|
1
|
Scholz H, Boivin FJ, Schmidt-Ott KM,
Bachmann S, Eckardt KU, Scholl UI and Persson PB: Kidney physiology
and susceptibility to acute kidney injury: Implications for
renoprotection. Nat Rev Nephrol. 17:335–349. 2021. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
Pan T, Jia P, Chen N, Fang Y, Liang Y, Guo
M and Ding X: Delayed Remote ischemic preconditioning
confersrenoprotection against septic acute kidney injury via
exosomal miR-21. Theranostics. 9:405–423. 2019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
He Y, Li X and Huang B, Yang Y, Luo N,
Song W and Huang B: Exosomal circvma21 derived from Adipose-derived
stem cells alleviates Sepsis-induced acute kidney injury by
targeting Mir-16-5p. Shock. 60:419–426. 2023.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
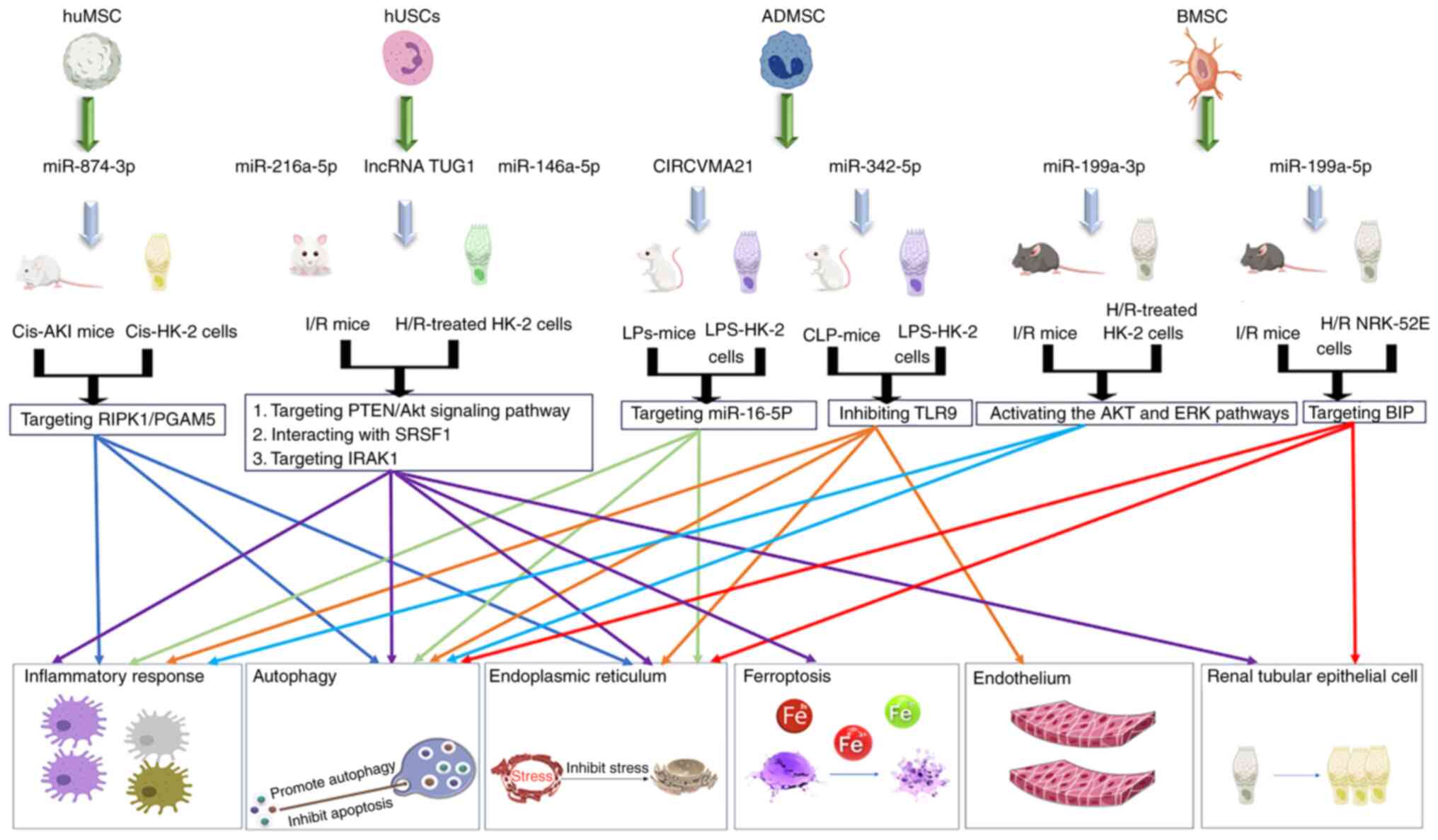
Jorgensen SCJ, Murray KP, Lagnf AM, Melvin
S, Bhatia S, Shamim MD, Smith JR, Brade KD, Simon SP, Nagel J, et
al: A multicenter evaluation of Vancomycin-associated acute kidney
injury in hospitalized patients with acute bacterial skin and skin
structure infections. Infect Dis Ther. 9:89–106. 2020. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Fathy N, Farouk S, Sayed RH and Fahim AT:
Ezetimibe ameliorates cisplatin-induced nephrotoxicity: A novel
therapeutic approach via modulating AMPK/Nrf2/TXNIP signaling.
