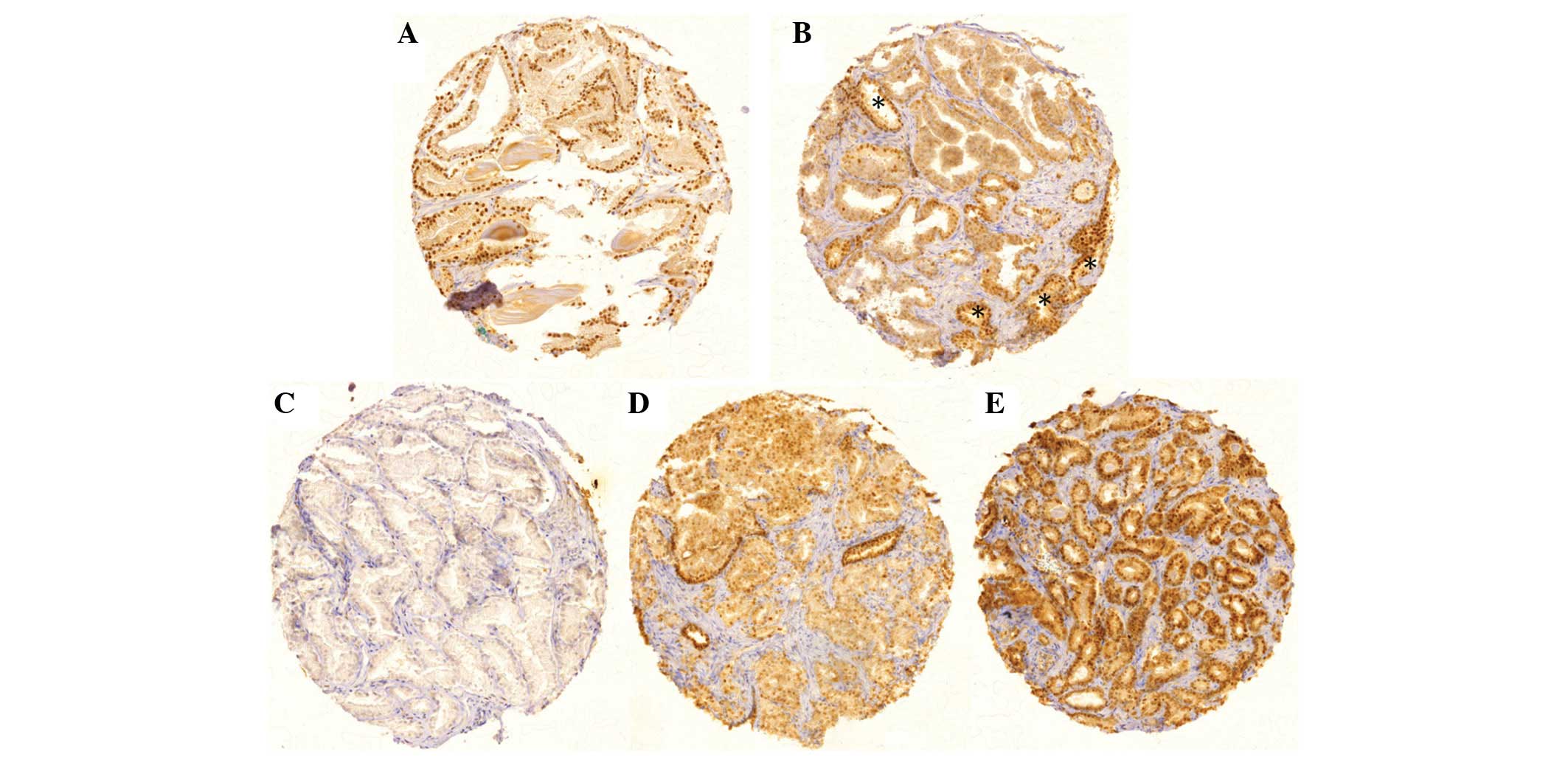
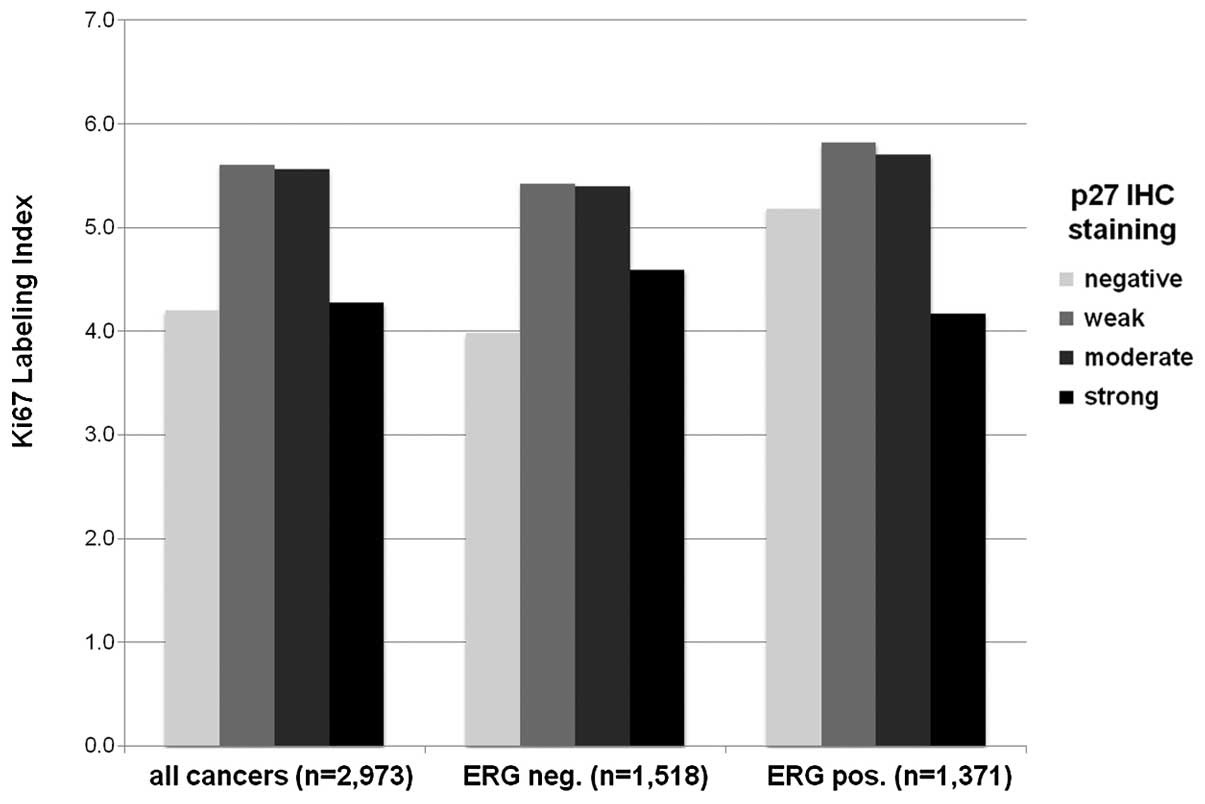
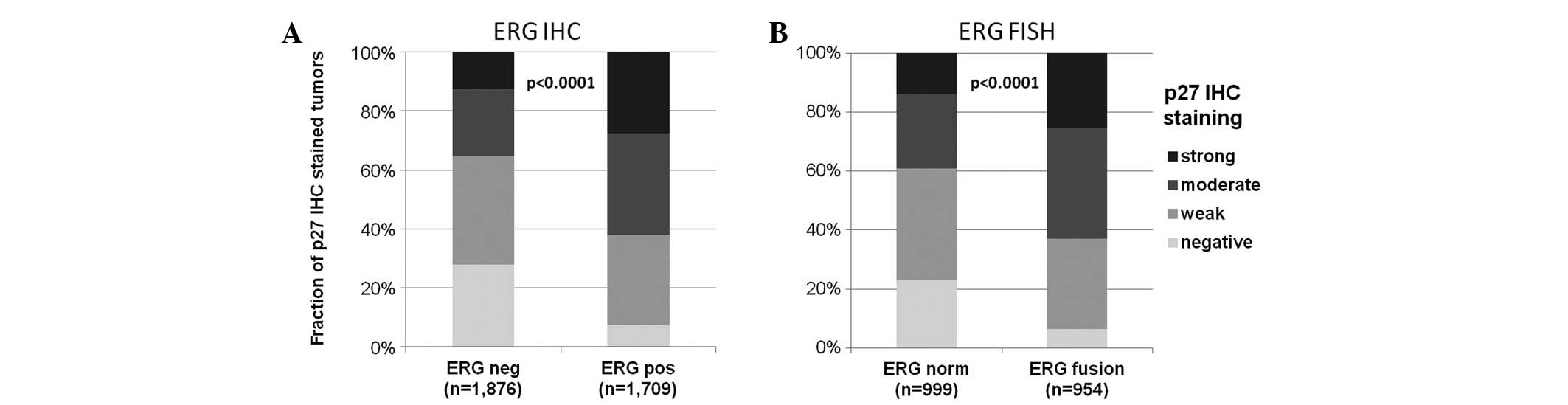
