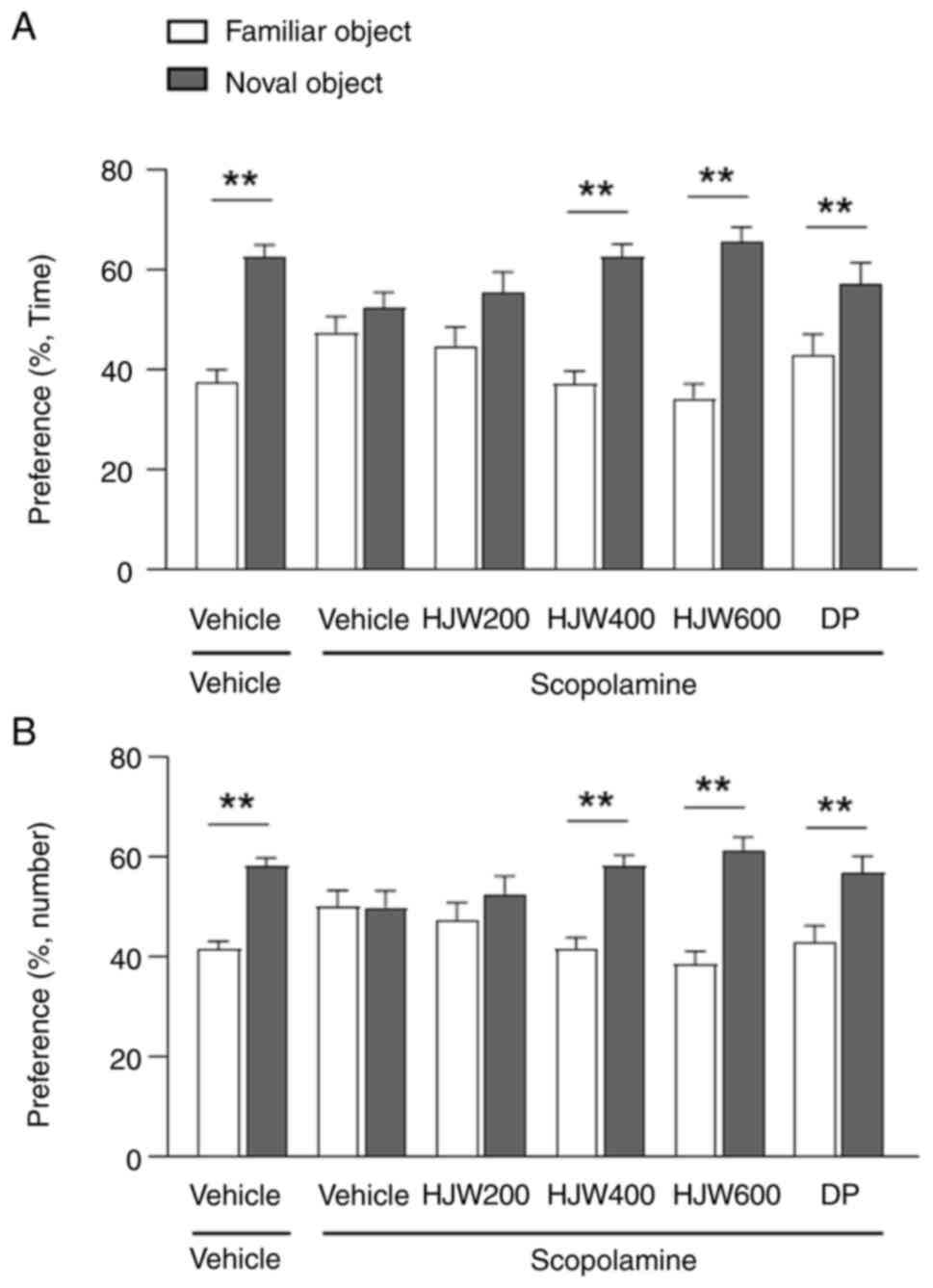
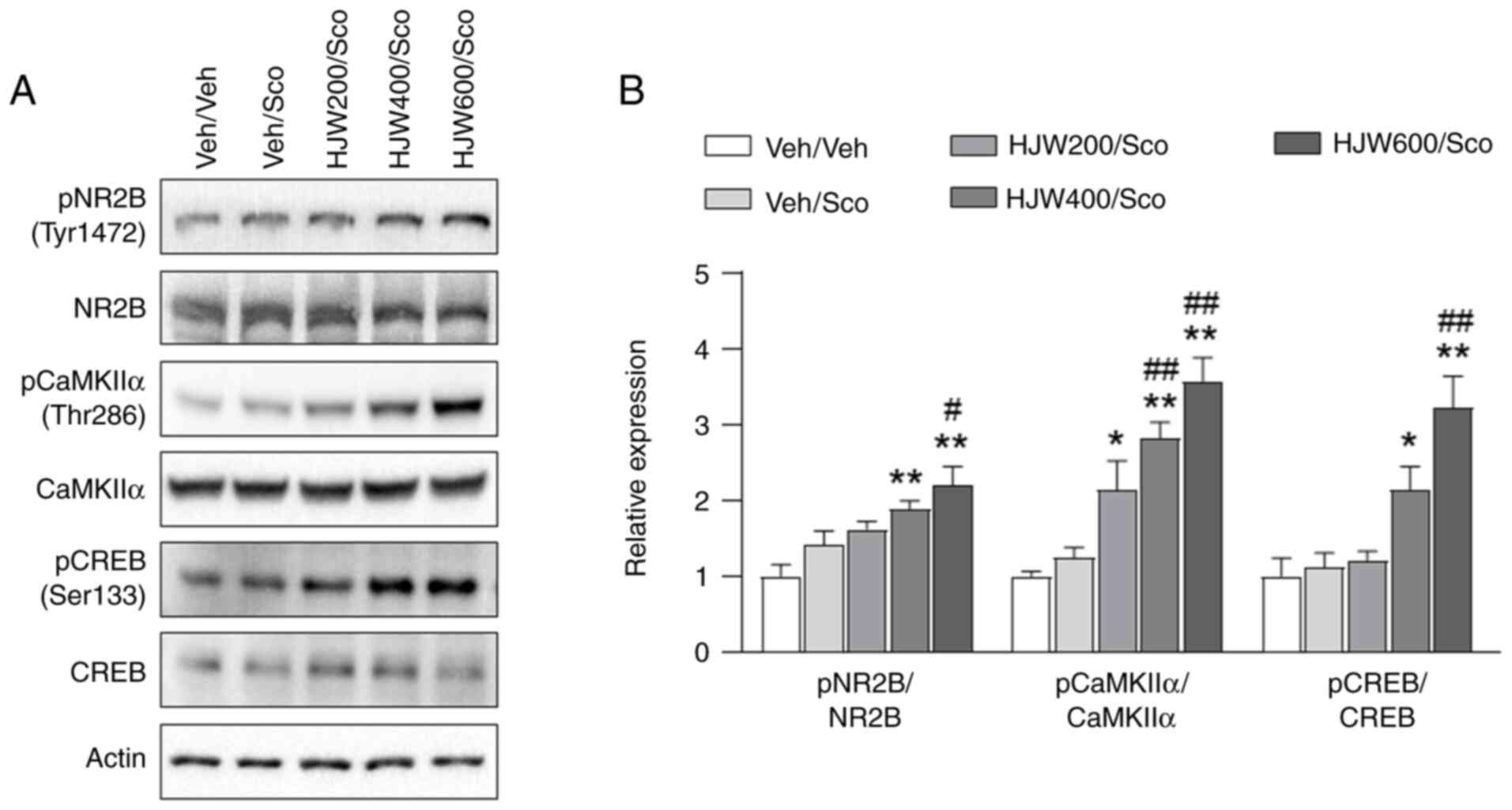
