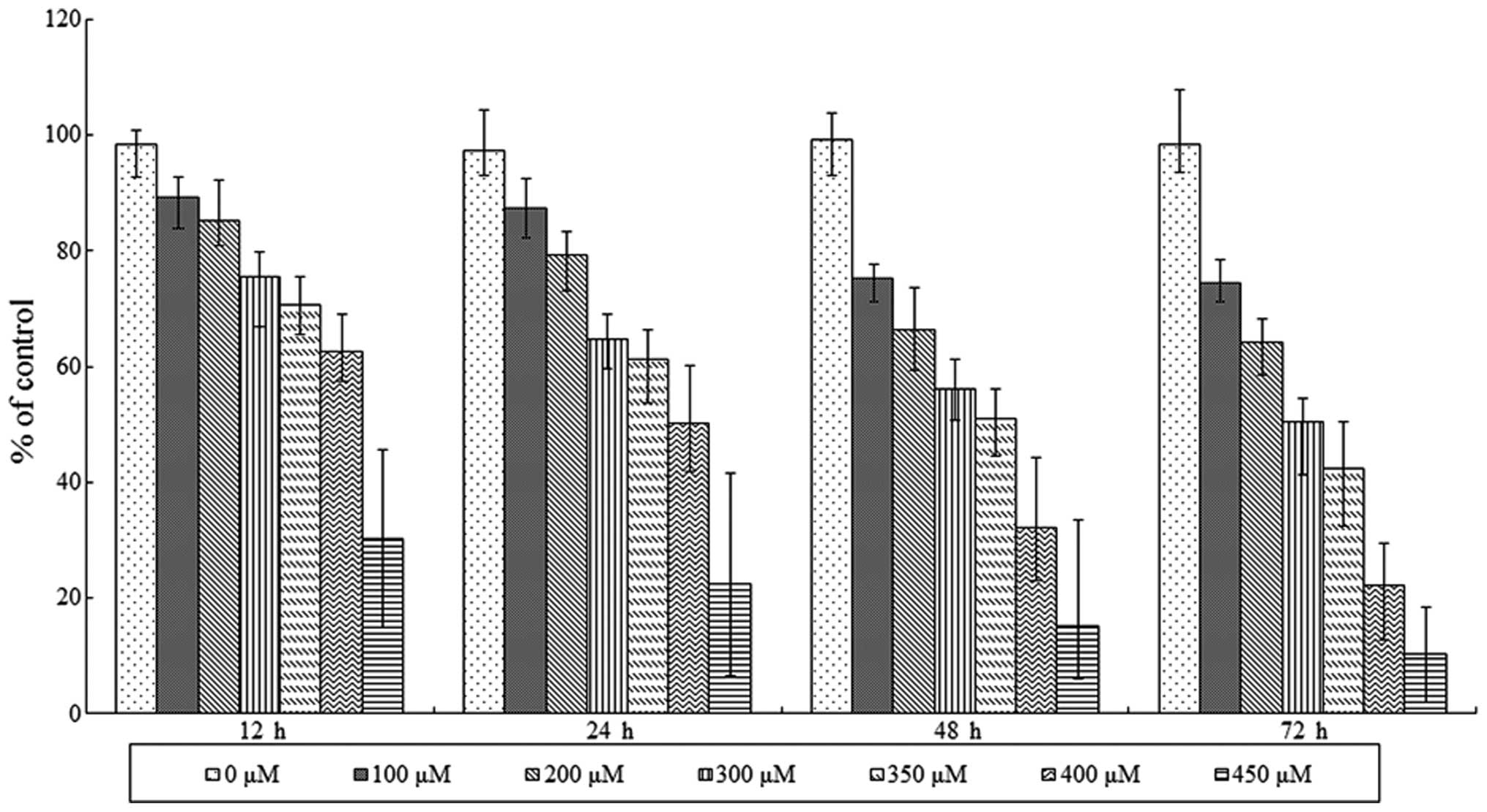
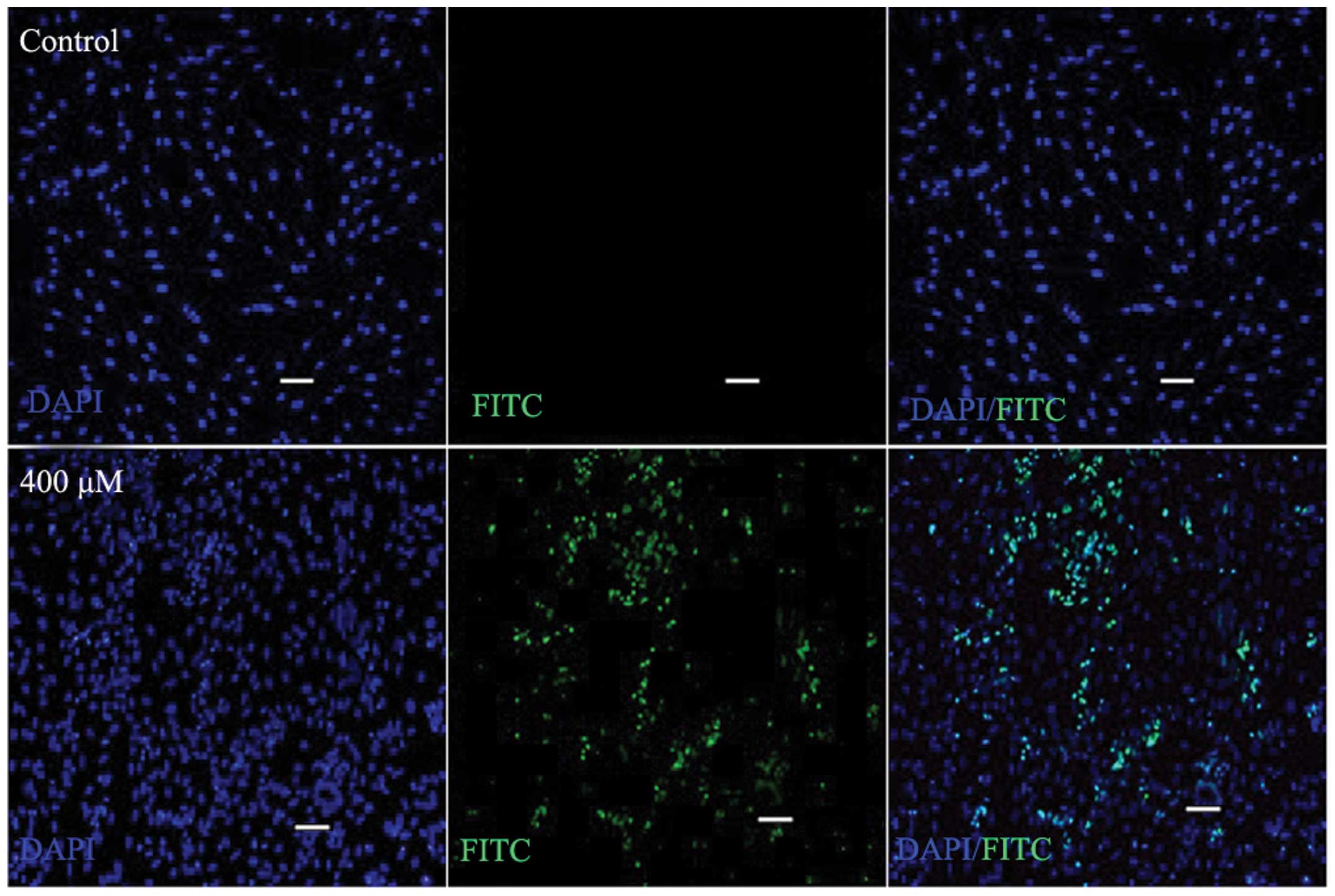
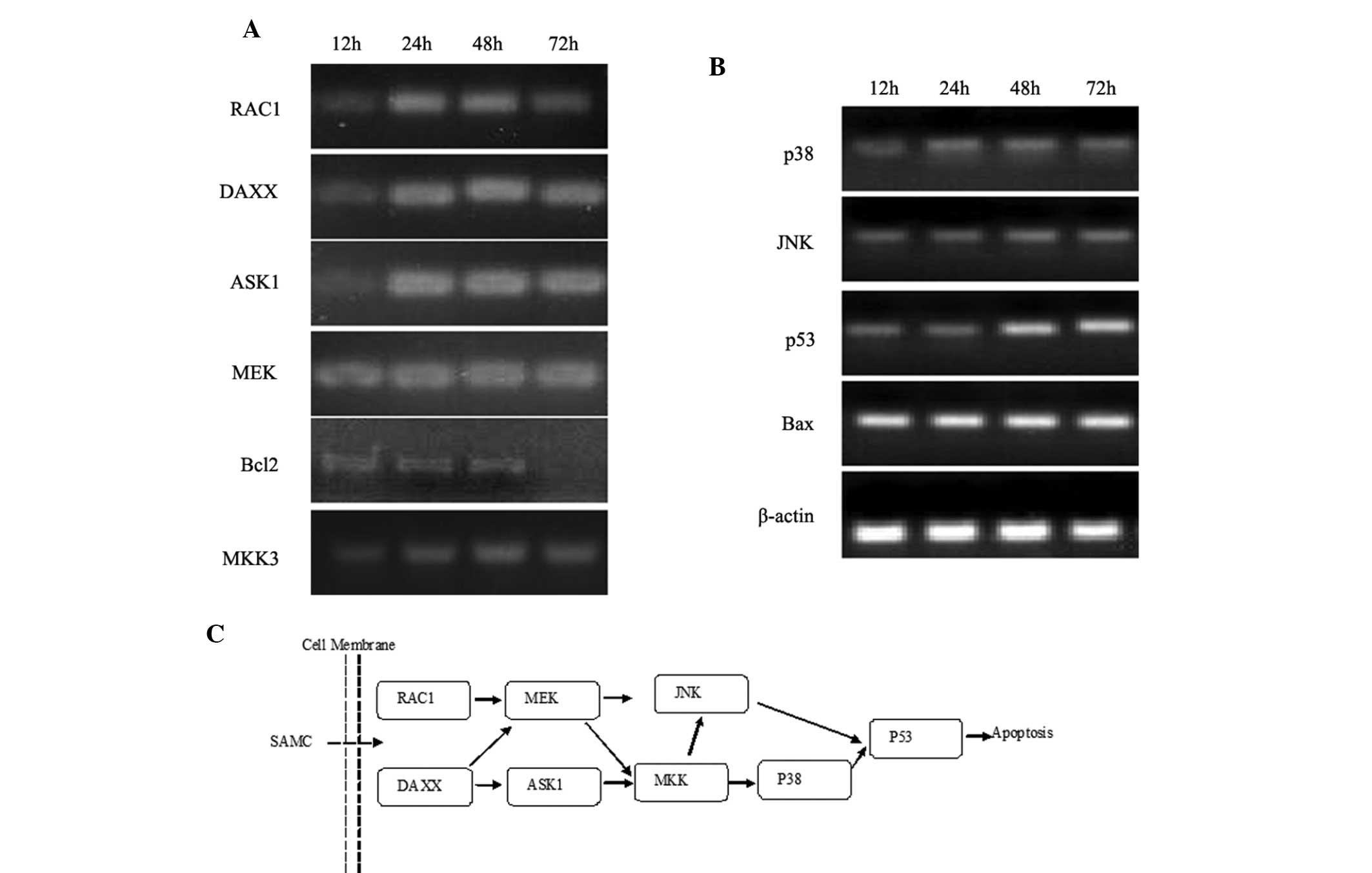
