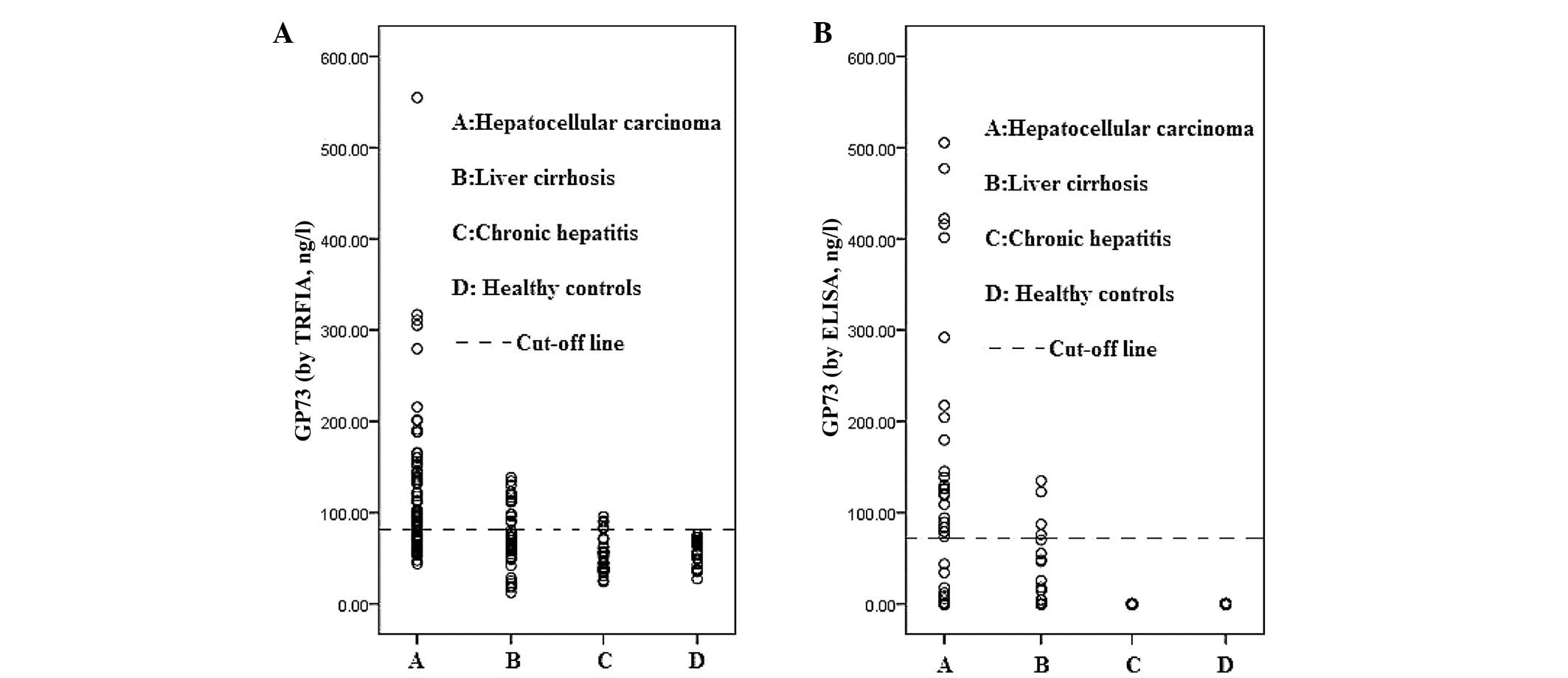
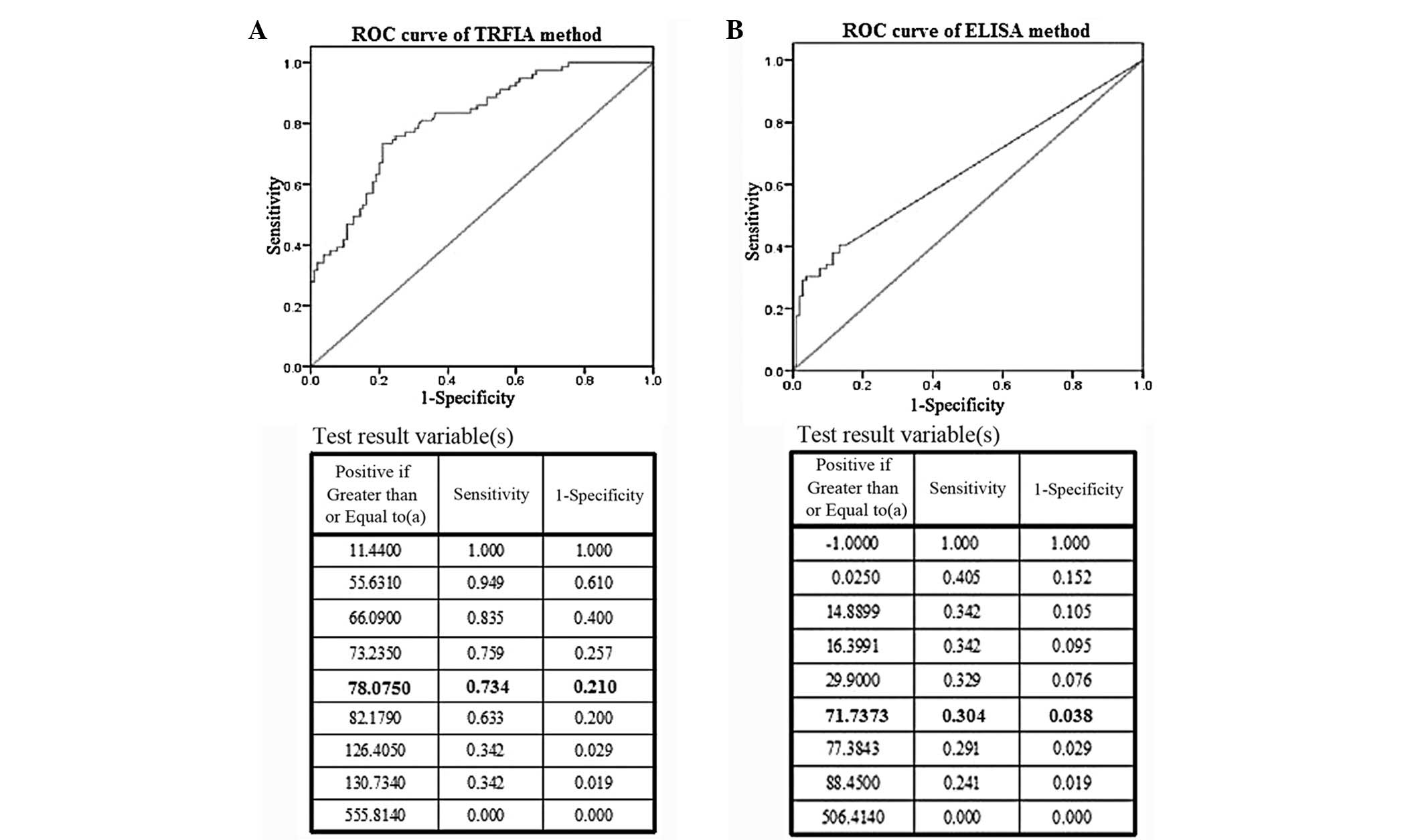
|
1
|
Thun MJ, DeLancey JO, Center MM, Jemal A
and Ward EM: The global burden of cancer: priorities for
prevention. Carcinogenesis. 31:100–110. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
Bosch FX, Ribes J, Cléries R and Díaz M:
Epidemiology of hepatocellular carcinoma. Clin Liver Dis.
9:191–211. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
Fattovich G, Stroffolini T, Zagni I and
Donato F: Hepatocellular carcinoma in cirrhosis: incidence and risk
factors. Gastroenterology. 127(5 Suppl 1): S35–S50. 2004.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
Zoli M, Magalotti D, Bianchi G, Gueli C,
Marchesini G and Pisi E: Efficacy of a surveillance program for
early detection of hepatocellular carcinoma. Cancer. 78:977–985.
1996. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Pateron D, Ganne N, Trinchet JC,
Aurousseau MH, Mal F, Meicler C, et al: Prospective study of
screening for hepatocellular carcinoma in Caucasian patients with
cirrhosis. J Hepatol. 20:65–71. 1994. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Oka H, Tamori A, Kuroki T, Kobayashi K and
Yamamoto S: Prospective study of alpha-fetoprotein in cirrhotic
patients monitored for development of hepatocellular carcinoma.
