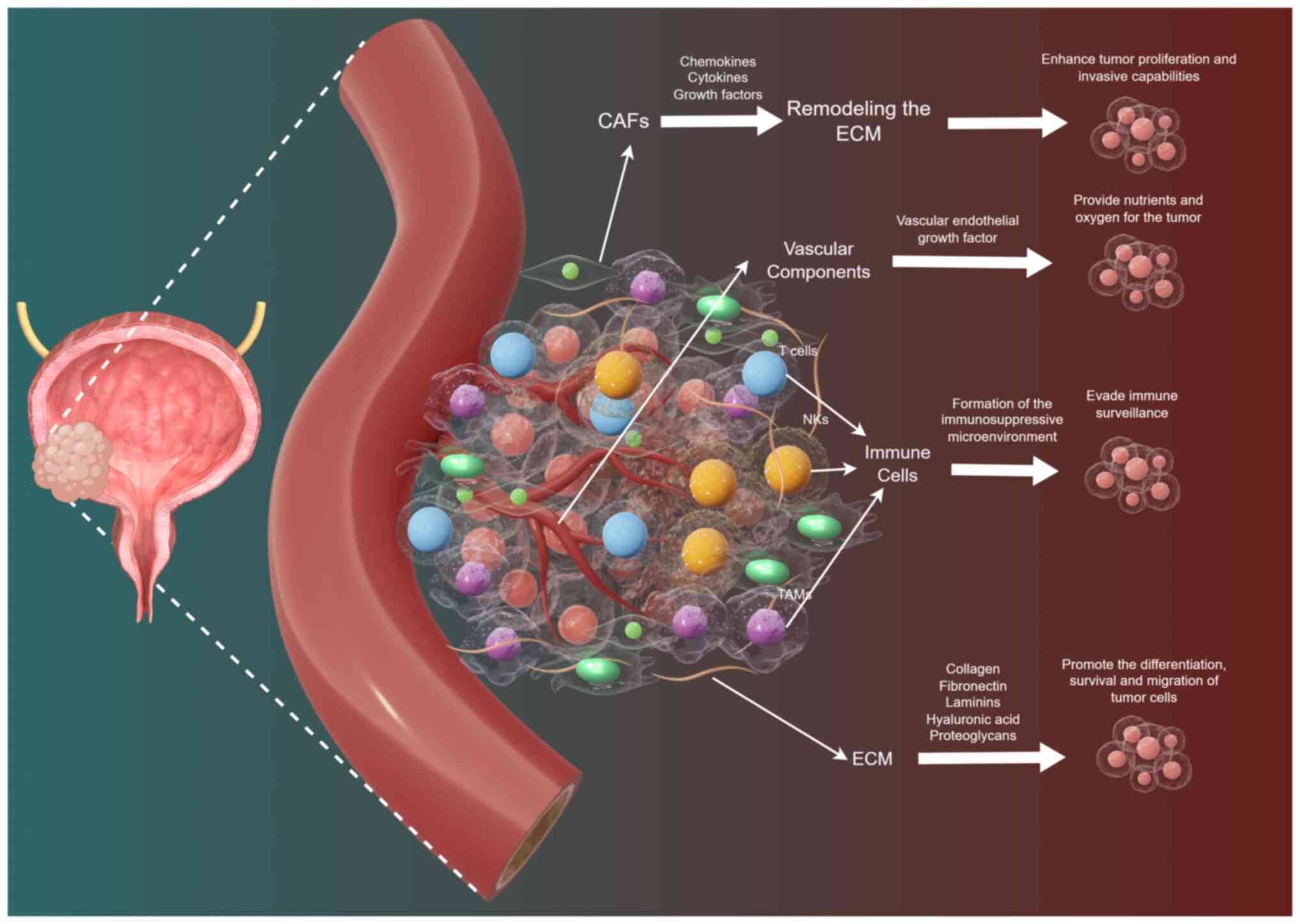
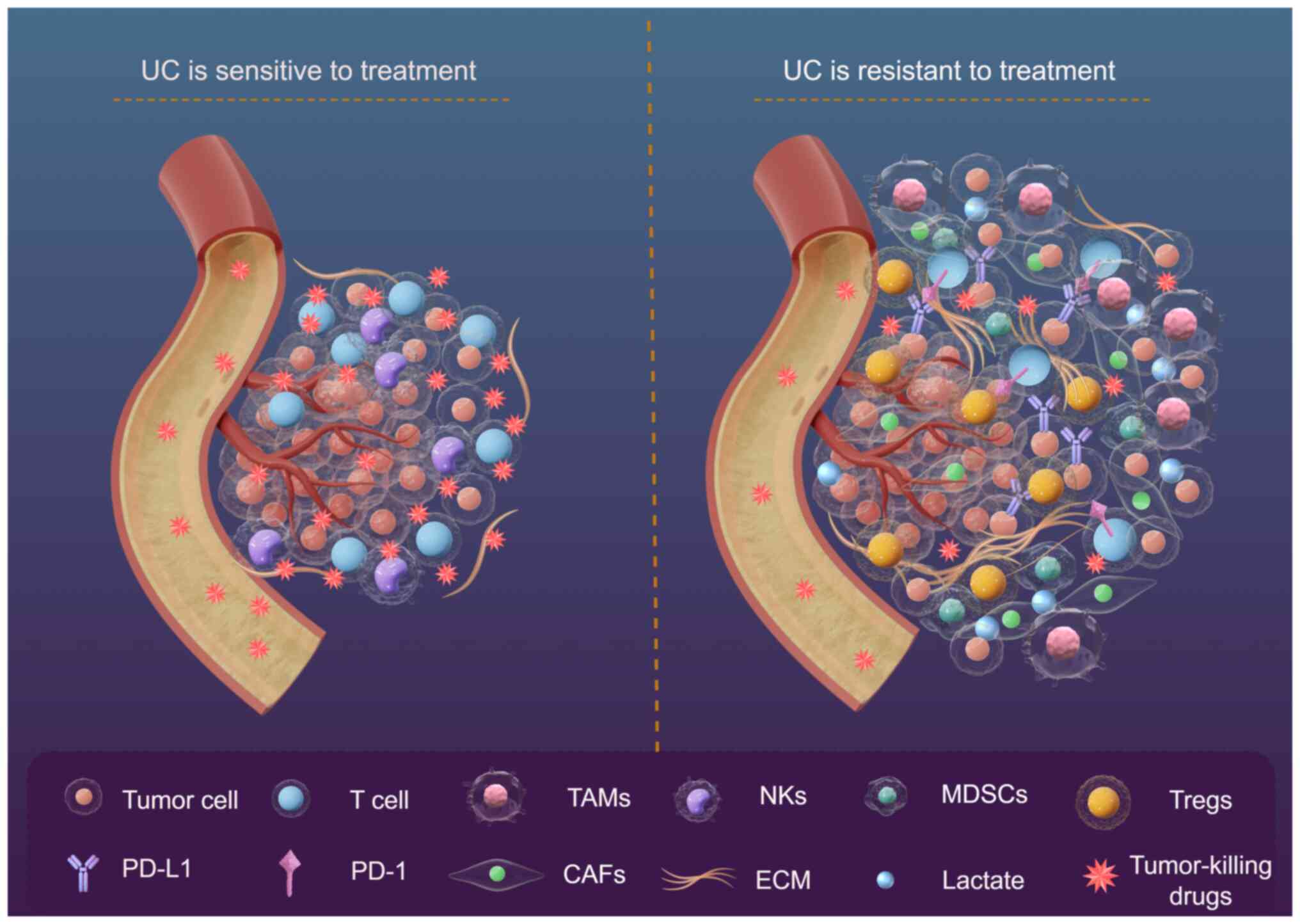
|
1
|
Warrick JI: Clinical significance of
histologic variants of bladder cancer. J Natl Compr Canc Netw.
15:1268–1274. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
Sung H, Ferlay J, Siegel RL, Laversanne M,
Soerjomataram I, Jemal A and Bray F: Global cancer statistics 2020:
GLOBOCAN estimates of incidence and mortality worldwide for 36
cancers in 185 countries. CA Cancer J Clin. 71:209–249.
2021.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
Nadal R, Valderrama BP and Bellmunt J:
Progress in systemic therapy for advanced-stage urothelial
carcinoma. Nat Rev Clin Oncol. 21:8–27. 2024. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
Babjuk M, Burger M, Capoun O, Cohen D,
Compérat EM, Dominguez Escrig JL, Gontero P, Liedberg F,
Masson-Lecomte A, Mostafid AH, et al: European association of
urology guidelines on non-muscle-invasive bladder cancer (Ta, T1,
and carcinoma in situ). Eur Urol. 81:75–94. 2022. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Alfred Witjes J, Max Bruins H, Carrión A,
Cathomas R, Compérat E, Efstathiou JA, Fietkau R, Gakis G, Lorch A,
Martini A, et al: European association of urology guidelines on
muscle-invasive and metastatic bladder cancer: Summary of the 2023
guidelines. Eur Urol. 85:17–31. 2024. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Vlachostergios PJ and Faltas BM: Treatment
resistance in urothelial carcinoma: an evolutionary perspective.
Nat Rev Clin Oncol. 15:495–509. 2018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Goenka A, Khan F, Verma B, Sinha P, Dmello
CC, Jogalekar MP, Gangadaran P and Ahn BC: Tumor microenvironment
signaling and therapeutics in cancer progression. Cancer Commun
(Lond). 43:525–561. 2023. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Xu C, Pei D, Liu Y, Yu Y, Guo J, Liu N and
Kang Z: Identification of a novel tumor microenvironment prognostic
signature for bladder urothelial carcinoma. Front Oncol.