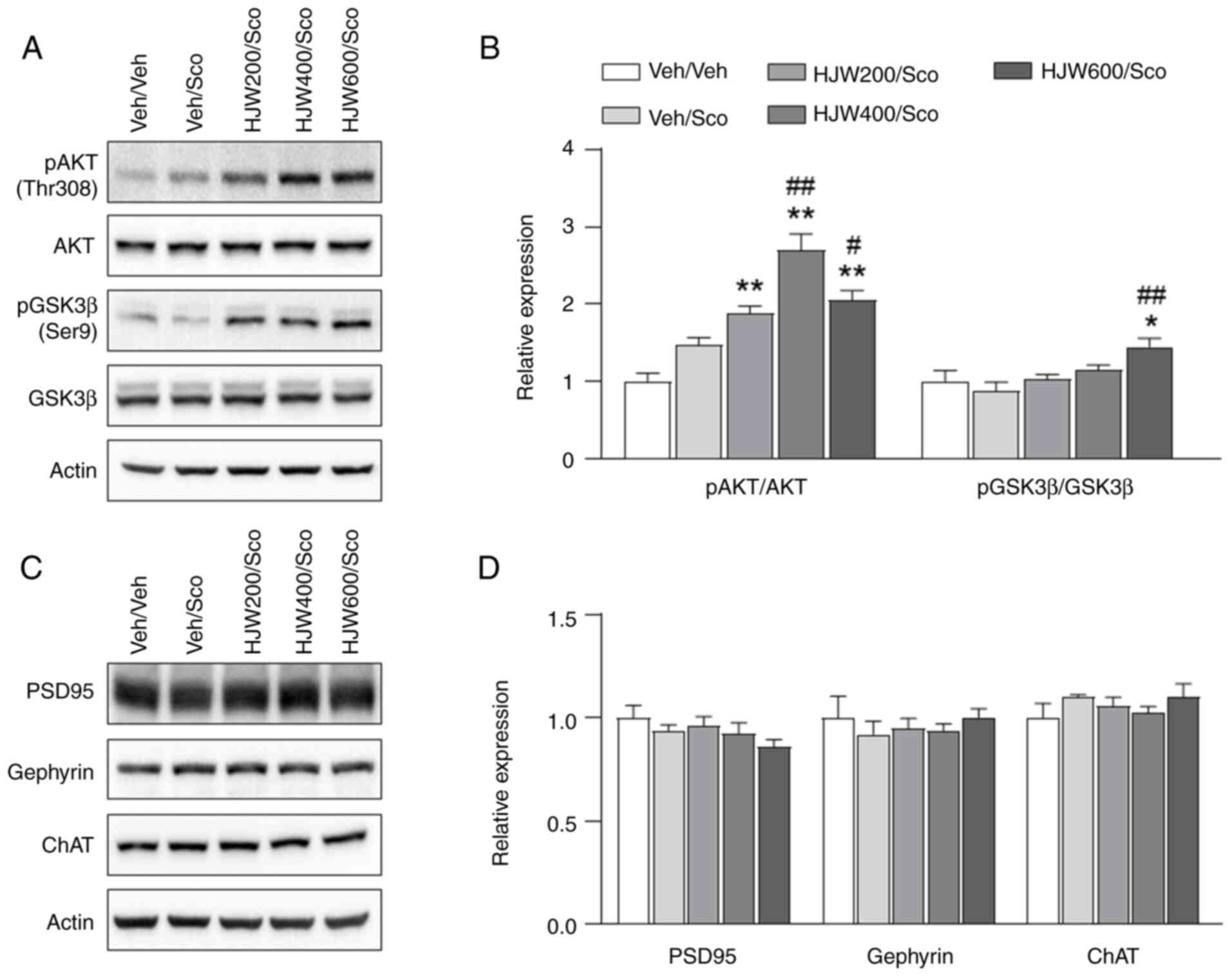
|
1
|
Nicholls LAB, Amanzio M, Guntekin B and
Keage H: Editorial: The cognitive ageing collection. Sci Rep.
