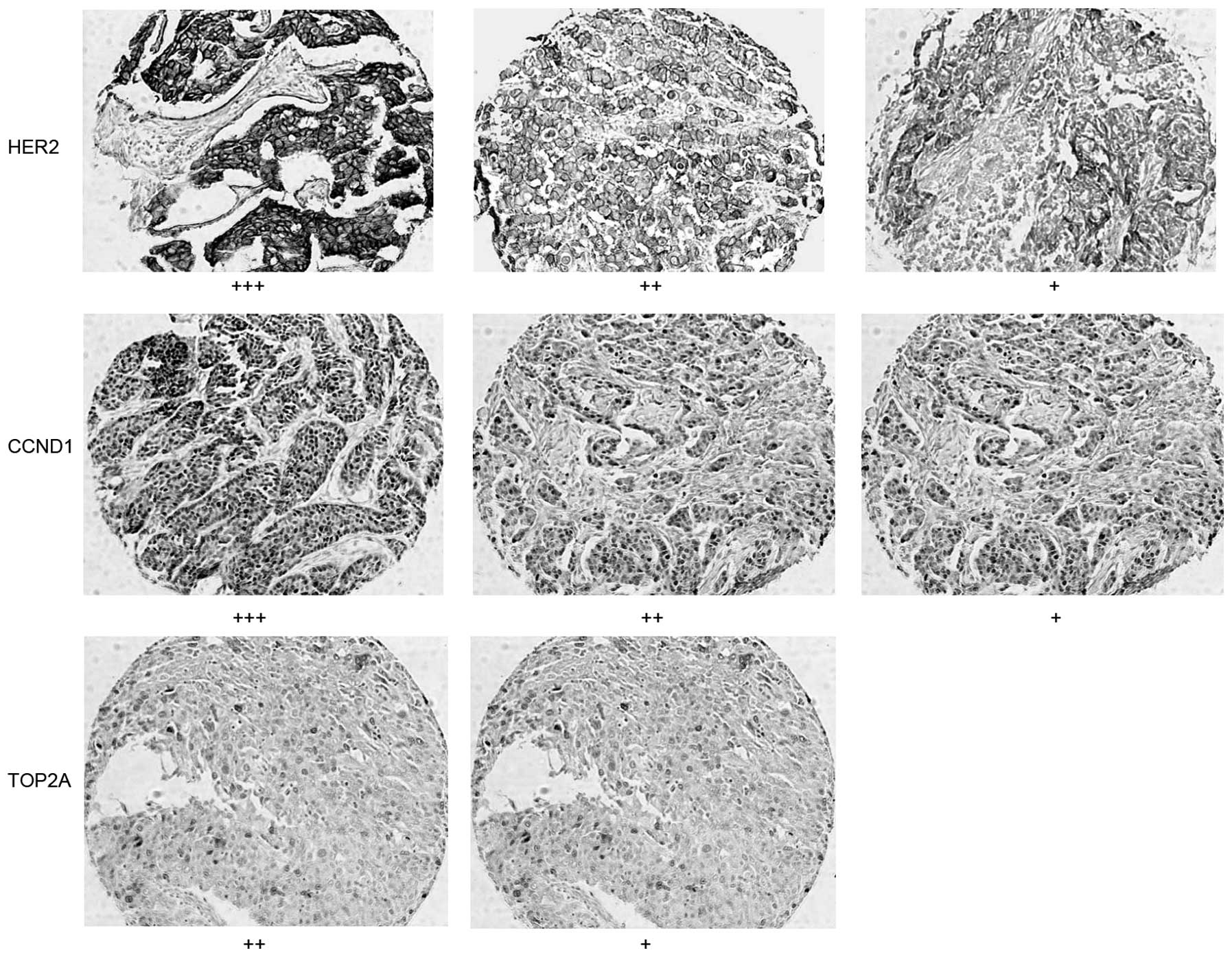
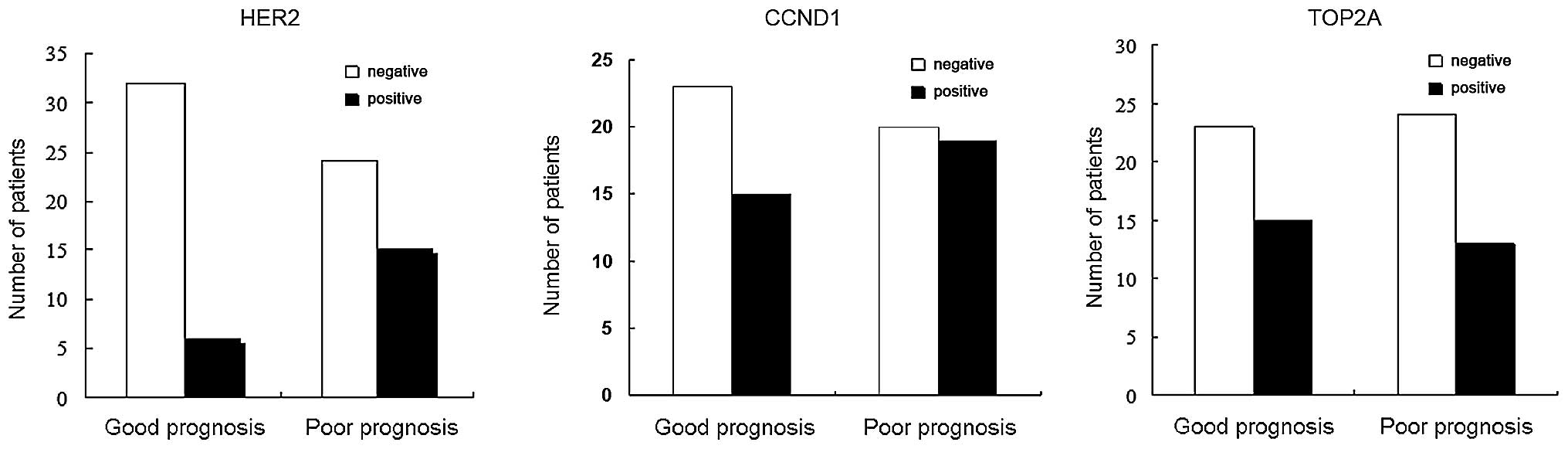
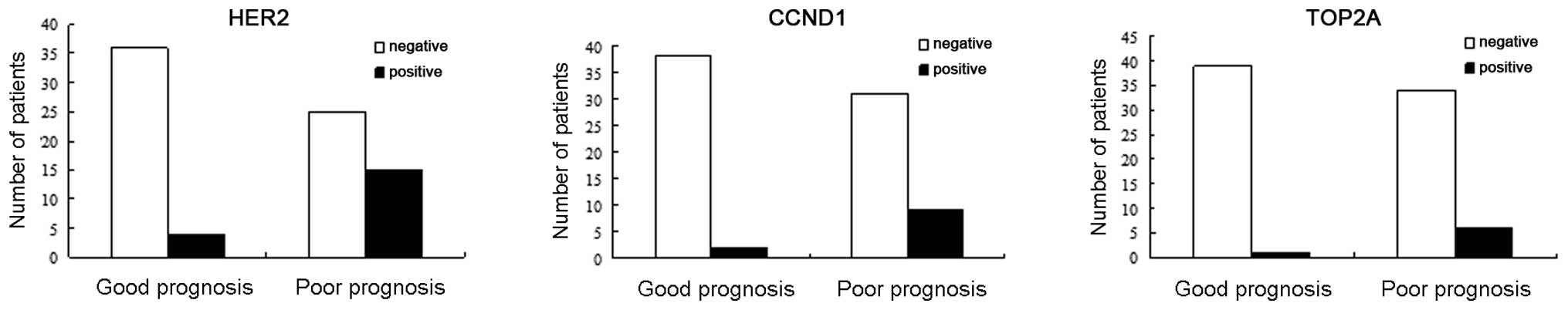
|
1
|
Wang YC, Wei LJ, Liu JT, Li SX and Wang
QS: Comparison of Cancer Incidence between China and the USA.
