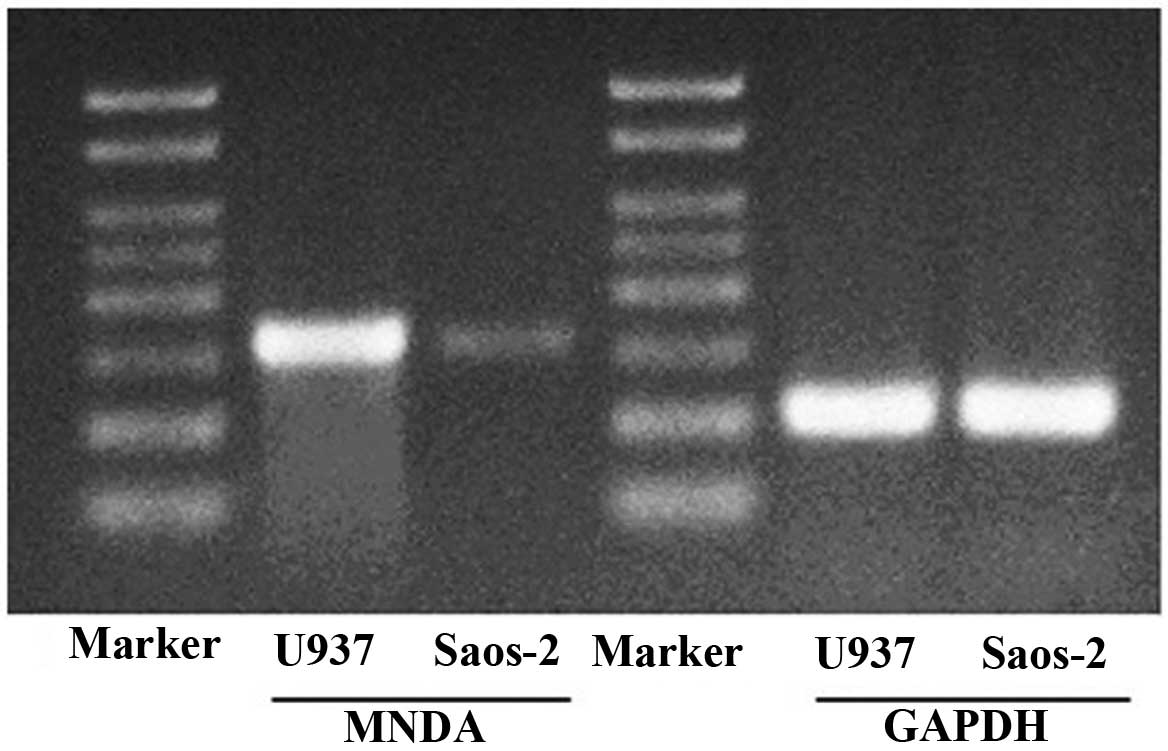
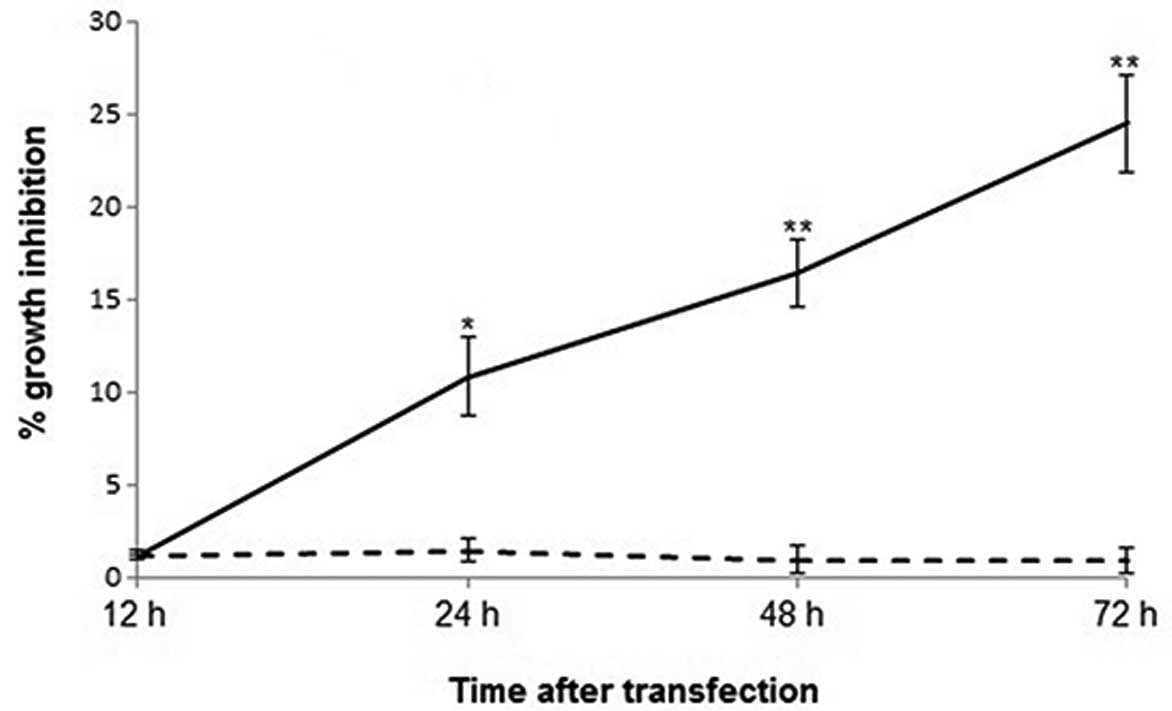
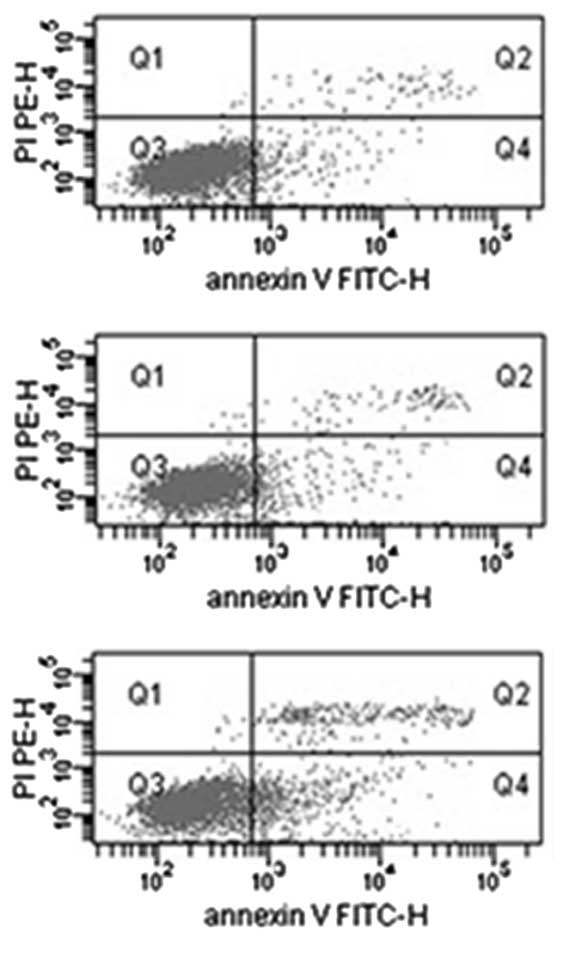
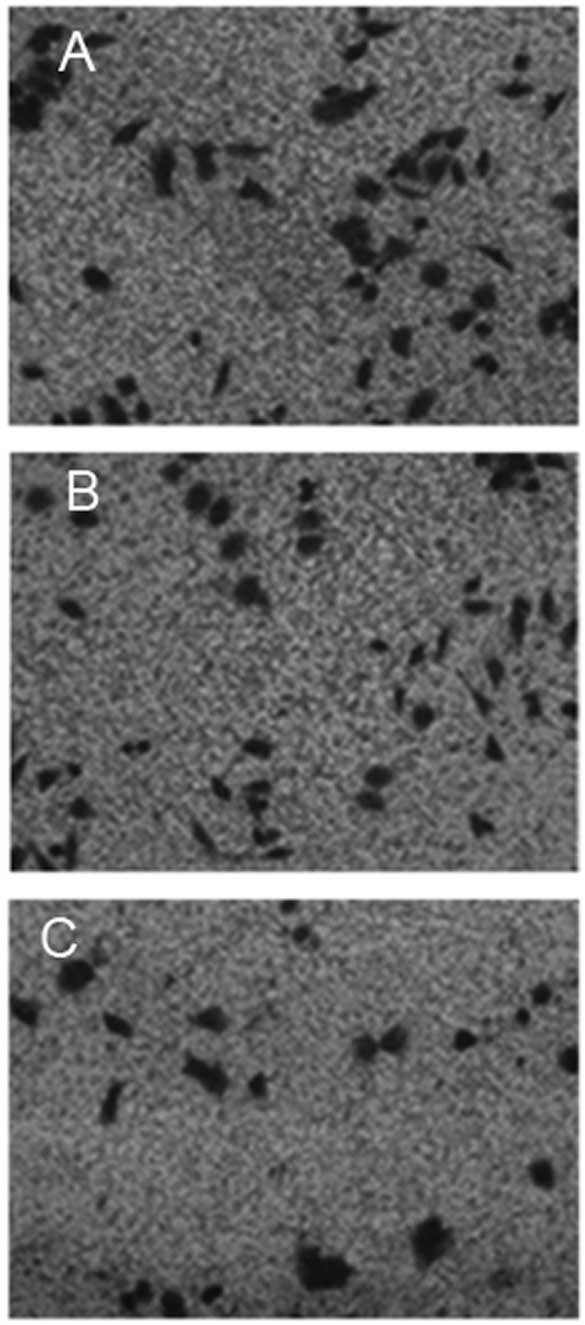
|
1
|
Longhi A, Errani C, De Paolis M, Mercuri M
and Bacci G: Primary bone osteosarcoma in the pediatric age: state
of the art. Cancer Treat Rev. 32:423–436. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
Ottaviani G and Jaffe N: The epidemiology
of osteosarcoma. Cancer Treat Res. 152:3–13. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
3
|
Mirabello L, Troisi RJ and Savage SA:
International osteosarcoma incidence patterns in children and
adolescents, middle ages and elderly persons. Int J Cancer.