FASEB J. 38:e233822024. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Li Y, Hu C, Zhai P, Zhang J, Jiang J, Suo
J, Hu B, Wang J, Weng X, Zhou X, et al: Fibroblastic reticular
cell-derived exosomes are a promising therapeutic approach for
septic acute kidney injury. Kidney Int. 105:508–523. 2024.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Huang TY, Chien MS and Su WT: Therapeutic
potential of pretreatment with exosomes derived from stem cells
from the apical papilla against Cisplatin-induced acute kidney
injury. Int J Mol Sci. 23:57212022. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Guo G, Wang Y, Kou W and Gan H:
Identifying the molecular mechanisms of sepsis-associated acute
kidney injury and predicting potential drugs. Front Genet.
13:10622932022. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Chen L, Xu JY and Tan HB: LncRNA TUG1
regulates the development of ischemia-reperfusion mediated acute
kidney injury through miR-494-3p/E-cadherin axis. J Inflamm (Lond).
18:122021. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Zhang X, Wang J, Zhang J, Tan Y, Li Y and
Peng Z: Exosomes highlight future directions in the treatment of
acute kidney injury. Int J Mol Sci. 24:155682023. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Jiao Y, Zhang T, Zhang C, Ji H, Tong X,
Xia R, Wang W, Ma Z and Shi X: Exosomal miR-30d-5p of neutrophils
induces M1 macrophage polarization and primes macrophage pyroptosis
in sepsis-related acute lung injury. Crit Care. 25:3562021.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Wang C, Zhu G, He W, Yin H, Lin F, Gou X
and Li X: BMSCs protect against renal ischemia-reperfusion injury
by secreting exosomes loaded with miR-199a-5p that target BIP to
inhibit endoplasmic reticulum stress at the very early reperfusion
stages. FASEB J. 33:5440–5456. 2019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Zhang W, Zhou B, Yang X, Zhao J, Hu J,
Ding Y, Zhan S, Yang Y, Chen J, Zhang F, et al: Exosomal
circEZH2_005, an intestinal injury biomarker, alleviates intestinal
ischemia/reperfusion injury by mediating Gprc5a signaling. Nat
Commun. 14:5437–5453. 2023. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Zhu G, Pei L, Lin F, Yin H, Li X, He W,
Liu N and Gou X: Exosomes from human-bone-marrow-derived
mesenchymal stem cells protect against renal ischemia/reperfusion
injury via transferring miR-199a-3p. J Cell Physiol.
234:23736–23749. 2019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Herman M, Randall GW, Spiegel JL,
Maldonado DJ and Simoes S: Endo-lysosomal dysfunction in
neurodegenerative diseases: Opinion on current progress and future
direction in the use of exosomes as biomarkers. Philos Trans R Soc
Lond B Biol Sci. 379:202203872024. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Ma Y, Brocchini S and Williams GR:
Extracellular Vesicle-embedded materials. J Control Release.
361:280–296. 2023. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Canney M, Clark EG and Hiremath S:
Biomarkers in acute kidney injury: On the cusp of a new era? J Clin
Invest. 133:e1714312023. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
Cao JY, Wang B, Tang TT, Wen Y, Li ZL,
Feng ST, Wu M, Liu D, Yin D, Ma KL, et al: Exosomal miR-125b-5p
deriving from mesenchymal stem cells promotes tubular repair by
suppression of p53 in ischemic acute kidney injury. Theranostics.
11:5248–5266. 2021. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
Wu YL, Li HF, Chen HH and Lin H: MicroRNAs
as biomarkers and therapeutic targets in Inflammation- and
Ischemia-Reperfusion-related acute renal injury. Int J Mol Sci.
21:67382020. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
Uccelli A, Moretta L and Pistoia V:
Mesenchymal stem cells in health and disease. Nat Rev Immunol.
8:726–736. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
Li X, Li C, Zhang L, Wu M, Cao K, Jiang F,
Chen D, Li N and Li W: The significance of exosomes in the
development and treatment of hepatocellular carcinoma. Mol Cancer.