12:8188602022. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Yao Z, Zhang H, Zhang X, Zhang Z, Jie J,
Xie K, Li F and Tan W: Identification of tumor
microenvironment-related signature for predicting prognosis and
immunotherapy response in patients with bladder cancer. Front
Genet. 13:9237682022. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Hu M, Li Y, Lu Y, Wang M, Li Y, Wang C, Li
Q and Zhao H: The regulation of immune checkpoints by the hypoxic
tumor microenvironment. PeerJ. 9:e113062021. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Biffi G and Tuveson DA: Diversity and
biology of cancer-associated fibroblasts. Physiol Rev. 101:147–176.
2021. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Pan Y, Yu Y, Wang X and Zhang T:
Tumor-associated macrophages in tumor immunity. Front Immunol.
11:5830842020. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Li WM, Chan TC, Huang SK, Wu WJ, Ke HL,
Liang PI, Wei YC, Shiue YL and Li CF: Prognostic utility of FBLN2
expression in patients with urothelial carcinoma. Front Oncol.
10:5703402020. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Li L, Liu W, Tang H, Wang X, Liu X, Yu Z,
Gao Y, Wang X and Wei M: Hypoxia-related prognostic model in
bladder urothelial reflects immune cell infiltration. Am J Cancer
Res. 11:5076–5093. 2021.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
He X, Yang Y, Li L, Zhang P, Guo H, Liu N,
Yang X and Xu F: Engineering extracellular matrix to improve drug
delivery for cancer therapy. Drug Discov Today. 25:1727–1734. 2020.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Liang T, Tao T, Wu K, Liu L, Xu W, Zhou D,
Fang H, Ding Q, Huang G and Wu S: Cancer-associated
fibroblast-induced remodeling of tumor microenvironment in
recurrent bladder cancer. Adv Sci (Weinh). 10:e23032302023.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Noeraparast M, Krajina K, Pichler R,
Niedersüß-Beke D, Shariat SF, Grünwald V, Ahyai S and Pichler M:
FGFR3 alterations in bladder cancer: Sensitivity and resistance to
targeted therapies. Cancer Commun (Lond). 44:1189–1208. 2024.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
Lee YC, Lam HM, Rosser C, Theodorescu D,
Parks WC and Chan KS: The dynamic roles of the bladder tumour
microenvironment. Nat Rev Urol. 19:515–533. 2022. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
Caramelo B, Zagorac S, Corral S, Marqués M
and Real FX: Cancer-associated fibroblasts in bladder cancer:
Origin, biology, and therapeutic opportunities. Eur Urol Oncol.
6:366–375. 2023. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
Zhong Q, Shou J, Ying J, Ling Y, Yu Y,
Shen Z, Zhang Y, Li N, Shi Y and Zhou A: High PD-L1 expression on
immune cells, but not on tumor cells, is a favorable prognostic
factor in urothelial carcinoma. Future Oncol. 17:2893–2905. 2021.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
Dong D, Yao Y, Song J, Sun L and Zhang G:
Cancer-associated fibroblasts regulate bladder cancer invasion and
metabolic phenotypes through autophagy. Dis Markers.
2021:66452202021. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22
|
Zheng H, An M, Luo Y, Diao X, Zhong W,
Pang M, Lin Y, Chen J, Li Y, Kong Y, et al: PDGFRα(+)ITGA11(+)
fibroblasts foster early-stage cancer lymphovascular invasion and
lymphatic metastasis via ITGA11-SELE interplay. Cancer Cell.
42:682–700.e12. 2024. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23
|
Yoshida GJ: Regulation of heterogeneous
cancer-associated fibroblasts: The molecular pathology of activated
signaling pathways. J Exp Clin Cancer Res. 39:1122020. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24
|
Rubio C, Munera-Maravilla E, Lodewijk I,
Suarez-Cabrera C, Karaivanova V, Ruiz-Palomares R, Paramio JM and
Dueñas M: Macrophage polarization as a novel weapon in conditioning
tumor microenvironment for bladder cancer: Can we turn demons into
gods? Clin Transl Oncol. 21:391–403. 2019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
25
|
Huang CP, Liu LX and Shyr CR:
Tumor-associated macrophages facilitate bladder cancer progression
by increasing cell growth, migration, invasion and cytokine
expression. Anticancer Res. 40:2715–2724. 2020. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
26
|
Leblond MM, Zdimerova H, Desponds E and
Verdeil G: Tumor-associated macrophages in bladder cancer:
Biological role, impact on therapeutic response and perspectives
for immunotherapy. Cancers (Basel). 13:47122021. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
27
|
Chiang Y, Lu LF, Tsai CL, Tsai YC, Wang
CC, Hsueh FJ, Huang CY, Chen CH, Pu YS and Cheng JC: C-C chemokine
receptor 4 (CCR4)-positive regulatory T cells interact with
tumor-associated macrophages to facilitate metastatic potential
after radiation. Eur J Cancer. 198:1135212024. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
28
|
Jin S, Zeng H, Liu Z, Jin K, Liu C, Yan S,
Yu Y, You R, Zhang H, Chang Y, et al: Stromal tumor-associated
macrophage infiltration predicts poor clinical outcomes in
muscle-invasive bladder cancer patients. Ann Surg Oncol.
