Introduction
Computed tomography (CT)-guided radiofrequency
ablation (RFA) is a widespread technique that is used to treat
selected liver malignancies where surgery is contraindicated or as
an adjunct to it. During recent years, the indications for RFA
application have been enhanced to include the palliative treatment
of cancer-related pain, particularly in patients with bone
malignancies (1). However, to date,
few studies have dealt with the use of RFA to relieve pain from
soft-tissue malignancies that are refractory to conventional
therapeutic modalities (2–5). The present study aimed to describe the
outcome following the use of RFA for the palliative management of a
painful supraclavicular soft-tissue metastasis of a skin melanoma
invading the brachial plexus. Written informed consent was obtained
from the patient's family.
Case report
A 38-year-old Caucasian male was referred to the
Department of Computed Tomography and Invasive Radiology,
Konstantopouleion-Agia Olga General Hospital (Athens, Greece) due
to a painful right supraclavicular soft-tissue metastasis of a skin
melanoma that was unresponsive to conventional therapy. The patient
had undergone a surgical excision of the skin melanoma, which was
located at the right scapular area, and a simultaneous resection of
the ipsilateral axillary metastatic nodes was performed 17 months
earlier, followed by a 6-month regimen of immunotherapy with
interferon-α and chemotherapy. At 14 months post-surgery, pain and
a degree of numbness gradually developed in the right upper limb.
Magnetic resonance imaging was performed and revealed a metastatic
mass of 7-cm in diameter in the right supraclavicular area. The
patient was subsequently administered 10 sessions of external beam
radiation therapy for a total dose of 48 Gy that proved ineffective
to relieve the symptoms or reduce the size of the mass.
Furthermore, the pain was unresponsive to aggressive therapy with
escalating doses of narcotic analgesics. A post-radiotherapy
CT-scan confirmed a 7-cm mass that occupied the right
supraclavicular space. Following a surgical consultation, the
lesion was considered to be inoperable due to brachial nerve plexus
infiltration, as indicated by the symptomatology.
Percutaneous RFA of the tumor under CT-guidance was
therefore decided upon. The procedure was performed under local
anesthesia assisted by oral benzodiazepines. Slices (5 mm) were
obtained using spiral CT. An Electrotom HiTT® 106
(Berchtold Holding GmbH, Tuttlingen, Germany) and a
