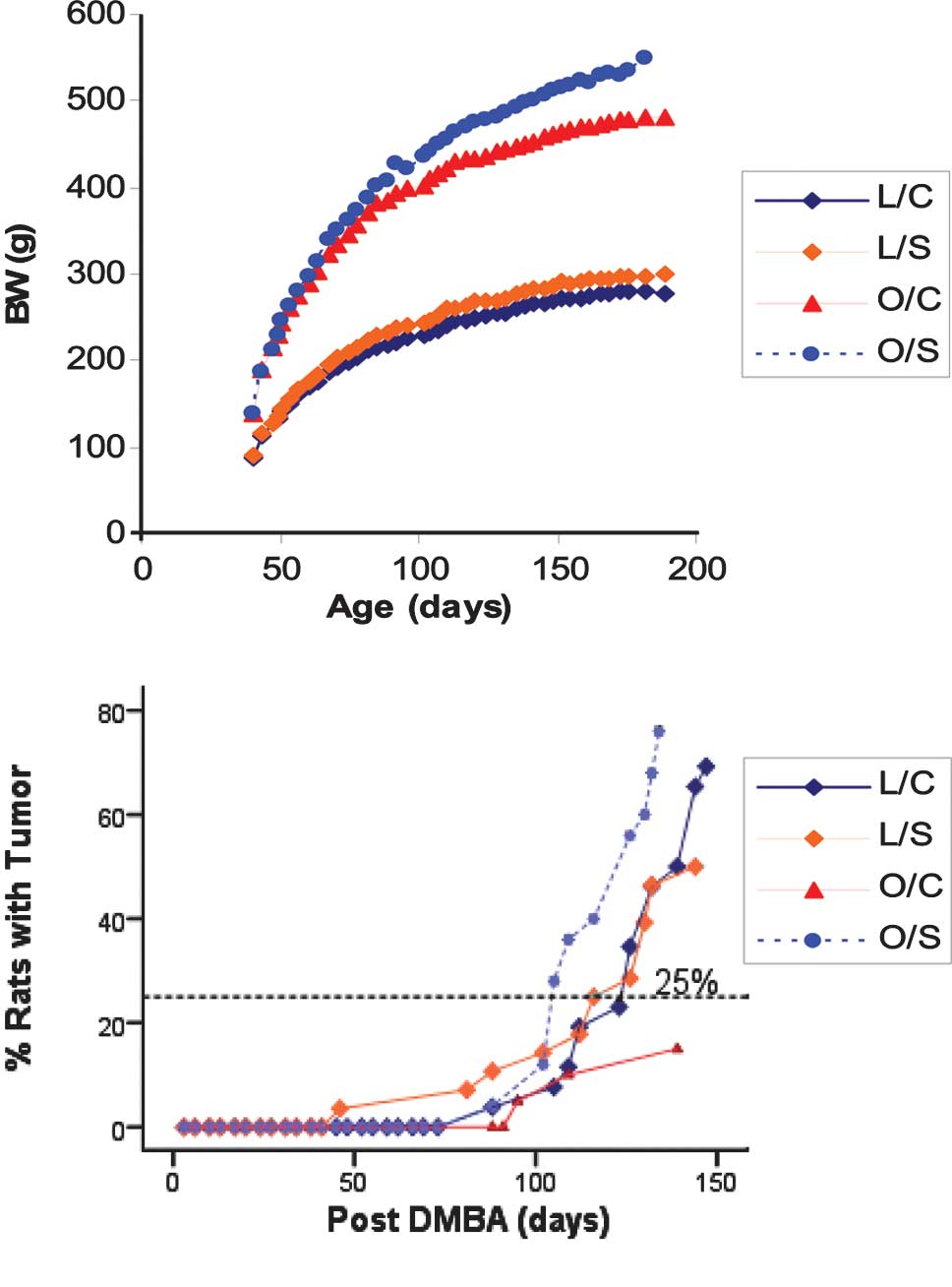
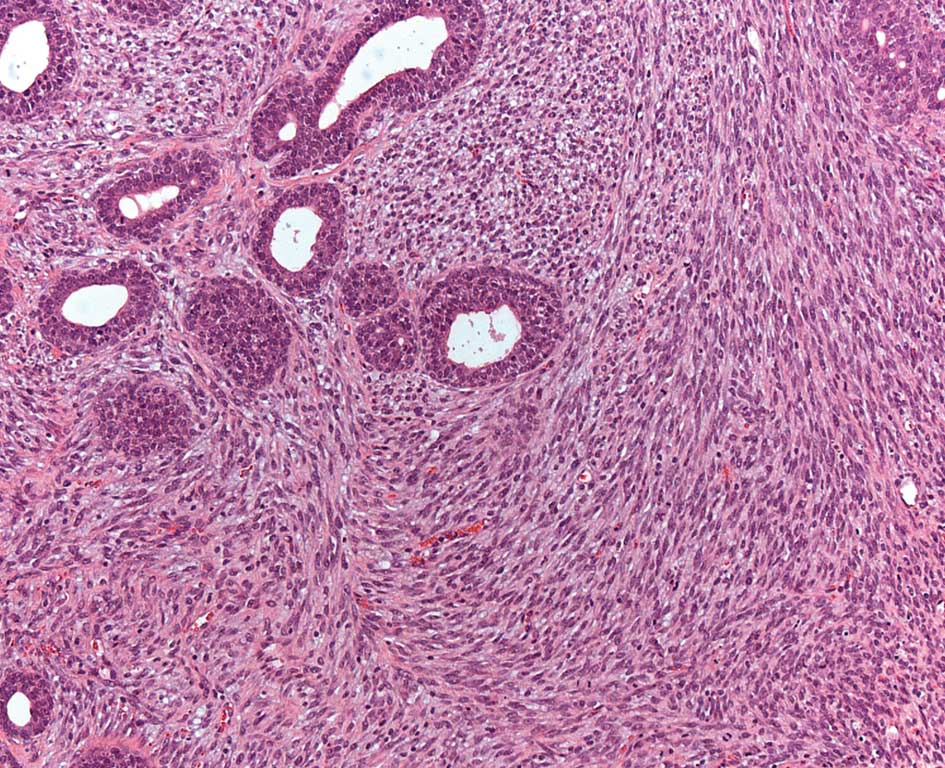
|
1
|
American Cancer Society. Cancer Facts and
Figures. 2010.
|
|
2
|
Calle EE, Rodriguez C, Walker-Thurmond K
and Thun MJ: Overweight, obesity, and mortality from cancer in a
prospectively studied cohort of U.S. adults. N Engl J Med.
348:1625–1638. 2003. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
Hakkak R, Korourian S, Shelnutt SR,
Lensing S, Ronis MJ and Badger TM: Diets containing whey proteins
or soy protein isolate protect against
7,12-dimethylbenz(a)anthracene-induced mammary tumors in female
rats. Cancer Epidemiol Biomarkers Prev. 9:113–117. 2000.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
Kris-Etherton PM, Hecker KD, Bonanome A,
et al: Bioactive compounds in foods: their role in the prevention
of cardiovascular disease and cancer. Am J Med. 113(Suppl 9):
71–88. 2002. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Peeters PH, Keinan-Boker L, van der Schouw
YT and Grobbee DE: Phytoestrogens and breast cancer risk. Review of
the epidemiological evidence. Breast Cancer Res Treat. 77:171–183.
2003. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Kelly GE, Nelson C, Waring MA, Joannou GE
and Reeder AY: Metabolites of dietary (soya) isoflavones in human
urine. Clin Chim Acta. 223:9–22. 1993. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Adlercreutz CH, Goldin BR, Gorbach SL, et
al: Soybean phytoestrogen intake and cancer risk. J Nutr.