29:2495–2503. 2022. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
29
|
Wu C, Duan L, Li H, Liu X, Cai T, Yang Y,
Yin Y, Chang W, Zhong L, Zhang L, et al: PD1(hi) CD200(hi) CD4(+)
exhausted T cell increase immunotherapy resistance and tumour
progression by promoting epithelial-mesenchymal transition in
bladder cancer. Clin Transl Med. 13:e13032023. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
30
|
Salkeni MA and Naing A: Interleukin-10 in
cancer immunotherapy: From bench to bedside. Trends Cancer.
9:716–725. 2023. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
31
|
Chen W: TGF-beta regulation of T cells.
Annu Rev Immunol. 41:483–512. 2023. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
32
|
Li B, Jin K, Liu Z, Su X, Xu Z, Liu G, Xu
J, Liu H, Chang Y, Wang Y, et al: Integrating molecular subtype and
CD8(+) T cells infiltration to predict treatment response and
survival in muscle-invasive bladder cancer. Cancer Immunol
Immunother. 73:662024. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
33
|
Bhardwaj N, Farkas AM, Gul Z and Sfakianos
JP: Harnessing natural killer cell function for genitourinary
cancers. Urol Clin North Am. 47:433–442. 2020. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
34
|
Wong JKM, McCulloch TR, Alim L, Omer N,
Mehdi AM, Tuong ZK, Bonfim-Melo A, Chung E, Nicol A, Simpson F, et
al: TGF-β signalling limits effector function capacity of NK cell
anti-tumour immunity in human bladder cancer. EBioMedicine.
104:1051762024. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
35
|
He C, Wang D, Shukla SK, Hu T, Thakur R,
Fu X, King RJ, Kollala SS, Attri KS, Murthy D, et al: Vitamin B6
competition in the tumor microenvironment hampers antitumor
functions of NK cells. Cancer Discov. 14:176–193. 2024. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
36
|
Yang YJ, Xu XQ, Zhang YC, Hu PC and Yang
WX: Establishment of a prognostic model related to tregs and
natural killer cells infiltration in bladder cancer. World J Clin
Cases. 11:3444–3456. 2023. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
37
|
Wang YA, Ranti D, Bieber C, Galsky M,
Bhardwaj N, Sfakianos JP and Horowitz A: NK cell-targeted
immunotherapies in bladder cancer: Beyond checkpoint inhibitors.
Bladder Cancer. 9:125–139. 2023. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
38
|
Söhngen C, Thomas DJ, Skowron MA, Bremmer
F, Eckstein M, Stefanski A, Driessen MD, Wakileh GA, Stühler K,
Altevogt P, et al: CD24 targeting with NK-CAR immunotherapy in
testis, prostate, renal and (luminal-type) bladder cancer and
identification of direct CD24 interaction partners. FEBS J.
290:4864–4876. 2023. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
39
|
Fus ŁP and Górnicka B: Role of
angiogenesis in urothelial bladder carcinoma. Cent European J Urol.
69:258–263. 2016.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
40
|
Jones A and Crew J: Vascular endothelial
growth factor and its correlation with superficial bladder cancer
recurrence rates and stage progression. Urol Clin North Am.
27:191–197. 2000. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
41
|
Bellmunt J, Hussain M and Dinney CP: Novel
approaches with targeted therapies in bladder cancer. Therapy of
bladder cancer by blockade of the epidermal growth factor receptor
family. Crit Rev Oncol Hematol. 46 (Suppl):S85–S104. 2003.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
42
|
Wu ZS, Ding W, Cai J, Bashir G, Li YQ and
Wu S: Communication of cancer cells and lymphatic vessels in
cancer: Focus on bladder cancer. Onco Targets Ther. 12:8161–8177.
2019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
43
|
Sleeman J, Schmid A and Thiele W: Tumor
lymphatics. Semin Cancer Biol. 19:285–297. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
44
|
Piao XM, Hwang B, Jeong P, Byun YJ, Kang
HW, Seo SP, Kim WT, Lee JY, Ha YS, Lee YS, et al: Collagen type
VI-α1 and 2 repress the proliferation, migration and invasion of
bladder cancer cells. Int J Oncol. 59:372021. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
45
|
Wątroba S, Wiśniowski T, Bryda J and
Kurzepa J: The role of matrix metalloproteinases in pathogenesis of
human bladder cancer. Acta Biochim Pol. 68:547–555. 2021.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
46
|
Dozmorov MG, Kyker KD, Saban R, Knowlton
N, Dozmorov I, Centola MB and Hurst RE: Analysis of the interaction
of extracellular matrix and phenotype of bladder cancer cells. BMC
Cancer. 6:122006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
47
|
Sleeboom JJF, van Tienderen GS,
Schenke-Layland K, van der Laan LJW, Khalil AA and Verstegen MMA:
The extracellular matrix as hallmark of cancer and metastasis: From
biomechanics to therapeutic targets. Sci Transl Med.