high-frequency-induced thermotherapy needle applicator (EZ 703-20;
diameter, 2.0 mm; shaft length, 150 mm; and electrode length, 20
mm) perfusable with normal saline solution were used. The patient
was placed in a prone position and the needle tip was proceeded
gradually from the posterior side of the trapezius muscle to the
tumor mass. Care was taken to gently change the direction of the
shaft in case of stimulation of the brachial plexus by contact.
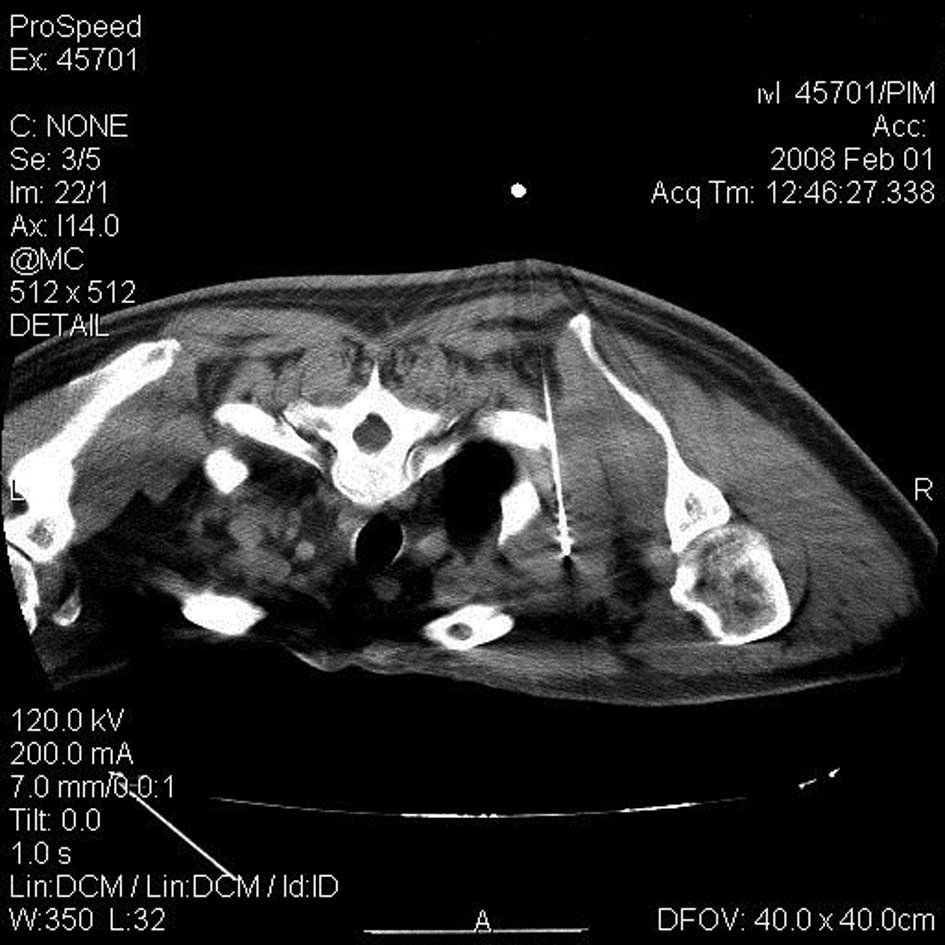
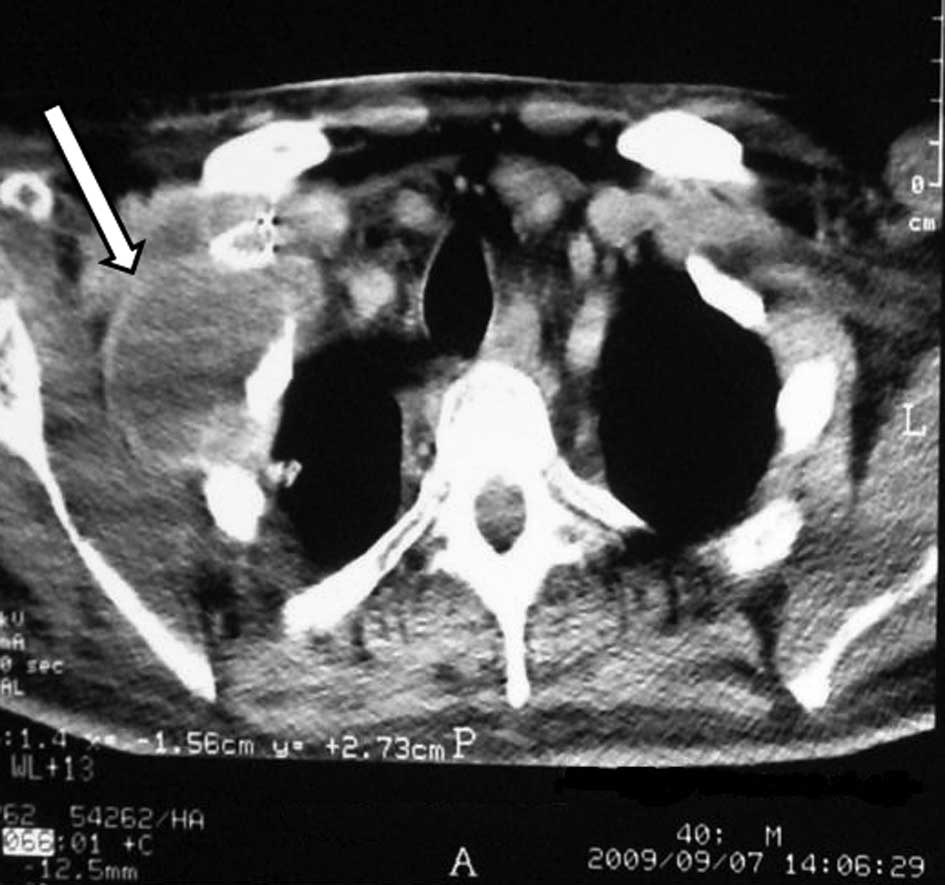
When the needle tip was positioned at the center of the lesion
(Fig. 1), 50 W radiofrequency
energy was applied for a total duration of 10 min with an
intermittent interval time of 9 min at 5 min. A CT image was
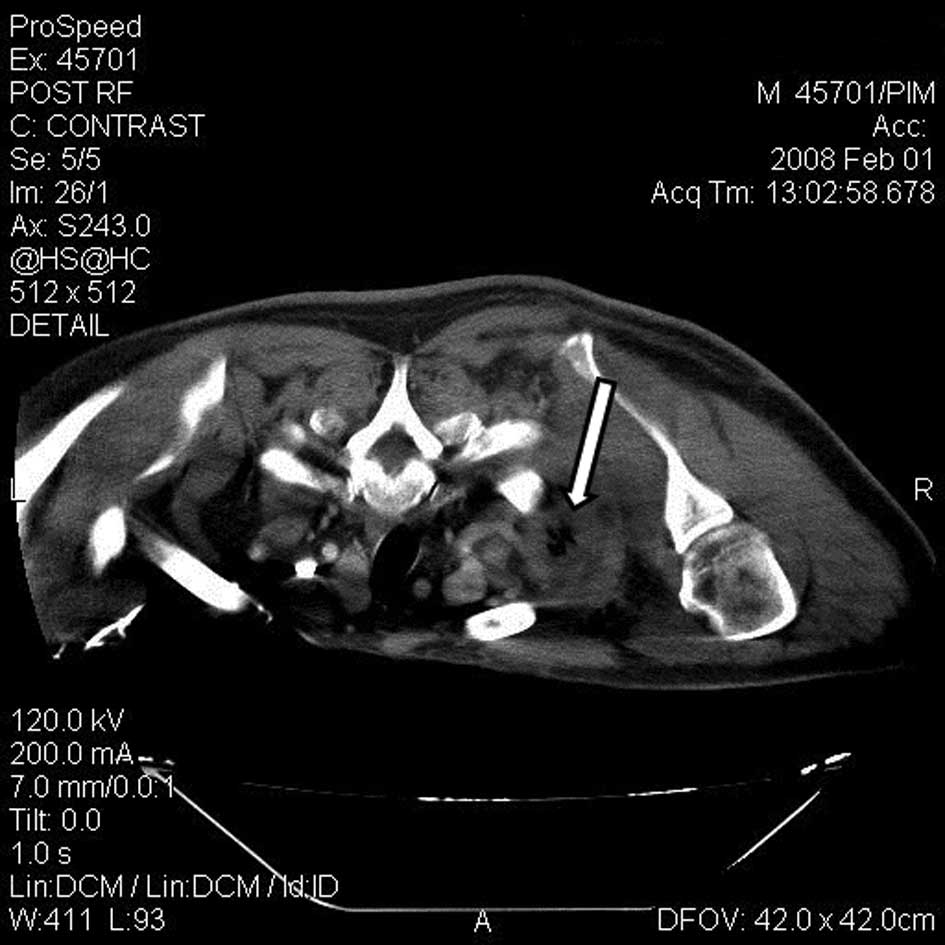
obtained at this interval to control tumor necrosis. Subsequent
dual-phase CT axial images at the end of the procedure confirmed
thermal necrosis of the tumor (Fig.
2). The patient remained hospitalized for 24 h.
Four days later, the pain decreased to a level that
was lower than prior to the RFA and the patient discontinued the
narcotic medication. The degree of upper limb numbness remained
unaffected. Overall, the patient demonstrated an improvement in the
daily quality of life following the thermal ablation of the lesion.