125:S757–S770. 1995.
|
|
8
|
Gridley DS, Kettering JD, Slater JM and
Nutter RL: Modification of spontaneous mammary tumors in mice fed
different sources of protein, fat and carbohydrate. Cancer Lett.
19:133–146. 1983.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Hargreaves DF, Potten CS, Harding C, et
al: Two-week dietary soy supplementation has an estrogenic effect
on normal premenopausal breast. J Clin Endocrinol Metab.
84:4017–4024. 1999.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Travis RC, Allen NE, Appleby PN, Spencer
EA, Roddam AW and Key TJ: A prospective study of vegetarianism and
isoflavone intake in relation to breast cancer risk in British
women. Int J Cancer. 122:705–710. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Cohen LA, Zhao Z, Pittman B and Scimeca
JA: Effect of intact and isoflavone-depleted soy protein on
NMU-induced rat mammary tumorigenesis. Carcinogenesis. 21:929–935.
2000. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Constantinou AI, Lantvit D, Hawthorne M,
Xu X, van Breemen RB and Pezzuto JM: Chemopreventive effects of soy
protein and purified soy isoflavones on DMBA-induced mammary tumors
in female Sprague-Dawley rats. Nutr Cancer. 41:75–81. 2001.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Gallo D, Giacomelli S, Cantelmo F, et al:
Chemoprevention of DMBA-induced mammary cancer in rats by dietary
soy. Breast Cancer Res Treat. 69:153–164. 2001. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Jin Z and MacDonald RS: Soy isoflavones
increase latency of spontaneous mammary tumors in mice. J Nutr.
132:3186–3190. 2002.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Ueda M, Niho N, Imai T, et al: Lack of
significant effects of genistein on the progression of
7,12-dimethylbenz(a)anthracene-induced mammary tumors in
ovariectomized Sprague-Dawley rats. Nutr Cancer. 47:141–147. 2003.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Hewitt AL and Singletary KW: Soy extract
inhibits mammary adenocarcinoma growth in a syngeneic mouse model.
Cancer Lett. 192:133–143. 2003. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Shao ZM, Wu J, Shen ZZ and Barsky SH:
Genistein exerts multiple suppressive effects on human breast
carcinoma cells. Cancer Res. 58:4851–4857. 1998.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
Allred CD, Allred KF, Ju YH, et al:
Dietary genistein results in larger MNU-induced, estrogen-dependent
mammary tumors following ovariectomy of Sprague-Dawley rats.
Carcinogenesis. 25:211–218. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
19
|
Ju YH, Allred CD, Allred KF, Karko KL,
Doerge DR and Helferich WG: Physiological concentrations of dietary
genistein dose-dependently stimulate growth of estrogen-dependent
human breast cancer (MCF-7) tumors implanted in athymic nude mice.
J Nutr. 131:2957–2962. 2001.
|
|
20
|
Bruning PF, van Doorn J, Bonfrer JM, et
al: Insulin-like growth-factor-binding protein 3 is decreased in
early-stage operable pre-menopausal breast cancer. Int J Cancer.
62:266–270. 1995. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
Del Giudice ME, Fantus IG, Ezzat S,
McKeown-Eyssen G, Page D and Goodwin PJ: Insulin and related
factors in premenopausal breast cancer risk. Cancer Res Treat.
47:111–120. 1998.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22
|
Hankinson SE, Willett WC, Colditz GA, et
al: Circulating concentrations of insulin-like growth factor-I and
risk of breast cancer. Lancet. 351:1393–1396. 1998. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23
|
Krajcik RA, Borofsky ND, Massardo S and
Orentreich NI: Insulin-like growth factor I (IGF-I), IGF-binding
proteins, and breast cancer. Cancer Epidemiol Biomarkers Prev.
11:1566–1573. 2002.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24
|
Muti P, Quattrin T, Grant BJ, et al:
Fasting glucose is a risk factor for breast cancer: a prospective
study. Cancer Epidemiol Biomarkers Prev. 11:1361–1368.
