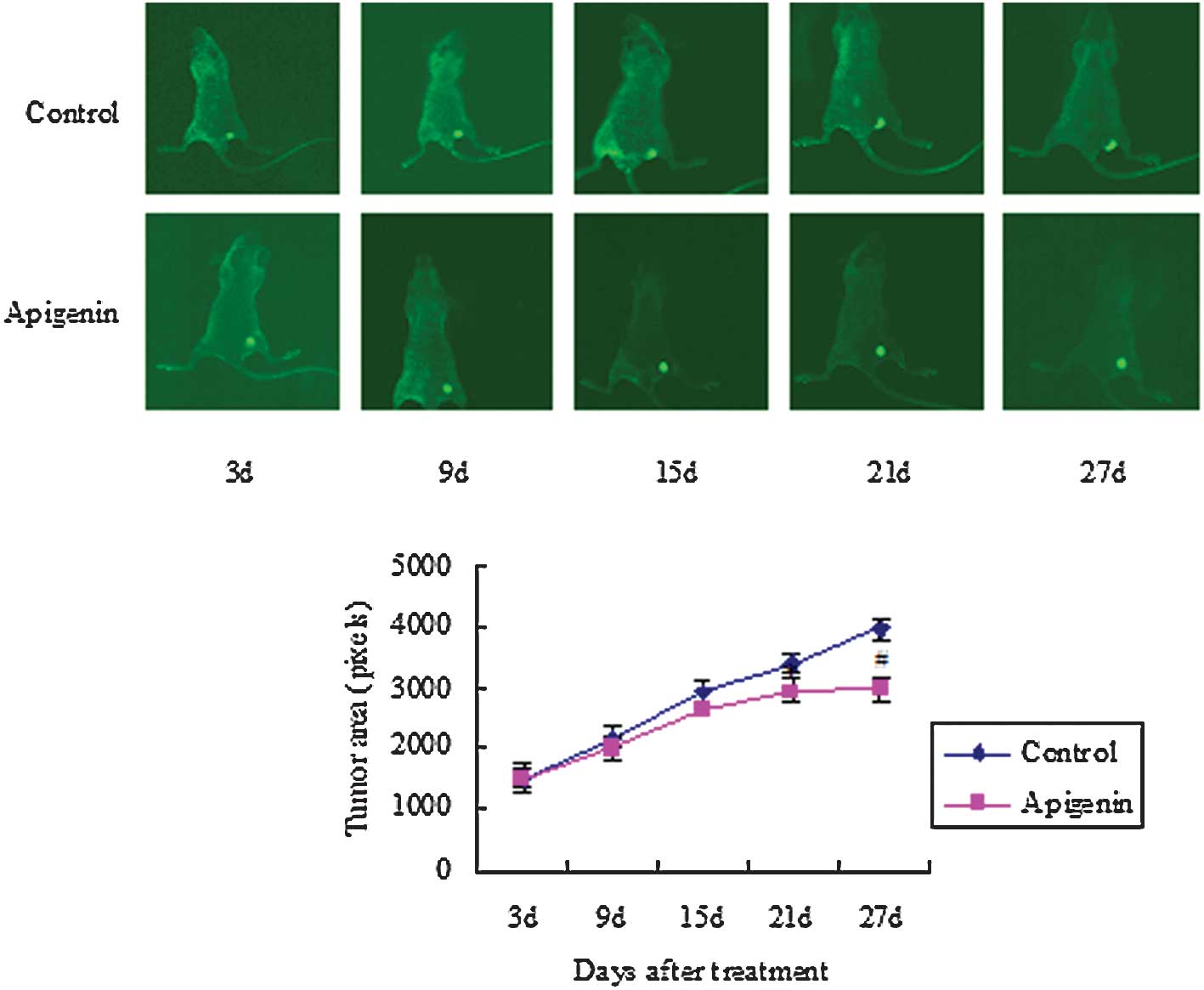
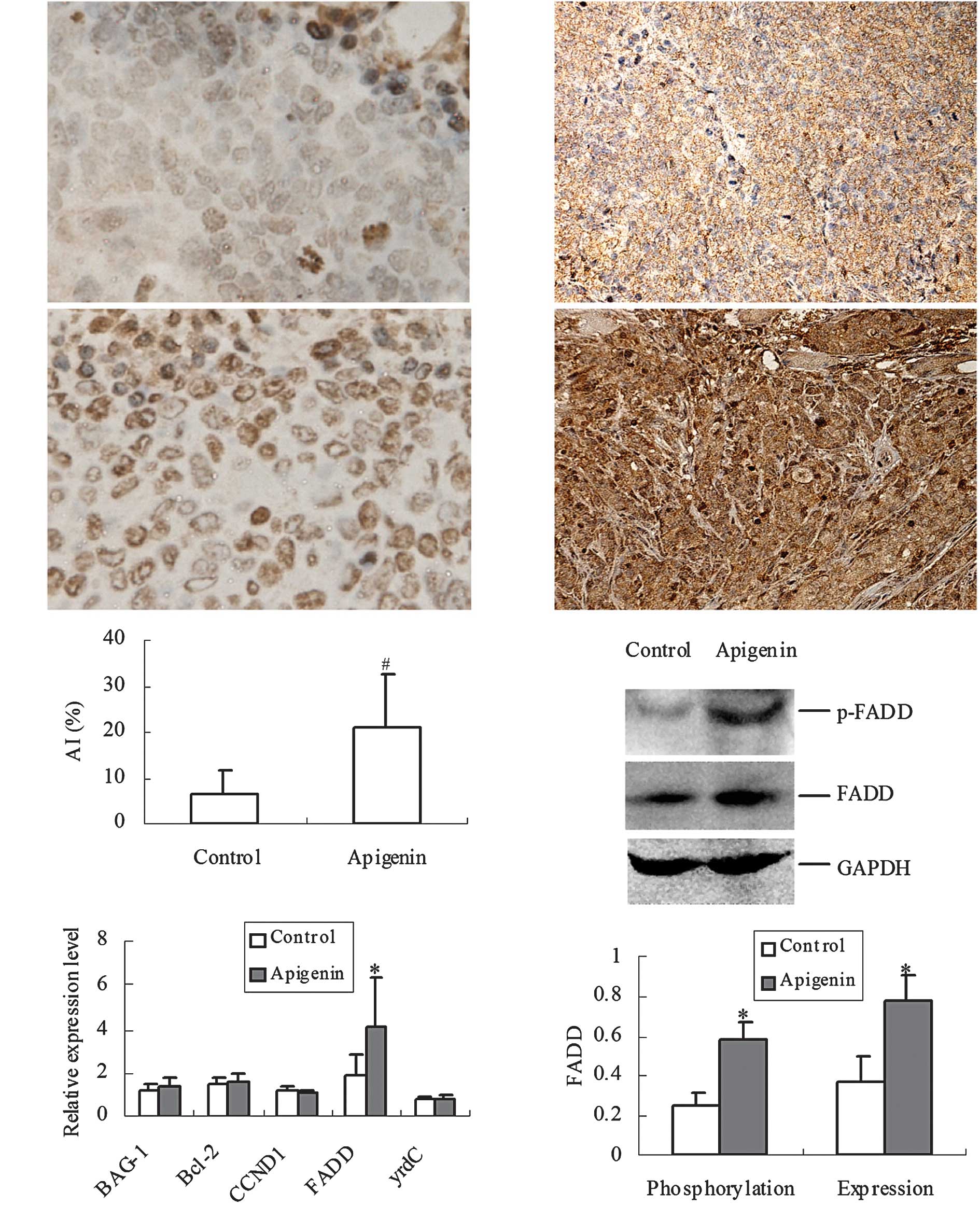
|
1
|
Jemal A, Siegel R, Ward E, Hao Y, Xu J and
Thun MJ: Cancer statistics. CA Cancer J Clin. 59:225–249. 2009.
|
|
2
|
Benson AB III: Epidemiology, disease
progression, and economic burden of colorectal cancer. J Manag Care
Pharm. 13:S5–S18. 2007.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
Noh HJ, Sung EG, Kim JY, Lee TJ and Song
IH: Suppression of phorbol-12-myristate-13-acetate-induced tumor
cell invasion by apigenin via the inhibition of p38
mitogen-activated protein kinase-dependent matrix
metalloproteinase-9 expression. Oncol Rep. 24:277–283. 2010.
|
|
4
|
Patel D, Shukla S and Gupta S: Apigenin
and cancer chemoprevention: Progress, potential and promise
(review). Int J Oncol. 30:233–245. 2007.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Farah M, Parhar K, Moussavi M, Eivemark S
and Salh B: 5,6-Dichloro-ribifuranosylbenzimidazole- and
apigenin-induced sensitization of colon cancer cells to
TNF-alpha-mediated apoptosis. Am J Physiol Gastrointest Liver
Physiol. 285:G919–G928. 2003. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
6
|
Wang W, Heideman L, Chung CS, Pelling JC,
Koehler KJ and Birt DF: Cell-cycle arrest at G2/M and growth
inhibition by apigenin in human colon carcinoma cell lines. Mol
Carcinog. 28:102–110. 2000. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Chung CS, Jiang Y, Cheng D and Birt DF:
Impact of adenomatous polyposis coli (APC) tumor supressor gene in
human colon cancer cell lines on cell cycle arrest by apigenin. Mol
Carcinog. 46:773–782. 2007. View
Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Au A, Li B, Wang W, Roy H, Koehler K and
Birt D: Effect of dietary apigenin on colonic ornithine
decarboxylase activity, aberrant crypt foci formation, and
tumorigenesis in different experimental models. Nutr Cancer.