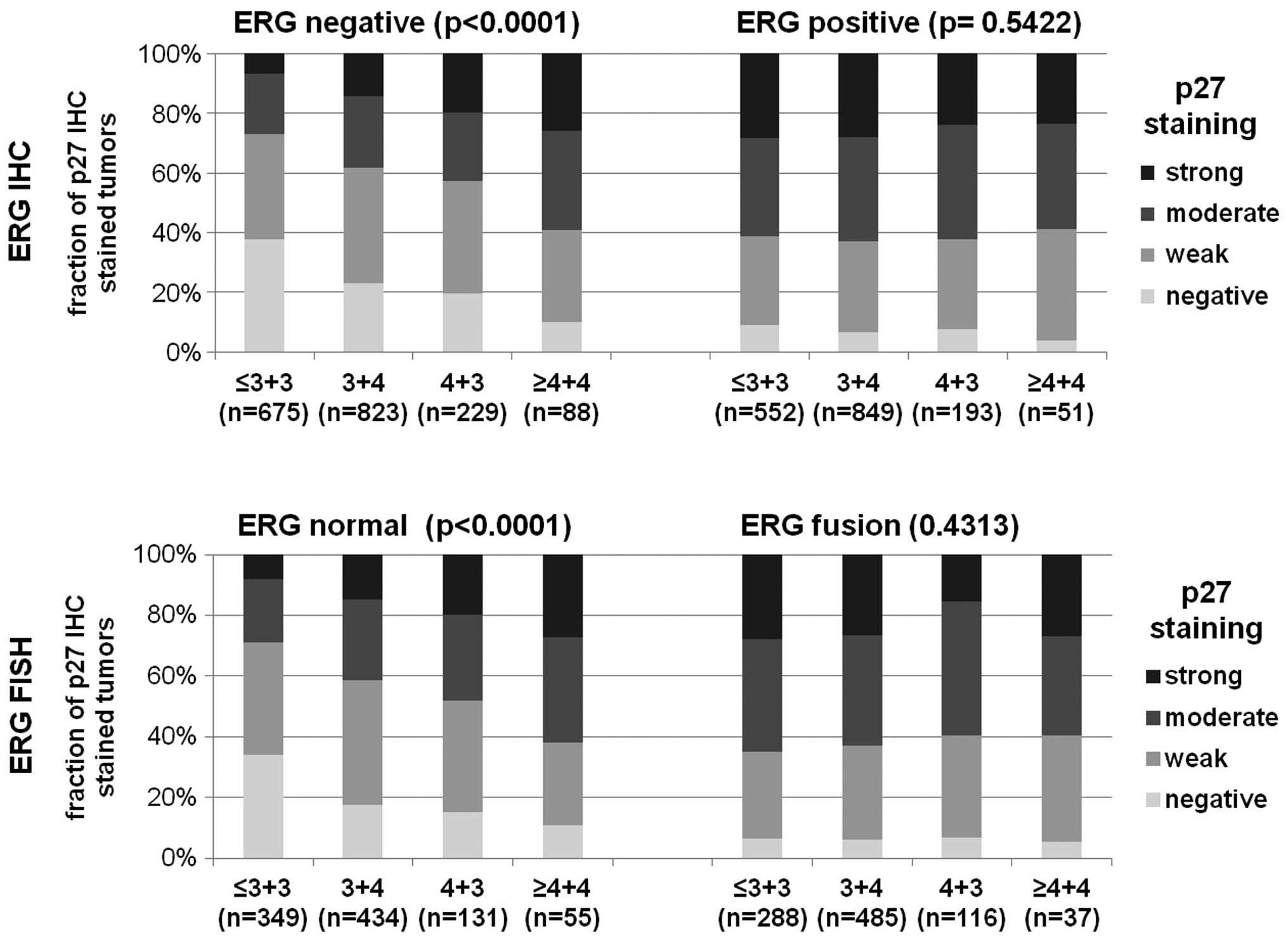
|
1
|
Cooperberg MR, Cowan J, Broering JM and
Carroll PR: High-risk prostate cancer in the United States,
1990–2007. World J Urol. 26:211–218. 2008.
