Introduction
Despite good responses to chemotherapy and
chemoradiotherapy, small cell lung cancer (SCLC) is characterized
by early and widespread metastases (1). Brain metastases are observed in ~10%
of patients at the time of the initial diagnosis, and an additional
40–50% may develop brain metastases during the course of their
disease (1). However, late isolated
solitary brain metastasis as a relapse of SCLC is rare (2). The present study describes two SCLC
patients with an isolated solitary brain metastasis at 18 and 14
months, respectively, following the completion of an initial
successful treatment for SCLC. This case report conformed to the
Ethical Guidelines for Clinical Studies issued by the Ministry of
Health, Labor and Welfare of Japan. Comprehensive informed consent
with regard to clinical significance was obtained from the
patients.
Case reports
Case 1
A 63-year-old male was admitted to the University of
Tsukuba Hospital (Mito, Japan) for an examination of a chest nodule
in the right upper lobe of the lung. On admission, the laboratory
examination revealed a hemoglobin level of 13.9 g/dl, a hematocrit
level of 41.6% and a lactate dehydrogenase level of 139 IU/l. The
serum level of neuron-specific enolase (NSE) was 19.9 ng/ml and the
pro-gastrin-releasing peptide (proGRP) level was elevated to 522.1
pg/ml. A chest X-ray and computed tomography (CT) scan revealed a
poorly-defined mass in the upper lobe of the right lung, with an
ipsilateral mediastinal lymph node swelling. A transbronchial
biopsy revealed the tumor to be SCLC. As no metastatic lesion was
identified, the tumor was diagnosed as limited disease-SCLC. The
patient was treated using chemoradiotherapy (chest irradiation up
to 65 Gy and four courses of chemotherapy) containing cisplatin (80
mg/m2, day 1 for 4 weeks) and etoposide (100
mg/m2, days 1–3, for 4 weeks), which resulted in a
complete response (CR). A requirement for prophylactic cranial