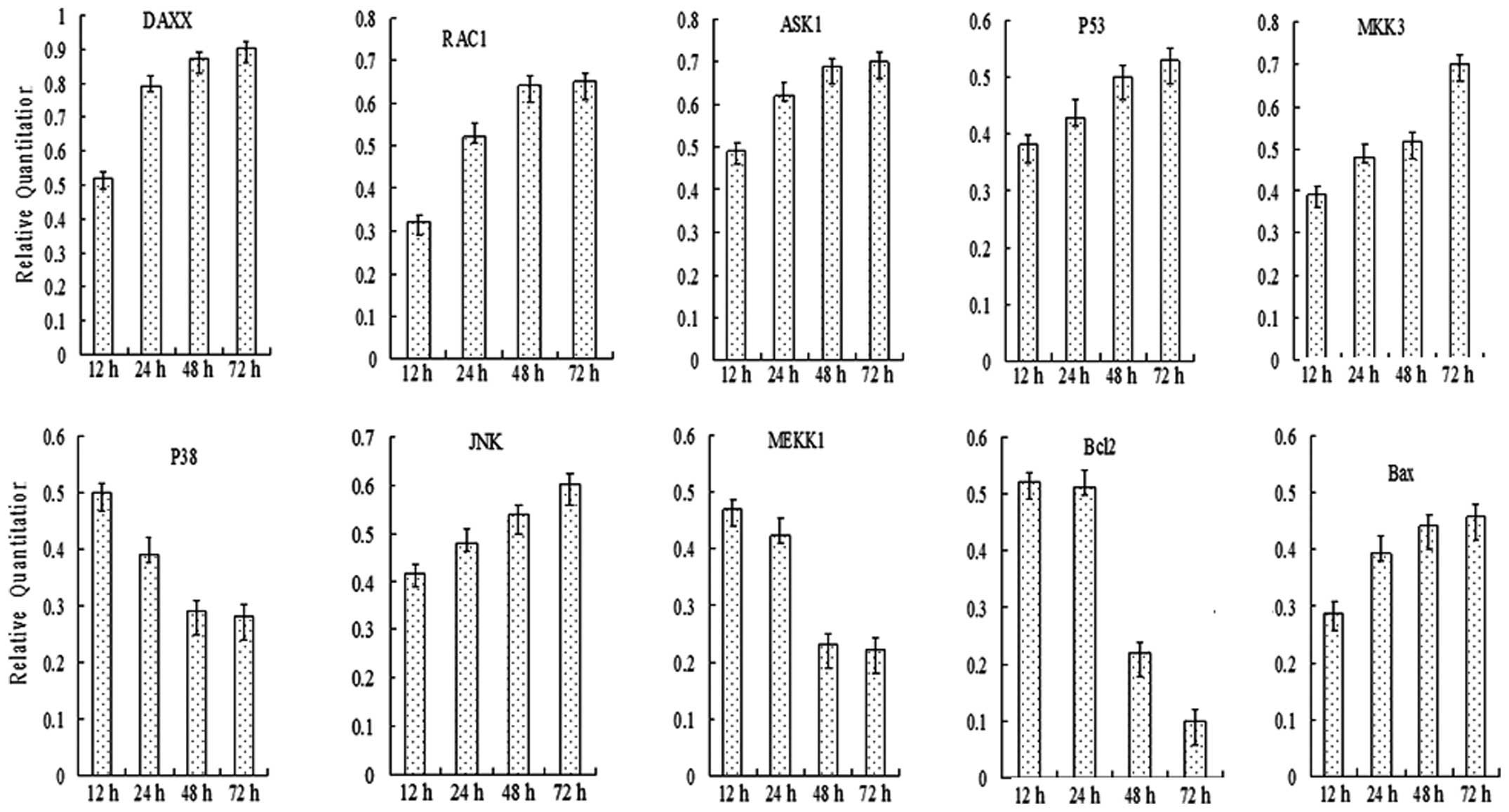
|
1
|
Milner JA: Garlic: its anticarcinogenic
and antitumorigenic properties. Nutr Rev. 54:S82–S86. 1996.
|
|
2
|
Dorey K, Barilá D, Gavin AC, Nebreda AR
and Superti-Furga G: Regulation of human c-Abl tyrosine kinase
activity in Xenopus oocytes and acceleration of
progesterone-induced G2/M transition by oncogenic forms. Biol Chem.