19:12020. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22
|
Vicencio JM, Yellon DM, Sivaraman V, Das
D, Boi-Doku C, Arjun S, Zheng Y, Riquelme JA, Kearney J, Sharma V,
et al: Plasma exosomes protect the myocardium from
ischemia-reperfusion injury. J Am Coll Cardiol. 65:1525–1236. 2015.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23
|
Damania A, Jaiman D, Teotia AK and Kumar
A: Mesenchymal stromal Cell-derived Exosome-rich fractionated
secretome confers a hepatoprotective effect in liver injury. Stem
Cell Res Ther. 9:312018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24
|
Huang Y and Yang L: Mesenchymal stem cells
and extracellular vesicles in therapy against kidney diseases. Stem
Cell Res Ther. 12:219–230. 2021. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
25
|
Gao F, Zuo B, Wang Y, Li S, Yang J and Sun
D: Protective function of exosomes from adipose tissue-derived
mesenchymal stem cells in acute kidney injury through SIRT1
pathway. Life Sci. 255:1177192020. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
26
|
Elahi FM, Farwell DG, Nolta JA and
Anderson JD: Preclinical translation of exosomes derived from
mesenchymal stem/stromal cells. Stem Cells. 38:15–21. 2020.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
27
|
Yu Y, Chen M, Guo Q, Shen L, Liu X, Pan J,
Zhang Y, Xu T, Zhang D and Wei G: Human umbilical cord mesenchymal
stem cell exosome-derived miR-874-3p targeting RIPK1/PGAM5
attenuates kidney tubular epithelial cell damage. Cell Mol Biol
Lett. 28:1202023. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
28
|
Zhang W, Zhang J and Huang H: Exosomes
from adipose-derived stem cells inhibit inflammation and oxidative
stress in LPS-acute kidney injury. Exp Cell Res. 420:1133322022.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
29
|
Zhou Y, Xu H, Xu W, Wang B, Wu H, Tao Y,
Zhang B, Wang M, Mao F, Yan Y, et al: Exosomes released by human
umbilical cord mesenchymal stem cells protect against
cisplatin-induced renal oxidative stress and apoptosis in vivo and
in vitro. Stem Cell Res Ther. 4:342013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
30
|
Xing Z, Zhao C, Liu H and Fan Y:
endothelial progenitor Cell-derived extracellular vesicles: A novel
candidate for regenerative medicine and disease treatment. Adv
Healthc Mater. 9:e20002552020. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
31
|
Liu W, Hu C, Zhang B, Li M, Deng F and
Zhao S: Exosomal microRNA-342-5p secreted from adipose-derived
mesenchymal stem cells mitigates acute kidney injury in sepsis mice
by inhibiting TLR9. Biol Proced Online. 25:102023. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
32
|
Li W, Wang W, He X, Liao Z, Aierken A, Hua
J, Wang Y, Lu D and Zhang S: Rapid recovery of male cats with
postrenal acute kidney injury by treating with allogeneic adipose
mesenchymal stem cell-derived extracellular vesicles. Stem Cell Res
Ther. 13:3792022. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
33
|
Li X, Liao J, Su X, Li W, Bi Z, Wang J, Su
Q, Huang H, Wei Y, Gao Y, et al: Human urine-derived stem cells
protect against renal ischemia/reperfusion injury in a rat model
via exosomal miR-146a-5p which targets IRAK1. Theranostics.
10:9561–9578. 2020. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
34
|
Zhang Y, Wang J, Yang B, Qiao R, Li A, Guo
H, Ding J, Li H, Ye H, Wu D, et al: Transfer of MicroRNA-216a-5p
from exosomes secreted by human Urine-derived stem cells reduces
renal Ischemia/reperfusion injury. Front Cell Dev Biol.
8:6105872020. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
35
|
Grange C, Papadimitriou E, Dimuccio V,
Pastorino C, Molina J, O'Kelly R, Niedernhofer LJ, Robbins PD,
Camussi G and Bussolati B: Urinary extracellular vesicles carrying
klotho improve the recovery of renal function in an acute tubular
injury model. Mol Ther. 28:490–502. 2020. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
36
|
Sun Z, Wu J, Bi Q and Wang W: Exosomal
lncRNA TUG1 derived from human urine-derived stem cells attenuates
renal ischemia/reperfusion injury by interacting with SRSF1 to
regulate ASCL4-mediated ferroptosis. Stem Cell Res Ther.
