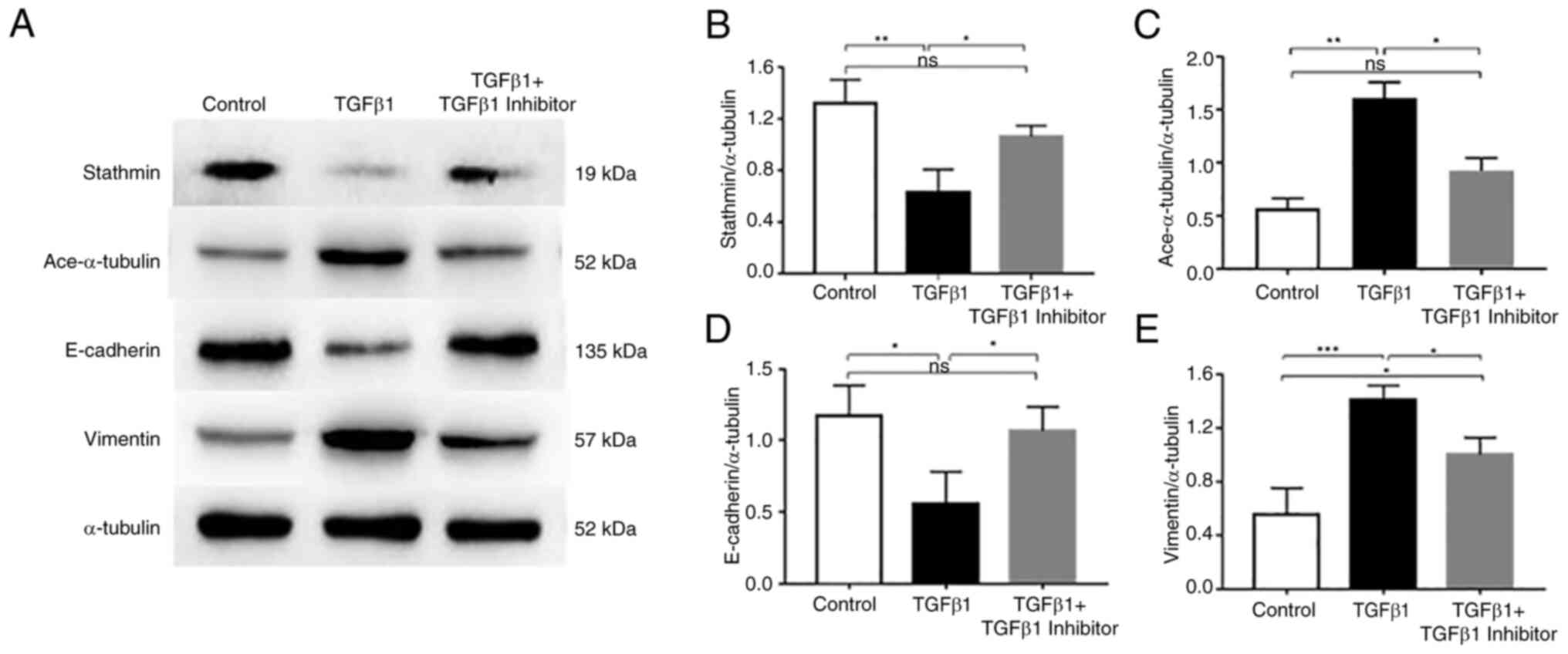
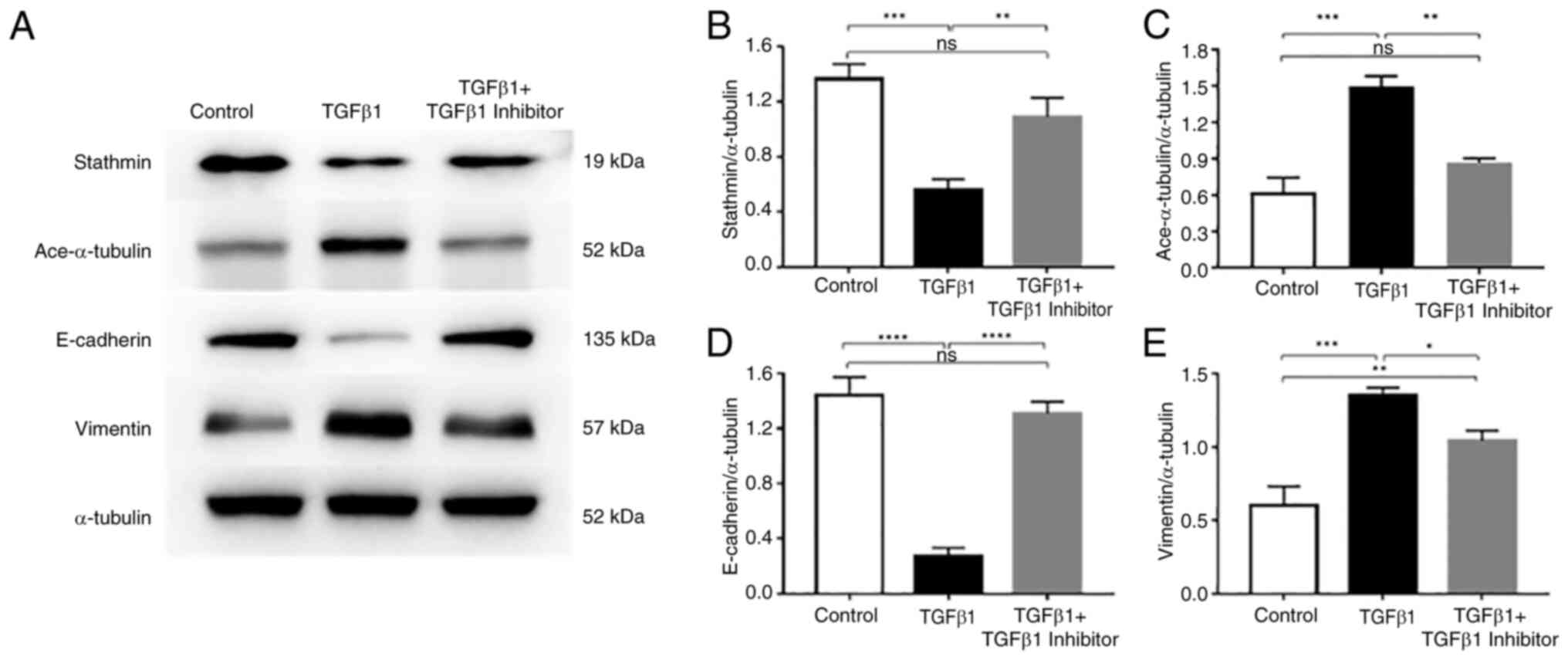
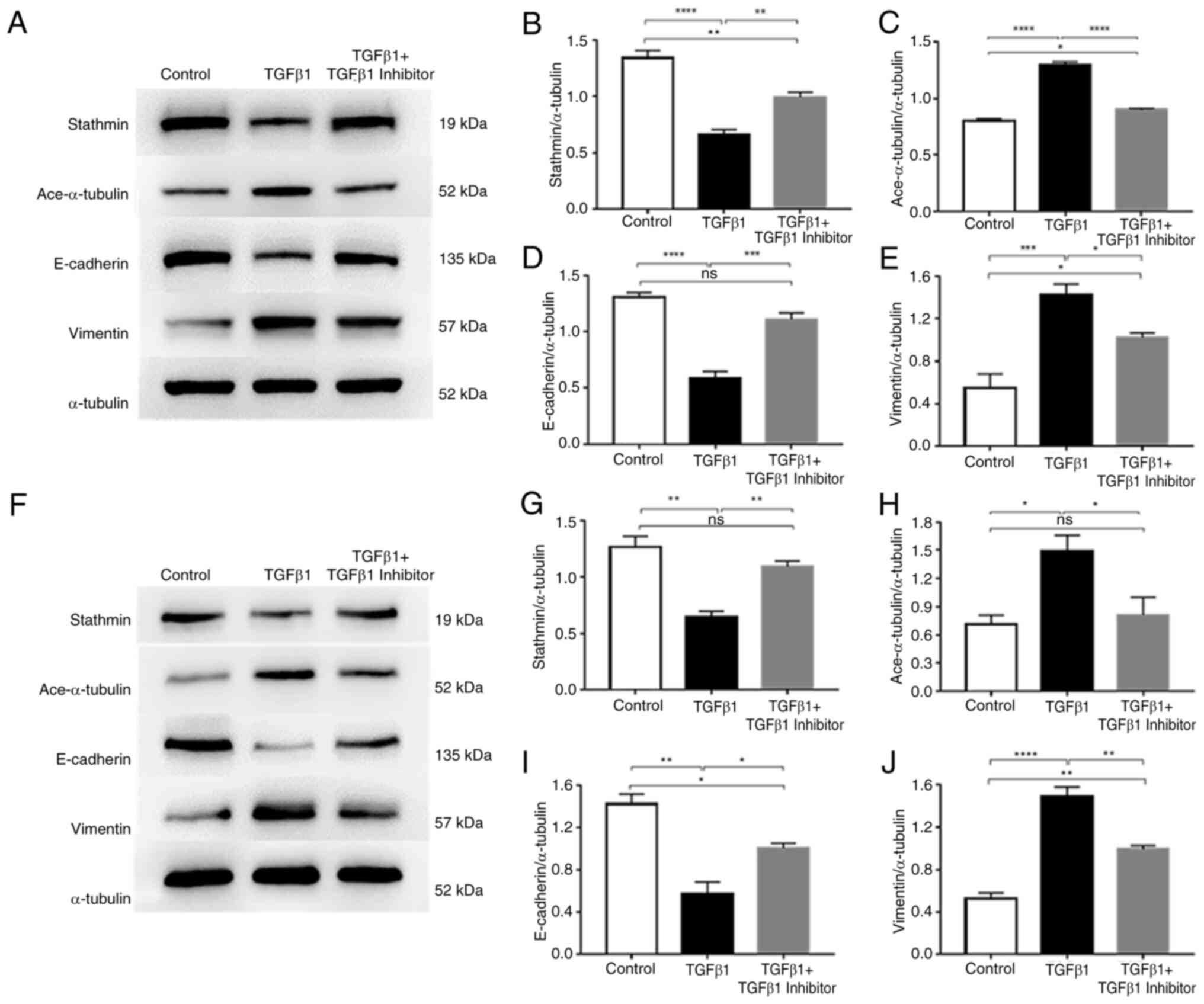