|
|
2
|
Samaratunga H and Epstein JI: What is the
molecular pathology of low-risk prostate cancer? World J Urol.
26:431–436. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
Rubin MA, Maher CA and Chinnaiyan AM:
Common gene rearrangements in prostate cancer. J Clin Oncol.
29:3659–3668. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
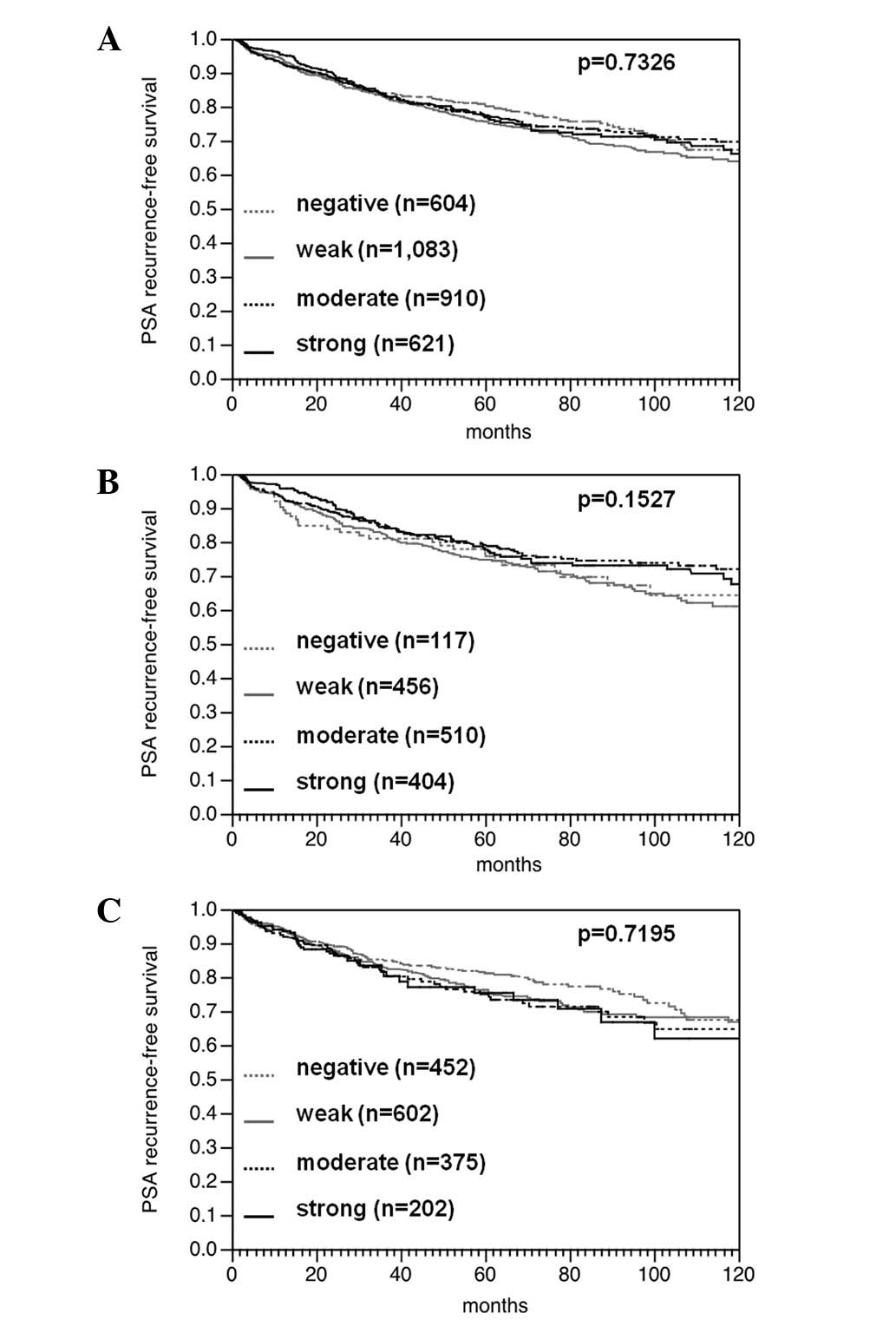
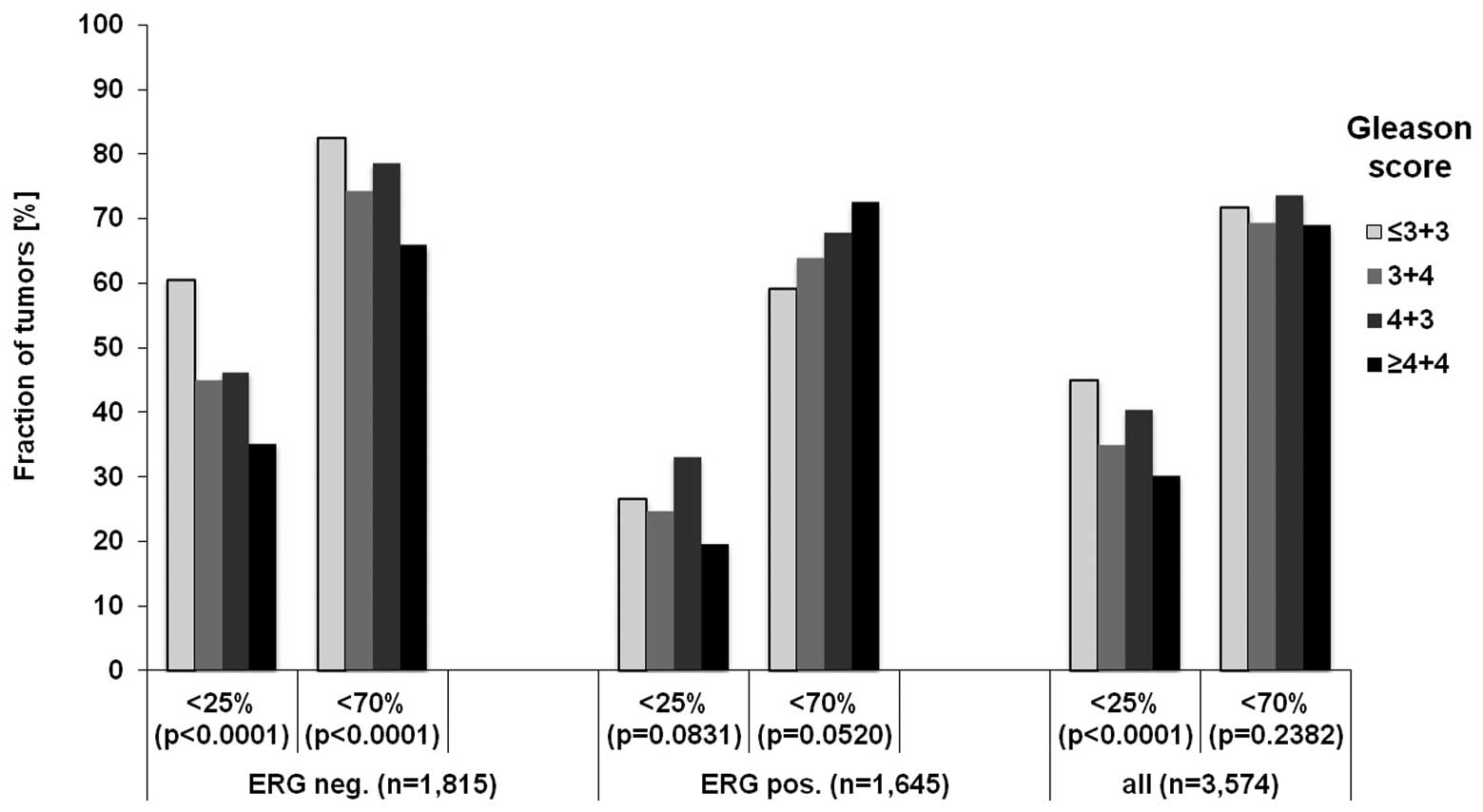
|
Tsihlias J, Kapusta L and Slingerland J:
The prognostic significance of altered cyclin-dependent kinase
inhibitors in human cancer. Annu Rev Med. 50:401–423. 1999.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Wander SA, Zhao D and Slingerland JM: p27:
a barometer of signaling deregulation and potential predictor of
response to targeted therapies. Clin Cancer Res. 17:12–18. 2011.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Swanson GP and Quinn D: Using molecular
markers to help predict who will fail after radical prostatectomy.
