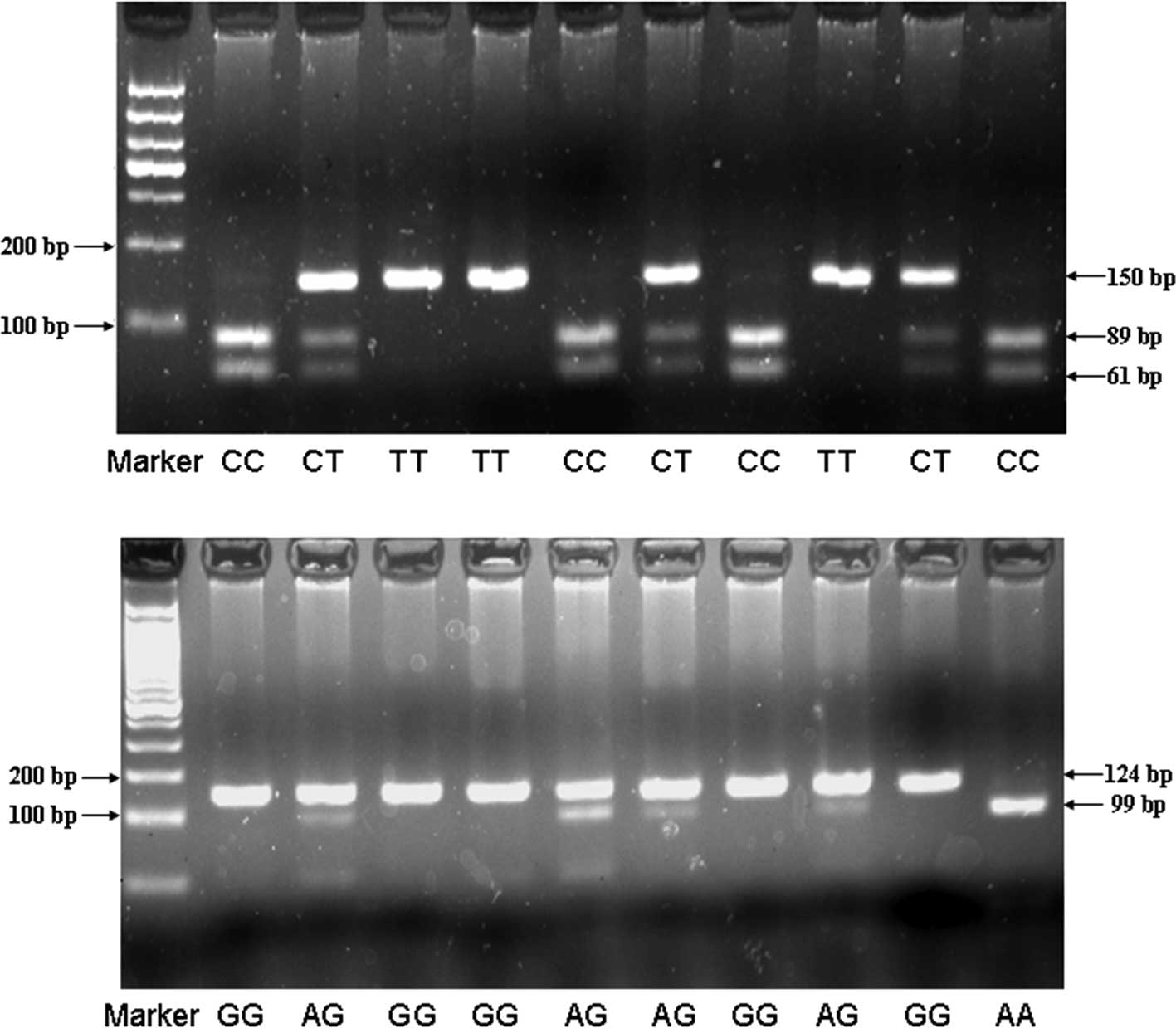
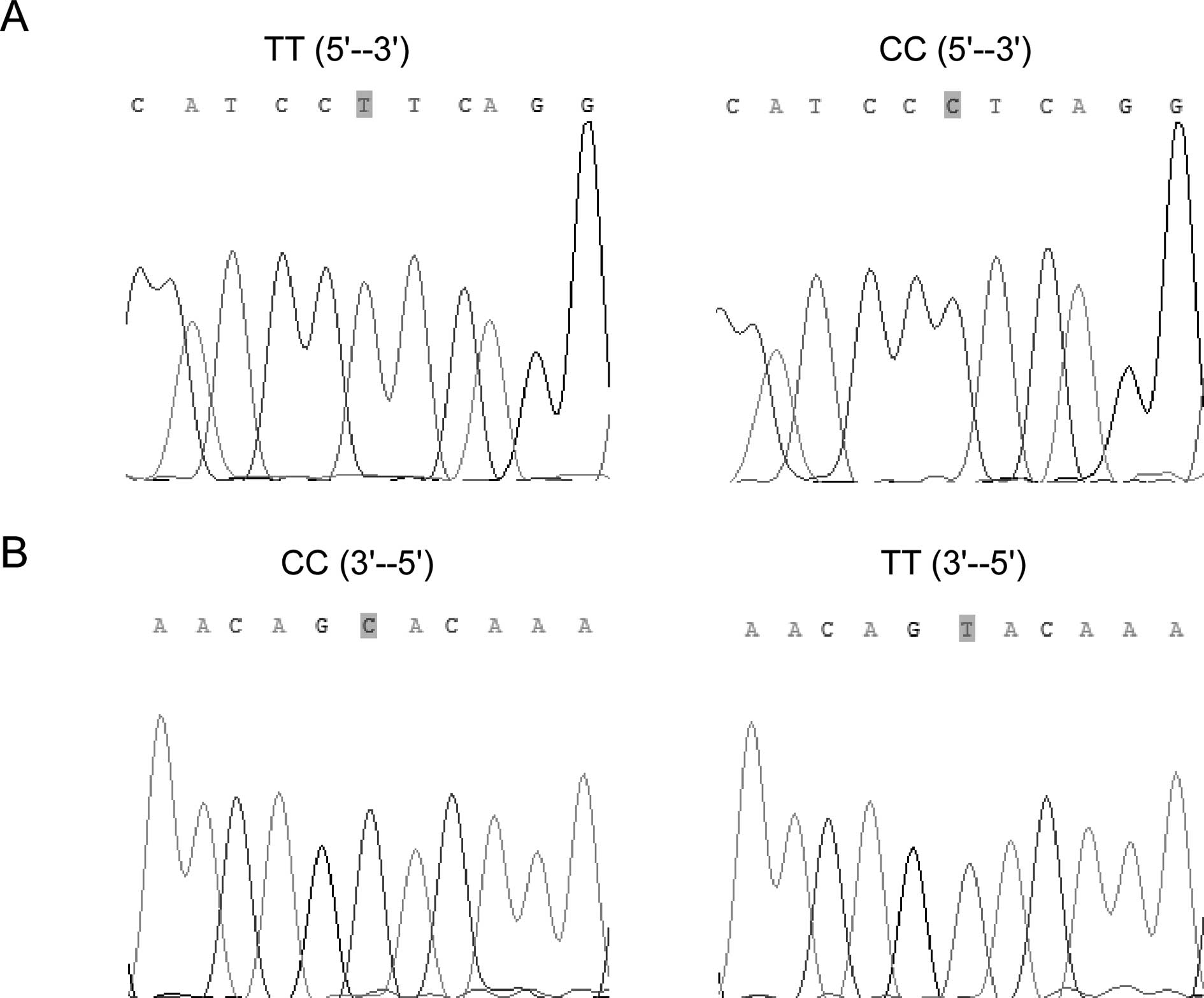
|
1
|
Parkin DM, Bray F, Ferlay J and Pisani P:
Global cancer statistics, 2002. CA Cancer J Clin. 55:74–108. 2005.
View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
2
|
Moss SF and Blaser MJ: Mechanisms of
disease: inflammation and the origins of cancer. Nat Clin Pract
Oncol. 2:90–97. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
Mantovani A, Allavena P, Sica A and
Balkwill F: Cancer-related inflammation. Nature. 454:436–444. 2008.
View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
4
|
Bierie B and Moses HL: Tumour
microenvironment: TGFbeta: the molecular Jekyll and Hyde of cancer.
Nat Rev Cancer. 6:506–520. 2006. View
Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Yang L, Anderson DE, Baecher-Allan C, et
al: IL-21 and TGF-beta are required for differentiation of human
T(H)17 cells. Nature. 454:350–352. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Veldhoen M, Hocking RJ, Atkins CJ,
Locksley RM and Stockinger B: TGFbeta in the context of an
inflammatory cytokine milieu supports de novo differentiation of
IL-17-producing T cells. Immunity. 24:179–189. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
7
|
Massague J, Blain SW and Lo RS: TGFbeta
signaling in growth control, cancer, and heritable disorders. Cell.
103:295–309. 2000. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Jin G, Wang L, Chen W, et al: Variant
alleles of TGFB1 and TGFBR2 are associated with a decreased risk of
gastric cancer in a Chinese population. Int J Cancer.