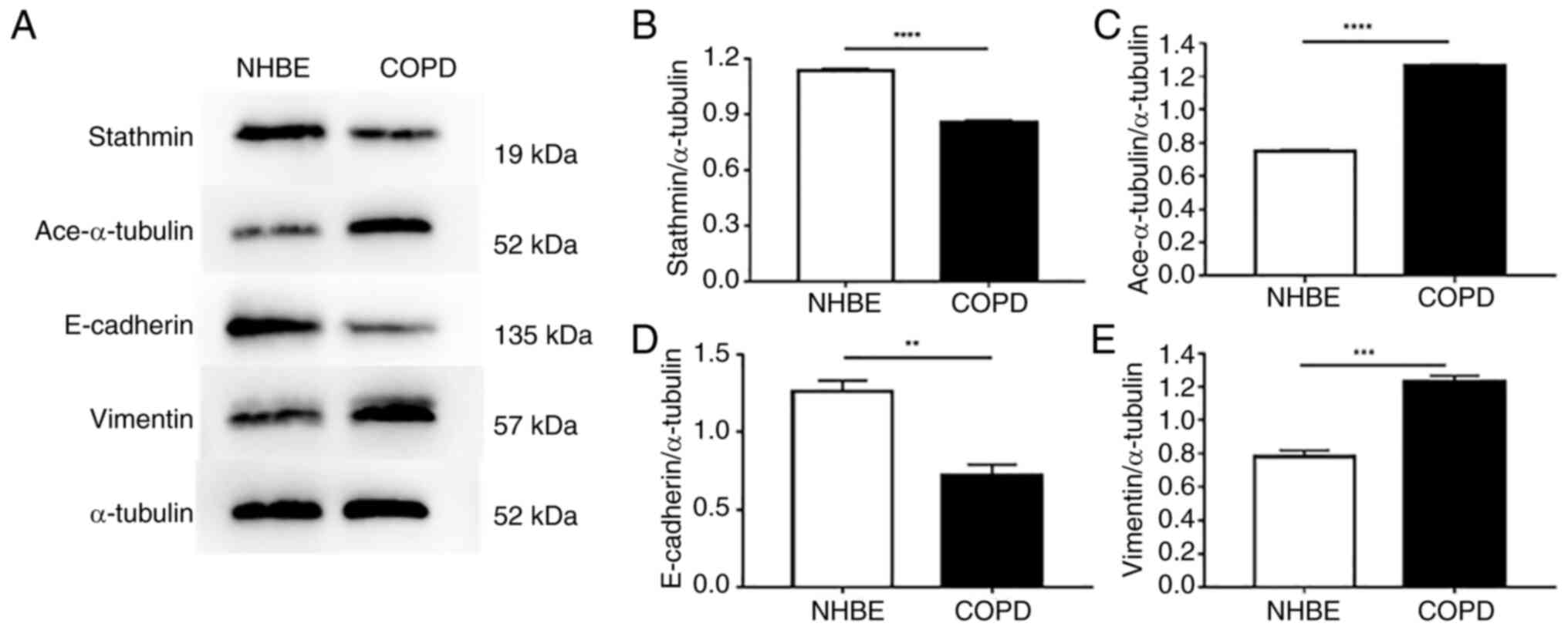
|
1
|
Yang J, Antin P, Berx G, Blanpain C,
Brabletz T, Bronner M, Campbell K, Cano A, Casanova J, Christofori
G, et al: Guidelines and definitions for research on
epithelial-mesenchymal transition. Nat Rev Mol Cell Biol.