2002.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
25
|
Peyrat JP, Bonneterre J, Hecquet B, et al:
Plasma insulin-like growth factor-1 (IGF-1) concentrations in human
breast cancer. Eur J Cancer Prev. 29A:492–497. 1993. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
26
|
Toniolo P, Bruning PF, Akhmedkhanov A, et
al: Serum insulin-like growth factor-I and breast cancer. Int J
Cancer. 88:828–832. 2000. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
27
|
Yu H, Jin F, Shu XO, et al: Insulin-like
growth factors and breast cancer risk in Chinese women. Cancer
Epidemiol Biomarkers Prev. 11:705–712. 2002.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
28
|
Khandwala HM, McCutcheon IE, Flyvbjerg A
and Friend KE: The effects of insulin-like growth factors on
tumorigenesis and neoplastic growth. Endocr Rev. 21:215–244. 2000.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
29
|
Yu H and Rohan T: Role of the insulin-like
growth factor family in cancer development and progression. J Natl
Cancer Inst. 92:1472–1489. 2000. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
30
|
Bruning PF, Bonfrer JM, van Noord PA, Hart
AA, de Jong-Bakker M and Nooijen WJ: Insulin resistance and
breast-cancer risk. Int J Cancer. 52:511–516. 1992. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
31
|
Kaaks R, Lundin E, Rinaldi S, et al:
Prospective study of IGF-I, IGF-binding proteins, and breast cancer
risk, in northern and southern Sweden. Cancer Causes Control.
13:307–316. 2002. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
32
|
Tartaglia LA, Dembski M, Weng X, et al:
Identification and expression cloning of a leptin receptor, OB-R.
Cell. 83:1263–1271. 1995. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
33
|
Chua SC Jr, Chung WK, Wu-Peng XS, et al:
Phenotypes of mouse diabetes and rat fatty due to mutations in the
OB (leptin) receptor. Science. 271:994–996. 1996. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
34
|
Zucker L and Zucker TF: Fatty, a new
mutation in the rat. J Heredity. 52:275–278. 1961.
|
|
35
|
Zucker TF and Zucker LM: Fat accretion and
growth in the rat. J Nutr. 80:6–19. 1963.
|
|
36
|
Zucker LM: Fat mobilization in vitro and
in vivo in the genetically obese Zucker rat ‘Fatty’. J Lipid Res.
13:234–243. 1972.
|
|
37
|
Bray GA, York DA and Fisler JS:
Experimental obesity: a homeostatic failure due to defective
nutrient stimulation of the sympathetic nervous system. Vitam Horm.
45:1–125. 1989. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
38
|
Bray GA: The Zucker-fatty rat: a review.
Fed Proc. 36:148–153. 1977.
|
|
39
|
Hakkak R, Holley AW, MacLeod S, et al:
Obesity promotes 7,12-dimethylbenz(a)anthracene-induced mammary
tumor development in female Zucker rats. Breast Cancer Research.
7:R627–R633. 2005. View
Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
40
|
Hakkak R, MacLeod S, Shaaf S, et al:
Obesity increases the incidence of
7,12-dimethylbenz(a)anthracene-induced mammary tumors in an
ovariectomized Zucker rat model. Int J Oncol. 30:557–563.
2007.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
41
|
Tovar AR, Torre-Villavazo I, Ochoa M, et
al: Soy protein reduces hepatic lipotoxicity in hyperinsulinemic
obese Zucker fa/fa rats. J Lipid Res. 46:1823–1832. 2005.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
42
|
Trujillo J, Ramirez V, Perez J, et al:
Renal protection by a soy diet in obese Zucker rats is associated
with restoration of nitric oxide generation. Am J Physiol Renal
Physiol. 288:F108–F116. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
43
|
Mezei O, Banz WJ, Steger RW, Peluso MR,
Winters TA and Shay N: Soy isoflavones exert antidiabetic and
hypolipidemic effects through the PPAR pathways in obese Zucker
rats and murine raw 264.7 cells. J Nutr. 133:1238–1243.