16:eadg38402024. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
48
|
Mancini A, Gentile MT, Pentimalli F,
Cortellino S, Grieco M and Giordano A: Multiple aspects of matrix
stiffness in cancer progression. Front Oncol. 14:14066442024.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
49
|
Eckstein M, Matek C, Wagner P, Erber R,
Büttner-Herold M, Wild PJ, Taubert H, Wach S, Sikic D, Wullich B,
et al: Proposal for a novel histological scoring system as a
potential grading approach for muscle-invasive urothelial bladder
cancer correlating with disease aggressiveness and patient
outcomes. Eur Urol Oncol. 7:128–138. 2024. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
50
|
Zhuang J, Shen L, Li M, Sun J, Hao J, Li
J, Zhu Z, Ge S, Zhang D, Guo H, et al: Cancer-associated
fibroblast-derived miR-146a-5p generates a niche that promotes
bladder cancer stemness and chemoresistance. Cancer Res.
83:1611–1627. 2023. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
51
|
Yu Y, Liang Y, Xie F, Zhang Z, Zhang P,
Zhao X, Zhang Z, Liang Z, Li D, Wang L, et al: Tumor-associated
macrophage enhances PD-L1-mediated immune escape of bladder cancer
through PKM2 dimer-STAT3 complex nuclear translocation. Cancer
Lett. 593:2169642024. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
52
|
Kalli M, Poskus MD, Stylianopoulos T and
Zervantonakis IK: Beyond matrix stiffness: Targeting force-induced
cancer drug resistance. Trends Cancer. 9:937–954. 2023. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
53
|
Frerichs LM, Frerichs B, Petzsch P, Köhrer
K, Windolf J, Bittersohl B, Hoffmann MJ and Grotheer V: Tumorigenic
effects of human mesenchymal stromal cells and fibroblasts on
bladder cancer cells. Front Oncol. 13:12281852023. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
54
|
Millet M, Bollmann E, Ringuette Goulet C,
Bernard G, Chabaud S, Huot MÉ, Pouliot F, Bolduc S and Bordeleau F:
Cancer-associated fibroblasts in a 3D engineered tissue model
induce tumor-like matrix stiffening and EMT transition. Cancers
(Basel). 14:38102022. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
55
|
Perez VM, Kearney JF and Yeh JJ: The PDAC
extracellular matrix: A review of the ECM protein composition,
tumor cell interaction, and therapeutic strategies. Front Oncol.
11:7513112021. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
56
|
Jing X, Yang F, Shao C, Wei K, Xie M, Shen
H and Shu Y: Role of hypoxia in cancer therapy by regulating the
tumor microenvironment. Mol Cancer. 18:1572019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
57
|
Ritterson Lew C, Guin S and Theodorescu D:
Targeting glycogen metabolism in bladder cancer. Nat Rev Urol.
12:383–391. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
58
|
Afonso J, Santos LL, Longatto-Filho A and
Baltazar F: Competitive glucose metabolism as a target to boost
bladder cancer immunotherapy. Nat Rev Urol. 17:77–106. 2020.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
59
|
Zhou J, Gu J, Qian Q, Zhang Y, Huang T, Li
X, Liu Z, Shao Q, Liang Y, Qiao L, et al: Lactate supports Treg
function and immune balance via MGAT1 effects on N-glycosylation in
the mitochondria. The Journal of clinical investigation. J Clin
Invest. 134:e1758972024. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
60
|
Afonso J, Santos LL, Miranda-Gonçalves V,
Morais A, Amaro T, Longatto-Filho A and Baltazar F: CD147 and
MCT1-potential partners in bladder cancer aggressiveness and
cisplatin resistance. Mol Carcinog. 54:1451–1466. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
61
|
Abd El-Fattah EE and Selim HM:
Reprograming immune microenvironment modulates CD47 cancer stem
cells in hepatocellular carcinoma. Int Immunopharmacol. 113((Pt
B)): 1094752022. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
62
|
Zhang Z, Yu Y, Zhang Z, Li D, Liang Z,
Wang L, Chen Y, Liang Y and Niu H: Cancer-associated
fibroblasts-derived CXCL12 enhances immune escape of bladder cancer
through inhibiting P62-mediated autophagic degradation of PDL1. J
Exp Clin Cancer Res. 42:3162023. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
63
|
Yang W, Han B, Chen Y and Geng F: SAAL1, a
novel oncogene, is associated with prognosis and immunotherapy in
multiple types of cancer. Aging (Albany NY). 14:6316–6337. 2022.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
64
|
Cheng M, Chen S, Li K, Wang G, Xiong G,
Ling R, Zhang C, Zhang Z, Han H, Chen Z, et al: CD276-dependent
efferocytosis by tumor-associated macrophages promotes immune
evasion in bladder cancer. Nat Commun. 15:28182024. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
65
|
Yang G, Shen W, Zhang Y, Liu M, Zhang L,
Liu Q, Lu HH and Bo J: Accumulation of myeloid-derived suppressor
cells (MDSCs) induced by low levels of IL-6 correlates with poor
prognosis in bladder cancer. Oncotarget. 8:38378–38388. 2017.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
66
|
Yang M, Wang B, Hou W, Zeng H, He W, Zhang
XK, Yan D, Yu H, Huang L, Pei L, et al: NAD(+) metabolism enzyme
NNMT in cancer-associated fibroblasts drives tumor progression and
resistance to immunotherapy by modulating macrophages in urothelial
bladder cancer. J Immunother Cancer. 12:e0092812024. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
67
|
Truskowski K, Amend SR and Pienta KJ:
Dormant cancer cells: Programmed quiescence, senescence, or both?
