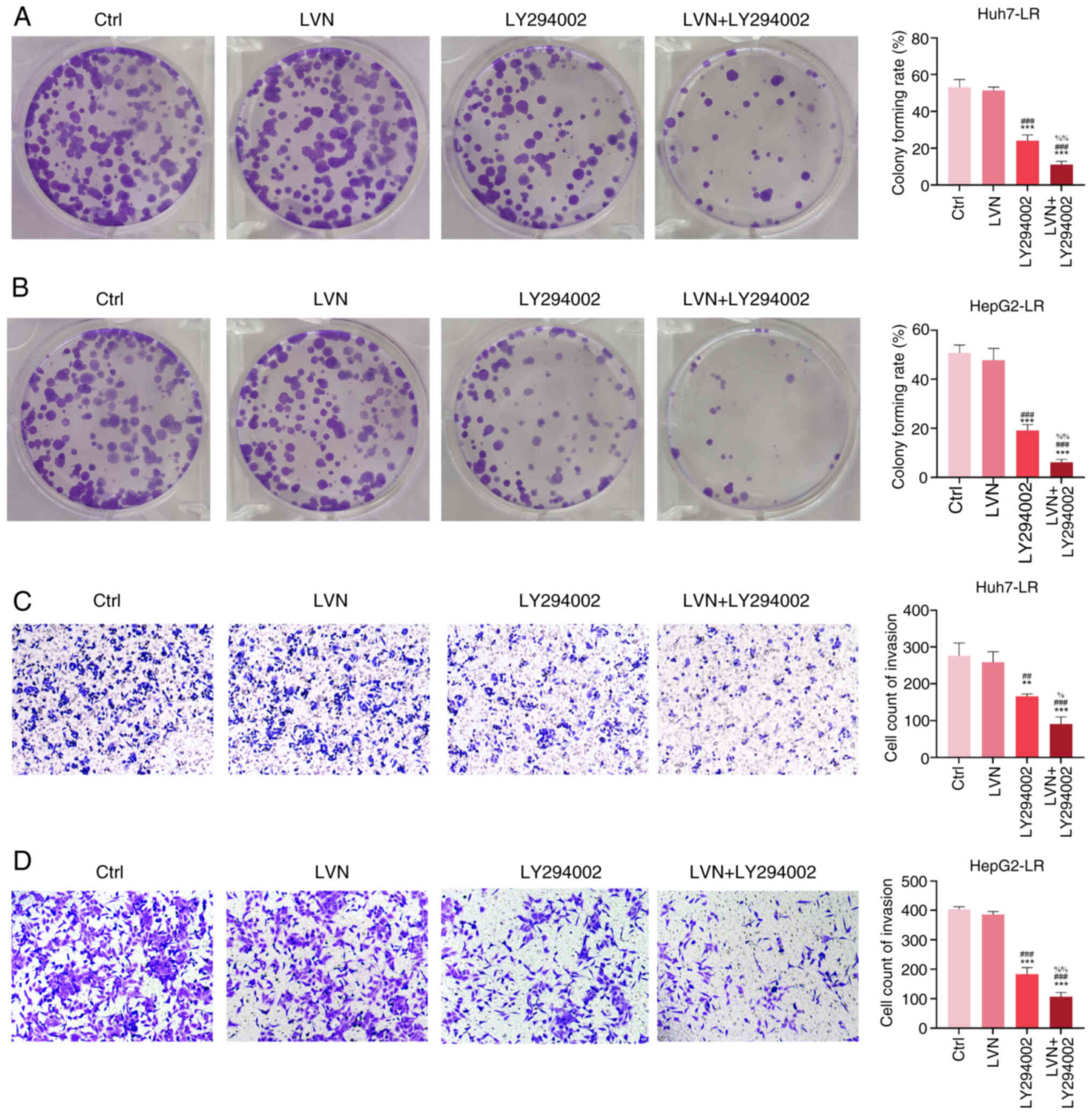
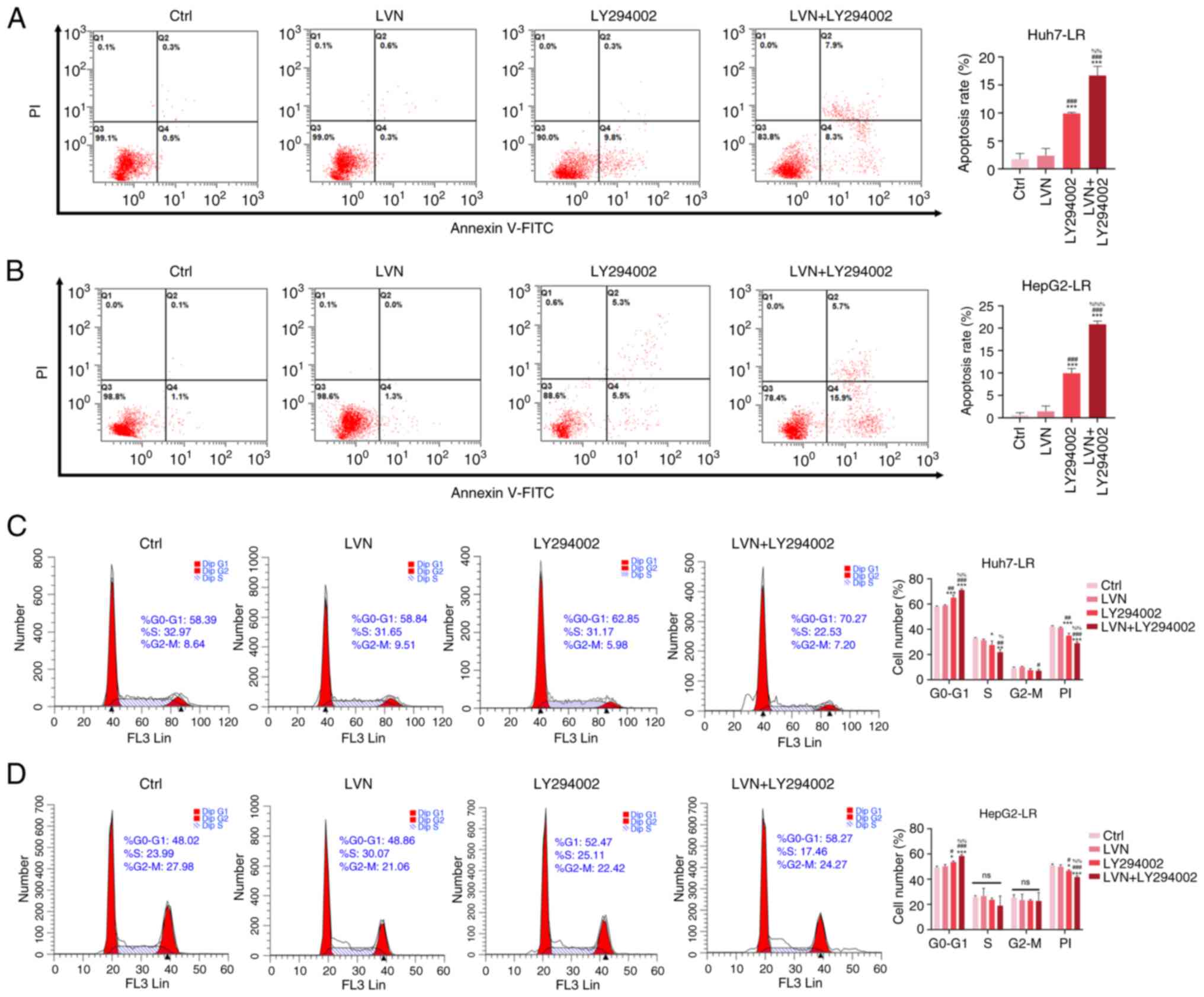
|
1
|
Rumgay H, Arnold M, Ferlay J, Lesi O,
Cabasag CJ, Vignat J, Laversanne M, McGlynn KA and Soerjomataram I:
Global burden of primary liver cancer in 2020 and predictions to
2040. J Hepatol. 77:1598–1606. 2022. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
Singal AG, Kanwal F and Llovet JM: Global
trends in hepatocellular carcinoma epidemiology: Implications for
screening, prevention and therapy. Nat Rev Clin Oncol. 20:864–884.
2023. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
Gordan JD, Kennedy EB, Abou-Alfa GK, Beal
E, Finn RS, Gade TP, Goff L, Gupta S, Guy J, Hoang HT, et al:
Systemic Therapy for advanced hepatocellular carcinoma: ASCO
guideline update. J Clin Oncol. 42:1830–1850. 2024. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
Zhao Y, Zhang YN, Wang KT and Chen L:
Lenvatinib for hepatocellular carcinoma: From preclinical
mechanisms to anti-cancer therapy. Biochim Biophys Acta Rev Cancer.