13:2972022. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
37
|
Thapa K, Singh TG and Kaur A: Targeting
ferroptosis in ischemia/reperfusion renal injury. Naunyn
Schmiedebergs Arch Pharmacol. 395:1331–1341. 2022. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
38
|
Zhou Y, Que KT, Zhang Z, Yi ZJ, Zhao PX,
You Y, Gong JP and Liu ZJ: Iron overloaded polarizes macrophage to
proinflammation phenotype through ROS/acetyl-p53 pathway. Cancer
Med. 7:4012–4022. 2018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
39
|
Wallach D, Kang TB and Kovalenko A:
Concepts of tissue injury and cell death in inflammation: A
historical perspective. Nat Rev Immunol. 14:51–59. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
40
|
Liu L, Ye Y, Lin R, Liu T, Wang S, Feng Z,
Wang X, Cao H, Chen X, Miao J, et al: Ferroptosis: A promising
candidate for exosome-mediated regulation in different diseases.
Cell Commun Signal. 22:62024. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
41
|
Dixon SJ, Lemberg KM, Lamprecht MR, Skouta
R, Zaitsev EM, Gleason CE, Patel DN, Bauer AJ, Cantley AM, Yang WS,
et al: Ferroptosis: An iron-dependent form of nonapoptotic cell
death. Cell. 149:1060–1072. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
42
|
Tsvetkov P, Coy S, Petrova B, Dreishpoon
M, Verma A, Abdusamad M, Rossen J, Joesch-Cohen L, Humeidi R,
Spangler RD, et al: Copper induces cell death by targeting
lipoylated TCA cycle proteins. Science. 375:1254–1261. 2022.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
43
|
Wu P, Tang Y, Jin C, Wang M, Li L, Liu Z,
Shi H, Sun Z, Hou X, Chen W, et al: Neutrophil membrane engineered
HuMSC sEVs alleviate cisplatin-induced AKI by enhancing cellular
uptake and targeting. J Nanobiotechnology. 20:3532022. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
44
|
Shi H, Xu X, Zhang B, Xu J, Pan Z, Gong A,
Zhang X, Li R, Sun Y, Yan Y, et al: 3,3′-Diindolylmethane
stimulates exosomal Wnt11 autocrine signaling in human umbilical
cord mesenchymal stem cells to enhance wound healing. Theranostics.
7:1674–1688. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
45
|
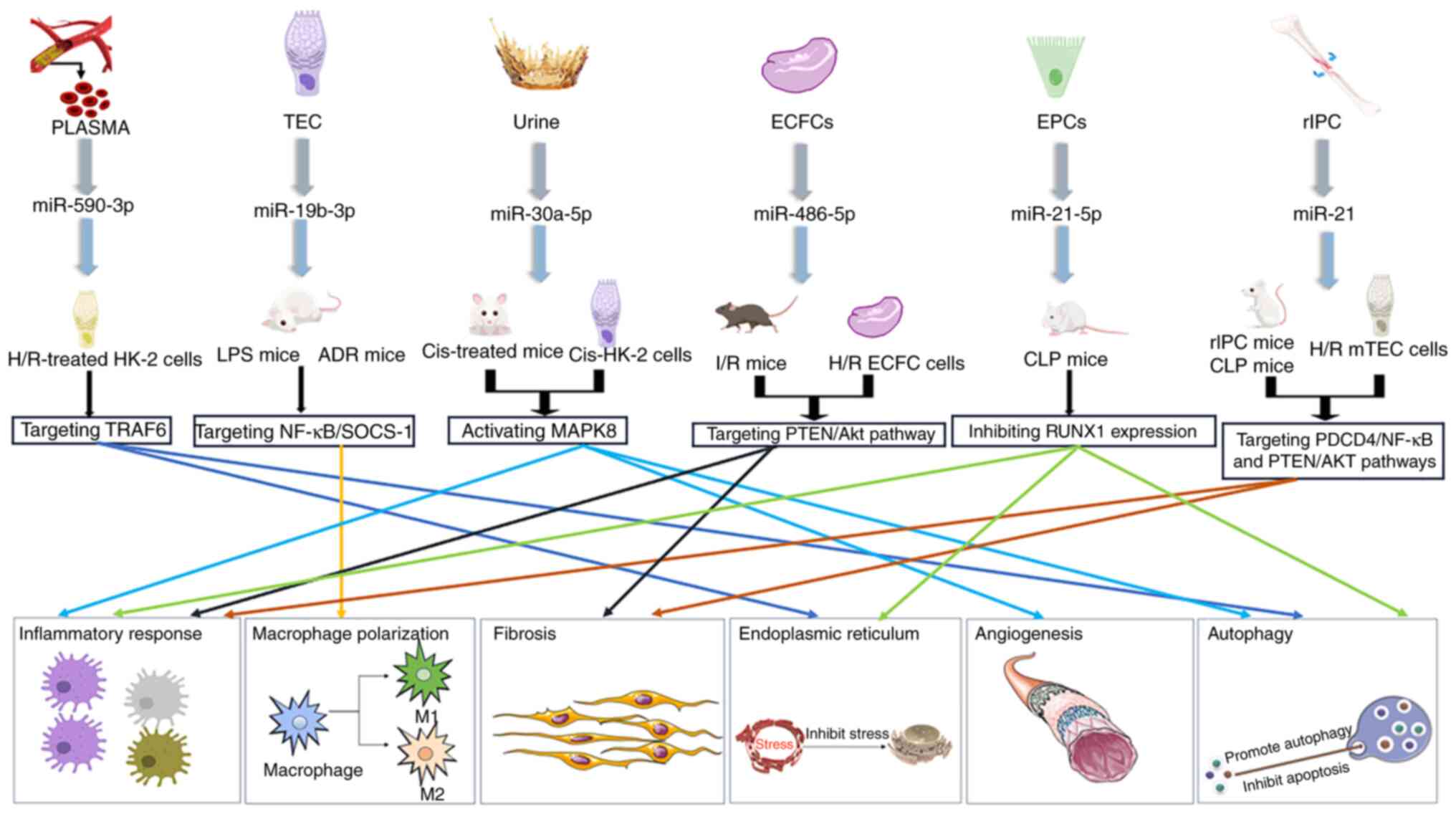
Ma M, Luo Q, Fan L, Li W, Li Q, Meng Y,
Yun C, Wu H, Lu Y, Cui S, et al: The urinary exosomes derived from
premature infants attenuate cisplatin-induced acute kidney injury
in mice via microRNA-30a-5p/mitogen-activated protein kinase 8
(MAPK8). Bioengineered. 13:1650–1665. 2022. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
46
|
Awdishu L, Le A, Amato J, Jani V, Bal S,
Mills RH, Carrillo-Terrazas M, Gonzalez DJ, Tolwani A, Acharya A,
et al: Urinary exosomes identify inflammatory pathways in
vancomycin associated acute kidney injury. Int J Mol Sci.
22:27842021. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