14:108692024. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
Hebert LE, Scherr PA, Bienias JL, Bennett
DA and Evans DA: Alzheimer disease in the US population: prevalence
estimates using the 2000 census. Arch Neurol. 60:1119–1122. 2003.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
Flores G, Flores-Gomez GD, Diaz A,
Penagos-Corzo JC, Iannitti T and Morales-Medina JC: Natural
products present neurotrophic properties in neurons of the limbic
system in aging rodents. Synapse. 75:e221852020. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
Zaninotto P, Batty GD, Allerhand M and
Deary IJ: Cognitive function trajectories and their determinants in
older people: 8 years of follow-up in the english longitudinal
study of ageing. J Epidemiol Community Health. 72:685–694. 2018.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Blinkouskaya Y and Weickenmeier J: Brain
shape changes associated with cerebral atrophy in healthy aging and
Alzheimer's disease. Front Mech Eng. 7:7056532021. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Chen L, Jiao J and Zhang Y: Therapeutic
approaches for improving cognitive function in the aging brain.
Front Neurosci. 16:10605562022. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Dickstein DL, Kabaso D, Rocher AB, Luebke
JI, Wearne SL and Hof PR: Changes in the structural complexity of
the aged brain. Aging Cell. 6:275–284. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Picciotto MR, Higley MJ and Mineur YS:
Acetylcholine as a neuromodulator: Cholinergic signaling shapes
nervous system function and behavior. Neuron. 76:116–129. 2012.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Rasmusson DD: The role of acetylcholine in
cortical synaptic plasticity. Behav Brain Res. 115:205–218. 2000.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Madrid LI, Jimenez-Martin J, Coulson EJ
and Jhaveri DJ: Cholinergic regulation of adult hippocampal
neurogenesis and hippocampus-dependent functions. Int J Biochem
Cell Biol. 134:1059692021. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Mustafab I, Elkamel A, Ibrahim G,
Elnashaie S and Chen P: Effect of Choline and acetate substrates on
bifurcation and chaotic behavior of acetylcholine neurocycle and
Alzheimer's and Parkinson's diseases. Journal of chemical
engineering science. 64:2096–2112. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
12
|
Moreira EL, de Oliveira J, Nunes JC,
Santos DB, Nunes FC, Vieira DS, Ribeiro-do-Valle RM, Pamplona FA,
de Bem AF, Farina M, et al: Age-related cognitive decline in
hypercholesterolemic LDL receptor knockout mice (LDLr-/-): evidence
of antioxidant imbalance and increased acetylcholinesterase
activity in the prefrontal cortex. J Alzheimers Dis. 32:495–511.
2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Hafez HS, Ghareeb DA, Saleh SR, Abady MM,
El Demellawy MA, Hussien H and Abdel-Monem N: Neuroprotective
effect of ipriflavone against scopolamine-induced memory impairment
in rats. Psychopharmacology (Berl). 234:3037–3053. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Blake MG, Krawczyk MC, Baratti CM and
Boccia MM: Neuropharmacology of memory consolidation and
reconsolidation: Insights on central cholinergic mechanisms. J
Physiol Paris. 108:286–291. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Gasiorowska A, Wydrych M, Drapich P,
Zadrozny M, Steczkowska M, Niewiadomski W and Niewiadomska G: The
biology and pathobiology of glutamatergic, cholinergic and
dopaminergic signaling in the aging brain. Front Aging Neurosci.
13:6549312021. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Chen ZR, Huang JB, Yang SL and Hong FF:
Role of cholinergic signaling in Alzheimer's disease. Molecules.
27:18162022. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Muller ML and Bohnen NI: Cholinergic
dysfunction in Parkinson's disease. Curr Neurol Neurosci Rep.