1874:1883912020. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Kudo M, Finn RS, Qin S, Han KH, Ikeda K,
Piscaglia F, Baron A, Park JW, Han G, Jassem J, et al: Lenvatinib
versus sorafenib in first-line treatment of patients with
unresectable hepatocellular carcinoma: A randomised phase 3
non-inferiority trial. Lancet. 391:1163–1173. 2018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Hiraoka A, Kumada T, Kariyama K, Takaguchi
K, Itobayashi E, Shimada N, Tajiri K, Tsuji K, Ishikawa T, Ochi H,
et al: Therapeutic potential of lenvatinib for unresectable
hepatocellular carcinoma in clinical practice: Multicenter
analysis. Hepatol Res. 49:111–117. 2019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Hu B, Zou T, Qin W, Shen X, Su Y, Li J,
Chen Y, Zhang Z, Sun H, Zheng Y, et al: Inhibition of EGFR
overcomes acquired lenvatinib resistance driven by STAT3-ABCB1
signaling in hepatocellular carcinoma. Cancer Res. 82:3845–3857.
2022. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Wang J, Yu H, Dong W, Zhang C, Hu M, Ma W,
Jiang X, Li H, Yang P and Xiang D: N6-methyladenosine-mediated
up-regulation of FZD10 regulates liver cancer stem cells'
properties and lenvatinib resistance through WNT/β-catenin and
Hippo signaling pathways. Gastroenterology. 164:990–1005. 2023.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Fu R, Jiang S, Li J, Chen H and Zhang X:
Activation of the HGF/c-MET axis promotes lenvatinib resistance in
hepatocellular carcinoma cells with high c-MET expression. Med
Oncol. 37:242020. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Qin Y, Han S, Yu Y, Qi D, Ran M, Yang M,
Liu Y and Li Y, Lu L, Liu Y and Li Y: Lenvatinib in hepatocellular
carcinoma: Resistance mechanisms and strategies for improved
efficacy. Liver Int. 44:1808–1831. 2024. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Liao ZH, Zhu HQ, Chen YY, Chen RL, Fu LX,
Li L, Zhou H, Zhou JL and Liang G: The epigallocatechin gallate
derivative Y6 inhibits human hepatocellular carcinoma by
inhibiting angiogenesis in MAPK/ERK1/2 and PI3K/AKT/HIF-1α/VEGF
dependent pathways. J Ethnopharmacol. 259:1128522020. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Liang H, Yin G, Shi G, Liu Z, Liu X and Li
J: Echinacoside regulates PI3K/AKT/HIF-1α/VEGF cross signaling axis
in proliferation and apoptosis of breast cancer. Anal Biochem.
684:1153602024. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Dong S, Liang S, Cheng Z, Zhang X, Luo L,
Li L, Zhang W, Li S, Xu Q, Zhong M, et al: ROS/PI3K/Akt and
Wnt/β-catenin signalings activate HIF-1α-induced metabolic
reprogramming to impart 5-fluorouracil resistance in colorectal
cancer. J Exp Clin Cancer Res. 41:152022. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Tian Y, Zhao L, Gui Z, Liu S, Liu C, Yu T
and Zhang L: PI3K/AKT signaling activates HIF1α to modulate the
biological effects of invasive breast cancer with
microcalcification. NPJ Breast Cancer. 9:932023. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Koppenol WH, Bounds PL and Dang CV: Otto
Warburg's contributions to current concepts of cancer metabolism.
Nat Rev Cancer. 11:325–337. 2011. View
Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Li S, Dai W, Mo W, Li J, Feng J, Wu L, Liu
T, Yu Q, Xu S, Wang W, et al: By inhibiting PFKFB3, aspirin
overcomes sorafenib resistance in hepatocellular carcinoma. Int J
Cancer. 141:2571–2584. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Feng J, Dai W, Mao Y, Wu L, Li J, Chen K,
Yu Q, Kong R, Li S, Zhang J, et al: Simvastatin re-sensitizes
hepatocellular carcinoma cells to sorafenib by inhibiting
HIF-1α/PPAR-γ/PKM2-mediated glycolysis. J Exp Clin Cancer Res.
39:242020. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
Wang S, Zhou L, Ji N, Sun C, Sun L, Sun J,
Du Y, Zhang N, Li Y, Liu W and Lu W: Targeting ACYP1-mediated
glycolysis reverses lenvatinib resistance and restricts
hepatocellular carcinoma progression. Drug Resist Updat.
