|
1
|
Kamangar F, Dores GM and Anderson WF:
Patterns of cancer incidence, mortality, and prevalence across five
continents: defining priorities to reduce cancer disparities in
different geographic regions of the world. J Clin Oncol.
24:2137–2150. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
Thomassen I, van Gestel YR, van Ramshorst
B, et al: Peritoneal carcinomatosis of gastric origin: a
population-based study on incidence, survival and risk factors. Int
J Cancer. 134:622–628. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
Chiang CY, Huang KH, Fang WL, et al:
Factors associated with recurrence within 2 years after curative
surgery for gastric adenocarcinoma. World J Surg. 35:2472–2478.
2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
Brancato S and Miner TJ: Surgical
management of gastric cancer: review and consideration for total
care of the gastric cancer patient. Curr Treat Options
Gastroenterol. 11:109–118. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Leung WK, Wu MS, Kakugawa Y, et al; Asia
Pacific Working Group on Gastric Cancer. Screening for gastric
cancer in Asia: current evidence and practice. Lancet Oncol.
9:279–287. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
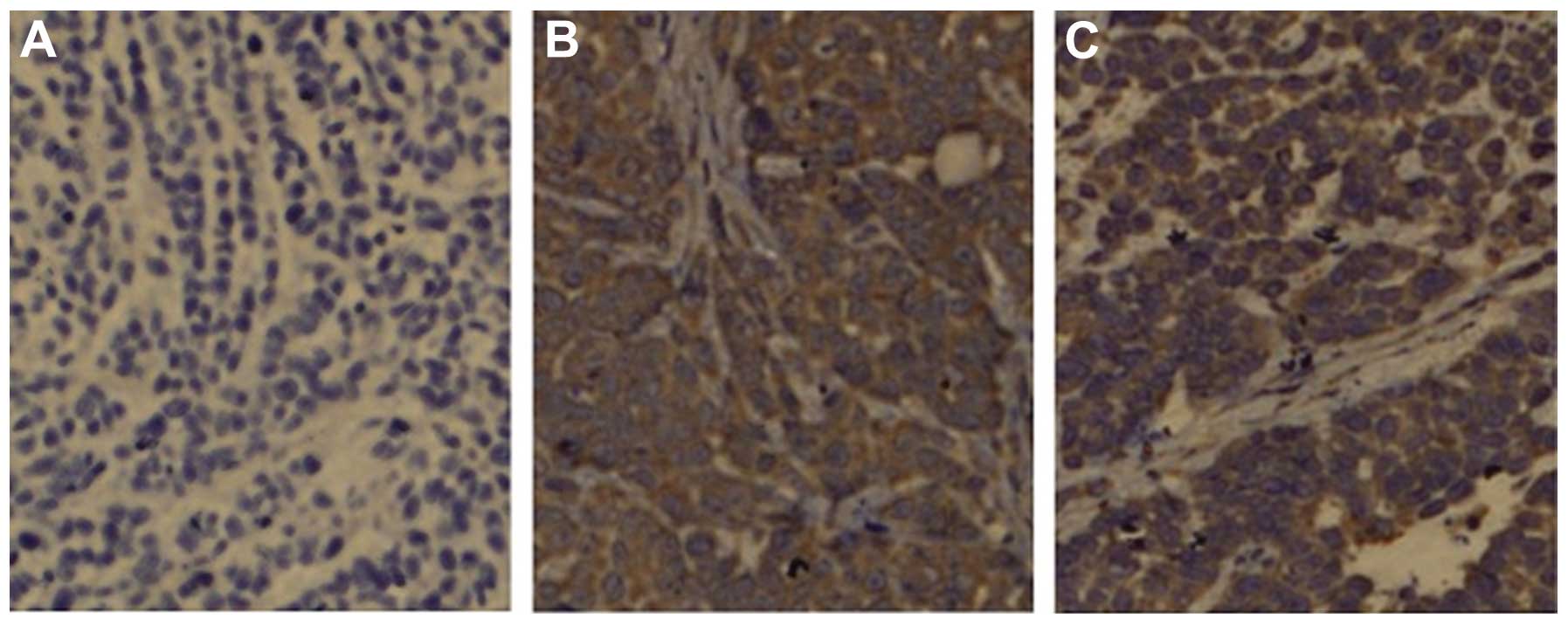
Xie ZJ, Liu Y, Jia LM and He YC:
Heparanase expression, degradation of basement membrane and low
degree of infiltration by immunocytes correlate with invasion and
progression of human gastric cancer. World J Gastroentero.