2003.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
44
|
Pathak DR and Whittemore AS: Combined
effects of body size, parity, and menstrual events on breast cancer
incidence in seven countries. Am J Epidemiol. 135:153–168.
1992.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
45
|
Peacock SL, White E, Daling JR, Voigt LF
and Malone KE: Relation between obesity and breast cancer in young
women. Am J Epidemiol. 149:339–346. 1999. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
46
|
Weiderpass E, Braaten T, Magnusson C, et
al: A prospective study of body size in different periods of life
and risk of premenopausal breast cancer. Cancer Epidemiol
Biomarkers Prev. 13:1121–1127. 2004.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
47
|
Simmen RC, Eason RR, Till SR, et al:
Inhibition of NMU-induced mammary tumorigenesis by dietary soy.
Cancer Lett. 224:45–52. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
48
|
Hsieh CY, Santell RC, Haslam SZ and
Helferich WG: Estrogenic effects of genistein on the growth of
estrogen receptor-positive human breast cancer (MCF-7) cells in
vitro and in vivo. Cancer Res. 58:3833–3838. 1998.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
49
|
Lee HP, Gourley L, Duffy SW, Esteve J, Lee
J and Day NE: Dietary effects on breast-cancer risk in singapore.
Lancet. 337:1197–1200. 1991. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
50
|
Wu AH, Yu MC, Tseng CC and Pike MC:
Epidemiology of soy exposures and breast cancer risk. Br J Cancer.
98:9–14. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
51
|
Trock BJ, Hilakivi-Clarke L and Clarke R:
Meta-analysis of soy intake and breast cancer risk. J Natl Cancer
Inst. 98:459–471. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
52
|
Messina MJ: Emerging evidence on the role
of soy in reducing prostate cancer risk. Nutr Rev. 61:117–131.
2003. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
53
|
Lee SA, Shu XO, Li H, et al: Adolescent
and adult soy food intake and breast cancer risk: results from the
Shanghai Women’s Health Study. Am J Clin Nutr. 89:1920–1926.
2009.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
54
|
Enderlin CA, Coleman EA, Stewart CB and
Hakkak R: Dietary soy intake and breast cancer risk. Oncol Nurs
Forum. 36:531–539. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
55
|
Wu Y, Cui K, Miyoshi K, et al: Reduced
circulating insulin-like growth factor I levels delay the onset of
chemically and genetically induced mammary tumors. Cancer Res.
63:4384–4388. 2003.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
56
|
Arjmandi BH, Khalil DA, Smith BJ, et al:
Soy protein has a greater effect on bone in postmenopausal women
not on hormone replacement therapy, as evidenced by reducing bone
resorption and urinary calcium excretion. J Clin Endocrinol Metab.
88:1048–1054. 2003. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
57
|
Khalil DA, Lucas EA, Juma S, Smith BJ,
Payton ME and Arjmandi BH: Soy protein supplementation increases
serum insulin-like growth factor-I in young and old men but does
not affect markers of bone metabolism. J Nutr. 132:2605–2608.
2002.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
58
|
Sanderson M, Shu XO, Yu H, et al:
Insulin-like growth factor-I, soy protein intake, and breast cancer
risk. Nutr Cancer. 50:8–15. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
59
|
Wangen KE, Duncan AM, Merz-Demlow BE, et
al: Effects of soy isoflavones on markers of bone turnover in
premenopausal and postmenopausal women. J Clin Endocr Metab.