Cancer Metastasis Rev. 42:37–47. 2023. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
68
|
Deng L, Jin K, Zhou X, Zhang Z, Ge L,
Xiong X, Su X, Jin D, Yuan Q, Zhang C, et al: Blockade of integrin
signaling reduces chemotherapy-induced premature senescence in
collagen cultured bladder cancer cells. Precis Clin Med.
5:pbac0072022. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
69
|
Yao Z, Yang L, Yang X, Liu F, Fu B and
Xiong J: Stimulator of interferon genes mediated immune senescence
reveals the immune microenvironment and prognostic characteristics
of bladder cancer. Heliyon. 10:e288032024. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
70
|
Francescangeli F, De Angelis ML, Rossi R,
Cuccu A, Giuliani A, De Maria R and Zeuner A: Dormancy, stemness,
and therapy resistance: interconnected players in cancer evolution.
Cancer Metastasis Rev. 42:197–215. 2023.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
71
|
Clinton TN, Chen Z, Wise H, Lenis AT,
Chavan S, Donoghue MTA, Almassi N, Chu CE, Dason S, Rao P, et al:
Genomic heterogeneity as a barrier to precision oncology in
urothelial cancer. Cell Rep. 41:1118592022. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
72
|
Lavallee E, Sfakianos JP and Mulholland
DJ: Tumor heterogeneity and consequences for bladder cancer
treatment. Cancers (Basel). 13:52972021. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
73
|
Ma G, Yang X, Liang Y, Wang L, Li D, Chen
Y, Liang Z, Wang Y and Niu H: Precision medicine and bladder cancer
heterogeneity. Bull Cancer. 105:925–931. 2018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
74
|
Chen H, Yang W, Xue X, Li Y, Jin Z and Ji
Z: Integrated analysis revealed an inflammatory cancer-associated
fibroblast-based subtypes with promising implications in predicting
the prognosis and immunotherapeutic response of bladder cancer
patients. Int J Mol Sci. 23:159702022. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
75
|
Qin Y, Zu X, Li Y, Han Y, Tan J, Cai C,
Shen E, Liu P, Deng G, Feng Z, et al: A cancer-associated
fibroblast subtypes-based signature enables the evaluation of
immunotherapy response and prognosis in bladder cancer. iScience.
26:1077222023. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
76
|
Cui C, Zhang H, Yang C, Yin M, Teng X,
Yang M, Kong D, Zhang J, Peng W, Chu Z, et al: Inhibition of JNK
signaling overcomes cancer-associated fibroblast-mediated
immunosuppression and enhances the efficacy of immunotherapy in
bladder cancer. Cancer Res. 84:4199–4213. 2024. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
77
|
Shan G, Zhou X, Gu J, Zhou D, Cheng W, Wu
H, Wang Y, Tang T and Wang X: Downregulated exosomal
microRNA-148b-3p in cancer associated fibroblasts enhance
chemosensitivity of bladder cancer cells by downregulating the
Wnt/beta-catenin pathway and upregulating PTEN. Cell Oncol (Dordr).