Prostate Cancer. 2011:2901602011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Tsihlias J, Kapusta LR, DeBoer G, et al:
Loss of cyclin-dependent kinase inhibitor p27Kip1 is a novel
prognostic factor in localized human prostate adenocarcinoma.
Cancer Res. 58:542–548. 1998.
|
|
8
|
Vis AN, Noordzij MA, Fitoz K, Wildhagen
MF, Schröder FH and van der Kwast TH: Prognostic value of cell
cycle proteins p27(kip1) and MIB-1, and the cell adhesion protein
CD44s in surgically treated patients with prostate cancer. J Urol.
164:2156–2161. 2000. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Vis AN, van Rhijn BW, Noordzij MA,
Schröder FH and van der Kwast TH: Value of tissue markers
p27(kip1), MIB-1, and CD44s for the pre-operative prediction of
tumour features in screen-detected prostate cancer. J Pathol.
197:148–154. 2002. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Yang RM, Naitoh J, Murphy M, et al: Low
p27 expression predicts poor disease-free survival in patients with
prostate cancer. J Urol. 159:941–945. 1998. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Revelos K, Petraki C, Gregorakis A, et al:
p27(kip1) and Ki-67 (MIB1) immunohistochemical expression in
radical prostatectomy specimens of patients with clinically
localized prostate cancer. In Vivo. 19:911–920. 2005.
|
|
12
|
Guo Y, Sklar GN, Borkowski A and Kyprianou
N: Loss of the cyclin-dependent kinase inhibitor p27(Kip1) protein
in human prostate cancer correlates with tumor grade. Clin Cancer
Res. 3:2269–2274. 1997.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Kuczyk M, Machtens S, Hradil K, et al:
Predictive value of decreased p27Kip1 protein expression for the
recurrence-free and long-term survival of prostate cancer patients.
Br J Cancer. 81:1052–1058. 1999. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
14
|
Kuczyk MA, Bokemeyer C, Hartmann J, et al:
Predictive value of altered p27Kip1 and p21WAF/Cip1 protein
expression for the clinical prognosis of patients with localized
prostate cancer. Oncol Rep. 8:1401–1407. 2001.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Cordon-Cardo C, Koff A, Drobnjak M, et al:
Distinct altered patterns of p27KIP1 gene expression in benign
prostatic hyperplasia and prostatic carcinoma. J Natl Cancer Inst.
90:1284–1291. 1998. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Cote RJ, Shi Y, Groshen S, et al:
Association of p27Kip1 levels with recurrence and survival in
patients with stage C prostate carcinoma. J Natl Cancer Inst.
90:916–920. 1998. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Cheville JC, Lloyd RV, Sebo TJ, et al:
Expression of p27kip1 in prostatic adenocarcinoma. Mod Pathol.
11:324–328. 1998.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
Erdamar S, Yang G, Harper JW, et al:
Levels of expression of p27KIP1 protein in human prostate and
prostate cancer: an immunohistochemical analysis. Mod Pathol.
12:751–755. 1999.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
Halvorsen OJ, Haukaas SA and Akslen LA:
Combined loss of PTEN and p27 expression is associated with tumor
cell proliferation by Ki-67 and increased risk of recurrent disease
in localized prostate cancer. Clin Cancer Res. 9:1474–1479.
2003.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
Nassif AE and Tambara Filho R:
Immunohistochemistry expression of tumor markers CD34 and P27 as a
prognostic factor of clinically localized prostate adenocarcinoma
after radical prostatectomy. Rev Col Bras Cir. 37:338–344.
