Introduction
Leiomyomas are benign tumors that originate from
smooth muscle, which have been identified throughout the
genitourinary tract (1). Following
the uterus, the most common tumor location is the renal capsule.
Leiomyomas also occur in the renal pelvis, bladder, spermatic cord,
epididymis, prostate and the glans penis (2). Scrotal smooth muscle tumors may be
further categorized as leiomyomas, bizarre leiomyomas and
leiomyosarcomas. However, bizarre leiomyomas of the scrotum are
particularly rare and a PubMed search reveals fewer than 14 reports
of symplastic, pleomorphic, bizarre and atypical leiomyomas of the
scrotum (3–14) (Table
I). Leiomyomas are usually painless in nature; however, they
may be associated with pain and the development of hydroceles
(3). In contrast to scrotal
leiomyosarcomas, scrotal leiomyomas with bizarre nuclei are not
hypercellular and they lack mitotic activity (8). As a relatively rare tumor, initial
diagnosis and differential diagnosis are complicated, the
management of which is usually surgical excision. In the present
study, a single case of bizarre leiomyoma of the scrotum is
reported, which may be mistaken for other scrotal tumors. This
study was approved by the ethics committee of Peking University
Shenzhen Hospital (Shenzhen, China) and written informed consent
was obtained from the patient.
 | Table IBizarre leiomyomas of the scrotum
reported in the literature. |
Table I
Bizarre leiomyomas of the scrotum
reported in the literature.
| Case | First author
(ref.) | Year | Age (years) | Diameter (cm) | Clinical
features | Position | Pathology |
|---|
| 1 | Nishiyama (4) | 1987 | 46 | 6 | Painless mass for 20
years | Left | Bizarre nuclei |
| 2 | De Rosa (10) | 1996 | 49 | NA | NA | NA | Bizarre nuclei |
| 3 | Slone (12) | 1998 | 53 | 3 | Painless mass for
several years | Left | Bizarre nuclei |
| 4 | Slone (12) | 1998 | 58 | 2 | Painless mass for
several years | Right | Bizarre nuclei |
| 5 | Slone (12) | 1998 | 44 | 2 | Painless mass for 4
years | Right | Bizarre nuclei |
| 6 | Rodruiguez-Parets
(13) | 1997 | NA | NA | NA | NA | Bizarre nuclei |
| 7 | Fadare (5) | 2003 | 69 | 3 | Painless mass for 5
years | Anterior | Bizarre nuclei |
| 8 | Kim (3) | 2003 | 65 | 1 | Accidental
discovery | Left | Bizarre nuclei |
| 9 | Sevilla (6) | 2004 | 43 | 3.5 | Accidental
discovery | NA | Bizarre nuclei |
| 10 | Cabello (11) | 2004 | 75 | 10.6 | Accidental
discovery | Right | Bizarre nuclei |
| 11 | Celia (7) | 2005 | 52 | 1.7 | Painful mass for 1
year | Right | Bizarre nuclei |
| 12 | Masood (8) | 2008 | 59 | 8.5 | Painless mass for 18
years | Right | Bizarre nuclei |
| 13 | Philip (14) | 2008 | 65 | 3 | Painless mass for 4
weeks | Right | Bizarre nuclei |
| 14 | Rao (9) | 2012 | 64 | 4 | Painless mass for 6
months | Anterior | Bizarre nuclei |
Case report
A 53-year-old male presented to his physician with a
painless scrotal mass located on the right side, which the patient
had first observed 2–3 months previously. The mass had remained
stable in size during that period. The patient was admitted to
Department of Urology, Peking University Shenzhen Hospital,
(Shenzhen, China) for further examination on April 13, 2012, and
was determined to be asymptomatic with a normal appetite and no
weight changes. The patient did not exhibit any urinary,
respiratory, cardiovascular or constitutional symptoms and had not
previously undergone surgery. There was no prior history of trauma,
inflammation or infection and no significant urological past
history. Physical examination revealed the patient was a
well-developed and well-nourished male. The patient was afebrile
with a heart rate of 92 beats per min, a temperature of 36.5°C,
blood pressure of 129/73 mmHg and respiratory rate of 18 breaths
per min. The chest was clear to percussion and auscultation, and no
masses were palpable on abdominal examination. Physical examination
identified a firm, elastic, non-tender mass on the right side of
the scrotum, located near the testis. The mass was ~1.0 cm in
diameter and no tenderness or erythema was observed. The lesion was
not fixed to the skin or adjacent deeper tissue, and no warmth or
discharge was noted. Testes on both sides were normal on palpation
with no inguinal lymphadenopathy observed.