125:229–234. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
Mirabello L, Troisi RJ and Savage SA:
Osteosarcoma incidence and survival rates from 1973 to 2004: data
from the Surveillance, Epidemiology, and End Results Program.
Cancer. 115:1531–1543. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Stiller CA and Parkin DM: Geographic and
ethnic variations in the incidence of childhood cancer. Brit Med
Bull. 52:682–703. 1996. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Stiller CA: International patterns of
cancer incidence in adolescents. Cancer Treat Rev. 33:631–645.
2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Mavrogenis AF, Rossi G, Palmerini E, et
al: Palliative treatments for advanced osteosarcoma. J BUON.
17:436–445. 2012.
|
|
8
|
Bacci G, Ferrari S, Bertoni F, et al:
Long-term outcome for patients with nonmetastatic osteosarcoma of
the extremity treated at the istituto ortopedico rizzoli according
to the istituto ortopedico rizzoli/osteosarcoma-2 protocol: an
updated report. J Clin Oncol. 18:4016–4027. 2000.
|
|
9
|
Bielack S, Carrle D and Casali PG; the
ESMO Guidelines Working Group. Osteosarcoma: ESMO clinical
recommendations for diagnosis, treatment and follow-up. Ann Oncol.
20:137–139. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Bellos F, Alpermann T, Gouberman E, et al:
Evaluation of flow cytometric assessment of myeloid nuclear
differentiation antigen expression as a diagnostic marker for
myelodysplastic syndromes in a series of 269 patients. Cytometry B
Clin Cytom. 82:295–304. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
11
|
Asefa B, Klarmann KD, Copeland NG, Gilbert
DJ, Jenkins NA and Keller JR: The interferon-inducible p200 family
of proteins: a perspective on their roles in cell cycle regulation
and differentiation. Blood Cells Mol Dis. 32:155–167. 2004.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Choubey D, Duan X, Dickerson E, et al:
Interferon-inducible p200-family proteins as novel sensors of
cytoplasmic DNA: role in inflammation and autoimmunity. J
Interferon Cytokine Res. 30:371–380. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Parmar S and Platanias LC: Interferons:
mechanisms of action and clinical applications. Curr Opin Oncol.
15:431–439. 2003. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
14
|
Zhang K, Kagan D, DuBois W, et al: Mndal,
a new interferon-inducible family member, is highly polymorphic,
suppresses cell growth, and may modify plasmacytoma susceptibility.
Blood. 114:2952–2960. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
15
|
Briggs RC, Shults KE, Flye LA, et al:
Dysregulated human myeloid nuclear differentiation antigen
expression in myelodysplastic syndromes: evidence for a role in
apoptosis. Cancer Res. 66:4645–4651. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
16
|
Rozzo SJ, Allard JD, Choubey D, et al:
Evidence for an interferon-inducible gene, Ifi202, in the
susceptibility to systemic lupus. Immunity. 15:435–443. 2001.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Keller U, von Bubnoff N, Peschel C and
Duyster J: Oncologist’s/haematologist’s view on the roles of
pathologists for molecular targeted cancer therapy. J Cell Mol Med.
14:805–817. 2010.
|
|
18
|
Choubey D, Deka R and Ho SM:
Interferon-inducible IFI16 protein in human cancers and autoimmune
diseases. Front Biosci. 13:598–608. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
Alimirah F, Chen J, Davis FJ and Choubey
D: IFI16 in human prostate cancer. Mol Cancer Res. 5:251–259. 2007.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
DeYoung KL, Ray ME, Su YA, et al: Cloning
a novel member of the human interferon-inducible gene family
associated with control of tumorigenicity in a model of human
melanoma. Oncogene. 15:453–457. 1997. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
Woerner SM, Kloor M, Schwitalle Y, et al:
The putative tumor suppressor AIM2 is frequently affected by
different genetic alterations in microsatellite unstable colon
cancers. Genes Chromosomes Cancer. 46:1080–1089. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
22
|
Li X, Wu WK, Sun B, et al:
Dihydroptychantol A, a macrocyclic bisbibenzyl derivative, induces
autophagy and following apoptosis associated with p53 pathway in
human osteosarcoma U2OS cells. Toxicol Appl Pharm. 251:146–154.
2011. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
23
|
Ouchi M and Ouchi T: Role of IFI16 in DNA
damage and checkpoint. Front Biosci. 13:236–239. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|