69:1009762023. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
Yeh YH, Hsiao HF, Yeh YC, Chen TW and Li
TK: Inflammatory interferon activates HIF-1α-mediated
epithelial-to-mesenchymal transition via PI3K/AKT/mTOR pathway. J
Exp Clin Cancer Res. 37:702018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
Liao Y, Luo Z, Lin Y, Chen H, Chen T, Xu
L, Orgurek S, Berry K, Dzieciatkowska M, Reisz JA, et al: PRMT3
drives glioblastoma progression by enhancing HIF1A and glycolytic
metabolism. Cell Death Dis. 13:9432022. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
Feng J, Li J, Wu L, Yu Q, Ji J, Wu J, Dai
W and Guo C: Emerging roles and the regulation of aerobic
glycolysis in hepatocellular carcinoma. J Exp Clin Cancer Res.
39:1262020. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22
|
Gao T, Zhang X, Zhao J, Zhou F, Wang Y,
Zhao Z, Xing J, Chen B, Li J and Liu S: SIK2 promotes reprogramming
of glucose metabolism through PI3K/AKT/HIF-1α pathway and
Drp1-mediated mitochondrial fission in ovarian cancer. Cancer Lett.
469:89–101. 2020. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23
|
Woo YM, Shin Y, Lee EJ, Lee S, Jeong SH,
Kong HK, Park EY, Kim HK, Han J, Chang M and Park JH: Inhibition of
aerobic glycolysis represses Akt/mTOR/HIF-1α axis and restores
tamoxifen sensitivity in antiestrogen-resistant breast cancer
cells. PLoS One. 10:e01322852015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24
|
Wei J and Wu J, Xu W, Nie H, Zhou R, Wang
R, Liu Y, Tang G and Wu J: Salvianolic acid B inhibits glycolysis
in oral squamous cell carcinoma via targeting PI3K/AKT/HIF-1α
signaling pathway. Cell Death Dis. 9:5992018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
25
|
Wang J, Shi J, Mi L, Li N, Han X, Zhao M,
Duan X, Han G, Hou J and Yin F: Identification and validation of a
lenvatinib resistance-related prognostic signature in HCC, in which
PFKFB4 contributes to tumor progression and lenvatinib resistance.
BMC Gastroenterol. 25:2872025. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
26
|
Livak KJ and Schmittgen TD: Analysis of
relative gene expression data using real-time quantitative PCR and
the 2(−Delta Delta C(T)) method. Methods. 25:402–408. 2001.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
27
|
Gonçalves AC, Richiardone E, Jorge J,
Polónia B, Xavier CPR, Salaroglio IC, Riganti C, Vasconcelos MH,
Corbet C and Sarmento-Ribeiro AB: Impact of cancer metabolism on
therapy resistance-clinical implications. Drug Resist Updat.
59:1007972021. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
28
|
Wang S, Cheng H, Li M, Gao D, Wu H, Zhang
S, Huang Y and Guo K: BNIP3-mediated mitophagy boosts the
competitive growth of Lenvatinib-resistant cells via energy
metabolism reprogramming in HCC. Cell Death Dis. 15:4842024.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
29
|
Shan Q, Yin L, Zhan Q, Yu J, Pan S, Zhuo
J, Zhou W, Bao J, Zhang L, Hong J, et al: The p-MYH9/USP22/HIF-1α
axis promotes lenvatinib resistance and cancer stemness in
hepatocellular carcinoma. Signal Transduct Target Ther. 9:2492024.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
30
|
Mazurakova A, Koklesova L, Csizmár SH,
Samec M, Brockmueller A, Šudomová M, Biringer K, Kudela E, Pec M,
Samuel SM, et al: Significance of flavonoids targeting
PI3K/Akt/HIF-1α signaling pathway in therapy-resistant cancer
cells-a potential contribution to the predictive, preventive, and
personalized medicine. J Adv Res. 55:103–118. 2024. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
31
|
Lee S, Choi EJ, Cho EJ, Lee YB, Lee JH, Yu
SJ, Yoon JH and Kim YJ: Inhibition of PI3K/Akt signaling suppresses
epithelial-to-mesenchymal transition in hepatocellular carcinoma
through the Snail/GSK-3/beta-catenin pathway. Clin Mol Hepatol.