Laboratory examination revealed that the patient’s
hemoglobin concentration was 142 g/l and white blood cell count was
5.84×109/l, with 53.0% granulocytes. Concentrations of
glucose, urea nitrogen and serum creatine were 4.87 mmol/l, 9.11
mmol/l and 107.3 μmol/l, respectively. Liver function tests and
serum electrolytes were recorded to be within normal limits. The
serum levels of certain tumor markers, such as α-fetoprotein and
β-human chorionic gonadotropin, were observed to be normal.
Following examination by a radiologist, the mass was diagnosed as a
sebaceous cyst.
A right percutaneous mass excision was performed on
April 17, 2012. The tumor was dissected from the tunica dartos and
no invasion of adjacent tissue was observed. The tumor was a solid,
well-circumscribed, 1.2×1.0×0.8 cm-sized, oval mass that originated
from the tunica dartos, which was independent of the testis,
epididymis and funiculus spermaticus. The pathological report
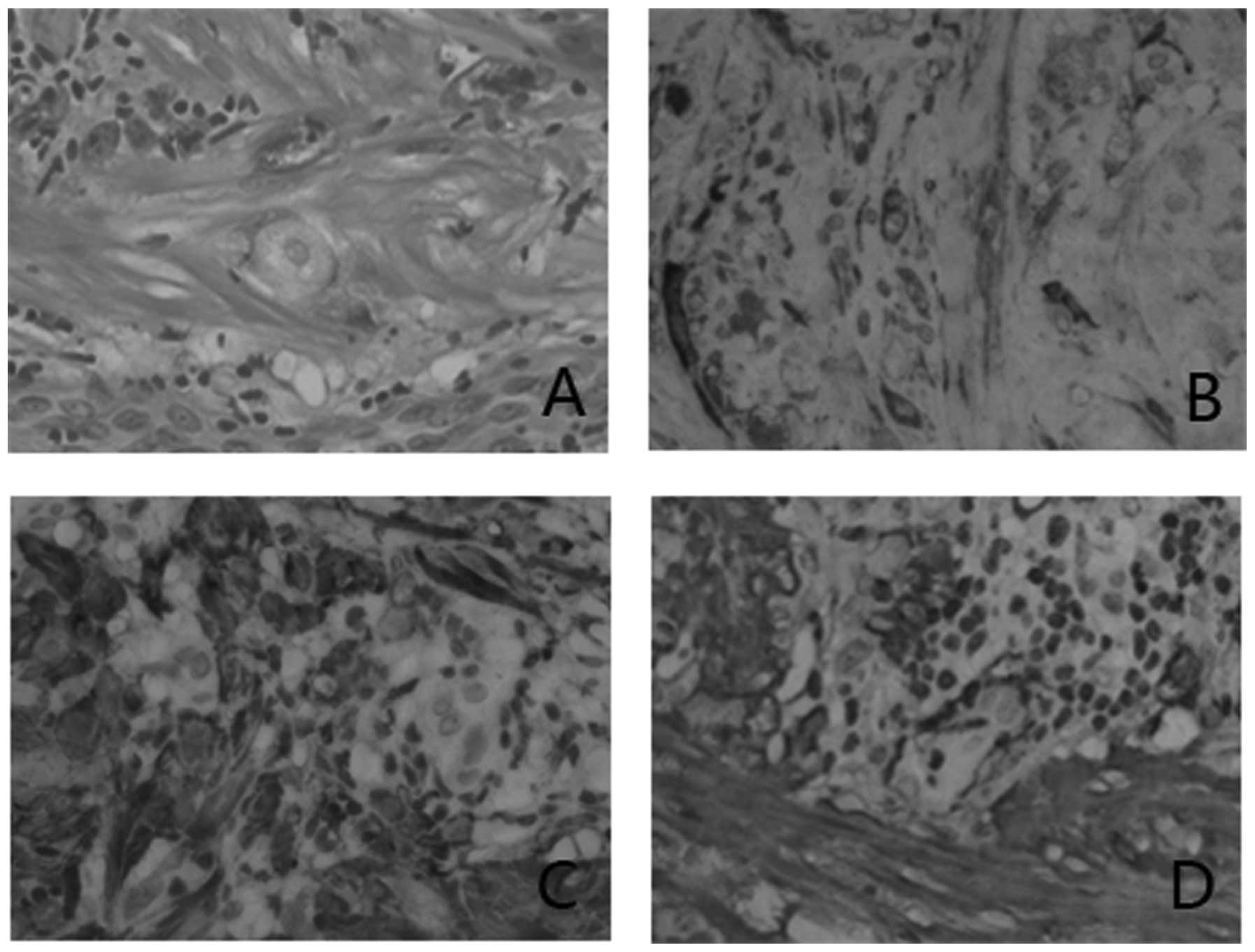
revealed clear surgical margins of the tumor. Microscopically, the
mass consisted of irregularly shaped cells, with certain tumor
cells exhibiting bizarre nuclei and demonstrating focal lymphocytic
infiltration into the stroma (Fig.
1). Immunohistochemical staining revealed that the tumor cells
were positive for P16, smooth muscle actin and caldesmin (Fig. 1). Following surgical resection of
the tumor, the patient was followed up for six months and no
problems were reported.
Discussion
Bizarre leiomyomas of the scrotum are extremely
rare; only 14 cases have been reported previously (3–9). In
the current study, the fifteenth case of bizarre leiomyoma of the
scrotum has been described. This case is the first reported in
China. The diagnosis in the present study was mainly based on
microscopic analysis and immunophenotype.
Previously reported cases tend to be asymptomatic
