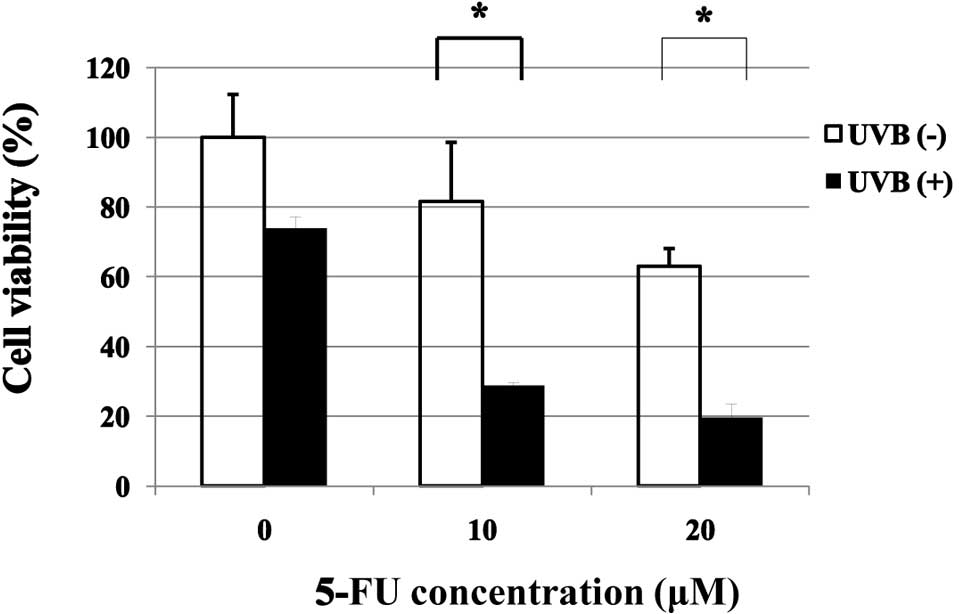
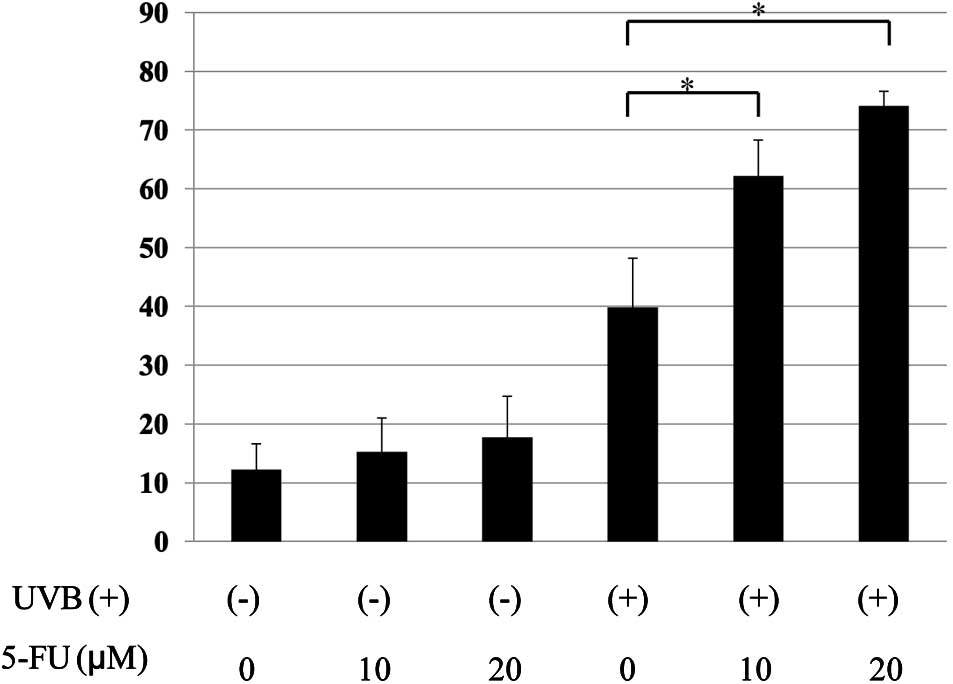
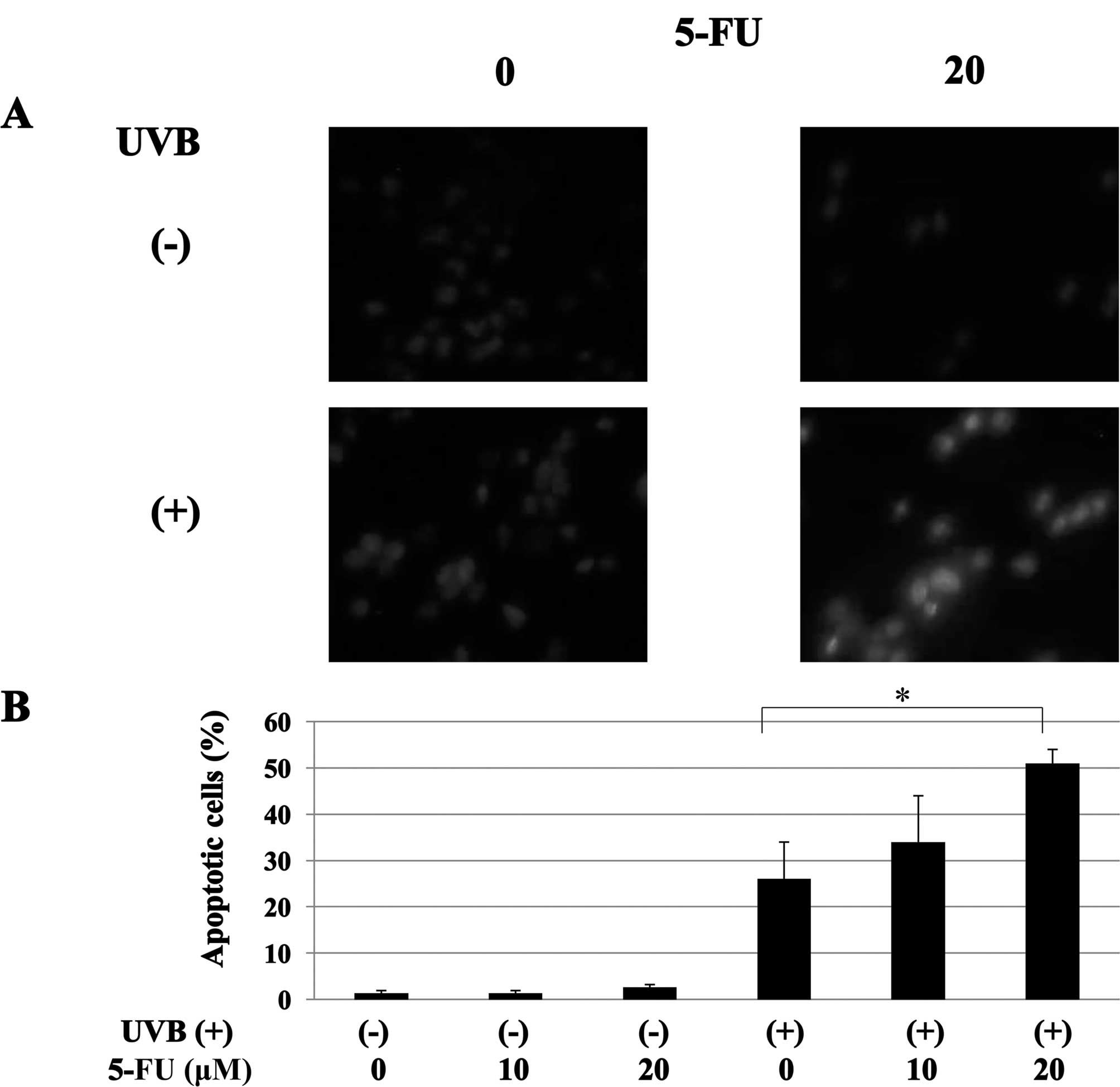
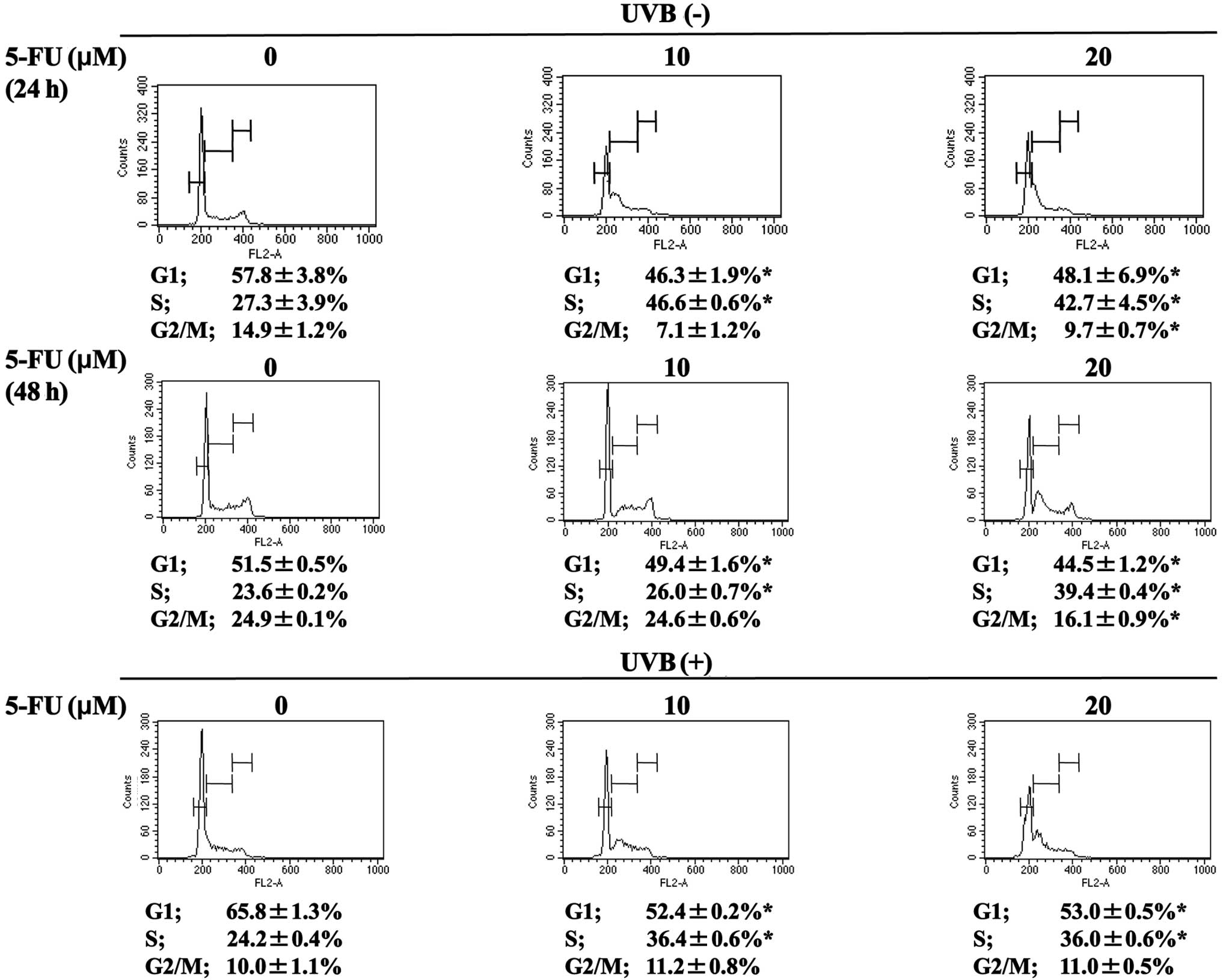
|
1
|
Lui H: Phototherapy of psoriasis: update
with practical pearls. J Cutan Med Surg. 6:17–21. 2002. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
Reynolds NJ, Franklin V, Gray JC, Diffey
BL and Farr PM: Narrow-band ultraviolet B and broad-band
ultraviolet A phototherapy in adult atopic eczema: a randomised
controlled trial. Lancet. 357:2012–2016. 2001. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
3
|
Hamzavi I, Jain H, McLean D, Shapiro J,
Zeng H and Lui H: Parametric modeling of narrowband UV-B
phototherapy for vitiligo using a novel quantitative tool: the
Vitiligo Area Scoring Index. Arch Dermatol. 140:677–683. 2004.