47
|
Vinas JL, Burger D, Zimpelmann J, Haneef
R, Knoll W, Campbell P, Gutsol A, Carter A, Allan DS and Burns KD:
Transfer of microRNA-486-5p from human endothelial colony forming
cell-derived exosomes reduces ischemic kidney injury. Kidney Int.
90:1238–1250. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
48
|
Burger D, Vinas JL, Akbari S, Dehak H,
Knoll W, Gutsol A, Carter A, Touyz RM, Allan DS and Burns KD: Human
endothelial colony-forming cells protect against acute kidney
injury: Role of exosomes. Am J Pathol. 185:2309–2323. 2015.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
49
|
Zhang Y, Huang H, Liu W, Liu S, Wang XY,
Diao ZL, Zhang AH, Guo W, Han X, Dong X and Katilov O: Endothelial
progenitor cells-derived exosomal microRNA-21-5p alleviates
sepsis-induced acute kidney injury by inhibiting RUNX1 expression.
Cell Death Dis. 12:3352021. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
50
|
Keung C, Nguyen TC, Lim R, Gerstenmaier A,
Sievert W and Moore GT: Local fistula injection of allogeneic human
amnion epithelial cells is safe and well tolerated in patients with
refractory complex perianal Crohn's disease: A phase I open label
study with long-term follow up. EBioMedicine. 98:10487992023.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
51
|
Chi D, Chen Y, Xiang C, Yao W, Wang H,
Zheng X, Xu D, Li N, Xie M, Wang S, et al: Human Amnion epithelial
cells and their derived exosomes alleviate Sepsis-associated acute
kidney injury via mitigating endothelial dysfunction. Front Med
(Lausanne). 9:8296062022. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
52
|
Kang X, Chen Y, Xin X, Liu M, Ma Y, Ren Y,
Ji J, Yu Q, Qu L, Wang S, et al: Human amniotic epithelial cells
and their derived exosomes protect against Cisplatin-induced acute
kidney injury without compromising its antitumor activity in mice.
Front Cell Dev Biol. 9:7520532021. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
53
|
Lv LL, Feng Y, Wu M, Wang B, Li ZL, Zhong
X, Wu WJ, Chen J, Ni HF, Tang TT, et al: Exosomal miRNA-19b-3p of
tubular epithelial cells promotes M1 macrophage activation in
kidney injury. Cell Death Differ. 27:210–226. 2020. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
54
|
Guo C, Cui Y, Jiao M, Yao J, Zhao J, Tian
Y, Dong J and Liao L: Crosstalk between proximal tubular epithelial
cells and other interstitial cells in tubulointerstitial fibrosis
after renal injury. Front Endocrinol (Lausanne). 14:12563752023.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
55
|
Chen Y, Zhang C, Du Y, Yang X, Liu M, Yang
W, Lei G and Wang G: Exosomal transfer of microRNA-590-3p between
renal tubular epithelial cells after renal Ischemia-reperfusion
injury regulates autophagy by targeting TRAF6. Chin Med J (Engl).