and painless in nature; therefore, patients may not seek medical
consultation for prolonged periods of time, sometimes decades, by
which time the tumors may have grown large enough to become
cosmetically undesirable or to cause ulceration of the overlying
skin. Of the 14 cases, 12 bizarre leiomyomas of the scrotum are
solitary, subcutaneous tumors ranged from 0.5 to 10 cm in diameter
(Table I). They usually present
between the fourth and seventh decades of life and clinically
present as a circumscribed swelling or pedunclated scrotal mass.
The tumors appear to occur with equal frequency on the right and
left side, and are often identified incidentally by physicians
during routine physical examinations. Thus far, all of the reported
cases of bizarre leiomyoma have been identified as benign tumors
and the prognosis has been good.
Ultrasound scans can provide useful information with
regard to scrotal mass diagnosis. However, it is difficult to
reliably identify malignant scrotal masses on the basis of
sonographic features alone. Resection of the mass may be required,
as preoperative and intraoperative findings may not be effective in
excluding malignancy. However, the frozen section procedure is
helpful when discriminating between malignant and benign lesions
(15).
The following four pathological features are used to
grade scrotal smooth muscle tumors: i) size ≥5 cm in dimension; ii)
infiltrating margin; iii) ≥5 mitotic figures per 10 high-power
fields; and iv) moderate cytological atypia. Tumors with only one
of the aforementioned features are considered benign; those
fulfilling two of the criteria are diagnosed as atypical or bizarre
leiomyomas; and tumors exhibiting three to four of these criteria
are classified as leiomyosarcomas (9). Immunohistochemistry is important in
determining the nature of spindle cells and conferring a final
diagnosis.