View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
4
|
Gathers RC, Scherschun L, Malick F,
Fivenson DP and Lim HW: Narrowband UVB phototherapy for early-stage
mycosis fungoides. J Am Acad Dermatol. 47:191–197. 2002. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
5
|
Matsuoka Y, Yoneda K, Katsuura J, et al:
Successful treatment of follicular cutaneous T-cell lymphoma
without mucinosis with narrow-band UVB-irradiation. J Eur Acad
Dermatol Venereol. 21:1121–1122. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
6
|
Snellman E, Klimenko T and Rantanen T:
Randomized half-side comparison of narrowband UVB and
trimethylpsoralen bath plus UVA treatments for psoriasis. Acta Derm
Venereol. 84:132–137. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Halliday GM: Inflammation, gene mutation
and photoimmuno-suppression in response to UVR-induced oxidative
damage contributes to photocarcinogenesis. Mutat Res. 571:107–120.
2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Griffiths HR, Mistry P, Herbert KE and
Lunec J: Molecular and cellular effects of ultraviolet
light-induced genotoxicity. Crit Rev Clin Lab Sci. 35:189–237.
1998. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Cotton J and Spandau DF: Ultraviolet
B-radiation dose influences the induction of apoptosis and p53 in
human keratinocytes. Radiat Res. 147:148–155. 1997. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Aufiero BM, Talwar H, Young C, et al:
Narrow-band UVB induces apoptosis in human keratinocytes. J
Photochem Photobiol B. 82:132–139. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Longley DB, Harkin DP and Johnston PG:
5-Fluorouracil: mechanisms of action and clinical strategies. Nat
Rev Cancer. 3:330–338. 2003. View
Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Huerta S, Gao X, Livingston EH, Kapur P,
Sun H and Anthony T: In vitro and in vivo radiosensitization of
colorectal cancer HT-29 cells by the smac mimetic JP-1201. Surgery.
148:346–353. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Dai Y, Liu M, Tang W, et al: Molecularly
targeted radiosensitization of human prostate cancer by modulating
inhibitor of apoptosis. Clin Cancer Res. 14:7701–7710. 2008.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Adamsen BL, Kravik L and De Angelis PM:
Cellular response to chemoradiotherapy, radiotherapy and
chemotherapy in two colorectal cancer cell lines. Radiat Res.
171:562–571. 2009. View
Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Wilson GD, Bentzen SM and Harari PM:
Biologic basis for combining drugs with radiation. Semin Radiat
Oncol. 16:2–9. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
16
|
Clarke M, Collins R, Darby S, et al:
Effects of radiotherapy and of differences in the extent of surgery
for early breast cancer on local recurrence and 15-year survival:
an overview of the randomised trials. Lancet. 366:2087–2106.