13:3772013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
Go J, Park HY, Lee DW, Maeng SY, Lee IB,
Seo YJ, An JP, Oh WK, Lee CH and Kim KS: Humulus japonicus
attenuates LPS-and scopolamine-induced cognitive impairment in
mice. Lab Anim Res. 38:212022. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
Kim YB, Kang EJ, Noh JR, An JP, Park JT,
Oh WK, Kim YH and Lee CH: Humulus japonicus ameliorates irritant
contact dermatitis by suppressing NF-ĸB p65-dependent inflammatory
responses in mice. Exp Ther Med. 26:4462023. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
Sung B, Chung JW, Bae HR, Choi JS, Kim CM
and Kim ND: Humulus japonicus extract exhibits antioxidative and
anti-aging effects via modulation of the AMPK-SIRT1 pathway. Exp
Ther Med. 9:1819–1826. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
McPartland JM: Cannabis systematics at the
levels of family, genus and species. Cannabis Cannabinoid Res.
3:203–212. 2018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22
|
Ovidi E, Laghezza Masci V, Taddei AR,
Torresi J, Tomassi W, Iannone M, Tiezzi A, Maggi F and Garzoli S:
Hemp (Cannabis sativa L., Kompolti cv.) and Hop (Humulus lupulus
L., Chinook cv.) essential oil and hydrolate: HS-GC-MS chemical
investigation and apoptotic activity evaluation. Pharmaceuticals
(Basel). 15:9762022. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23
|
Carbone K and Gervasi F: An updated review
of the genus humulus: A valuable source of bioactive compounds for
health and disease prevention. Plants (Basel).
11:34342022.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24
|
Lee HJ, Dhodary B, Lee JY, An JP, Ryu YK,
Kim KS, Lee CH and Oh WK: Dereplication of components coupled with
HPLC-qTOF-MS in the active fraction of humulus japonicus and it's
protective effects against Parkinson's disease mouse model.
Molecules. 24:14352019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
25
|
Ryu YK, Kang Y, Go J, Park HY, Noh JR, Kim
YH, Hwang JH, Choi DH, Han SS, Oh WK, et al: Humulus japonicus
prevents dopaminergic neuron death in 6-hydroxydopamine-induced
models of Parkinson's disease. J Med Food. 20:116–123. 2017.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
26
|
Park TS, Ryu YK, Park HY, Kim JY, Go J,
Noh JR, Kim YH, Hwang JH, Choi DH, Oh WK, et al: Humulus japonicus
inhibits the progression of Alzheimer's disease in a APP/PS1
transgenic mouse model. Int J Mol Med. 39:21–30. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
27
|
Thein W, Choi WS, Po WW, Khing TM, Jeong
JH and Sohn UD: Ameliorative effects of Humulus japonicus extract
and polysaccharide-rich extract of Phragmites rhizoma in rats with
gastrointestinal dysfunctions induced by water avoidance stress.
Evid Based Complement Alternat Med. 2022:99937432022. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
28
|
Kim OK, Yun JM, Lee M, Park SJ, Kim D, Oh
DH, Kim HS and Kim GY: A mixture of humulus japonicus increases
longitudinal bone growth rate in sprague dawley rats. Nutrients.
12:26252020. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
29
|
Chung YH, Bang JS, Kang CM, Goh JW, Lee
HS, Hong SM, Kim DS, Park ES, Jung TW, Shin YK, et al: Aqueous
extract of humulus japonicus attenuates hyperlipidemia and fatty
liver in obese mice. J Med Food. 21:999–1008. 2018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
30
|
Falsafi SK, Deli A, Hoger H, Pollak A and
Lubec G: Scopolamine administration modulates muscarinic, nicotinic
and NMDA receptor systems. PLoS One. 7:e320822012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
31
|
Kim CY, Seo Y, Lee C, Park GH and Jang JH:
Neuroprotective effect and molecular mechanism of [6]-gingerol
against scopolamine-induced amnesia in C57BL/6 mice. Evid Based
Complement Alternat Med. 2018:89415642018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
32
|
Garber JC, Barbee RW, Beelitzki JT, et al:
Guide for the care and use of laboratory animals. 8th Edition.
National Academies Press; Washington, DC: pp. 1–246. 2011
|
|
33
|
Seibenhener ML and Wooten MC: Use of the
open field maze to measure locomotor and anxiety-like behavior in
mice. J Vis Exp. 6:e524342015.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
34
|
Shang Q, Chen G, Zhang P, Zhao W, Chen H,
Yu D, Yu F, Liu H, Zhang X, He J, et al: Myristic acid alleviates
hippocampal aging correlated with GABAergic signaling. Front Nutr.