26:529–539. 2020. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
32
|
Vogel A, Qin S, Kudo M, Su Y, Hudgens S,
Yamashita T, Yoon JH, Fartoux L, Simon K, López C, et al:
Lenvatinib versus sorafenib for first-line treatment of
unresectable hepatocellular carcinoma: Patient-reported outcomes
from a randomised, open-label, non-inferiority, phase 3 trial.
Lancet Gastroenterol Hepatol. 6:649–658. 2021. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
33
|
Rimini M, Rimassa L, Ueshima K, Burgio V,
Shigeo S, Tada T, Suda G, Yoo C, Cheon J, Pinato DJ, et al:
Atezolizumab plus bevacizumab versus lenvatinib or sorafenib in
non-viral unresectable hepatocellular carcinoma: An international
propensity score matching analysis. ESMO Open. 7:1005912022.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
34
|
He Y, Sun MM, Zhang GG, Yang J, Chen KS,
Xu WW and Li B: Targeting PI3K/Akt signal transduction for cancer
therapy. Signal Transduct Target Ther. 6:4252021. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
35
|
Ren F, Wu K, Yang Y, Yang Y, Wang Y and Li
J: Dandelion polysaccharide exerts anti-angiogenesis effect on
hepatocellular carcinoma by regulating VEGF/HIF-1α expression.
Front Pharmacol. 11:4602020. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
36
|
Liu S, Ai Z, Hu Y, Ren G, Zhang J, Tang P,
Zou H, Li X and Wang Y, Nan B and Wang Y: Ginseng glucosyl
oleanolate inhibit cervical cancer cell proliferation and
angiogenesis via PI3K/AKT/HIF-1α pathway. NPJ Sci Food. 8:1052024.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
37
|
Zhou P, Zheng ZH, Wan T, Wu J, Liao CW and
Sun XJ: Vitexin inhibits gastric cancer growth and metastasis
through HMGB1-mediated Inactivation of the PI3K/AKT/mTOR/HIF-1α
signaling pathway. J Gastric Cancer. 21:439–456. 2021. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
38
|
Liu X, Liu L, Chen K, Sun L, Li W and
Zhang S: Huaier shows anti-cancer activities by inhibition of cell
growth, migration and energy metabolism in lung cancer through
PI3K/AKT/HIF-1α pathway. J Cell Mol Med. 25:2228–2237. 2021.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
39
|
Zhao J, Lin E, Cai C, Zhang M, Li D, Cai
S, Zeng G, Yin Z, Wang B, Li P, et al: Combined treatment of
tanshinone i and epirubicin revealed enhanced inhibition of
hepatocellular carcinoma by targeting PI3K/AKT/HIF-1α. Drug Des
Devel Ther. 16:3197–3213. 2022. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
40
|
Zeng Q, Nie X, Li L, Liu HF, Peng YY, Zhou
WT, Hu XJ, Xu XY and Chen XL: Salidroside promotes sensitization to
doxorubicin in human cancer cells by affecting the PI3K/Akt/HIF
signal pathway and inhibiting the expression of
tumor-resistance-related proteins. J Nat Prod. 85:196–204. 2022.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
41
|
Yan S, Chen L, Zhuang H, Yang H, Yang Y,
Zhang N and Liu R: HDAC inhibition sensitize hepatocellular
carcinoma to lenvatinib via suppressing AKT activation. Int J Biol
Sci. 20:3046–3060. 2024. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
42
|
Hou W, Bridgeman B, Malnassy G, Ding X,
Cotler SJ, Dhanarajan A and Qiu W: Integrin subunit beta 8
contributes to lenvatinib resistance in HCC. Hepatol Commun.
6:1786–1802. 2022. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
43
|
Sun S, Guo C, Gao T, Ma D, Su X, Pang Q
and Zhang R: Hypoxia Enhances Glioma Resistance to
Sulfasalazine-Induced Ferroptosis by Upregulating SLC7A11 via
PI3K/AKT/HIF-1 α axis. Oxid Med Cell Longev. 2022:78624302022.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
44
|
He X, Hikiba Y, Suzuki Y, Nakamori Y,
Kanemaru Y, Sugimori M, Sato T, Nozaki A, Chuma M and Maeda S: EGFR
inhibition reverses resistance to lenvatinib in hepatocellular
carcinoma cells. Sci Rep. 12:80072022. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
45
|
Vander Heiden MG, Cantley LC and Thompson
CB: Understanding the Warburg effect: The metabolic requirements of
cell proliferation. Science. 324:1029–1033. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
46
|
Xu F, Huang M, Chen Q, Niu Y, Hu Y, Hu P,
Chen D, He C, Huang K, Zeng Z, et al: LncRNA HIF1A-AS1 promotes
gemcitabine resistance of pancreatic cancer by enhancing glycolysis
through modulating the AKT/YB1/HIF1α pathway. Cancer Res.