54:243–251. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
9
|
Leibovitz A, Stinson JC, McCombs WB III,
McCoy CE, Mazur KC and Mabry ND: Classification of human colorectal
adenocarcinoma cell lines. Cancer Res. 36:4562–4569.
1976.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Zhao L, Wang H, Li J, Liu Y and Ding Y:
Overexpression of Rho GDP-dissociation inhibitor alpha is
associated with tumor progression and poor prognosis of colorectal
cancer. J Proteome Res. 7:3994–4003. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Liu L, Zhang QL, Jiang HY and Ding YQ:
Establishment of a whole-body visualization model of orthotopically
implanted colorectal carcinoma and metastasis model in nude mice.
Nan Fang Yi Ke Da Xue Xue Bao. 27:1161–1163. 11662007.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Cemazar M, Golzio M, Escoffre JM, Couderc
B, Sersa G and Teissié J: In vivo imaging of tumor growth after
electrochemotherapy with cisplatin. Biochem Biophys Res Commun.
348:997–1002. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Yin F, Giuliano AE and van Herle AJ:
Signal pathways involved in apigenin inhibition of growth and
induction of apoptosis of human anaplastic thyroid cancer cells
(ARO). Anticancer Res. 19:4297–4303. 1999.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Choi EJ and Kim GH: 5-Fluorouracil
combined with apigenin enhances anticancer activity through
induction of apoptosis in human breast cancer MDA-MB-453 cells.
Oncol Rep. 22:1533–1537. 2009.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Arber N, Doki Y, Han EK, Sgambato A, Zhou
P, Kim NH, Delohery T, Klein MG, Holt PR and Weinstein IB:
Antisense to cyclin D1 inhibits the growth and tumorigenicity of
human colon cancer cells. Cancer Res. 57:1569–1574. 1997.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Barnes JD, Arhel NJ, Lee SS, Sharp A,
Al-Okail M, Packham G, Hague A, Paraskeva C and Williams AC:
Nuclear BAG-1 expression inhibits apoptosis in colorectal
adenoma-derived epithelial cells. Apoptosis. 10:301–311. 2005.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Tao GQ, Yang M, Jiang HH, Yan YQ and Wang
XH: The experiment on expression of human yrdC promotes
proliferation of colon cancer SW-480 cells. Shanghai Med J.
31:596–598. 2008.
|
|
18
|
Ofner D, Riehemann K, Maier H, Riedmann B,
Nehoda H, Tötsch M, Böcker W, Jasani B and Schmid KW:
Immunohistochemically detectable bcl-2 expression in colorectal
carcinoma: correlation with tumor stage and patient survival. Br J
Cancer. 72:981–985. 1995. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
Chinnaiyan AM, Tepper CG, Seldin MF,
O'Rourke K, Kischkel FC, Hellbardt S, Krammer PH, Peter ME and
Dixit VM: FADD/MORT1 is a common mediator of CD95 (Fas/APO-1) and
tumor necrosis factor receptor-induced apoptosis. J Biol Chem.
271:4961–4965. 1996. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
Boldin MP, Varfolomeev EE, Pancer Z, Mett
IL, Camonis JH and Wallach D: A novel protein that interacts with
the death domain of Fas/APO1 contains a sequence motif related to
the death domain. J Biol Chem. 270:7795–7798. 1995. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
Chinnaiyan AM, O'Rourke K, Tewari M and
Dixit VM: FADD, a novel death domain-containing protein, interacts
with the death domain of Fas and initiates apoptosis. Cell.
81:505–512. 1995. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22
|
Yanase N, Kanetaka Y and Mizuguchi J:
Interferon-α-induced apoptosis via tumor necrosis factor-related
apoptosis-inducing ligand (TRAIL)-dependent and -independent
manner. Oncol Rep. 18:1031–1038. 2007.
|
|
23
|
Lu HF, Lai KC, Hsu SC, Lin HJ, Yang MD,
Chen YL, Fan MJ, Yang JS, Cheng PY, Kuo CL and Chung JG: Curcumin
induces apoptosis through FAS and FADD, in caspase-3-dependent and
-independent pathways in the N18 mouse-rat hybrid retina ganglion
cells. Oncol Rep. 22:97–104. 2009.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24
|
Delmas D, Rébé C, Lacour S, Filomenko R,
Athias A, Gambert P, Cherkaoui-Malki M, Jannin B, Dubrez-Daloz L,
Latruffe N and Solary E: Resveratrol-induced apoptosis is
associated with Fas redistribution in the rafts and the formation
of a death-inducing signaling complex in colon cancer cells. J Biol
Chem. 278:41482–41490. 2003. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
25
|
Scaffidi C, Volkland J, Blomberg I,
Hoffmann I, Krammer PH and Peter ME: Phosphorylation of FADD/MORT1
at serine 194 and association with a 70-kDa cell cycle-regulated
protein kinase. J Immunol. 164:1236–1242. 2000. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|