9:9075262022. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
35
|
Lueptow LM: Novel object recognition test
for the investigation of learning and memory in mice. J Vis Exp.
557182017.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
36
|
Vorhees CV and Williams MT: Morris water
maze: Procedures for assessing spatial and related forms of
learning and memory. Nat Protoc. 1:848–858. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
37
|
Go J, Maeng SY, Chang DH, Park HY, Min KS,
Kim JE, Choi YK, Noh JR, Ro H, Kim BC, et al: Agathobaculum
butyriciproducens improves ageing-associated cognitive impairment
in mice. Life Sci. 339:1224132024. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
38
|
Wang DM, Yang YJ, Zhang L, Zhang X, Guan
FF and Zhang LF: Naringin enhances CaMKII activity and improves
long-term memory in a mouse model of Alzheimer's disease. Int J Mol
Sci. 14:5576–5586. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
39
|
Gomez-Oliva R, Martinez-Ortega S,
Atienza-Navarro I, Domínguez-García S, Bernal-Utrera C,
Geribaldi-Doldán N, Verástegui C, Ezzanad A, Hernández-Galán R,
Nunez-Abades P, et al: Rescue of neurogenesis and age-associated
cognitive decline in SAMP8 mouse: Role of transforming growth
factor-alpha. Aging Cell. 22:e138292023. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
40
|
Ge W, Ren C, Xing L, Guan L, Zhang C, Sun
X, Wang G, Niu H and Qun S: Ginkgo biloba extract improves
cognitive function and increases neurogenesis by reducing Abeta
pathology in 5×FAD mice. Am J Transl Res. 13:1471–1482.
2021.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
41
|
Garcia-Cabezas MA, John YJ, Barbas H and
Zikopoulos B: Distinction of neurons, glia and endothelial cells in
the cerebral cortex: An algorithm based on cytological features.
Front Neuroanat. 10:1072016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
42
|
Jang S, Chun JH and Kim KB: Analysis on
recent studies trends of humulus japonicus-focusing on research of
medical sciences. J Pediatrics Korean Med. 38:97–112. 2024.
|
|
43
|
Sun JL, Kim YJ, Cho W, Park SS, Abd El-Aty
AM, Mobarak EH, Jung TW and Jeong JH: The extract of humulus
japonicus inhibits lipogenesis and promotes lipolysis via PKA/p38
signaling. Obes Facts. 17:513–523. 2024. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
44
|
Antunes M and Biala G: The novel object
recognition memory: neurobiology, test procedure and its
modifications. Cogn Process. 13:93–110. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
45
|
Anacker C and Hen R: Adult hippocampal
neurogenesis and cognitive flexibility-linking memory and mood. Nat
Rev Neurosci. 18:335–346. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
46
|
Kida S: A functional role for CREB as a
positive regulator of memory formation and LTP. Exp Neurobiol.
21:136–140. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
47
|
Wang H, Xu J, Lazarovici P, Quirion R and
Zheng W: cAMP response element-binding protein (CREB): A possible
signaling molecule link in the pathophysiology of schizophrenia.
Front Mol Neurosci. 11:2552018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
48
|
Kang CM, Bang JS, Park SY, Jung TW, Kim
HC, Chung YH and Jeong JH: The aqueous extract of humulus japonicus
ameliorates cognitive dysfunction in Alzheimer's disease models via
modulating the cholinergic system. J Med Food. 25:943–951.
2022.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
49
|
Anand KS and Dhikav V: Hippocampus in
health and disease: An overview. Ann Indian Acad Neurol.
15:239–246. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
50
|
Zhao C, Deng W and Gage FH: Mechanisms and
functional implications of adult neurogenesis. Cell. 132:645–660.
