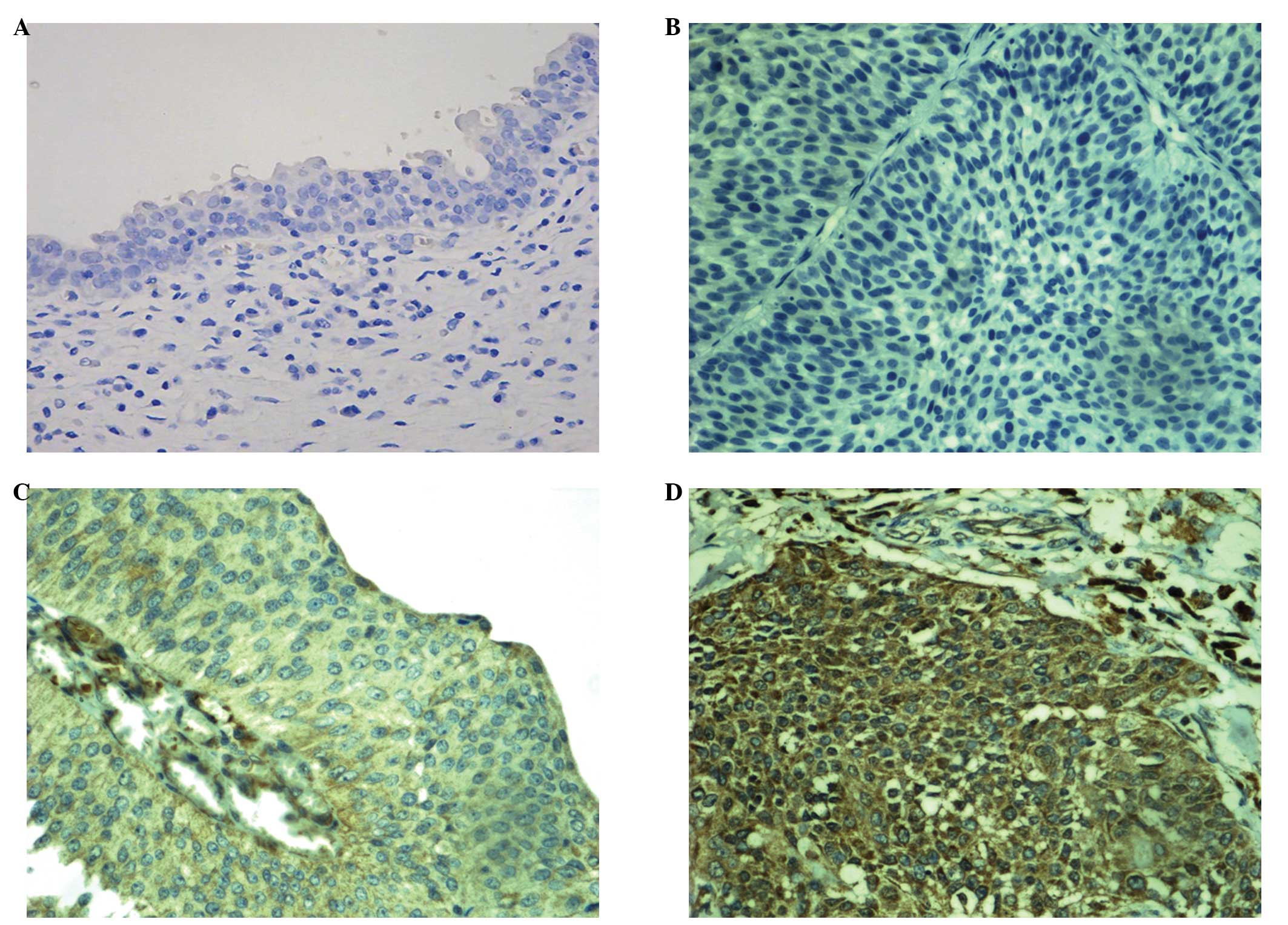
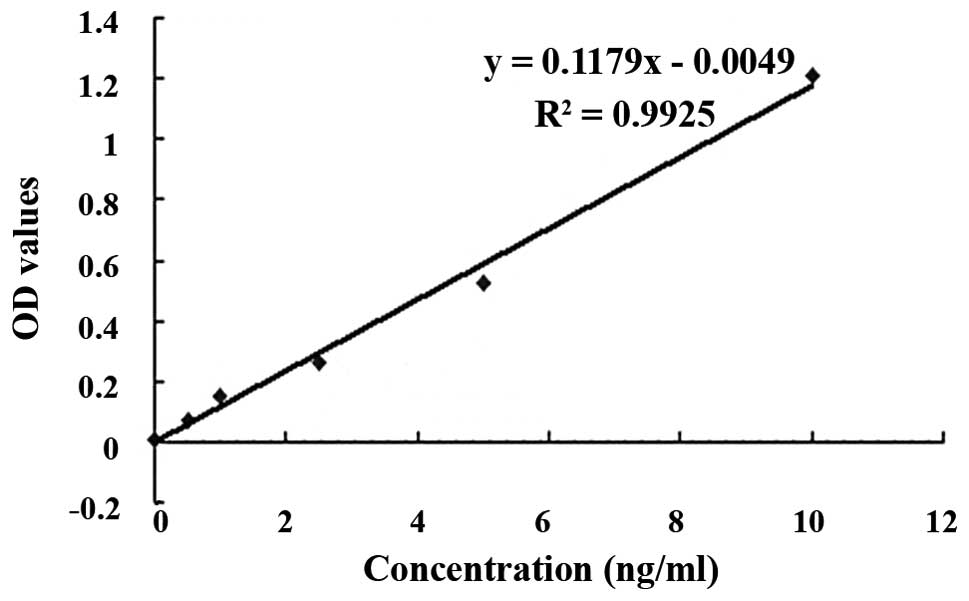
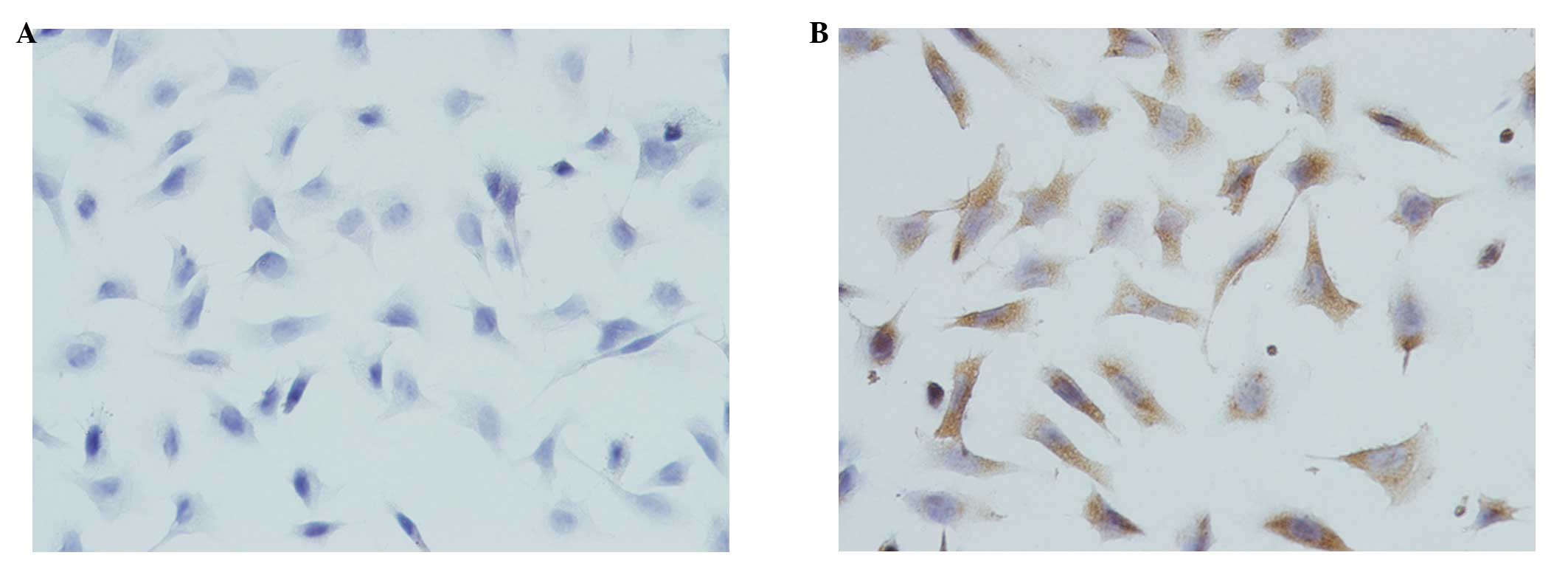
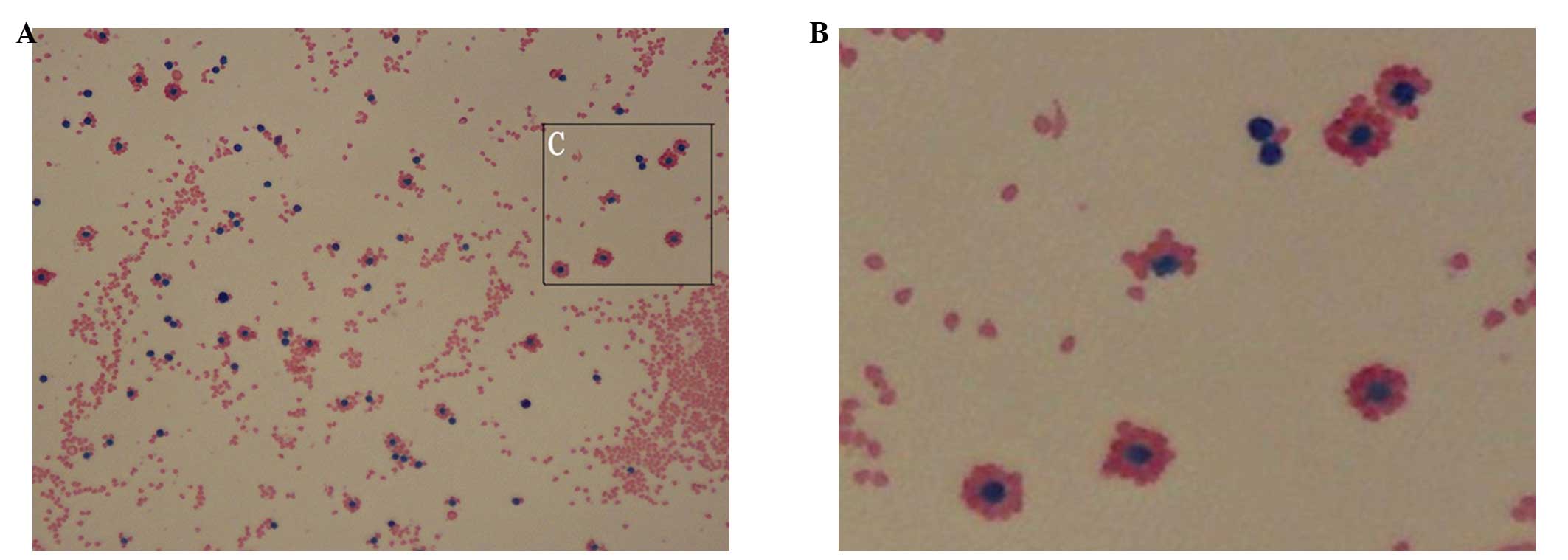
|
1
|
van Rhijn BW, Burger M, Lotan Y, et al:
Recurrence and progression of disease in non-muscle-invasive
bladder cancer: from epidemiology to treatment strategy. Eur Urol.
56:430–442. 2009.
|
|
2
|
Parkin MD, Bray F, Ferlay J and Pisani P:
Global cancer statistics, 2002. CA Cancer J Clin. 55:74–108.
2005.
|
|
3
|
Shin T, Kennedy G, Gorski K, et al:
Cooperative B7-1/2 (CD80/CD86) and B7-DC costimulation of
CD4+ T cells independent of the PD-1 receptor. J Exp
Med. 198:31–38. 2003.
|
|
4
|