44:45–59. 2021. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
78
|
Sun M, Zeng H, Jin K, Liu Z, Hu B, Liu C,
Yan S, Yu Y, You R, Zhang H, et al: Infiltration and polarization
of tumor-associated macrophages predict prognosis and therapeutic
benefit in muscle-invasive bladder cancer. Cancer Immunol
Immunother. 71:1497–1506. 2022. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
79
|
Hu B, Wang Z, Zeng H, Qi Y, Chen Y, Wang
T, Wang J, Chang Y, Bai Q, Xia Y, et al: Blockade of DC-SIGN(+)
tumor-associated macrophages reactivates antitumor immunity and
improves immunotherapy in muscle-invasive bladder cancer. Cancer
Res. 80:1707–1719. 2020. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
80
|
An HW, Hou DY, Yang J, Wang ZQ, Wang MD,
Zheng R, Zhang NY, Hu XJ, Wang ZJ, Wang L, et al: A bispecific
glycopeptide spatiotemporally regulates tumor microenvironment for
inhibiting bladder cancer recurrence. Sci Adv. 9:eabq82252023.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
81
|
Roma-Rodrigues C, Mendes R, Baptista PV
and Fernandes AR: Targeting tumor microenvironment for cancer
therapy. Int J Mol Sci. 20:8402019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
82
|
Necchi A, Ramlau R, Falcón González A,
Chaudhry A, Todenhöfer T, Tahbaz R, Fontana E, Giannatempo P,
Deville JL, Pouessel D, et al: Derazantinib alone and with
atezolizumab in metastatic urothelial carcinoma with activating
FGFR aberrations. JNCI Cancer Spectr. 8:pkae0302024. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
83
|
Wei Y, Wang Y, Liu N, Qi R, Xu Y, Li K,
Feng Y and Shi B: A FAK inhibitor boosts anti-PD1 immunotherapy in
a hepatocellular carcinoma mouse model. Front Pharmacol.
12:8204462022. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
84
|
Zhang B, Li N, Gao J, Zhao Y, Jiang J, Xie
S, Zhang C, Zhang Q, Liu L, Wang Z, et al: Targeting of focal
adhesion kinase enhances the immunogenic cell death of PEGylated
liposome doxorubicin to optimize therapeutic responses of immune
checkpoint blockade. J Exp Clin Cancer Res. 43:512024. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
85
|
de Ruiter BM, van Hattum JW, Lipman D, de
Reijke TM, van Moorselaar RJA, van Gennep EJ, Maartje Piet AH,
Donker M, van der Hulle T, Voortman J, et al: Phase 1 study of
chemoradiotherapy combined with nivolumab ± ipilimumab for the
curative treatment of muscle-invasive bladder cancer. Eur Urol.
82:518–526. 2022. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
86
|
Balar AV, Kamat AM, Kulkarni GS, Uchio EM,
Boormans JL, Roumiguié M, Krieger LEM, Singer EA, Bajorin DF,
Grivas P, et al: Pembrolizumab monotherapy for the treatment of
high-risk non-muscle-invasive bladder cancer unresponsive to BCG
(KEYNOTE-057): An open-label, single-arm, multicentre, phase 2
study. Lancet Oncol. 22:919–930. 2021. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
87
|
Grivas P, Koshkin VS, Chu X, Cole S, Jain
RK, Dreicer R, Cetnar JP, Sundi D, Gartrell BA, Galsky MD, et al:
PrECOG PrE0807: A phase 1b feasibility trial of neoadjuvant
nivolumab without and with lirilumab in patients with
muscle-invasive bladder cancer ineligible for or refusing
cisplatin-based neoadjuvant chemotherapy. Eur Urol Oncol.
7:914–922. 2024. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
88
|
Powles T, Csőszi T, Özgüroğlu M, Matsubara
N, Géczi L, Cheng SY, Fradet Y, Oudard S, Vulsteke C, Morales
Barrera R, et al: Pembrolizumab alone or combined with chemotherapy
versus chemotherapy as first-line therapy for advanced urothelial
carcinoma (KEYNOTE-361): A randomised, open-label, phase 3 trial.
Lancet Oncol. 22:931–945. 2021. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
89
|
Qu YY, Sun Z, Han W, Zou Q, Xing N, Luo H,
Zhang X, He C, Bian XJ, Cai J, et al: Camrelizumab plus famitinib
for advanced or metastatic urothelial carcinoma after
platinum-based therapy: Data from a multicohort phase 2 study. J
Immunother Cancer. 10:e0044272022. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
90
|
Sundahl N, De Wolf K, Rottey S,
Decaestecker K, De Maeseneer D, Meireson A, Goetghebeur E, Fonteyne
V, Verbeke S, De Visschere P, et al: A phase I/II trial of
fixed-dose stereotactic body radiotherapy with sequential or
concurrent pembrolizumab in metastatic urothelial carcinoma:
evaluation of safety and clinical and immunologic response. J
Transl Med. 15:1502017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
91
|
Attalla S, Taifour T and Muller W:
Tailoring therapies to counter the divergent immune landscapes of
breast cancer. Front Cell Dev Biol. 11:11117962023. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
92
|
Hsu MM, Xia Y, Troxel A, Delbeau D,
Francese K, Leis D, Shepherd D and Balar AV: Outcomes with
first-line PD-1/PD-L1 inhibition in advanced urothelial cancer: A
single institution experience. Clin Genitourin Cancer.