Hepatology. 19:61–66. 1994. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Malaguarnera G, Giordano M, Paladina I,
Berretta M, Cappellani A and Malaguarnera M: Serum markers of
hepatocellular carcinoma. Dig Dis Sci. 55:2744–2755. 2010.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Zhou Y, Yin X, Ying J and Zhang B: Golgi
protein 73 versus alpha-fetoprotein as a biomarker for
hepatocellular carcinoma: a diagnostic meta-analysis. BMC Cancer.
12:172012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Cui R, He J, Zhang F, Wang B, Ding H, Shen
H, et al: Diagnostic value of protein induced by vitamin K absence
(PIVKAII) and hepatoma-specific band of serum gamma-glutamyl
transferase (GGTII) as hepatocellular carcinoma markers
complementary to alpha-fetoprotein. Br J Cancer. 88:1878–1882.
2003. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
10
|
Kladney RD, Bulla GA, Guo L, Mason AL,
Tollefson AE, Simon DJ, et al: GP73, a novel Golgi-localized
protein upregulated by viral infection. Gene. 249:53–65. 2000.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Kladney RD, Cui X, Bulla GA, Brunt EM and
Fimmel CJ: Expression of GP73, a resident Golgi membrane protein,
in viral and nonviral liver disease. Hepatology. 35:1431–1440.
2002. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Block TM, Comunale MA, Lowman M, Steel LF,
Romano PR, Fimmel C, et al: Use of targeted glycoproteomics to
identify serum glycoproteins that correlate with liver cancer in
woodchucks and humans. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA. 102:779–784. 2005.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Comunale MA, Mattu TS, Lowman MA, Evans
AA, London WT, Semmes OJ, et al: Comparative proteomic analysis of
de-N-glycosylated serum from hepatitis B carriers reveals
polypeptides that correlate with disease status. Proteomics.
4:826–838. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Hu JS, Wu DW, Liang S and Miao XY: GP73, a
resident Golgi glycoprotein, is sensibility and specificity for
hepatocellular carcinoma of diagnosis in a hepatitis B-endemic
Asian population. Med Oncol. 27:339–345. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Marrero JA, Romano PR, Nikolaeva O, Steel
L, Mehta A, Fimmel CJ, et al: GP73, a resident Golgi glycoprotein,
is a novel serum marker for hepatocellular carcinoma. J Hepatol.
43:1007–1012. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Zhu J, Jiang F, Ni HB, Xiao MB, Chen BY,
Ni WK, et al: Combined analysis of serum γ-glutamyl transferase
isoenzyme II, α-L-fucosidase and α-fetoprotein detected using a
commercial kit in the diagnosis of hepatocellular carcinoma. Exp
Ther Med. 5:89–94. 2013.
|
|
17
|
Mao Y, Yang H, Xu H, Lu X, Sang X, Du S,
et al: Golgi protein 73 (GOLPH2) is a valuable serum marker for
hepatocellular carcinoma. Gut. 59:1687–1693. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
Saffroy R, Pham P, Reffas M, Takka M,
Lemoine A and Debuire B: New perspectives and strategy research
biomarkers for hepatocellular carcinoma. Clin Chem Lab Med.
45:1169–1179. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
Xu KC, Meng XY, Shi YC, Ge ZJ, Ye L, Yu ZJ
and Yang DM: The diagnostic value of a hepatoma-specific band of
serum gamma-glutamyl transferase. Int J Cancer. 36:667–669. 1985.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
Xu K, Meng XY, Wu JW, Shen B, Shi YC and
Wei Q: Diagnostic value of serum gamma-glutamyl transferase
isoenzyme for hepatocellular carcinoma: a 10-year study. Am J
Gastroenterol. 87:991–995. 1992.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
Liu X, Wan X, Li Z, Lin C, Zhan Y and Lu
X: Golgi protein 73(GP73), a useful serum marker in liver diseases.
Clin Chem Lab Med. 49:1311–1316. 2011.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22
|
Sun Y, Yang H, Mao Y, Xu H, Zhang J, Li G,
et al: Increased Golgi protein 73 expression in hepatocellular
carcinoma tissue correlates with tumor aggression but not survival.
J Gastroenterol Hepatol. 26:1207–1212. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23
|
Kawamoto S, Moriwaki K, Nakagawa T, Terao
M, Shinzaki S, Yamane-Ohnuki N, et al: Overexpression of
α1,6-fucosyltransferase in hepatoma enhances expression of Golgi
phosphoprotein 2 in a fucosylation-independent manner. Int J Oncol.
39:203–208. 2011.
|