Hsu FJ and Komarovskaya M: CTLA4 blockade
maximizes antitumor T-cell activation by dendritic cells presenting
idiotype protein or opsonized anti-CD20 antibody-coated lymphoma
cells. J Immunother. 25:455–468. 2002.
|
|
5
|
Nagamori M, Kawaguchi S, Murakami M, et
al: Intrinsic and extrinsic manipulation of B7/CTLA-4 interaction
for induction of anti-tumor immunity against osteosarcoma cells.
Anticancer Res. 22:3223–3227. 2002.
|
|
6
|
Liu X, Gao JX, Wen J, et al: B7DC/PDL2
promotes tumor immunity by a PD-1-independent mechanism. J Exp Med.
197:1721–1730. 2003.
|
|
7
|
Sica GL, Choi IH, Zhu G, et al: B7-H4, a
molecule of the B7 family, negatively regulates T cell immunity.
Immunity. 18:849–861. 2003.
|
|
8
|
Choi IH, Zhu G, Sica GL, et al: Genomic
organization and expression analysis of B7-H4, an immune inhibitory
molecule of the B7 family. J Immunol. 171:4650–4654. 2003.
|
|
9
|
Mao YX, Chen YJ, Ge Y, et al: Recombinant
human B7-H4 expressed in Escherichia coli inhibits T lymphocyte
proliferation and IL-2 secretion in vitro. Acta Pharmaco1 Sin.
27:741–746. 2006.
|
|
10
|
Simon I, Zhuo S, Corra1 L, et al: B7-H4 is
a novel membrane-bound protein and a candidate serum and tissue
biomarker for ovarian cancer. Cancer Res. 66:1570–1575. 2006.
|
|
11
|
Sun Y, Wang Y, Zhao J, et al: B7-H3 and
B7-H4 expression in non-small-cell lung cancer. Lung Cancer.