2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
51
|
Kang EJ, Kim JH, Kim YE, Lee H, Jung KB,
Chang DH, Lee Y, Park S, Lee EY, Lee EJ, et al: The secreted
protein Amuc_1409 from Akkermansia muciniphila improves gut health
through intestinal stem cell regulation. Nat Commun. 15:29832024.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
52
|
Zeng Q, Zheng M, Zhang T and He G:
Hippocampal neurogenesis in the APP/PS1/nestin-GFP triple
transgenic mouse model of Alzheimer's disease. Neuroscience.
314:64–74. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
53
|
Ding Y, Li L, Wang S, Cao Y, Yang M, Dai
Y, Lin H, Li J, Liu Y, Wang Z, et al: Electroacupuncture promotes
neurogenesis in the dentate gyrus and improves pattern separation
in an early Alzheimer's disease mouse model. Biol Res. 56:652023.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
54
|
Culig L, Chu X and Bohr VA: Neurogenesis
in aging and age-related neurodegenerative diseases. Ageing Res
Rev. 78:1016362022. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
55
|
McGinley LM, Kashlan ON, Bruno ES, Chen
KS, Hayes JM, Kashlan SR, Raykin J, Johe K, Murphy GG and Feldman
EL: Human neural stem cell transplantation improves cognition in a
murine model of Alzheimer's disease. Sci Rep. 8:147762018.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
56
|
Gleeson JG, Lin PT, Flanagan LA and Walsh
CA: Doublecortin is a microtubule-associated protein and is
expressed widely by migrating neurons. Neuron. 23:257–271. 1999.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
57
|
Hampel H, Vergallo A, Afshar M,
Akman-Anderson L, Arenas J, Benda N, Batrla R, Broich K, Caraci F,
Cuello AC, et al: Blood-based systems biology biomarkers for
next-generation clinical trials in Alzheimer's disease. Dialogues
Clin Neurosci. 21:177–191. 2019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
58
|
Schliebs R and Arendt T: The cholinergic
system in aging and neuronal degeneration. Behav Brain Res.
221:555–563. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
59
|
Anand P and Singh B: A review on
cholinesterase inhibitors for Alzheimer's disease. Arch Pharm Res.
36:375–399. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
60
|
Veena J, Rao BS and Srikumar BN:
Regulation of adult neurogenesis in the hippocampus by stress,
acetylcholine and dopamine. J Nat Sci Biol Med. 2:26–37. 2011.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
61
|
Cooper-Kuhn CM, Winkler J and Kuhn HG:
Decreased neurogenesis after cholinergic forebrain lesion in the
adult rat. J Neurosci Res. 77:155–165. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
62
|
Marucci G, Buccioni M, Ben DD, Lambertucci
C, Volpini R and Amenta F: Efficacy of acetylcholinesterase
inhibitors in Alzheimer's disease. Neuropharmacology.
190:1083522021. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
63
|
Zucker RS: Calcium- and activity-dependent
synaptic plasticity. Curr Opin Neurobiol. 9:305–313. 1999.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
64
|
Rotenberg A, Mayford M, Hawkins RD, Kandel
ER and Muller RU: Mice expressing activated CaMKII lack low
frequency LTP and do not form stable place cells in the CA1 region
of the hippocampus. Cell. 87:1351–1361. 1996. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
65
|
Omkumar RV, Kiely MJ, Rosenstein AJ, Min
KT and Kennedy MB: Identification of a phosphorylation site for
calcium/calmodulindependent protein kinase II in the NR2B subunit
of the N-methyl-D-aspartate receptor. J Biol Chem. 271:31670–31678.
1996. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
66
|
Chang JY, Parra-Bueno P, Laviv T, Szatmari
EM, Lee SR and Yasuda R: CaMKII autophosphorylation is necessary
for optimal integration of Ca(2+) signals during LTP induction, but
not maintenance. Neuron. 94:800–808. e42017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
67
|
Giese KP, Fedorov NB, Filipkowski RK and
Silva AJ: Autophosphorylation at Thr286 of the alpha
calcium-calmodulin kinase II in LTP and learning. Science.