2005.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Shikama N, Sekiguchi K and Nakamura N:
Management of locoregional recurrence of breast cancer. Breast
Cancer. May 7–2010.(Epub ahead of print).
|
|
18
|
Taylor ME: Breast cancer: chest wall
recurrences. Curr Treat Options Oncol. 3:175–177. 2002. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
Holme SA and Mills CM: Crotamiton and
narrow-band UVB phototherapy: novel approaches to alleviate
pruritus of breast carcinoma skin infiltration. J Pain Symptom
Manage. 22:803–805. 2001. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
Nakayama S, Katoh EM, Tsuzuki T and
Kobayashi S: Protective effect of alpha-tocopherol-6-O-phosphate
against ultraviolet B-induced damage in cultured mouse skin. J
Invest Dermatol. 121:406–411. 2003. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
Cai BX, Luo D, Lin XF and Gao J: Compound
K suppresses ultraviolet radiation-induced apoptosis by inducing
DNA repair in human keratinocytes. Arch Pharm Res. 31:1483–1488.
2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22
|
Fergin P: Photodynamic therapy of
dermatoses other than non-melanoma skin cancer. Australas J
Dermatol. 46(Suppl 3): S272005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23
|
Babilas P, Karrer S, Sidoroff A,
Landthaler M and Szeimies RM: Photodynamic therapy in dermatology –
an update. Photodermatol Photoimmunol Photomed. 21:142–149.
2005.
|
|
24
|
Saad ED and Hoff PM: UFT and oral
leucovorin as radiation sensitizers in rectal and other
gastrointestinal malignancies. Cancer Invest. 21:624–629. 2003.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
25
|
Zenda S, Onozawa Y, Tahara M, et al:
Feasibility study of single agent cisplatin and concurrent
radiotherapy in Japanese patients with squamous cell carcinoma of
the head and neck: preliminary results. Jpn J Clin Oncol.
37:725–729. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
26
|
Choy H, Rodriguez FF, Koester S,
Hilsenbeck S and von Hoff DD: Investigation of taxol as a potential
radiation sensitizer. Cancer. 71:3774–3778. 1993. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
27
|
Hamaoka T, Furuya Y, Yamamoto K and Kuroda
Y: MCF-7 growth inhibition by ultraviolet radiation and
5-fluorouracil: the importance of treatment sequence. Cancer Lett.
154:183–187. 2000. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
28
|
Lawrence TS, Blackstock AW and McGinn C:
The mechanism of action of radiosensitization of conventional
chemotherapeutic agents. Semin Radiat Oncol. 13:13–21. 2003.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
29
|
Byfield J: Useful interactions between
5-fluorouracil and radiation in man: 5-fluorouracil as a
radiosensitizer. CRC Press; Boca Raton, FL: 1990
|
|
30
|
McKay BC, Becerril C, Spronck JC and
Ljungman M: Ultraviolet light-induced apoptosis is associated with
S-phase in primary human fibroblasts. DNA Repair (Amst). 1:811–820.
2002. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
31
|
Sasaki K, Tsuno NH, Sunami E, et al:
Chloroquine potentiates the anti-cancer effect of 5-fluorouracil on
colon cancer cells. BMC Cancer. 10:3702010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
32
|
Lawrence TS, Davis MA and Loney TL:
Fluoropyrimidine-mediated radiosensitization depends on cyclin
E-dependent kinase activation. Cancer Res. 56:3203–3206.
1996.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
33
|
Naida JD, Davis MA and Lawrence TS: The
effect of activation of wild-type p53 function on
fluoropyrimidine-mediated radiosensitization. Int J Radiat Oncol
Biol Phys. 41:675–680. 1998. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
34
|
Lawrence TS, Davis MA, Tang HY and Maybaum
J: Fluoro-deoxyuridine-mediated cytotoxicity and radiosensitization
require S phase progression. Int J Radiat Biol. 70:273–280. 1996.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
35
|
Panno ML, Giordano F, Mastroianni F, et
al: Breast cancer cell survival signal is affected by bergapten
combined with an ultraviolet irradiation. FEBS Lett. 584:2321–2326.
2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
36
|
Fraile RJ, Baker LH, Buroker TR, Horwitz J
and Vaitkevicius VK: Pharmacokinetics of 5-fluorouracil
administered orally, by rapid intravenous and by slow infusion.
Cancer Res. 40:2223–2228. 1980.PubMed/NCBI
|