135:2467–2477. 2022.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
56
|
Ganesh A and Testai FD: Remote ischemic
conditioning for acute ischemic stroke: Does stroke etiology
matter? Stroke. 55:880–882. 2024. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
57
|
Han R, Yang X, Ji X and Zhou B: Remote
ischemic preconditioning prevents high-altitude cerebral edema by
enhancing glucose metabolic reprogramming. CNS Neurosci Ther.
30:e700262024. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
58
|
Torregroza C, Gnaegy L, Raupach A,
Stroethoff M, Feige K, Heinen A, Hollmann MW and Huhn R: Influence
of hyperglycemia and diabetes on cardioprotection by humoral
factors released after remote ischemic preconditioning (RIPC). Int
J Mol Sci. 22:88802021. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
59
|
Mukai A, Suehiro K, Kimura A, Fujimoto Y,
Funao T, Mori T and Nishikawa K: Protective effects of remote
ischemic preconditioning against spinal cord ischemia-reperfusion
injury in rats. J Thorac Cardiovasc Surg. 163:e137–e156. 2022.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
60
|
Wang Y, Liu X, Wang B, Sun H, Ren Y and
Zhang H: Compounding engineered mesenchymal stem cell-derived
exosomes: A potential rescue strategy for retinal degeneration.
Biomed Pharmacother. 173:1164242024. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
61
|
Wang Y, Huo Y, Zhao C, Liu H, Shao Y, Zhu
C, An L, Chen X and Chen Z: Engineered exosomes with enhanced
stability and delivery efficiency for glioblastoma therapy. J
Control Release. 368:170–183. 2024. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
62
|
Donoso-Quezada J, Ayala-Mar S and
Gonzalez-Valdez J: State-of-the-art exosome loading and
functionalization techniques for enhanced therapeutics: A review.
Crit Rev Biotechnol. 40:804–820. 2020. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
63
|
Piffoux M, Volatron J, Cherukula K,
Aubertin K, Wilhelm C, Silva AKA and Gazeau F: Engineering and
loading therapeutic extracellular vesicles for clinical
translation: A data reporting frame for comparability. Adv Drug
Deliv Rev. 178:1139722021. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
64
|
Mousavi SM, Hashemi SA, Gholami A,
Kalashgrani MY, Vijayakameswara Rao N, Omidifar N, Hsiao WW, Lai CW
and Chiang WH: Plasma-enabled smart nanoexosome platform as
emerging immunopathogenesis for clinical viral infection.
Pharmaceutics. 14:10542022. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
65
|
Tran PHL, Wang T, Yin W, Tran TTD, Nguyen
TNG, Lee BJ and Duan W: Aspirin-loaded nanoexosomes as cancer
therapeutics. Int J Pharm. 572:1187862019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
66
|
Ji P, Yang Z, Li H, Wei M, Yang G, Xing H
and Li Q: Smart exosomes with lymph node homing and
immune-amplifying capacities for enhanced immunotherapy of
metastatic breast cancer. Mol Ther Nucleic Acids. 26:987–996. 2021.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
67
|
Latifkar A, Hur YH, Sanchez JC, Cerione RA
and Antonyak MA: New insights into extracellular vesicle biogenesis
and function. J Cell Sci. 132:jcs2224062019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
68
|
Guo M, Ge X, Wang C, Yin Z, Jia Z, Hu T,
Li M, Wang D, Han Z, Wang L, et al: Intranasal delivery of
Gene-edited microglial exosomes improves neurological outcomes
after intracerebral hemorrhage by regulating neuroinflammation.
Brain Sci. 13:6392023. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
69
|
Hyun J, Eom J, Im J, Kim YJ, Seo I, Kim
SW, Im GB, Kim YH, Lee DH, Park HS, et al: Fibroblast function
recovery through rejuvenation effect of nanovesicles extracted from
human adipose-derived stem cells irradiated with red light. J
Control Release. 368:453–465. 2024. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
70
|
Xiong J, Liu Z, Jia L, Sun Y, Guo R, Xi T,
Li Z, Wu M, Jiang H and Li Y: Bioinspired engineering ADSC
nanovesicles thermosensitive hydrogel enhance autophagy of dermal
papilla cells for androgenetic alopecia treatment. Bioact Mater.
