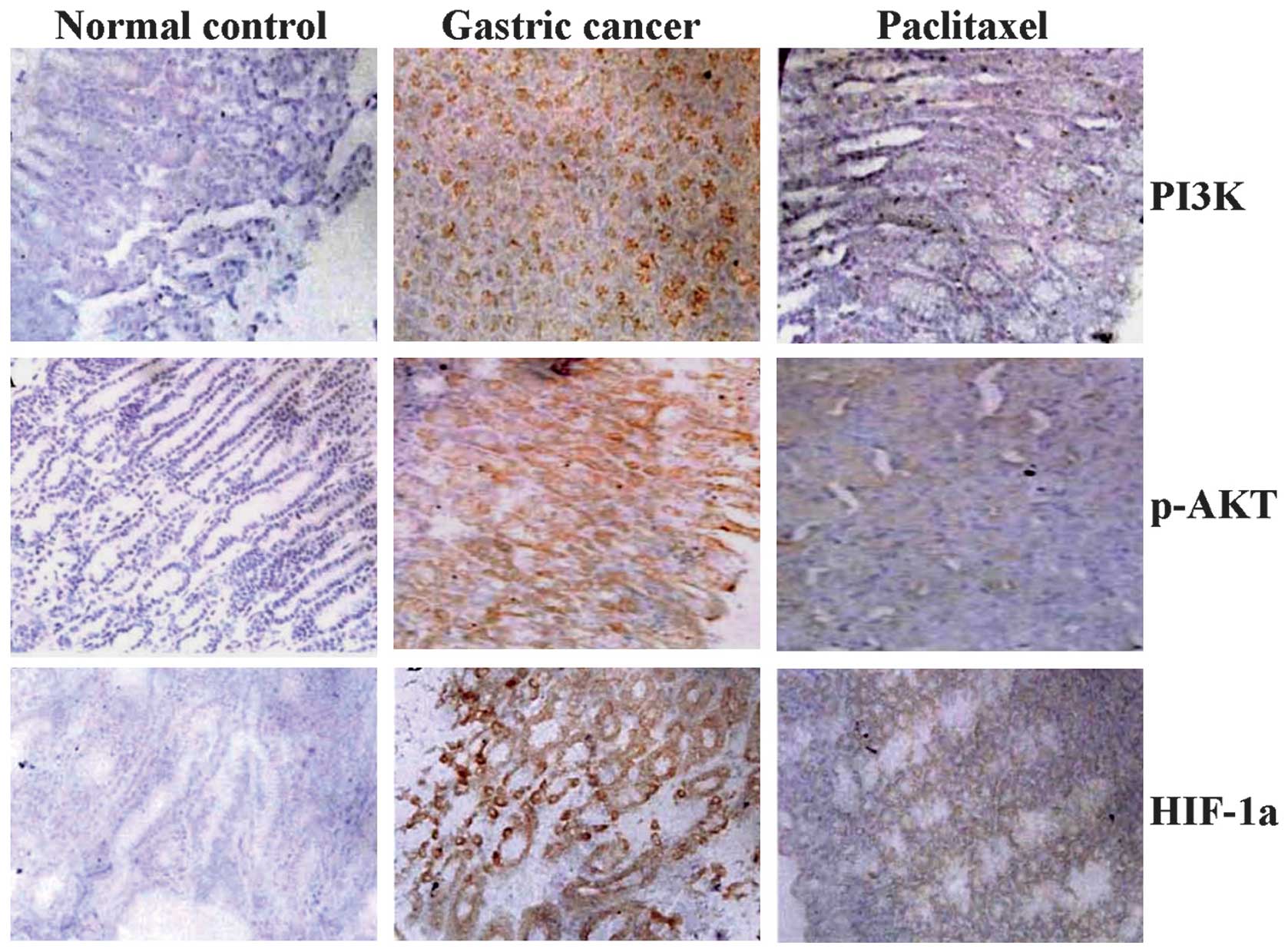
|
1
|
Jemal A, Bray F, Center MM, et al: Global
cancer statistics. CA Cancer J Clin. 61:69–90. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
2
|
Tajima Y, Yamazaki K, Makino R, et al:
Gastric and intestinal phenotypic marker expression in early
differentiated-type tumors of the stomach: clinicopathologic
significance and genetic background. Clin Cancer Res. 12:6469–6479.