85:3043–3048. 2000.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
60
|
Hakkak R, Holley AW, Bunn RC, Winters A
and MacLeod S: Effects of obesity on serum insulin growth factor 1
(IGF-1) levels in lean and obese female Zucker rats following DMBA
treatment. FASEB J. 19:A9932005.
|
|
61
|
Allen NE, Appleby PN, Davey GK, Kaaks R,
Rinaldi S and Key TJ: The associations of diet with serum
insulin-like growth factor I and its main binding proteins in 292
women meat-eaters, vegetarians, and vegans. Cancer Epidemiol
Biomarkers Prev. 11:1441–1448. 2002.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
62
|
Devine A, Rosen C, Mohan S, Baylink D and
Prince RL: Effects of zinc and other nutritional factors on
insulin-like growth factor I and insulin-like growth factor binding
proteins in postmenopausal women. Am J Clin Nutr. 68:200–206.
1998.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
63
|
Giovannucci E, Pollak M, Liu Y, et al:
Nutritional predictors of insulin-like growth factor I and their
relationships to cancer in men. Cancer Epidemiol Biomarkers Prev.
12:84–89. 2003.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
64
|
Gunnell D, Oliver SE, Peters TJ, et al:
Are diet-prostate cancer associations mediated by the IGF axis? A
cross-sectional analysis of diet, IGF-I and IGFBP-3 in healthy
middle-aged men. Br J Cancer. 88:1682–1686. 2003. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
65
|
Heald AH, Cade JE, Cruickshank JK,
Anderson S, White A and Gibson JM: The influence of dietary intake
on the insulin-like growth factor (IGF) system across three ethnic
groups: a population-based study. Public Health Nutr. 6:175–180.
2003. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
66
|
Holmes MD, Pollak MN, Willett WC and
Hankinson SE: Dietary correlates of plasma insulin-like growth
factor I and insulin-like growth factor binding protein 3
concentrations. Cancer Epidemiol Biomarkers Prev. 11:852–861.
2002.
|
|
67
|
Ma J, Giovannucci E, Pollak M, et al: Milk
intake, circulating levels of insulin-like growth factor-I, and
risk of colorectal cancer in men. J Natl Cancer Inst. 93:1330–1336.
2001. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
68
|
Mucci LA, Tamimi R, Lagiou P, et al: Are
dietary influences on the risk of prostate cancer mediated through
the insulin-like growth factor system? BJU Int. 87:814–820. 2001.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
69
|
Nagata C, Shimizu H, Takami R, Hayashi M,
Takeda N and Yasuda K: Dietary soy and fats in relation to serum
insulin-like growth factor-1 and insulin-like growth factor-binding
protein-3 levels in premenopausal Japanese women. Nutr Cancer.
45:185–189. 2003. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
70
|
Probst-Hensch NM, Wang H, Goh VH, Seow A,
Lee HP and Yu MC: Determinants of circulating insulin-like growth
factor I and insulin-like growth factor binding protein 3
concentrations in a cohort of Singapore men and women. Cancer
Epidemiol Biomarkers Prev. 12:739–746. 2003.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
71
|
Signorello LB, Kuper H, Lagiou P, et al:
Lifestyle factors and insulin-like growth factor 1 levels among
elderly men. Eur J Cancer Prev. 9:173–178. 2000. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
72
|
Vrieling A, Voskuil DW, Bueno-de-Mesquita
HB, et al: Dietary determinants of circulating insulin-like growth
factor (IGF)-I and IGF binding proteins 1, -2 and -3 in women in
the Netherlands. Cancer Causes Control. 15:787–796. 2004.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
73
|
Rinaldi S, Toniolo P, Muti P, et al:
IGF-I, IGFBP-3 and breast cancer in young women: a pooled
re-analysis of three prospective studies. Eur J Cancer Prev.
14:493–496. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
74
|
Bohlke K, Cramer DW, Trichopoulos D and
Mantzoros CS: Insulin-like growth factor-I in relation to
premenopausal ductal carcinoma in situ of the breast. Epidemiology.
9:570–573. 1998. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
75
|
Woodside JV, Campbell MJ, Denholm EE, et
al: Short-term phytoestrogen supplementation alters insulin-like
growth factor profile but not lipid or antioxidant status. J Nutr
Biochem. 17:211–215. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|