irradiation (PCI) was indicated, however, whole brain irradiation
was not administered as the patient did not want the therapy.
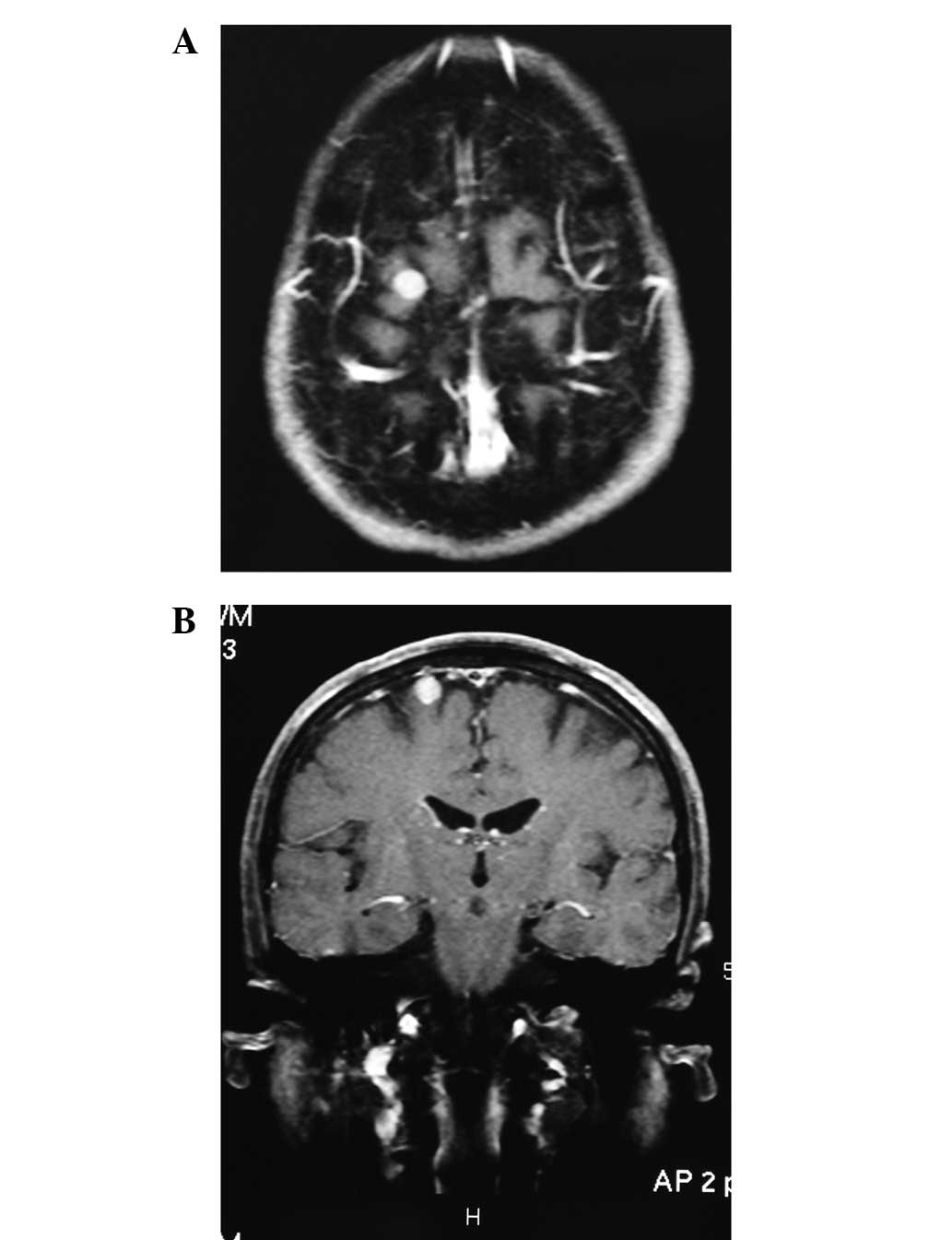
Subsequent to 18 months from the initial diagnosis of SCLC, a
metastatic lesion was observed in the right temporal lobe of the
cerebral hemisphere during a follow-up magnetic resonance imaging
(MRI) scan (Fig. 1). The patient
was administered 30 Gy whole grain irradiation and four courses of
platinum-containing chemotherapy consisting of cisplatin (80
mg/m2, day 1 for 4 weeks) and etoposide (100
mg/m2, days 1–3 for 4 weeks). The patient eventually
succumbed to cardiac disease seven years after the recurrence.
However, no further recurrence was observed until the patient
succumbed.
Case 2
A 67-year-old male was admitted to Mito Medical
Center, University of Tsukuba (Mito, Japan) for an examination of a
chest nodule in the right upper lobe of the lung. On admission, the
laboratory examination revealed a hemoglobin level of 15.0 g/dl, a
hematocrit level of 42.7% and a lactate dehydrogenase level of 223
IU/l. The serum level of NSE was 9.2 ng/ml and the proGRP level was
12.7 pg/ml. A chest X-ray and CT scan revealed a poorly-defined
mass in the upper lobe of the right lung, with an ipsilateral
mediastinal lymph node swelling. A transbronchial biopsy revealed
the tumor to be SCLC. As no metastatic lesion was identified, the
tumor was diagnosed as a limited disease-SCLC. The patient was
treated using chemoradiotherapy (chest irradiation up to 65 Gy and
four courses of chemotherapy) containing cisplatin (80
mg/m2, day 1 for 4 weeks) and etoposide (100
mg/m2, days 1–3 for 4 weeks), which resulted in a CR. A
requirement for prophylactic cranial irradiation (PCI) was
indicated, however, it was not administered to the patient as he
was concerned about a decline in intellectual level due to the
possible neuropsychological problems associated with the treatment.