In conclusion, to our knowledge, only a small number
of cases of bizarre leiomyomas of the scrotum have been reported in
the literature thus far. This case report highlights diagnostic and
treatment issues associated with this rare tumor type.
Histologically, the tumor behaves differently to conventional
leiomyomas and leiomyosarcomas; therefore, definitive diagnosis is
established by pathological evaluation. Correct diagnosis is
important to avoid overdiagnosis and unnecessary clinical
treatment.
Acknowledgements
This study was supported by the National Natural
Science Foundation of China (no. 81101922), the Medical Scientific
Research Foundation of Guangdong Province of China (nos. A2012584
and A2013606) and the Science and Technology Development Fund
Project of Shenzhen (no. JCYJ20130402114702124).
References
|
1
|
Das AK, Bolick D, Little NA and Walther
PJ: Pedunculated scrotal mass: leiomyoma of scrotum. Urology.
39:376–379. 1992. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
Bremmer F, Kessel FJ, Behnes CL, Trojan L
and Heinrich E: Leiomyoma of the tunica albuginea, a case report of
a rare tumour of the testis and review of the literature. Diagn
Pathol. 7:1402012. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
3
|
Kim NR, Sung CO and Han J: Bizarre
leiomyoma of the scrotum. J Korean Med Sci. 18:452–454. 2003.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
Nishiyama N, Hibi H, Yanaoka M and Naide
Y: A case of bizarre leiomyoma of the scrotum. Hinyokika Kiyo.
33:961–963. 1987.(In Japanese).
|
|
5
|
Fadare O, Wang S and Mariappan MR:
Pathologic quiz case: a 69-year-old asymptomatic man with a scrotal
mass. Atypical (symplastic or bizarre) leiomyoma of the scrotum.
Arch Pathol Lab Med. 128:e37–e38. 2004.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Sevilla Chica F, Meseguer García P, Roca
Estellés MJ, Gómez Castro A, Mola Arizo MJ and Sala Aznar A:
Atypical or bizarre leiomyoma of the scrotum. Report of one case
and bibliographic review. Arch Esp Urol. 57:428–431. 2004.(In
Spanish).
|
|
7
|
Celia A, Bruschi M, De Stefani S, et al:
Bizarre leiomyoma of scrotum. Arch Ital Urol Androl. 77:113–114.
2005.
|
|
8
|
Masood J, Voulgaris S, Atkinson P and Carr
TW: A rare symplastic or bizarre leiomyoma of the scrotum: a case
report and review of the literature. Cases J. 1:3812008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Rao S, Fimate P, Ramakrishnan R and
Rajendiran S: Atypical leiomyoma of scrotum. J Cutan Aesthet Surg.
5:216–217. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
10
|
De Rosa G, Boscaino A, Giordano G, et al:
Symplastic leiomyoma of the scrotum. A case report. Pathologica.
88:55–57. 1996.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Cabello BR, López MB, Verdú TF, et al:
Giant bizarre scrotal leiomyoma. Arch Esp Urol. 57:847–851.
2004.(In Spanish).
|
|
12
|
Slone S and O’Connor D: Scrotal leiomyomas
with bizarre nuclei: a report of three cases. Mod Pathol.
11:282–287. 1998.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Rodriguez-Parets JO, Silva AJ, Hernandez
MA, et al: Atypical scrotal leiomyoma. A case report. Actas Urol
Esp. 22:613–615. 1997.(In Spanish).
|
|
14
|
Philip J, Manikandan R, Vishwanathan P and
Mathew J: Symplastic scrotal leiomyoma: a case report. J Med Case
Rep. 2:2952008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Ozkan L, Ozkurkcugil C, Gok ND, Ozkan TA
and Yildiz K: Angioleiomyoma of the scrotal wall. J Chin Med Assoc.
74:275–276. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|