21:341–352. 2020. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
Ilan Y: Microtubules: From understanding
their dynamics to using them as potential therapeutic targets. J
Cell Physiol. 234:7923–7937. 2019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
Gupta KK, Li C, Duan A, Alberico EO, Kim
OV, Alber MS and Goodson HV: Mechanism for the
catastrophe-promoting activity of the microtubule destabilizer
Op18/stathmin. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA. 110:20449–20454. 2013.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
Matsuyama A: In vivo destabilization of
dynamic microtubules by HDAC6-mediated deacetylation. EMBO J.
21:6820–6831. 2002. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Xu Z, Schaedel L, Portran D, Aguilar A,
Gaillard J, Marinkovich MP, Théry M and Nachury MV: Microtubules
acquire resistance from mechanical breakage through intralumenal
acetylation. Science. 356:328–332. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Lu Y, Liu C, Xu YF, Cheng H, Shi S, Wu CT
and Yu XJ: Stathmin destabilizing microtubule dynamics promotes
malignant potential in cancer cells by epithelial-mesenchymal
transition. Hepatobiliary Pancreat Dis Int. 13:386–394. 2014.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Wattanathamsan O and Pongrakhananon V:
Emerging role of microtubule-associated proteins on cancer
metastasis. Front Pharmacol. 13:9354932022. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Lee YZ, Yap HM, Shaari K, Tham CL,
Sulaiman MR and Israf DA: Blockade of Eosinophil-induced bronchial
Epithelial-mesenchymal transition with a geranyl acetophenone in a
coculture model. Front Pharmacol. 8:8372017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Kim BN, Ahn DH, Kang N, Yeo CD, Kim YK,
Lee KY, Kim TJ, Lee SH, Park MS, Yim HW, et al: TGF-β induced EMT
and stemness characteristics are associated with epigenetic
regulation in lung cancer. Sci Rep. 10:105972020. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Hasan NAHM, Harith HH, Israf DA and Tham
CL: The differential effects of commercial specialized media on
cell growth and transforming growth factor beta 1-induced
epithelial-mesenchymal transition in bronchial epithelial cells.
Mol Biol Rep. 47:3511–3519. 2020. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Mak JCW, Chan-Yeung MMW, Ho SP, Chan KS,
Choo K, Yee KS, Chau CH, Cheung AH and Ip MS; Members of Hong Kong
Thoracic Society COPD Study Group, : Elevated plasma TGF-β1 levels
in patients with chronic obstructive pulmonary disease. Respir Med.
