, Yang LJ, Qi CC, Xia
QR and Ge JF: Exosomes derived from bone-marrow mesenchymal stem
cells alleviate cognitive decline in AD-like mice by improving
BDNF-related neuropathology. J Neuroinflammation. 19:352022.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
44
|
Xu S, Cheuk YC, Jia Y, Chen T, Chen J, Luo
Y, Cao Y, Guo J, Dong L, Zhang Y, et al: Bone marrow mesenchymal
stem cell-derived exosomal miR-21a-5p alleviates renal fibrosis by
attenuating glycolysis by targeting PFKM. Cell Death Dis.
13:8762022. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
45
|
Gao L, Qiu F, Cao H, Li H, Dai G, Ma T,
Gong Y, Luo W, Zhu D, Qiu Z, et al: Therapeutic delivery of
microRNA-125a-5p oligonucleotides improves recovery from myocardial
ischemia/reperfusion injury in mice and swine. Theranostics.
13:685–703. 2023. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
46
|
Li M, Li S, Du C, Zhang Y, Li Y, Chu L,
Han X, Galons H, Zhang Y, Sun H and Yu P: Exosomes from different
cells: Characteristics, modifications, and therapeutic
applications. Eur J Med Chem. 207:1127842020. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
47
|
Nakao Y, Fukuda T, Zhang Q, Sanui T,
Shinjo T, Kou X, Chen C, Liu D, Watanabe Y, Hayashi C, et al:
Exosomes from TNF-α-treated human gingiva-derived MSCs enhance M2
macrophage polarization and inhibit periodontal bone loss. Acta
Biomater. 122:306–324. 2021. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
48
|
Liu R, Cao H, Zhang S, Cai M, Zou T, Wang
G, Zhang D, Wang X, Xu J, Deng S, et al: ZBP1-mediated apoptosis
and inflammation exacerbate steatotic liver ischemia/reperfusion
injury. J Clin Invest. 134:e1804512024. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
49
|
Xu M, Li X and Song L: Baicalin regulates
macrophages polarization and alleviates myocardial
ischaemia/reperfusion injury via inhibiting JAK/STAT pathway. Pharm
Biol. 58:655–663. 2020. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
50
|
Zhu S, Yao F, Qiu H, Zhang G, Xu H and Xu
J: Coupling factors and exosomal packaging microRNAs involved in
the regulation of bone remodelling. Biol Rev Camb Philos Soc.
93:469–480. 2018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
51
|
Zhao S, Huang M, Yan L, Zhang H, Shi C,
Liu J, Zhao S, Liu H and Wang B: Exosomes derived from
baicalin-pretreated mesenchymal stem cells alleviate hepatocyte
ferroptosis after acute liver injury via the Keap1-NRF2 pathway.
Oxid Med Cell Longev. 2022:82872272022. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
52
|
Zhang B, Su L, Chen Z, Wu M, Wei J and Lin
Y: Exosomes derived from baicalin-pretreated bone mesenchymal stem
cells improve Th17/Treg imbalance after hepatic
ischemia-reperfusion via FGF21 and the JAK2/STAT3 pathway. IUBMB
Life. 76:534–547. 2024. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
53
|
Pryma CS, Ortega C, Dubland JA and Francis
GA: Pathways of smooth muscle foam cell formation in
atherosclerosis. Curr Opin Lipidol. 30:117–124. 2019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
54
|
Grootaert MOJ, Finigan A, Figg NL, Uryga
AK and Bennett MR: SIRT6 protects smooth muscle cells from
senescence and reduces atherosclerosis. Circ Res. 128:474–491.
2021. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
55
|
Zhu J, Liu B, Wang Z, Wang D, Ni H, Zhang
L and Wang Y: Exosomes from nicotine-stimulated macrophages
accelerate atherosclerosis through miR-21-3p/PTEN-mediated VSMC
migration and proliferation. Theranostics. 9:6901–6919. 2019.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
56
|
Li H, Zhuang W, Xiong T, Park WS, Zhang S,
Zha Y, Yao J, Wang F, Yang Y, Chen Y, et al: Nrf2 deficiency
attenuates atherosclerosis by reducing LOX-1-mediated proliferation
and migration of vascular smooth muscle cells. Atherosclerosis.
347:1–16. 2022. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
57
|
Guo B, Zhuang TT, Li CC, Li F, Shan SK,
Zheng MH, Xu QS, Wang Y, Lei LM, Tang KX, et al: MiRNA-132/212
encapsulated by adipose tissue-derived exosomes worsen
atherosclerosis progression. Cardiovasc Diabetol. 23:3312024.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
58
|
Liu J, Zhang X, Yu Z and Zhang T: Exosomes
promote atherosclerosis progression by regulating
Circ_100696/miR-503-5p/PAPPA axis-mediated vascular smooth muscle
cells proliferation and migration. Int Heart J. 64:918–927. 2023.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
59
|
Park JY, Park HM, Kim S, Jeon KB, Lim CM,
Hong JT and Yoon DY: Human IL-32θA94V mutant attenuates
monocyte-endothelial adhesion by suppressing the expression of
ICAM-1 and VCAM-1 via binding to cell surface receptor integrin
αVβ3 and αVβ6 in TNF-α-stimulated HUVECs. Front Immunol.
14:11603012023. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
60
|
Feng X, Du M, Li S, Zhang Y, Ding J, Wang
J, Wang Y and Liu P: Hydroxysafflor yellow A regulates
lymphangiogenesis and inflammation via the inhibition of PI3K on
regulating AKT/mTOR and NF-κB pathway in macrophages to reduce
atherosclerosis in ApoE-/- mice. Phytomedicine. 112:1546842023.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
61
|
Morigi M, Perico L and Benigni A: Sirtuins
in renal health and disease. J Am Soc Nephrol. 29:1799–1809. 2018.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
62
|
Kauppinen A, Suuronen T, Ojala J,
Kaarniranta K and Salminen A: Antagonistic crosstalk between NF-κB
and SIRT1 in the regulation of inflammation and metabolic
disorders. Cell Signal. 25:1939–1948. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
63
|
Wei K, Yu L, Li J, Gao J, Chen L, Liu M,
Zhao X, Li M, Shi D and Ma X: Platelet-derived exosomes regulate
endothelial cell inflammation and M1 macrophage polarization in
coronary artery thrombosis via modulating miR-34a-5p expression.
Sci Rep. 14:174292024. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|