120:1330–1335. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Li T, Cao BW, Dai Y, Cui H, Yang HL and Xu
CQ: Correlation of transforming growth factor beta-1 gene
polymorphisms C-509T and T869C and the risk of gastric cancer in
China. J Gastroenterol Hepatol. 23:638–642. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Zhang P, Di JZ, Zhu ZZ, et al: Association
of transforming growth factor-beta 1 polymorphisms with genetic
susceptibility to TNM stage I or II gastric cancer. Jpn J Clin
Oncol. 38:861–866. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Guan X, Zhao H, Niu J, Tan D, Ajani JA and
Wei Q: Polymorphisms of TGFB1 and VEGF genes and survival of
patients with gastric cancer. J Exp Clin Cancer Res. 28:942009.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Guan X, Zhao H, Niu J, Tang D, Ajani JA
and Wei Q: The VEGF -634G>C promoter polymorphism is associated
with risk of gastric cancer. BMC Gastroenterol. 9:772009.
|
|
13
|
Yamaguchi N and Kakizoe T: Synergistic
interaction between Helicobacter pylori gastritis and diet
in gastric cancer. Lancet Oncol. 2:88–94. 2001.
|
|
14
|
Kountouras J, Zavos C, Chatzopoulos D and
Katsinelos P: New aspects of Helicobacter pylori infection
involvement in gastric oncogenesis. J Surg Res. 146:149–158.
2008.
|
|
15
|
Messa C, Di Leo A, Greco B, et al:
Successful eradicating treatment of Helicobacter pylori in
patients with chronic gastritis: gastric levels of cytokines,
epidermal growth factor and polyamines before and after therapy.
Immunopharmacol Immunotoxicol. 18:1–13. 1996.
|
|
16
|
Kandulski A, Wex T, Kuester D, et al:
Naturally occurring regulatory T cells (CD4+,
CD25high, FOXP3+) in the antrum and cardia
are associated with higher H. pylori colonization and
increased gene expression of TGF-beta1. Helicobacter. 13:295–303.
2008.
|
|
17
|
Rad R, Brenner L, Bauer S, et al:
CD25+/Foxp3+ T cells regulate gastric
inflammation and Helicobacter pylori colonization in vivo.
Gastroenterology. 131:525–537. 2006.
|
|
18
|
Raghavan S, Fredriksson M, Svennerholm AM,
Holmgren J and Suri-Payer E: Absence of
CD4+CD25+ regulatory T cells is associated
with a loss of regulation leading to increased pathology in
Helicobacter pylori-infected mice. Clin Exp Immunol.
132:393–400. 2003.
|
|
19
|
Qi P, Chen YM, Wang H, et al: -509C>T
polymorphism in the TGF-beta1 gene promoter, impact on the
hepatocellular carcinoma risk in Chinese patients with chronic
hepatitis B virus infection. Cancer Immunol Immunother.
58:1433–1440. 2009.
|
|
20
|
Kobayashi M, Nagata S, Iwasaki T, et al:
Dedifferentiation of adenocarcinomas by activation of
phosphatidylinositol 3-kinase. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA.
96:4874–4879. 1999. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
Xu Q, Karouji Y, Kobayashi M, Ihara S,
Konishi H and Fukui Y: The PI 3-kinase-Rac-p38 MAP kinase pathway
is involved in the formation of signet-ring cell carcinoma.
Oncogene. 22:5537–5544. 2003. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22
|
Atsumi T, Kato K, Uno K, et al:
Pathophysiological role of the activation of p38 mitogen-activated
protein kinases in poorly differentiated gastric cancer. Pathol
Int. 57:635–644. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23
|
Massague J: TGFbeta in cancer. Cell.
134:215–230. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
24
|
Bierie B and Moses HL: Transforming growth
factor beta (TGF-beta) and inflammation in cancer. Cytokine Growth
Factor Rev. 21:49–59. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
25
|
Kaklamani VG, Baddi L, Liu J, et al:
Combined genetic assessment of transforming growth factor-beta
signaling pathway variants may predict breast cancer risk. Cancer
Res. 65:3454–3461. 2005.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
26
|
Nakamura M, Katano M, Kuwahara A, et al:
Transforming growth factor beta1 (TGF-beta1) is a preoperative
prognostic indicator in advanced gastric carcinoma. Br J Cancer.
78:1373–1378. 1998. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
27
|
Vagenas K, Spyropoulos C, Gavala V and
Tsamandas AC: TGFbeta1, TGFbeta2, and TGFbeta3 protein expression
in gastric carcinomas: correlation with prognostic factors and
patient survival. J Surg Res. 139:182–188. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|