81:5678–5691. 2021. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
47
|
Wang Z, Wu L, Zhou Y, Chen Z, Zhang T, Wei
H and Wang Z: Protein and metabolic profiles of tyrosine kinase
inhibitors co-resistant liver cancer cells. Front Pharmacol.
15:13942412024. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
48
|
Hoxhaj G and Manning BD: The PI3K-AKT
network at the interface of oncogenic signalling and cancer
metabolism. Nat Rev Cancer. 20:74–88. 2020. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
49
|
Sun Y, Liu W, Zhao Q, Zhang R, Wang J, Pan
P, Shang H, Liu C and Wang C: Down-regulating the expression of
miRNA-21 inhibits the glucose metabolism of A549/DDP cells and
promotes cell death through the PI3K/AKT/mTOR/HIF-1α pathway. Front
Oncol. 11:6535962021. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
50
|
Sun LT, Zhang LY, Shan FY, Shen MH and
Ruan SM: Jiedu Sangen decoction inhibits chemoresistance to
5-fluorouracil of colorectal cancer cells by suppressing glycolysis
via PI3K/AKT/HIF-1α signaling pathway. Chin J Nat Med. 19:143–152.
2021.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
51
|
Shi T, Ma Y, Cao L, Zhan S, Xu Y, Fu F,
Liu C, Zhang G, Wang Z, Wang R, et al: B7-H3 promotes aerobic
glycolysis and chemoresistance in colorectal cancer cells by
regulating HK2. Cell Death Dis. 10:3082019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
52
|
Åbacka H, Hansen JS, Huang P, Venskutonytė
R, Hyrenius-Wittsten A, Poli G, Tuccinardi T, Granchi C, Minutolo
F, Hagström-Andersson AK and Lindkvist-Petersson K: Targeting GLUT1
in acute myeloid leukemia to overcome cytarabine resistance.
Haematologica. 106:1163–1166. 2021. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
53
|
Martin SP, Fako V, Dang H, Dominguez DA,
Khatib S, Ma L, Wang H, Zheng W and Wang XW: PKM2 inhibition may
reverse therapeutic resistance to transarterial chemoembolization
in hepatocellular carcinoma. J Exp Clin Cancer Res. 39:992020.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
54
|
Li F, Zhang H, Huang Y, Li D, Zheng Z, Xie
K, Cao C, Wang Q, Zhao X, Huang Z, et al: Single-cell transcriptome
analysis reveals the association between histone lactylation and
cisplatin resistance in bladder cancer. Drug Resist Updat.
73:1010592024. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
55
|
Chen H, Li Y, Li H, Chen X, Fu H, Mao D,
Chen W, Lan L, Wang C, Hu K, et al: NBS1 lactylation is required
for efficient DNA repair and chemotherapy resistance. Nature.
631:663–669. 2024. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
56
|
Lu Y, Zhu J, Zhang Y, Li W, Xiong Y, Fan
Y, Wu Y, Zhao J, Shang C, Liang H and Zhang W: Lactylation-driven
IGF2BP3-mediated serine metabolism reprogramming and RNA
m6A-modification promotes lenvatinib resistance in HCC. Adv Sci
(Weinh). 11:e24013992024. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
57
|
Dong R, Fei Y, He Y, Gao P, Zhang B, Zhu
M, Wang Z, Wu L, Wu S, Wang X, et al: Lactylation-driven HECTD2
limits the response of hepatocellular carcinoma to lenvatinib. Adv
Sci (Weinh). 12:e24125592025. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
58
|
Li F, Si W, Xia L, Yin D, Wei T, Tao M,
Cui X, Yang J, Hong T and Wei R: Positive feedback regulation
between glycolysis and histone lactylation drives oncogenesis in
pancreatic ductal adenocarcinoma. Mol Cancer. 23:902024. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
59
|
Wei S, Zhang J, Zhao R, Shi R, An L, Yu Z,
Zhang Q, Zhang J, Yao Y, Li H and Wang H: Histone lactylation
promotes malignant progression by facilitating USP39 expression to
target PI3K/AKT/HIF-1α signal pathway in endometrial carcinoma.
Cell Death Discov. 10:1212024. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|