2006. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
3
|
Li Q and Yang Z: Expression of
phospho-ERK1/2 and PI3-K in benign and malignant gallbladder
lesions and its clinical and pathological correlations. J Exp Clin
Cancer Res. 28:652009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
Uegaki K, Kanamori Y, Kigawa J, et al:
PTEN-positive and phosphorylated-Akt-negative expression is a
predictor of survival for patients with advanced endometrial
carcinoma. Oncol Rep. 14:389–392. 2005.
|
|
5
|
Sun ZJ, Chen G, Hu X, et al: Activation of
PI3K/Akt/IKK-alpha/NF-kappaB signaling pathway is required for the
apoptosis-evasion in human salivary adenoid cystic carcinoma: its
inhibition by quercetin. Apoptosis. 15:850–863. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
6
|
Chakravarti A, Zhai G, Suzuki Y, et al:
The prognostic significance of phosphatidylinositol 3-kinase
pathway activation in human gliomas. J Clin Oncol. 22:1926–1933.
2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Xue G, Restuccia DF, Lan Q, et al:
Akt/PKB-mediated phosphorylation of Twist1 promotes tumor
metastasis via mediating cross-talk between PI3K/Akt and TGF-β
signaling axes. Cancer Discov. 2:248–259. 2012.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Valkov A, Kilvaer TK, Sorbye SW, et al:
The prognostic impact of Akt isoforms, PI3K and PTEN related to
female steroid hormone receptors in soft tissue sarcomas. J Transl
Med. 9:2002011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Lee GW, Go SI, Cho YJ, et al:
Hypoxia-inducible factor-1α and excision repair cross-complementing
1 in patients with small cell lung cancer who received front-line
platinum-based chemotherapy: a retrospective study. J Thorac Oncol.
7:528–534. 2012.
|
|
10
|
Park S, Ha SY, Cho HY, et al: Prognostic
implications of hypoxia-inducible factor-1α in epidermal growth
factor receptor-negative non-small cell lung cancer. Lung Cancer.
72:100–107. 2011.
|
|
11
|
Argyriou P, Papageorgiou SG, Panteleon V,
et al: Hypoxia-inducible factors in mantle cell lymphoma:
implication for an activated mTORC1→HIF-1α pathway. Ann Hematol.
90:315–322. 2011.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Mottet D, Dumont V, Deccache Y, et al:
Regulation of hypoxia-inducible factor-1alpha protein level during
hypoxic conditions by the phosphatidylinositol
3-kinase/Akt/glycogen synthase kinase 3beta pathway in HepG2 cells.
J Biol Chem. 278:31277–31285. 2003. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
13
|
Koshikawa N, Hayashi J, Nakagawara A and
Takenaga K: Reactive oxygen species-generating mitochondrial DNA
mutation up-regulates hypoxia-inducible factor-1alpha gene
transcription via phosphatidylinositol 3-kinase-Akt/protein kinase
C/histone deacetylase pathway. J Biol Chem. 284:33185–33194. 2009.
View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
14
|
Xu K, Ding Q, Fang Z, et al: Silencing of
HIF-1alpha suppresses tumorigenicity of renal cell carcinoma
through induction of apoptosis. Cancer Gene Ther. 17:212–222. 2010.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Tanaka H, Yamamoto M, Hashimoto N, et al:
Hypoxia-independent overexpression of hypoxia-inducible factor
1alpha as an early change in mouse hepatocarcinogenesis. Cancer
Res. 66:11263–11270. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
16
|
Fang J, Ding M, Yang L, et al:
PI3K/PTEN/AKT signaling regulates prostate tumor angiogenesis. Cell
Signal. 19:2487–2497. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Shi Y, Chen L, Li J, et al: Prognostic and
predictive values of pERK1/2 and pAkt-1 expression in non-small
cell lung cancer patients treated with adjuvant chemotherapy.