103:1083–1089. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Mahmood MQ, Reid D, Ward C, Muller HK,
Knight DA, Sohal SS and Walters EH: Transforming growth factor
(TGF) β 1 and Smad signalling pathways: A likely key to
EMT-associated COPD pathogenesis. Respirology. 22:133–140. 2017.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Chakir J, Shannon J, Molet S, Fukakusa M,
Elias J, Laviolette M, Boulet LP and Hamid Q: Airway
remodeling-associated mediators in moderate to severe asthma:
Effect of steroids on TGF-β, IL-11, IL-17, and type I and type III
collagen expression. J Allergy Clin Immunol. 111:1293–1298. 2003.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Grada A, Otero-Vinas M, Prieto-Castrillo
F, Obagi Z and Falanga V: Research techniques made simple: Analysis
of collective cell migration using the wound healing assay. J
Invest Dermatol. 137:e11–e16. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Janke C and Chloë Bulinski J:
Post-translational regulation of the microtubule cytoskeleton:
Mechanisms and functions. Nat Rev Mol Cell Biol. 12:773–786. 2011.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Lee J, Choi JH and Joo CK: TGF-β1
regulates cell fate during epithelial-mesenchymal transition by
upregulating survivin. Cell Death Dis. 4:e714. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Shah N, Kumar S, Zaman N, Pan CC,
Bloodworth JC, Lei W, Streicher JM, Hempel N, Mythreye K and Lee
NY: TAK1 activation of alpha-TAT1 and microtubule hyperacetylation
control AKT signaling and cell growth. Nat Commun. 9:16962018.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
Sohal SS, Reid D, Soltani A, Ward C,
Weston S, Muller HK, Wood-Baker R and Walters EH: Evaluation of
epithelial mesenchymal transition in patients with chronic
obstructive pulmonary disease. Respir Res. 12:1302011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
Milara J, Peiró T, Serrano A and Cortijo
J: Epithelial to mesenchymal transition is increased in patients
with COPD and induced by cigarette smoke. Thorax. 68:410–420. 2013.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
Gohy ST, Hupin C, Fregimilicka C, Detry
BR, Bouzin C, Gaide Chevronay H, Lecocq M, Weynand B, Ladjemi MZ,
Pierreux CE, et al: Imprinting of the COPD airway epithelium for
dedifferentiation and mesenchymal transition. Eur Respir J.
45:1258–1272. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
Eapen MS, Lu W, Hackett TL, Singhera GK,
Mahmood MQ, Hardikar A, Ward C, Walters EH and Sohal SS: Increased
myofibroblasts in the small airways, and relationship to
remodelling and functional changes in smokers and COPD patients:
Potential role of epithelial-mesenchymal transition. ERJ Open Res.
7:00876–02020. 2021. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22
|
Belletti B, Nicoloso MS, Schiappacassi M,
Berton S, Lovat F, Wolf K, Canzonieri V, D'Andrea S, Zucchetto A,
Friedl P, et al: Stathmin activity influences sarcoma cell shape,
motility, and metastatic potential. Mol Biol Cell. 19:2003–2013.
2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23
|
Singer S, Malz M, Herpel E, Warth A,
Bissinger M, Keith M, Muley T, Meister M, Hoffmann H, Penzel R, et
al: Coordinated expression of stathmin family members by far
upstream sequence Element-Binding Protein-1 increases motility in
Non-small cell lung cancer. Cancer Res. 69:2234–2243. 2009.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24
|
Itoigawa Y, Harada N, Harada S, Katsura Y,
Makino F, Ito J, Nurwidya F, Kato M, Takahashi F, Atsuta R and
Takahashi K: TWEAK enhances TGF-β-induced epithelial-mesenchymal
transition in human bronchial epithelial cells. Respir Res.
16:482015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
25
|
Lv J, Sun B, Mai Z, Jiang M and Du J:
CLDN-1 promoted the epithelial to migration and mesenchymal
transition (EMT) in human bronchial epithelial cells via Notch
pathway. Mol Cell Biochem. 432:91–98. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
26
|
Doerner AM and Zuraw BL: TGF-β1 induced
epithelial to mesenchymal transition (EMT) in human bronchial
epithelial cells is enhanced by IL-1β but not abrogated by
corticosteroids. Respir Res. 10:1002009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
27
|
Malm SW, Amouzougan EA and Klimecki WT:
Fetal bovine serum induces sustained, but reversible,
epithelial-mesenchymal transition in the BEAS-2B cell line. Toxicol
In Vitro. 50:383–390. 2018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
28
|
Biaoxue R, Hua L, Tian F and Wenlong G:
Increased stathmin in serum as a potential tumor marker for lung
adenocarcinoma. Jpn J Clin Oncol. 47:342–349. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