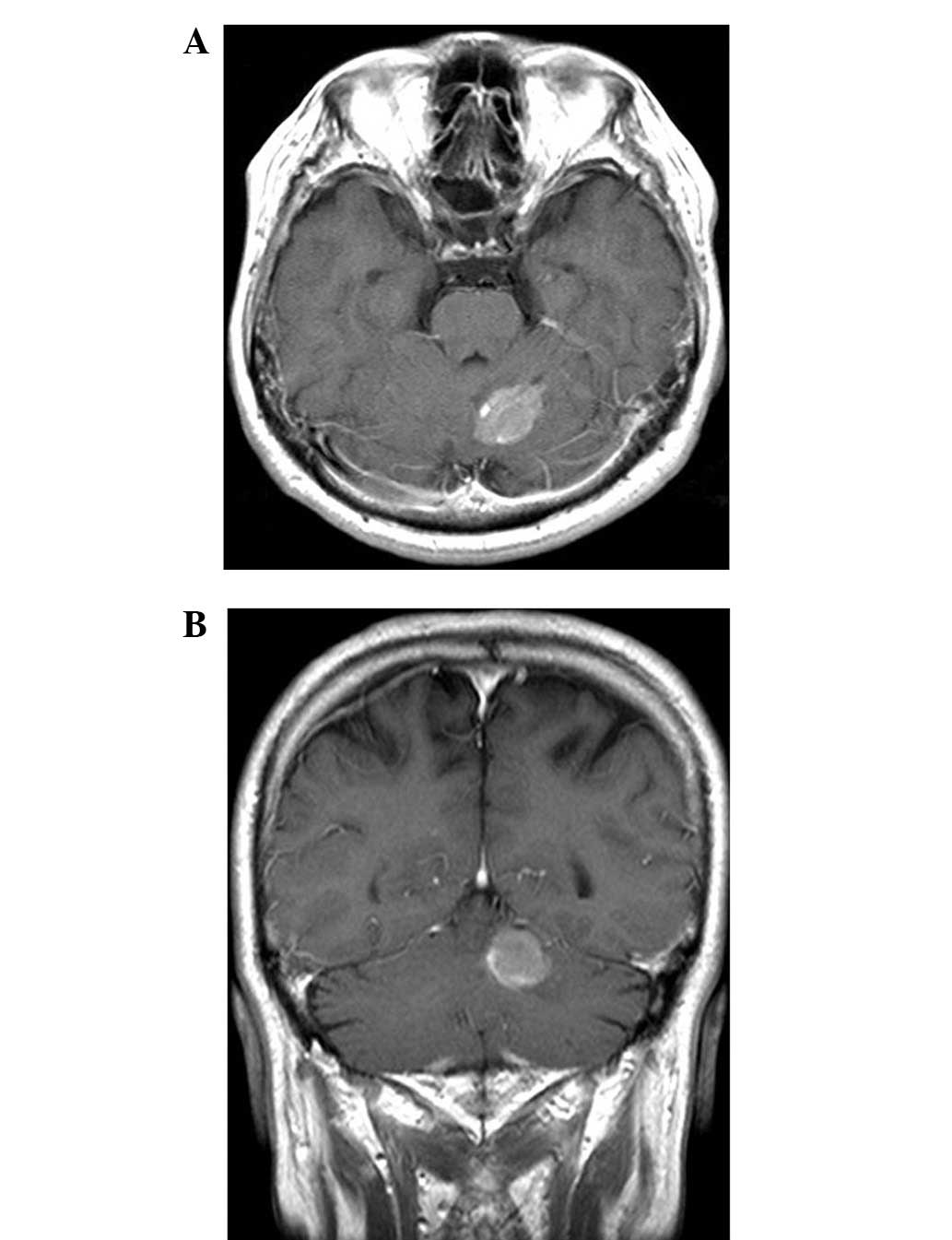
At 14 months after the initial diagnosis of SCLC, a metastatic
lesion was identified in the left cerebellar hemisphere on a
follow-up MRI scan (Fig. 2). The
patient was administered 30 Gy whole grain irradiation and four
courses of platinum-containing chemotherapy. The patient remains
well at 30 months post-recurrence.