36:112–125. 2024.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
71
|
Tan X, Zhang J, Heng Y, Chen L, Wang Y, Wu
S, Liu X, Xu B, Yu Z and Gu R: Locally delivered hydrogels with
controlled release of nanoscale exosomes promote cardiac repair
after myocardial infarction. J Control Release. 368:303–317. 2024.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
72
|
Chen Z, Hu F, Xiang J, Zhou X, Wu B, Fan
B, Tang H, Liu B and Chen L: Mesoporous microneedles enabled
localized controllable delivery of stimulator of interferon gene
agonist nanoexosomes for FLASH radioimmunotherapy against breast
cancer. ACS Appl Mater Interfaces. 16:58180–58190. 2024. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
73
|
Tan A, Rajadas J and Seifalian AM:
Exosomes as nano-theranostic delivery platforms for gene therapy.
Adv Drug Deliv Rev. 65:357–367. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
74
|
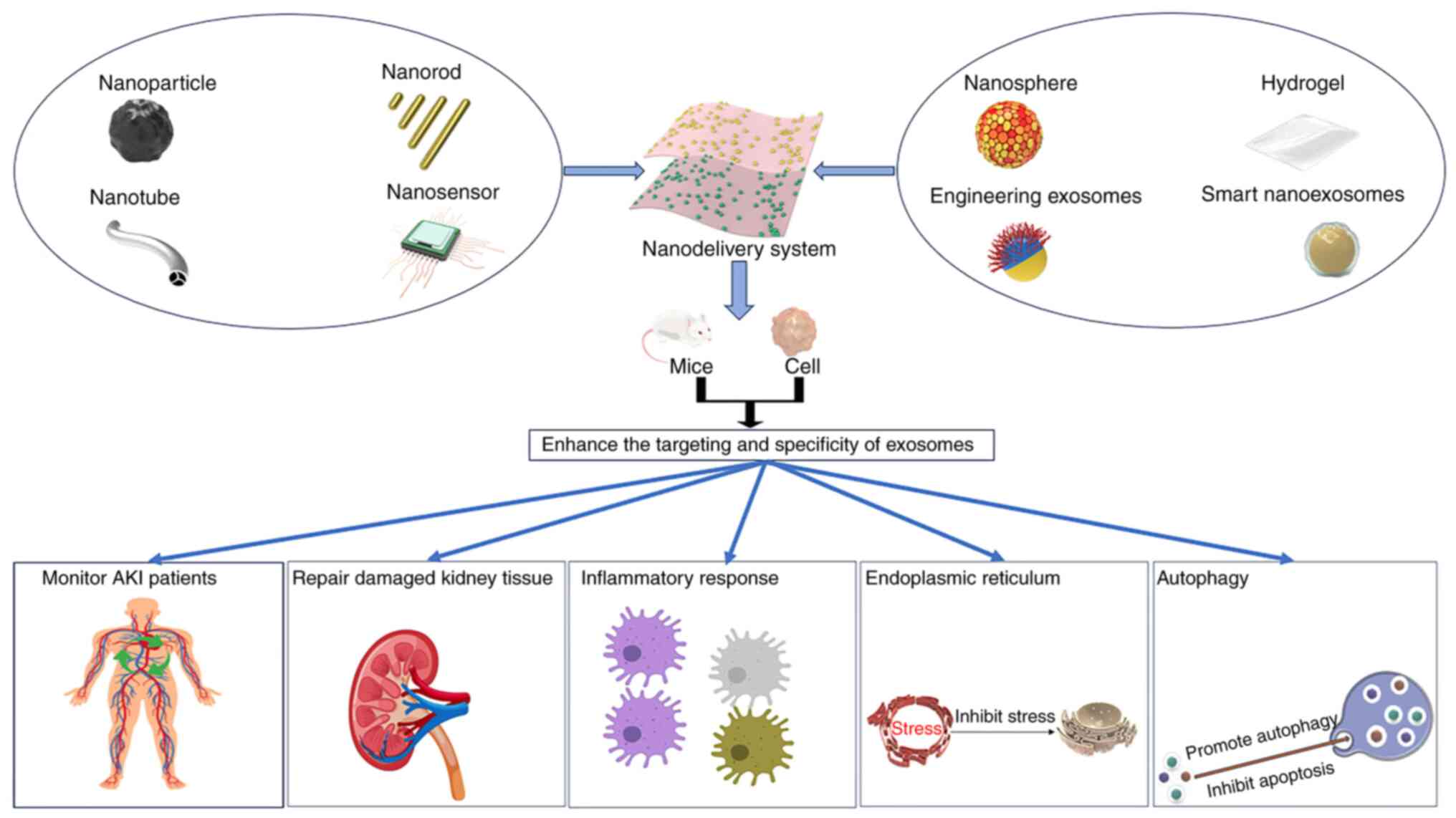
Zhao Y, Pu M, Wang Y, Yu L, Song X and He
Z: Application of nanotechnology in acute kidney injury: From
diagnosis to therapeutic implications. J Control Release.