18:e209–e216. 2020. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
93
|
Huang J, Zhang L, Wan D, Zhou L, Zheng S,
Lin S and Qiao Y: Extracellular matrix and its therapeutic
potential for cancer treatment. Signal Transduct Target Ther.
6:1532021. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
94
|
Guan Z, Sun Y, Mu L, Jiang Y and Fan J:
Tenascin-C promotes bladder cancer progression and its action
depends on syndecan-4 and involves NF-κB signaling activation. BMC
Cancer. 22:2402022. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
95
|
Yuan Z, Li Y, Zhang S, Wang X, Dou H, Yu
X, Zhang Z, Yang S and Xiao M: Extracellular matrix remodeling in
tumor progression and immune escape: From mechanisms to treatments.
Mol Cancer. 22:482023. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
96
|
Pang X, He X, Qiu Z, Zhang H, Xie R, Liu
Z, Gu Y, Zhao N, Xiang Q and Cui Y: Targeting integrin pathways:
Mechanisms and advances in therapy. Signal Transduct Target Ther.
8:12023. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
97
|
Bergonzini C, Kroese K, Zweemer AJM and
Danen EHJ: Targeting integrins for cancer therapy-disappointments
and opportunities. Front Cell Dev Biol. 10:8638502022. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
98
|
Hou J, Yan D, Liu Y, Huang P and Cui H:
The roles of integrin α5β1 in human cancer. Onco Targets Ther.
13:13329–13344. 2020. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
99
|
Felsenstein KM and Theodorescu D:
Precision medicine for urothelial bladder cancer: Update on tumour
genomics and immunotherapy. Nat Rev Urol. 15:92–111. 2018.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
100
|
Grausenburger R, Herek P, Shariat SF and
Englinger B: Recent contributions of single-cell and spatial
profiling to the understanding of bladder cancer. Curr Opin Urol.
34:236–243. 2024. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
101
|
Zhang Z, Liang Z, Li D, Wang L, Chen Y,
Liang Y, Jiao W and Niu H: Development of a CAFs-related gene
signature to predict survival and drug response in bladder cancer.
Hum Cell. 35:649–664. 2022. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
102
|
Li F, Zheng Z, Chen W, Li D, Zhang H, Zhu
Y, Mo Q, Zhao X, Fan Q, Deng F, et al: Regulation of cisplatin
resistance in bladder cancer by epigenetic mechanisms. Drug Resist
Updat. 68:1009382023. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
103
|
Liu YR, Ortiz-Bonilla CJ and Lee YF:
Extracellular vesicles in bladder cancer: Biomarkers and beyond.
Int J Mol Sci. 19:28222018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
104
|
Meeks JJ, Al-Ahmadie H, Faltas BM, Taylor
JA III, Flaig TW, DeGraff DJ, Christensen E, Woolbright BL,
McConkey DJ and Dyrskjøt L: Genomic heterogeneity in bladder
cancer: Challenges and possible solutions to improve outcomes. Nat
Rev Urol. 17:259–270. 2020. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
105
|
Benjamin DJ and Lyou Y: Advances in
immunotherapy and the TGF-β resistance pathway in metastatic
bladder cancer. Cancers (Basel). 13:57242021. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
106
|
Massari F, Santoni M, Ciccarese C,
Brunelli M, Conti A, Santini D, Montironi R, Cascinu S and Tortora
G: Emerging concepts on drug resistance in bladder cancer:
Implications for future strategies. Crit Rev Oncol Hematol.
96:81–90. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
107
|
Huang L, Xie Q, Deng J and Wei WF: The
role of cancer-associated fibroblasts in bladder cancer
progression. Heliyon. 9:e198022023. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
108
|
Li F, Zhang H, Huang Y, Li D, Zheng Z, Xie
K, Cao C, Wang Q, Zhao X, Huang Z, et al: Single-cell transcriptome
analysis reveals the association between histone lactylation and
cisplatin resistance in bladder cancer. Drug Resist Updat.
73:1010592024. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
109
|
Meng X, Xiao W, Sun J, Li W, Yuan H, Yu T,
Zhang X and Dong W: CircPTK2/PABPC1/SETDB1 axis promotes
EMT-mediated tumor metastasis and gemcitabine resistance in bladder
cancer. Cancer Lett. 554:2160232023. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
110
|
Kang HW, Kim WJ, Choi W and Yun SJ: Tumor
heterogeneity in muscle-invasive bladder cancer. Transl Androl
Urol. 9:2866–2880. 2020. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
111
|
Kim HJ, Ji YR and Lee YM: Crosstalk
between angiogenesis and immune regulation in the tumor
microenvironment. Arch Pharm Res. 45:401–416. 2022. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|