380:223–230. 1999.
|
|
3
|
Rahman K and Lowe GM: Garlic and
cardiovascular disease: a critical review. J Nutr. 136(Suppl 3):
736S–740S. 2006.
|
|
4
|
Sodimu O, Joseph PK and Augusti KT:
Certain biochemical effects of garlic oil on rats maintained on
high fat-high cholesterol diet. Experientia. 40:78–80. 1984.
|
|
5
|
Lee Y: Induction of apoptosis by
S-allylmercapto-L-cysteine, a biotransformed garlic derivative, on
a human gastric cancer cell line. Int J Mol Med. 21:765–770.
2008.
|
|
6
|
Medina-Campos ON, Barrera D, Segoviano
Murillo S, et al: S-allylcysteine scavenges singlet oxygen and
hypochlorous acid and protects LLC-PK(1) cells of potassium
dichromate-induced toxicity. Food Chem Toxicol. 45:2030–2039.
2007.
|
|
7
|
Xiao D, Pinto JT, Soh JW, et al: Induction
of apoptosis by the garlic-derived compound S-allylmercaptocysteine
(SAMC) is associated with microtubule depolymerization and c-Jun
NH(2)-terminal kinase 1 activation. Cancer Res. 63:6825–6837.
2003.
|
|
8
|
Chomczynski P: A reagent for the
single-step simultaneous isolation of RNA, DNA and proteins from
cell and tissue samples. Biotechniques. 15:532–534. 536–537.
1993.
|
|
9
|
Qi R and Wang Z: Pharmacological effects
of garlic extract. Trends Pharmacol Sci. 24:62–63. 2003.
|
|
10
|
Ko LJ and Prives C: p53: puzzle and
paradigm. Genes Dev. 10:1054–1072. 1996.
|
|
11
|
Eliyahu D, Raz A, Gruss P, Givol D and
Oren M: Participation of p53 cellular tumor antigen in
transformation of normal embryonic cells. Nature. 312:646–649.
1984.
|
|
12
|
Jenkins JR, Rudge K and Currie GA:
Cellular immortalization by a cDNA clone encoding the
transformation-associated phosphoprotein p53. Nature. 312:651–654.
1984.
|
|
13
|
Kastan MB, Onyekwere O, Sidransky D,
Vogelstein B and Craig RW: Participation of p53 protein in the
cellular response to DNA damage. Cancer Res. 51:6304–6311.
1991.
|
|
14
|
Hemann MT and Lowe SW: The p53-Bcl-2
connection. Cell Death Differ. 13:1256–1259. 2006.
|
|
15
|
Basu A and Haldar S: The relationship
between Bcl2, Bax and p53: consequences for cell cycle progression
and cell death. Mol Hum Reprod. 4:1099–1109. 1998.
|
|
16
|
Cuevas BD, Abell AN and Johnson GL: Role
of mitogen-activated protein kinase kinase kinases in signal
integration. Oncogene. 26:3159–3171. 2007.
|
|
17
|
Perdiguero E, Ruiz-Bonilla V, Gresh L, et
al: Genetic analysis of p38 MAP kinases in myogenesis: fundamental
role of p38alpha in abrogating myoblast proliferation. EMBO J.
26:1245–1256. 2007.
|
|
18
|
Shibata W, Maeda S, Hikiba Y, et al: c-Jun
NH2-terminal kinase 1 is a critical regulator for the development
of gastric cancer in mice. Cancer Res. 68:5031–5039. 2008.
|
|
19
|
Demidov ON, Kek C, Shreeram S, et al: The
role of the MKK6/p38 MAPK pathway in Wip1-dependent regulation of
ErbB2-driven mammary gland tumorigenesis. Oncogene. 26:2502–2506.
2007.
|
|
20
|
Dolado I, Swat A, Ajenjo N, De Vita G,
Cuadrado A and Nebreda AR: p38alpha MAP kinase as a sensor of
reactive oxygen species in tumorigenesis. Cancer Cell. 11:191–205.
2007.
|
|
21
|
Saunders PA, Cooper JA, Roodell MM, et al:
Quantification of active caspase 3 in apoptotic cells. Anal
Biochem. 284:114–124. 2000.
|
|
22
|
Scharfenberg K, Wagner R and Wagner KG:
The cytotoxic effect of ajoene, a natural product from garlic,
investigated with different cell lines. Cancer Lett. 53:103–108.
1990.
|