29
|
Yurong L, Biaoxue R, Wei L, Zongjuan M,
Hongyang S, Ping F, Wenlong G, Shuanying Y and Zongfang L: Stathmin
overexpression is associated with growth, invasion and metastasis
of lung adenocarcinoma. Oncotarget. 8:26000–26012. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
30
|
Nie W, Xu M, Gan L, Huang H, Xiu Q and Li
B: Overexpression of stathmin 1 is a poor prognostic biomarker in
non-small cell lung cancer. Lab Invest. 95:56–64. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
31
|
Zhao L, Zhang D, Shen Q, Jin M, Lin Z, Ma
H, Huang S, Zhou P, Wu G and Zhang T: KIAA1199 promotes metastasis
of colorectal cancer cells via microtubule destabilization
regulated by a PP2A/stathmin pathway. Oncogene. 38:935–949. 2019.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
32
|
Nishioka M, Venkatesan N, Dessalle K,
Mogas A, Kyoh S, Lin TY, Nair P, Baglole CJ, Eidelman DH, Ludwig MS
and Hamid Q: Fibroblast-epithelial cell interactions drive
epithelial-mesenchymal transition differently in cells from normal
and COPD patients. Respir Res. 16:722015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
33
|
Jolly MK, Ward C, Eapen MS, Myers S,
Hallgren O, Levine H and Sohal SS: Epithelial-mesenchymal
transition, a spectrum of states: Role in lung development,
homeostasis, and disease. Dev Dyn. 247:346–358. 2018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
34
|
Williams K, Ghosh R, Giridhar PV, Gu G,
Case T, Belcher SM and Kasper S: Inhibition of stathmin1
accelerates the metastatic process. Cancer Res. 72:5407–5417. 2012.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
35
|
Liu J, Cao J and Zhao X: miR-221
facilitates the TGFbeta1-induced epithelial-mesenchymal transition
in human bladder cancer cells by targeting STMN1. BMC Urol.
15:362015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
36
|
Li N, Jiang P, Du W, Wu Z, Li C, Qiao M,
Yang X and Wu M: Siva1 suppresses epithelial-mesenchymal transition
and metastasis of tumor cells by inhibiting stathmin and
stabilizing microtubules. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA. 108:12851–12856.
2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
37
|
Langenickel TH, Olive M, Boehm M, San H,
Crook MF and Nabel EG: KIS protects against adverse vascular
remodeling by opposing Stathmin-mediated VSMC migration in mice. J
Clin Invest. 118:3848–3859. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
38
|
Xu K and Harrison RE: Down-regulation of
stathmin is required for the phenotypic changes and classical
activation of macrophages. J Biol Chem. 290:19245–19260. 2015.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
39
|
Gu S, Liu Y, Zhu B, Ding K, Yao TP, Chen
F, Zhan L, Xu P, Ehrlich M, Liang T, et al: Loss of α-Tubulin
acetylation is associated with TGF-β-induced Epithelial-mesenchymal
transition. J Biol Chem. 291:5396–5405. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
40
|
Iuzzolino A, Pellegrini FR, Rotili D,
Degrassi F and Trisciuoglio D: The α-tubulin acetyltransferase
ATAT1: Structure, cellular functions, and its emerging role in
human diseases. Cell Mol Life Sci. 81:1932024. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
41
|
Schaedel L, Lorenz C, Schepers AV, Klumpp
S and Köster S: Vimentin intermediate filaments stabilize dynamic
microtubules by direct interactions. Nat Commun. 12:37992021.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
42
|
Saldanha R, Tri Ho Thanh M, Krishnan N,
Hehnly H and Patteson AE: Vimentin supports cell polarization by
enhancing centrosome function and microtubule acetylation. J R Soc
Interface. 21:202306412024. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
43
|
Kamitani S, Yamauchi Y, Kawasaki S, Takami
K, Takizawa H, Nagase T and Kohyama T: Simultaneous stimulation
with TGF-β1 and TNF-α Induces epithelial mesenchymal transition in
bronchial epithelial cells. Int Arch Allergy Immunol. 155:119–128.
2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
44
|
Fischer KD and Agrawal DK: Vitamin D
regulating TGF-β induced epithelial-mesenchymal transition. Respir
Res. 15:1462014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
45
|
Du J, Hong S, Dong L, Cheng B, Lin L, Zhao
B, Chen YG and Chen X: Dynamic sialylation in transforming growth
Factor-β (TGF-β)-induced epithelial to mesenchymal transition. J
Biol Chem. 290:12000–12013. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
46
|
Machado-Neto JA, de Melo Campos P, Favaro
P, Lazarini M, da Silva Santos Duarte A, Lorand-Metze I, Costa FF,
Saad ST and Traina F: Stathmin 1 inhibition amplifies
ruxolitinib-induced apoptosis in JAK2V617F cells. Oncotarget.
6:29573–29584. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|