336:233–251. 2021. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
75
|
Sun T, Jiang D, Rosenkrans ZT, Ehlerding
EB, Ni D, Qi C, Kutyreff CJ, Barnhart TE, Engle JW, Huang P and Cai
W: A Melanin-based natural antioxidant defense nanosystem for
theranostic application in acute kidney injury. Adv Funct Mater.
29:10.1002/adfm.201904833. 2019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
76
|
Mi L, Wang P, Yan J, Qian J, Lu J, Yu J,
Wang Y, Liu H, Zhu M, Wan Y and Liu S: A novel photoelectrochemical
immunosensor by integration of nanobody and TiO2
nanotubes for sensitive detection of serum cystatin C. Anal Chim
Acta. 902:107–114. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
77
|
Rubio-Navarro A, Carril M, Padro D,
Guerrero-Hue M, Tarin C, Samaniego R, Cannata P, Cano A, Villalobos
JM, Sevillano ÁM, et al: CD163-macrophages are involved in
Rhabdomyolysis-induced kidney injury and may be detected by MRI
with targeted Gold-coated iron oxide nanoparticles. Theranostics.
6:896–914. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
78
|
Anwar M, Muhammad F, Akhtar B, Ur Rehman S
and Saleemi MK: Nephroprotective effects of curcumin loaded
chitosan nanoparticles in cypermethrin induced renal toxicity in
rabbits. Environ Sci Pollut Res Int. 27:14771–14779. 2020.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
79
|
Yu H, Jin F, Liu D, Shu G, Wang X, Qi J,
Sun M, Yang P, Jiang S, Ying X and Du Y: ROS-responsive nano-drug
delivery system combining mitochondria-targeting ceria
nanoparticles with atorvastatin for acute kidney injury.
Theranostics. 10:2342–2357. 2020. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
80
|
Qin Y, Rouatbi N, Wang JT, Baker R, Spicer
J, Walters AA and Al-Jamal KT: Plasmid DNA ionisable lipid
nanoparticles as non-inert carriers and potent immune activators
for cancer immunotherapy. J Control Release. 369:251–265. 2024.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
81
|
Koo J, Lim C and Oh KT: Recent advances in
intranasal administration for Brain-targeting delivery: A
comprehensive review of Lipid-based nanoparticles and
Stimuli-responsive gel formulations. Int J Nanomedicine.
19:1767–1807. 2024. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
82
|
Wang L, Wei X, He X, Xiao S, Shi Q, Chen
P, Lee J, Guo X, Liu H and Fan Y: Osteoinductive dental pulp stem
Cell-derived extracellular Vesicle-loaded multifunctional hydrogel
for bone regeneration. ACS Nano. 18:8777–8797. 2024. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
83
|
Peng J, Yang T, Chen S, Deng N, Luo X,
Liao R and Su B: Utilization of hydrogels in mesenchymal stem
cell-based therapy for kidney diseases. Tissue Eng Part B Rev.
30:315–326. 2024. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
84
|
Han DS, Erickson C, Hansen KC,
Kirkbride-Romeo L, He Z, Rodell CB and Soranno DE: Mesenchymal stem
cells delivered locally to Ischemia-reperfused kidneys via
injectable hyaluronic acid hydrogels decrease extracellular matrix
remodeling 1 month after injury in male mice. Cells. 12:17712023.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
85
|
Wang H, Shang Y, Chen X, Wang Z, Zhu D,
Liu Y, Zhang C, Chen P, Wu J, Wu L, et al: Delivery of MSCs with a
hybrid β-Sheet peptide hydrogel consisting IGF-1C domain and D-Form
peptide for acute kidney injury therapy. Int J Nanomedicine.
15:4311–4324. 2020. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
86
|
Xue HY and Wong HL: Targeting megalin to
enhance delivery of anti-clusterin small-interfering RNA
nanomedicine to chemo-treated breast cancer. Eur J Pharm Biopharm.
81:24–32. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
87
|
Oroojalian F, Rezayan AH, Mehrnejad F, Nia
AH, Shier WT, Abnous K and Ramezani M: Efficient megalin targeted
delivery to renal proximal tubular cells mediated by
modified-polymyxin B-polyethylenimine based nano-gene-carriers.
Mater Sci Eng C Mater Biol Appl. 79:770–782. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
88
|
Oroojalian F, Rezayan AH, Shier WT, Abnous
K and Ramezani M: Megalin-targeted enhanced transfection efficiency
in cultured human HK-2 renal tubular proximal cells using
aminoglycoside-carboxyalkyl-polyethylenimine-containing nanoplexes.
Int J Pharm. 523:102–120. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|