Discussion
The late relapse of lung cancer has been a growing
topic of discussion due to the high level of curability and the
possibility of a long survival time in patients. Among the various
malignancies, the late relapse of SCLC is well known but uncommon
(2–5). In the literature, there have been
seven cases of SCLC that have relapsed following ≥10 years of
disease-free survival (6–11). In all the cases, the relapse
occurred in the intrathoracic region, including in the lungs, the
mediastinal lymph nodes or the pleural space. Three cases also
experienced brain metastasis (6,8,10).
Patients with lung adenocarcinomas rarely develop isolated solitary
brain metastasis and certain patients have favorable prognoses
(3–5). The present study describes two cases
of an isolated solitary brain metastasis as a relapse of SCLC. The
literature was searched for the cases of patients with a late
isolated solitary brain metastasis as a relapse of SCLC, and only
one such case was identified (2).
The patient was a long-term survivor of SCLC who was treated with
radiation alone and suffered a rare relapse of SCLC, with a
solitary brain metastasis 6.5 years after the initial treatment
(2). The patient was administered
radiation therapy and succumbed to the brain metastasis 8.5 years
after the initial treatment (2). An
autopsy revealed no tumor recurrence at the primary site and no
distant metastases, with the exception of the brain metastasis. The
histology of the brain tumor was confirmed to be that of SCLC
(2). In the patients of the present
study, the brain metastases were identified during a routine
follow-up brain CT scan or MRI, without any presenting symptoms.
The patients were disease free for more than two years after the
successful treatment using whole brain irradiation and additional
platinum-containing chemotherapy. A pathological confirmation of
the brain metastasis was not obtained. No other disease was located
using systemic imaging evaluation at the time of the identification
of the brain lesion and there was a good response to the whole
brain irradiation and subsequent chemotherapy. The tumors were
evaluated clinically as brain metastases from SCLC. With the
exception of patients with tumors of the lung, there have only been
two patients with isolated brain metastasis as the sole
manifestation of a late relapse (12,13).
One case was of a late onset of isolated intracranial metastasis of
a liposarcoma in the right lower extremity (12). The relapse was identified 26 years
after the initial therapy (12).
The other case was of an isolated brain metastasis in a patient
with breast cancer nine years after the initial therapy (13). In the two cases, additional therapy
was unsuccessful in controlling the disease progression (12,13).
The mechanism of this form of rare metastasis remains to be
elucidated. SCLC cells metastasize at a certain point of their
clinical course and may survive at the metastatic sites, escaping
from the immune mechanism with no rapid growth. Following a period
of long-term dormancy, the cells may then initiate growth again
(14).
PCI has been proposed as a form of treatment in SCLC
that reduces the incidence of brain metastases and significantly
improves overall survival in limited- and extensive disease-SCLC in
patients who respond to first-line treatment (15). It has been suggested that this
treatment may increase neuropsychological syndromes and brain
abnormalities, as indicated by CT scans (16,17).
However, no significant increase in late sequelae has been shown in
clinical trials between patients with and without PCI (14,18,19).
As the patients in the present study had the limited disease form,
they were informed that there were indications that PCI should be
performed at the time of their good response to first-time
treatment. The patients refused PCI for fear of the appearance of
neuropsychological symptoms. However, once diagnosed with an
isolated solitary brain metastasis, the patients underwent whole
brain irradiation. The two patients developed no neuropsychological
symptoms.
To the best of our knowledge, the two cases of
isolated solitary brain metastasis relapse of SCLC of the present
study are the first to have been described. As shown in the present
study, there are patients who may be expected to have long-term
survival following the additional therapy for brain metastasis,
therefore careful follow-up is necessary to detect metastatic
lesions as early as possible, particularly for patients who have
refused PCI.
References
|
1
|
Quan AL, Videtic GM and Suh JH: Brain
metastases in small cell lung cancer. Oncology (Williston Park).