The overall satisfaction for pain control following the procedure
was 8/10 according to the visual analogue scale (VAS). Accordingly,
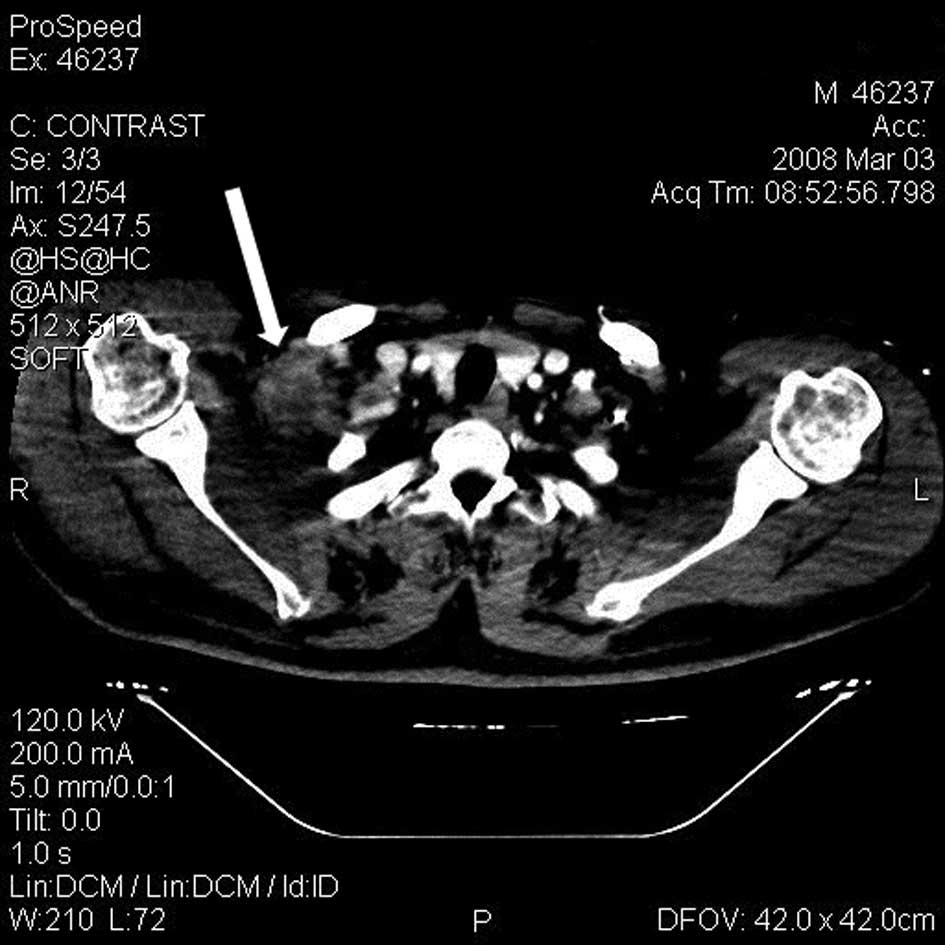
a CT scan at the one-month post-RFA follow-up revealed shrinkage of
the initial mass to 3 cm in diameter (Fig. 3). The patient declined to undergo a
control CT scan at 6 months due to a lack of significant pain.
At 19 months post-RFA, the patient presented with a
gradual reappearance of the pain in the same area. However, the
limited upper limb motility remained unchanged. A CT scan was
obtained that revealed an 8-cm soft-tissue local recurrence with
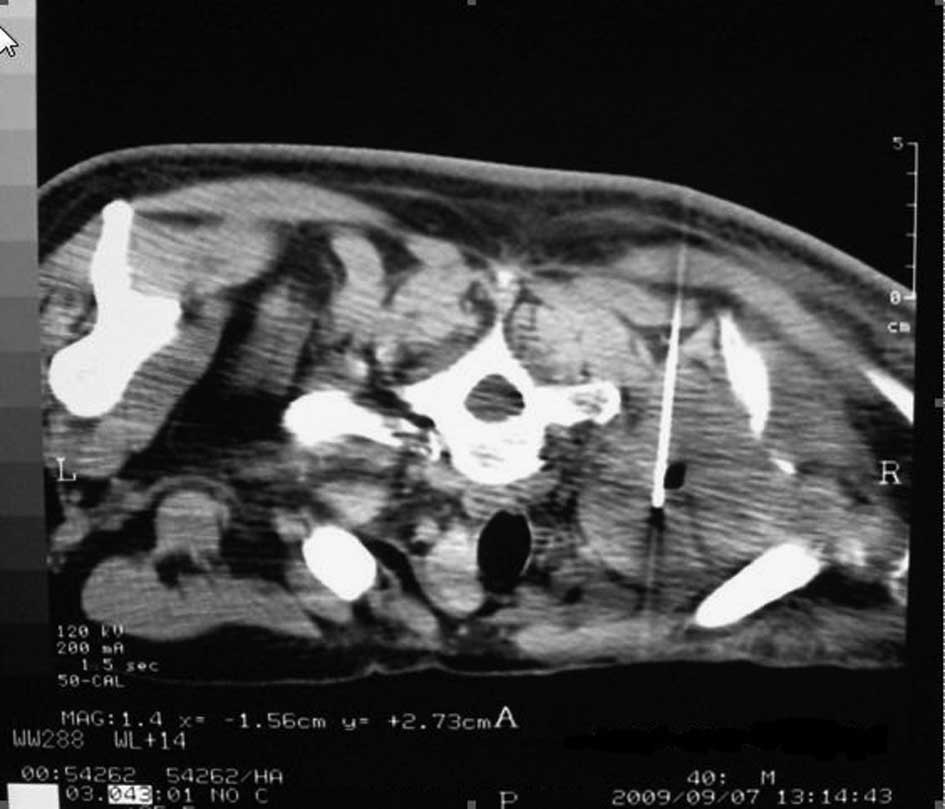
identical imaging signs as prior to the RFA. A repeat RFA was
performed in the same manner as described previously (Figs. 4 and 5) and a follow-up CT scan at one month
post-RFA revealed mass necrosis without shrinkage. Although the
pain relief following the second RFA was less than following the
initial procedure, the patient confirmed a clinical benefit that
corresponded to 6/10 satisfaction for pain control according to the
VAS. At 2 months after the repeat RFA, the patient presented with
tolerable pain that was easily controlled with minor oral
analgesics.