2010.
|
|
21
|
Vlachostergios PJ, Karasavvidou F, Kakkas
G, et al: Lack of prognostic significance of p16 and p27 after
radical prostatectomy in hormone-naïve prostate cancer. J Negat
Results Biomed. 11:22012.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22
|
Wu TT, Wang JS, Jiaan BP, et al: Role of
p21(WAF1) and p27(KIP1) in predicting biochemical recurrence for
organ-confined prostate adenocarcinoma. J Chin Med Assoc. 70:11–15.
2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23
|
Minner S, Enodien M, Sirma H, et al: ERG
status is unrelated to PSA recurrence in radically operated
prostate cancer in the absence of antihormonal therapy. Clin Cancer
Res. 17:5878–5888. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24
|
Minner S, Jessen B, Stiedenroth L, et al:
Low level HER2 overexpression is associated with rapid tumor cell
proliferation and poor prognosis in prostate cancer. Clin Cancer
Res. 16:1553–1560. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
25
|
Thomas GV, Schrage MI, Rosenfelt L, et al:
Preoperative prostate needle biopsy p27 correlates with subsequent
radical prostatectomy p27, Gleason grade and pathological stage. J
Urol. 164:1987–1991. 2000. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
26
|
Mukai M, Dong Q, Hardy MP, Kiyokawa H,
Peterson RE and Cooke PS: Altered prostatic epithelial
proliferation and apoptosis, prostatic development, and serum
testosterone in mice lacking cyclin-dependent kinase inhibitors.
Biol Reprod. 73:951–958. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
27
|
Shen MM and Abate-Shen C: Molecular
genetics of prostate cancer: new prospects for old challenges.
Genes Dev. 24:1967–2000. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
28
|
Sreenath TL, Dobi A, Petrovics G and
Srivastava S: Oncogenic activation of ERG: A predominant mechanism
in prostate cancer. J Carcinog. 10:372011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
29
|
Clark JP and Cooper CS: ETS gene fusions
in prostate cancer. Nat Rev Urol. 6:429–439. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
30
|
Setlur SR, Mertz KD, Hoshida Y, et al:
Estrogen-dependent signaling in a molecularly distinct subclass of
aggressive prostate cancer. J Natl Cancer Inst. 100:815–825. 2008.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
31
|
Jhavar S, Brewer D, Edwards S, et al:
Integration of ERG gene mapping and gene-expression profiling
identifies distinct categories of human prostate cancer. BJU Int.
103:1256–1269. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
32
|
Brase JC, Johannes M, Mannsperger H, et
al: TMPRSS2-ERG -specific transcriptional modulation is associated
with prostate cancer biomarkers and TGF-β signaling. BMC Cancer.
11:5072011.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
33
|
Taylor BS, Schultz N, Hieronymus H, et al:
Integrative genomic profiling of human prostate cancer. Cancer
Cell. 18:11–22. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
34
|
Müller J, Ehlers A, Burkhardt L, et al:
Loss of p(Ser2448)-mTOR expression is linked to adverse prognosis
and tumor progression in ERG-fusion-positive cancers. Int J Cancer.
132:1333–1340. 2012.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
35
|
Minner S, Wittmer C, Graefen M, et al:
High level PSMA expression is associated with early PSA recurrence
in surgically treated prostate cancer. Prostate. 71:281–288. 2011.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
36
|
Tennstedt P, Köster P, Bruchmann A, et al:
The impact of the number of cores on tissue microarray studies
investigating prostate cancer biomarkers. Int J Oncol. 40:261–268.
2012.
|
|
37
|
El Gammal AT, Bruchmann M, Zustin J, et
al: Chromosome 8p deletions and 8q gains are associated with tumor
progression and poor prognosis in prostate cancer. Clin Cancer Res.
16:56–64. 2010.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
38
|
Schlomm T, Iwers L, Kirstein P, et al:
Clinical significance of p53 alterations in surgically treated
prostate cancers. Mod Pathol. 21:1371–1378. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
39
|
Schlomm T, Kirstein P, Iwers L, et al:
Clinical significance of epidermal growth factor receptor protein
overexpression and gene copy number gains in prostate cancer. Clin
Cancer Res. 13:6579–6584. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|