18:961–972; discussion 974, 979–80, 987. 2004.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
Saito Y, Hayakawa K, Mitsuhashi N, et al:
Late relapse of small cell lung cancer treated with radiation
therapy alone - case report. Lung Cancer. 10:319–324. 1994.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
Luketich JD, Martini N, Ginsberg RJ, et
al: Successful treatment of solitary extracranial metastases from
non-small cell lung cancer. Ann Thorac Surg. 60:1609–1611. 1995.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
Shahidi H and Kvale PA: Long-term survival
following surgical treatment of solitary brain metastasis in
non-small cell lung cancer. Chest. 109:271–276. 1996. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Kagohashi K, Satoh H, Yamashita YT and
Sekizawa K: Brain metastasis as the first manifestation of lung
cancer. Am J Med. 114:4202003. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Niiranen A: Long-term survival in small
cell carcinoma of the lung. Eur J Cancer Clin Oncol. 24:749–752.
1988. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Johnson BE, Linnoila RI, Williams JP, et
al: Risk of second aerodigestive cancers increases in patients who
survive free of small-cell lung cancer for more than 2 years. J
Clin Oncol. 13:101–111. 1995.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Lassen U, Osterlind K, Hansen M, et al:
Long-term survival in small-cell lung cancer. Posttreatment
characteristics in patients surviving 5 to 18+ years - an analysis
of 1,714 consecutive patients. J Clin Oncol. 13:1215–1220.
1995.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Kitamoto Y, Hayakawa K, Mitsuhashi N, et
al: Redevelopment of small cell lung cancer after a long
disease-free period: a case report. Jpn J Clin Oncol. 32:30–32.
2002. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Al-Ajam M, Seymour A, Mooty M and Leaf A:
Ten years of disease-free survival between two diagnoses of
small-cell lung cancer: A case report and a literature review. Med
Oncol. 22:89–97. 2005.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Matsui K, Sawa T, Suzuki H, et al: Relapse
of stage I small cell lung cancer ten or more years after the start
of treatment. Jpn J Clin Oncol. 36:457–461. 2006.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Arepally G, Kenyon LC and Lavi E: Late
onset of isolated central nervous system metastasis of liposarcoma
- a case report. Am J Clin Oncol. 19:351–355. 1996. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Issa CM, Semrau R, Kath R and Höffken K:
Isolated brain metastases as the sole manifestation of a late
relapse in breast cancer. J Cancer Res Clin Oncol. 128:61–63. 2002.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Shtivelman E: A link between metastasis
and resistance to apoptosis of variant small cell lung carcinoma.
Oncogene. 14:2167–2173. 1997. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Blanchard P and Le Péchoux C: Prophylactic
cranial irradiation in lung cancer. Curr Opin Oncol. 22:94–101.
2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Fonseca R, O'Neill BP, Foote RL, et al:
Cerebral toxicity in patients treated for small cell carcinoma of
the lung. Mayo Clin Proc. 74:461–465. 1999. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Welzel T, Niethammer A, Mende U, et al:
Diffusion tensor imaging screening of radiation-induced changes in
the white matter after prophylactic cranial irradiation of patients
with small cell lung cancer: first results of a prospective study.
AJNR Am J Neuroradiol. 29:379–383. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
18
|
Wolfson AH, Bae K, Komaki R, et al:
Primary analysis of a phase II randomized trial Radiation Therapy
Oncology Group (RTOG) 0212: impact of different total doses and
schedules of prophylactic cranial irradiation on chronic
neurotoxicity and quality of life for patients with limited-disease
small-cell lung cancer. Int J Radiat Oncol Biol Phys. 81:77–84.
2011.
|
|
19
|
Le Péchoux C, Laplanche A, Faivre-Finn C,
et al; Prophylactic Cranial Irradiation (PCI) Collaborative Group.
Clinical neurological outcome and quality of life among patients
with limited small-cell cancer treated with two different doses of
prophylactic cranial irradiation in the intergroup phase III trial
(PCI99-01, EORTC 22003-08004, RTOG 0212 and IFCT 99-01). Ann Oncol.
22:1154–1163. 2011.
|