Tumour Biol. 32:381–390. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
18
|
McCubrey JA, Steelman LS, Abrams SL, et
al: Roles of the RAF/MEK/ERK and PI3K/PTEN/AKT pathways in
malignant transformation and drug resistance. Adv Enzyme Regul.
46:249–279. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
Liang K, Lu Y, Li X, et al: Differential
roles of phosphoinositide-dependent protein kinase-1 and akt1
expression and phosphorylation in breast cancer cell resistance to
Paclitaxel, Doxorubicin, and gemcitabine. Mol Pharmacol.
70:1045–1052. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
20
|
Abrams SL, Steelman LS, Shelton JG, et al:
Enhancing therapeutic efficacy by targeting non-oncogene addicted
cells with combinations of signal transduction inhibitors and
chemotherapy. Cell Cycle. 9:1839–1846. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
Zhang Y, Liu X, Zhang J, et al: The
expression and clinical significance of PI3K, pAkt and VEGF in
colon cancer. Oncol Lett. 4:763–766. 2012.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22
|
Kim JG, Chae YS, Sohn SK, et al: Clinical
significance of genetic variations in the PI3K/PTEN/AKT/mTOR
pathway in Korean patients with colorectal cancer. Oncology.
79:278–282. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23
|
Isobe T, Aoyagi K, Koufuji K, et al:
Clinicopathological significance of hypoxia-inducible factor-1
alpha (HIF-1α) expression in gastric cancer. Int J Clin Oncol.
18:293–304. 2013.
|
|
24
|
Hu L, Hofmann J, Lu Y, et al: Inhibition
of phosphatidylinositol 3′-kinase increases efficacy of paclitaxel
in in vitro and in vivo ovarian cancer models. Cancer Res.
62:1087–1092. 2002.
|
|
25
|
Xu R, Nakano K, Iwasaki H, et al: Dual
blockade of phosphatidylinositol 3′-kinase and mitogen-activated
protein kinase pathways overcomes paclitaxel-resistance in
colorectal cancer. Cancer Lett. 306:151–160. 2011.
|
|
26
|
Kim SH, Juhnn YS and Song YS: Akt
involvement in paclitaxel chemoresistance of human ovarian cancer
cells. Ann N Y Acad Sci. 1095:82–89. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
27
|
Zeng L, Kizaka-Kondoh S, Itasaka S, et al:
Hypoxia inducible factor-1 influences sensitivity to paclitaxel of
human lung cancer cell lines under normoxic conditions. Cancer Sci.
98:1394–1401. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
28
|
Fekete M, Santiskulvong C, Eng C and
Dorigo O: Effect of PI3K/Akt pathway inhibition-mediated G1 arrest
on chemosensitization in ovarian cancer cells. Anticancer Res.
32:445–452. 2012.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
29
|
Shafee N, Kaluz S, Ru N and Stanbridge EJ:
PI3K/Akt activity has variable cell-specific effects on expression
of HIF target genes, CA9 and VEGF, in human cancer cell lines.
Cancer Lett. 282:109–115. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
30
|
Zhong H, Chiles K, Feldser D, et al:
Modulation of hypoxia-inducible factor 1alpha expression by the
epidermal growth factor/phosphatidylinositol 3-kinase/PTEN/AKT/FRAP
pathway in human prostate cancer cells: implications for tumor
angiogenesis and therapeutics. Cancer Res. 60:1541–1545. 2000.
|
|
31
|
Jiao M and Nan KJ: Activation of PI3
kinase/Akt/HIF-1α pathway contributes to hypoxia-induced
epithelial-mesenchymal transition and chemoresistance in
hepatocellular carcinoma. Int J Oncol. 40:461–468. 2012.
|
|
32
|
Manohar SM, Padgaonkar AA, Jalota-Badhwar
A, et al: A novel inhibitor of hypoxia-inducible factor-1α P3155
also modulates PI3K pathway and inhibits growth of prostate cancer
cells. BMC Cancer. 11:3382011.
|