53:143–151. 2006.
|
|
12
|
Krambeck AE, Thompson RH, Dong H, et al:
B7-H4 expression in renal cell carcinoma and tumor vasculature:
associations with cancer progression and survival. Proc Natl Acad
Sci USA. 103:10391–10396. 2006.
|
|
13
|
Tringler B, Zhuo S, Pilkington G, et al:
B7-H4 is highly expressed in ductal and lobular breast cancer. Cli
Cancer Res. 11:1842–1848. 2005.
|
|
14
|
Zang X, Thompson RH, Al-Ahmadie HA, et al:
B7-H3 and B7x are highly expressed in human prostate cancer and
associated with disease spread and poor outcome. Proc Natl Acad Sci
USA. 104:19458–19463. 2007.
|
|
15
|
Kryczek I, Wei S, Zou L, et al: Cutting
edge: induction of B7-H4 on APCs through IL-10: novel suppressive
mode for regulatory T cells. J Immunol. 177:40–44. 2006.
|
|
16
|
Suh WK, Wang S, Duncan GS, et al:
Generation and characterization of B7-H4/B7Sl/B7x-deficient mice.
Mol Cell Biol. 26:6403–6411. 2006.
|
|
17
|
Margel D, Tal R, Golan S, et al: Long-term
follow-up of patients with Stage T1 high-grade transitional cell
carcinoma managed by Bacille Calmette-Guérin immunotherapy.
Urology. 69:78–82. 2007.
|
|
18
|
Porena M, Del Zingaro M, Lazzeri M, et al:
Bacillus Calmette-Guérin versus gemcitabine for intravesical
therapy in high-risk superficial bladder cancer: a randomised
prospective study. Urol Int. 84:23–27. 2010.
|
|
19
|
Hinotsu S, Akaza H, Naito S, et al:
Maintenance therapy with bacillus Calmette-Guérin Connaught strain
clearly prolongs recurrence-free survival following transurethral
resection of bladder tumor for non-muscle-invasive bladder cancer.
BJU Int. 108:187–195. 2011.
|
|
20
|
Järvinen R, Kaasinen E, Sankila A and
Rintala E; FinnBladder Group. Long-term efficacy of maintenance
bacillus Calmette-Guérin versus maintenance mitomycin C
instillation therapy in frequently recurrent TaT1 tumours without
carcinoma in situ: a subgroup analysis of the prospective,
randomised FinnBladder I study with a 20-year follow-up. Eur Urol.
56:260–265. 2009.
|
|
21
|
Duchek M, Johansson R, Jahnson S, et al:
Members of the Urothelial Cancer Group of the Nordic Association of
Urology: Bacillus Calmette-Guérin is superior to a combination of
epirubicin and interferon-alpha2b in the intravesical treatment of
patients with stage T1 urinary bladder cancer. A prospective,
randomized, Nordic study. Eur Urol. 57:25–31. 2010.
|
|
22
|
Sobin LH, Gospodariwicz M and Wittekind C:
TNM classification of malignant tumors. UICC International Union
Against Cancer. 7th edition. Wiley-Blackwell; Hoboken, USA: pp.
262–265. 2009
|
|
23
|
Sauter G, Algaba F, Amin M, et al: Tumour
of urinary system: non-invasive urothelial neoplasis. WHO
Classification of Tumours Pathology and Genetics of Tumors of the
Urinary System and Male Genital Organs. Eble JN, Sauter G, Epstein
JI and Sesterhenn IA: IARCC Press; Lyon: 2004
|
|
24
|
Thompson RH, Zang X, Lohse CM, et al:
Serum-soluble B7x is elevated in renal cell carcinoma patients and
is associated with advanced stage. Cancer Res. 68:6054–6058.
2008.
|
|
25
|
Miyatake T, Tringler B, Liu W, et al:
B7-H4 (DD-0110) is overexpressed in high risk uterine endometrioid
adenocarcinomas and inversely correlated with tumor T-cell
infiltration. Gynecol Oncol. 106:119–127. 2007.
|
|
26
|
Simon I, Katsaros D, Rigault de la
Longrais I, et al: B7-H4 is over-expressed in early-stage ovarian
cancer and is independent of CA125 expression. Gynecol Oncol.
106:334–341. 2007.
|
|
27
|
Acuto O and Michel F: CD28-mediated
co-stimulation: a quantitative support for TCR signaling. Nat Rev
Immunol. 3:939–951. 2003.
|
|
28
|
Alegre ML, Frauwirth KA and Thompson CB:
T-cell regulation by CD28 and CTLA-4. Nat Rev Immunol. 1:220–228.
2001.
|
|
29
|
Jiang J, Gross D, Elbaum P and Murasko DM:
Aging affects initiation and continuation of T cell proliferation.
Mech Ageing Dev. 128:332–339. 2007.
|