Discussion
Cancer-related pain and narcotic analgesic
dependency is of major concern in the quality of life of patients
with soft-tissue metastasis that involves a major nerve plexus.
Several treatment modalities, including chemotherapy, radiotherapy
and when possible, surgical excision, are employed to control the
disease and its symptoms (6).
However once they become ineffective, escalating doses of narcotics
are required (7). The present study
describes a patient with a supraclavicular soft-tissue metastasis
invading the brachial plexus, which caused severe debilitating
symptoms of pain and numbness in the upper limb. The lesion was
unresponsive to chemotherapy and radiotherapy, and an effective
surgical excision was not considered feasible due to nerve
infiltration. As a result, the patient required considerable doses
of strong opioids that further compromised his quality of life.
According to the present case and the existing
literature (2–5), RFA appears efficient in the palliation
of symptoms of painful soft-tissue metastatic malignancies when
other therapies are ineffective. Sanou et al(5) reported a series of 12 patients with
painful primary or secondary soft-tissue neoplasms in various
locations of the body who were treated with RFA and achieved
partial or complete response in the short- and the long-term. In
particular, a patient with a 10-cm metastatic bronchial cancer in
the scapular region involving the brachial plexus had 60%
short-term palliation of the pain according to the VAS. The
durability of the effect of the RFA was not documented in this case
since the patient succumbed due to complications of the disease.
RFA is a minimally invasive, repeatable and low-cost procedure. In
numerous cases, RFA may be performed under local anesthesia and has
the advantage of a short hospital stay. RFA ablation relieved the
present patient from narcotic analgesic use and side-effects,
resulting in a substantial improvement in the quality of life. The
palliative effect of RFA is not permanent, but may provide relief
for a significant period of time, as symptoms in this case only
recurred after 19 months.
However, the value of RFA to treat painful
metastasis has not been studied sufficiently in order to assess the
exact role of the procedure in palliation and to standardize its
precise therapeutic indications. To the best of our knowledge, this
is the first case that is described in the literature with regard
to the application of RFA in the supraclavicular fossa to alleviate
neoplastic compressive symptoms. Further research is required to
evaluate the effectiveness of RFA in relieving pain from
soft-tissue metastasis in this area as a first-line approach
compared with chemoradiation and/or medical treatment with narcotic
analgesics. RFA is therefore a promising method, but one that
currently should be used for selected cases where conventional
therapies have failed. Furthermore, the present study demonstrated
that the procedure may be safely applied to a disease that is
localized to the supraclavicular space. Likewise, RFA may be
beneficial in the palliation of metastases from other primary
cancers that commonly arise there.
In conclusion, in the present case of painful
supraclavicular soft-tissue metastasis invading the brachial
plexus, RFA proved to be feasible and offered substantial
palliation of the symptoms, freedom from narcotic analgesic use and
improvements to the quality of life. Further investigation is
essential for an improved definition of the role of RFA in the
palliation of metastatic disease of the supraclavicular fossa.
References
|
1
|
Dupuy DE, Liu D, Hartfeil D, et al:
Percutaneous radiofrequency ablation of painful osseous metastases:
a multicenter American College of Radiology Imaging Network trial.
Cancer. 116:989–997. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
2
|
Thanos L, Mylona S, Kalioras V, Pomoni M
and Batakis N: Palliation of painful perineal metastasis treated
with radiofrequency thermal ablation. Cardiovasc Intervent Radiol.
28:381–383. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
Locklin JK, Mannes A, Berger A and Wood
BJ: Palliation of soft tissue cancer pain with radiofrequency
ablation. J Support Oncol. 2:439–445. 2004.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
Nair RT, van Sonnenberg E, Shankar S,
Morrison PR, Gill RR, Tuncali K and Silverman SG: Visceral and
soft-tissue tumors: radiofrequency and alcohol ablation for pain
relief - initial experience. Radiology. 248:1067–1076. 2008.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Sanou R, Bazin C, Krakowski I, et al:
Radiofrequency ablation for palliation of soft tissue tumor pain. J
Radiol. 91:281–286. 2010.(In French).
|
|
6
|
Lam L, Krementz E, McGinness C and Godfrey
R: Melanoma of the clavicular region: multimodal treatment. Arch
Surg. 136:1054–1058. 2001. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Hanks GW, Conno F, Cherny N, et al; Expert
Working Group of the Research Network of the European Association
for Palliative Care. Morphine and alternative opioids in cancer
pain: the EAPC recommendations. Br J Cancer. 84:587–593. 2001.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|