279:870–873. 1998. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
68
|
Sheng M, Thompson MA and Greenberg ME:
CREB: A Ca(2+)-regulated transcription factor phosphorylated by
calmodulin-dependent kinases. Science. 252:1427–1430. 1991.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
69
|
Saura CA and Valero J: The role of CREB
signaling in Alzheimer's disease and other cognitive disorders. Rev
Neurosci. 22:153–169. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
70
|
Soares MO, Alves RC, Pires PC, Oliveira MB
and Vinha AF: Angolan Cymbopogon citratus used for therapeutic
benefits: nutritional composition and influence of solvents in
phytochemicals content and antioxidant activity of leaf extracts.
Food Chem Toxicol. 60:413–418. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
71
|
Cieniak C, Walshe-Roussel B, Liu R,
Muhammad A, Saleem A, Haddad PS, Cuerrier A, Foster BC and Arnason
JT: Phytochemical comparison of the water and ethanol leaf extracts
of the cree medicinal plant, Sarracenia purpurea L.
(Sarraceniaceae). J Pharm Pharm Sci. 18:484–493. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
72
|
Wang H, Wang H, Cheng H and Che Z:
Ameliorating effect of luteolin on memory impairment in an
Alzheimer's disease model. Mol Med Rep. 13:4215–4220. 2016.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
73
|
Liu R, Gao M, Qiang GF, Zhang TT, Lan X,
Ying J and Du GH: The anti-amnesic effects of luteolin against
amyloid beta(25–35) peptide-induced toxicity in mice involve the
protection of neurovascular unit. Neuroscience. 162:1232–1243.
2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
74
|
Olasehinde TA and Olaokun OO: The
beneficial role of apigenin against cognitive and neurobehavioural
dysfunction: A systematic review of preclinical investigations.
Biomedicines. 12:1782024. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
75
|
Achour M, Ferdousi F, Sasaki K and Isoda
H: Luteolin modulates neural stem cells fate determination: In
vitro study on human neural stem cells and in vivo study on
LPS-Induced depression mice model. Front Cell Dev Biol.
9:7532792021. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
76
|
Li HZ, Liu KG, Zeng NX, Wu XF, Lu WJ, Xu
HF, Yan C and Wu LL: Luteolin enhances choroid plexus 5-MTHF brain
transport to promote hippocampal neurogenesis in LOD rats. Front
Pharmacol. 13:8265682022. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
77
|
Jordan SA, Cunningham DG and Marles RJ:
Assessment of herbal medicinal products: Challenges and
opportunities to increase the knowledge base for safety assessment.
Toxicol Appl Pharmacol. 243:198–216. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
78
|
Petrovska BB: Historical review of
medicinal plants' usage. Pharmacogn Rev. 6:1–5. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
79
|
Agidew MG: Phytochemical analysis of some
selected traditional medicinal plants in Ethiopia. Bulletin of the
National Research Centre. 46:872022. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
80
|
Hossain MA and Nagooru MR: Biochemical
profiling and total flavonoids contents of leaves crude extract of
endemic medicinal plant Corydyline terminalis L. Kunth. Pharma J.
3:25–30. 2011.
|
|
81
|
Butnariu M, Quispe C, Herrera-Bravo J,
Fernández-Ochoa Á, Emamzadeh-Yazdi S, Adetunji CO, Memudu AE,
Otlewska A, Bogdan P, Antolak H, et al: A review on tradescantia:
Phytochemical Constituents, biological activities and
health-promoting effects. Front Biosci (Landmark Ed). 27:1972022.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
82
|
Proestos C: The benefits of plant extracts
for human health. Foods. 9:16532020. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
83
|
Plaskova A and Mlcek J: New insights of
the application of water or ethanol-water plant extract rich in
active compounds in food. Front Nutr. 10:11187612023. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
84
|
Oulhaj A, Jerneren F, Refsum H, Smith AD
and de Jager CA: Omega-3 fatty acid status enhances the prevention
of cognitive decline by B vitamins in mild cognitive impairment. J
Alzheimers Dis. 50:547–557. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|