Cancer Biol Med. 9:128–132. 2012.
|
|
2
|
Tinoco G, Warsch S, Glück S, et al:
Treating breast cancer in the 21st centrury: emerging biological
therapies. J Cancer. 4:117–132. 2013.
|
|
3
|
Alphandéry EL: Perspectives of breast
cancer thermotherapies. J Cancer. 5:472–479. 2014.
|
|
4
|
Goldhirsch A, Glick JH, Gelber RD, Coates
AS and Senn HJ: Meeting highlights: International Consensus Panel
on the Treatment of Primary Breast Cancer. Seventh International
Conference on Adjuvant Therapy of Primary Breast Cancer. J Clin
Oncol. 19:3817–3827. 2001.
|
|
5
|
Rosen PP, Groshen S, Saigo PE, Kinne DW
and Hellman S: Pathological prognostic factors in stage I (T1N0M0)
and stage II (T1N1M0) breast carcinoma: a study of 644 patients
with median follow-up of 18 years. J Clin Oncol. 7:1239–1251.
1989.
|
|
6
|
Tamoxifen for early breast cancer: an
overview of the randomised trials. Early Breast Cancer Trialists’
Collaborative Group. Lancet. 351:1451–1467. 1998.
|
|
7
|
Fisher B, Redmond C, Fisher ER and Caplan
R: Relative worth of estrogen or progesterone receptor and
pathologic characteristics of differentiation as indicators of
prognosis in node negative breast cancer patients: findings from
National Surgical Adjuvant Breast and Bowel Project Protocol B-06.
J Clin Oncol. 6:1076–1087. 1988.
|
|
8
|
Saimura M, Fukutomi T, Tsuda H, et al:
Prognosis of a series of 763 consecutive node-negative invasive
breast cancer patients without adjuvant therapy: analysis of
clinicopathological prognostic factor. J Surg Oncol. 71:101–105.
1999.
|
|
9
|
Hui R, Campbell DH, Lee CS, et al: EMS1
amplification can occur independently of CCND1 or INT-2
amplification at 11q13 and may identify different phenotypes in
primary breast cancer. Oncogene. 15:1617–1623. 1997.
|
|
10
|
Kallioniemi OP, Kallioniemi A, Kurisu W,
et al: ERBB2 amplification in breast cancer analyzed by
fluorescence in situ hybridization. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA.
89:5321–5325. 1992.
|
|
11
|
Rummukainen JK, Salminen T, Lundin J, et
al: Amplification of c-myc by fluorescence in situ hybridization in
a population-based breast cancer tissue array. Mod Pathol.
14:1030–1035. 2001.
|
|
12
|
Jerjees DA, Alabdullah M, Green AR, et al:
Prognostic and biological significance of proliferation and HER2
expression in the luminal class of breast cancer. Breast Cancer Res
Treat. 145:317–330. 2014.
|
|
13
|
Figueroa-Magalhães MC, Jelovac D, Connolly
RM and Wolff AC: Treatment of HER2-positive breast cancer. Breast.
23:128–136. 2014.
|
|
14
|
Bautista S and Theillet C: CCND1 and FGFR1
coamplification results in the colocalization of 11q13 and 8p12
sequences in breast tumor nuclei. Genes Chromosomes Cancer.
22:268–277. 1998.
|
|
15
|
Sidoni A, Ferri I, Cavaliere A, et al:
Detection of HER-2/neu (c-erbB-2) overexpression and amplification
in breast carcinomas with ambiguous immunohistochemical results. A
further contribution to defining the role of fluorescent in situ
hybridization. Anticancer Res. 26:2333–2337. 2006.
|
|
16
|
Winchester DP: Breast cancer in young
women. Surg Clin North Am. 76:279–287. 1996.
|
|
17
|
Han W, Kim SW, Park IA, et al: Young age:
an independent risk factor for disease-free survival in women with
operable breast cancer. BMC Cancer. 4:822004.
|
|
18
|
Chen WG, Li JW, Zhu L, Li YF and Zhu JX:
Analysis of prognosis of breast cancer in women under 35 years of
age (report of 157 cases). Zhong Liu. 2:135–137. 2001.(In
Chinese).
|
|
19
|
Chung M, Chang HR, Bland KI and Wanebo HJ:
Younger women with breast carcinoma have a poorer prognosis than
older women. Cancer. 77:97–103. 1996.
|
|
20
|
Fowble BL, Schultz DJ, Overmoyer B, et al:
The influence of young age on outcome in early stage breast cancer.
Int J Radiat Oncol Biol Phys. 30:23–33. 1994.
|
|
21
|
Mirza AN, Mirza NQ, Vlastos G and
Singletary SE: Prognostic factors in node-negative breast cancer: a
review of studies with sample size more than 200 and follow-up more
than 5 years. Ann Surg. 235:10–26. 2002.
|
|
22
|
Salama JK, Heimann R, Lin F, et al: Does
the number of lymph nodes examined in patients with lymph
node-negative breast carcinoma have prognostic significance?
Cancer. 103:664–671. 2005.
|
|
23
|
No authors listed. Polychemotherapy for
early breast cancer: an overview of the randomised trials. Early
Breast Cancer Trialists’ Collaborative Group. Lancet. 352:930–942.
1998.
|
|
24
|
Fisher B, Jeong JH, Anderson S and Wolmark
N: Treatment of axillary lymph node-negative, estrogen
receptor-negative breast cancer: updated findings from National
Surgical Adjuvant Breast and Bowel Project clinical trials. J Natl
Cancer Inst. 96:1823–1831. 2004.
|
|
25
|
Fisher B, Jeong JH, Bryant J, et al:
Treatment of lymph-node-negative, oestrogen-receptor-positive
breast cancer: long-term findings from National Surgical Adjuvant
Breast and Bowel Project randomised clinical trials. Lancet.
364:858–868. 2004.
|
|
26
|
Slamon DJ, Clark GM, Wong SG, et al: Human
breast cancer: correlation of relapse and survival with
amplification of the HER-2/neu oncogene. Science. 235:177–182.
1987.
|
|
27
|
van de Vijver MJ, Peterse JL, Mooi WJ, et
al: Neu-protein overexpression in breast cancer. Association with
comedo-type ductal carcinoma in situ and limited prognostic value
in stage II breast cancer. N Engl J Med. 319:1239–1245. 1988.
|
|
28
|
Ross JS, Fletcher JA, Linette GP, et al:
The Her-2/neu gene and protein in breast cancer 2003: biomarker and
target of therapy. Oncologist. 8:307–325. 2003.
|
|
29
|
Hajduk M: Topoisomerase II alpha - a
fundamental prognostic factor in breast carcinoma. Pol J Pathol.
60:67–75. 2009.
|
|
30
|
Rudolph P, MacGrogan G, Bonichon F, et al:
Prognostic significance of Ki-67 and topoisomerase IIalpha
expression in infiltrating ductal carcinoma of the breast. A
multivariate analysis of 863 cases. Breast Cancer Res Treat.
55:61–71. 1999.
|
|
31
|
Depowski PL, Rosenthal SI, Brien TP,
Stylos S, Johnson RL and Ross JS: Topoisomerase IIalpha expression
in breast cancer: correlation with outcome variables. Mod Pathol.
13:542–547. 2000.
|
|
32
|
Schwab M: Amplification of oncogenes in
human cancer cells. Bioessays. 20:473–479. 1998.
|
|
33
|
Casimiro MC, Wang C, Li Z, et al: Cyclin
D1 determines estrogen signaling in the mammary gland in vivo. Mol
Endocrinol. 27:1415–1428. 2013.
|
|
34
|
Hernández-Hernández OT and Camacho-Arroyo
I: Regulation of gene expression by progesterone in cancer cells:
effects on cyclin D1, EGFR and VEGF. Mini Rev Med Chem. 13:635–642.
2013.
|
|
35
|
Cheng CW, Liu YF, Yu JC, et al: Prognostic
significance of cyclin D1, β-catenin, and MTA1 in patients with
invasive ductal carcinoma of the breast. Ann Surg Oncol.
19:4129–4139. 2012.
|
|
36
|
Mylona E, Tzelepis K, Theohari I, et al:
Cyclin D1 in invasive breast carcinoma: favourable prognostic
significance in unselected patients and within subgroups with an
aggressive phenotype. Histopathology. 62:472–480. 2013.
|
|
37
|
Vogel C, de Abreu RS, Ko D, et al:
Sequence signatures and mRNA concentration can explain two-thirds
of protein abundance variation in a human cell line. Mol Syst Biol.
6:4002010.
|
|
38
|
Schwanhäusser B, Busse D, Li N, et al:
Global quantification of mammalian gene expression control. Nature.
473:337–342. 2011.
|