14:3812–3818. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
7
|
Su JM, Gui L, Zhou YP and Zha XL:
Expression of focal adhesion kinase and alpha5 and beta1 integrins
in carcinomas and its clinical significance. World J Gastroenterol.
8:613–618. 2002.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Golubovskaya VM, Ho B, Zheng M, et al:
Disruption of focal adhesion kinase and p53 interaction with small
molecule compound R2 reactivated p53 and blocked tumor growth. BMC
Cancer. 13:3422013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Hao HF, Naomoto Y, Bao XH, et al: Progress
in researches about focal adhesion kinase in gastrointestinal
tract. World J Gastroenterol. 15:5916–5923. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Park JH, Lee BL, Yoon J, et al: Focal
adhesion kinase (FAK) gene amplification and its clinical
implications in gastric cancer. Hum Pathol. 41:1664–1673. 2010.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Wu Z, Li X, Sunkara M, et al: PIPKIγ
regulates focal adhesion dynamics and colon cancer cell invasion.
PLoS One. 6:e247752011. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
12
|
Kamo N, Naomoto Y, Shirakawa Y, et al:
Involvement of focal adhesion kinase in the progression and
prognosis of gastrointestinal stromal tumors. Hum Pathol.
40:1643–1649. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Dy GK: The role of focal adhesion kinase
in lung cancer. Anticancer Agents Med Chem. 13:581–583. 2013.
View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
14
|
Mitra SK, Lim ST, Chi A and Schlaepfer DD:
Intrinsic focal adhesion kinase activity controls orthotopic breast
carcinoma metastasis via the regulation of urokinase plasminogen
activator expression in a syngeneic tumor model. Oncogene.
25:4429–4440. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Dassie JP, Liu XY, Thomas GS, et al:
Systemic administration of optimized aptamer-siRNA chimeras
promotes regression of PSMA-expressing tumors. Nat Biotechnol.
27:839–849. 2009. View
Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Zagzag D, Friedlander DR, Margolis B, et
al: Molecular events implicated in brain tumor angiogenesis and
invasion. Pediatr Neurosurg. 33:49–55. 2000. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Liu B, Huang J, Zhou Y, et al:
Lentivirus-mediated LOX-1-RNA interference attenuates oxidative
stress-induced apoptosis in myocardial cells. Nan Fang Yi Ke Da Xue
Xue Bao. 32:165–168. 2012.(In Chinese). PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
Tan TW, Yang WH, Lin YT, et al: Cyr61
increases migration and MMP-13 expression via alphavbeta3 integrin,
FAK, ERK and AP-1-dependent pathway in human chondrosarcoma cells.
Carcinogenesis. 30:258–268. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
Ren K, Jin H, Bian C, et al: MR-1
modulates proliferation and migration of human hepatoma HepG2 cells
through myosin light chains-2 (MLC2)/focal adhesion kinase
(FAK)/Akt signaling pathway. J Biol Chem. 283:35598–35605. 2008.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
Sonoda Y, Hada N, Kaneda T, et al: A
synthetic glycosphingolipid-induced antiproliferative effect in
melanoma cells is associated with suppression of FAK, Akt, and Erk
activation. Biol Pharm Bull. 31:1279–1283. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
Hauck CR, Sieg DJ, Hsia DA, Loftus JC,
Gaarde WA, Monia BP and Schlaepfer DD: Inhibition of focal adhesion
kinase expression or activity disrupts epidermal growth
factor-stimulated signaling promoting the migration of invasive
human carcinoma cells. Cancer Res. 61:7079–7090. 2001.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22
|
Li S, Dong W, Zong Y, et al:
Polyethylenimine-complexed plasmid particles targeting focal
adhesion kinase function as melanoma tumor therapeutics. Mol Ther.
15:515–523. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23
|
Megison ML, Stewart JE, Nabers HC, et al:
FAK inhibition decreases cell invasion, migration and metastasis in
MYCN amplified neuroblastoma. Clin Exp Metastasis. 30:555–568.
2013. View Article : Google Scholar :
|
|
24
|
Tsutsumi K, Kasaoka T, Park HM, et al:
Tumor growth inhibition by synthetic and expressed siRNA targeting
focal adhesion kinase. Int J Oncol. 33:215–224. 2008.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
25
|
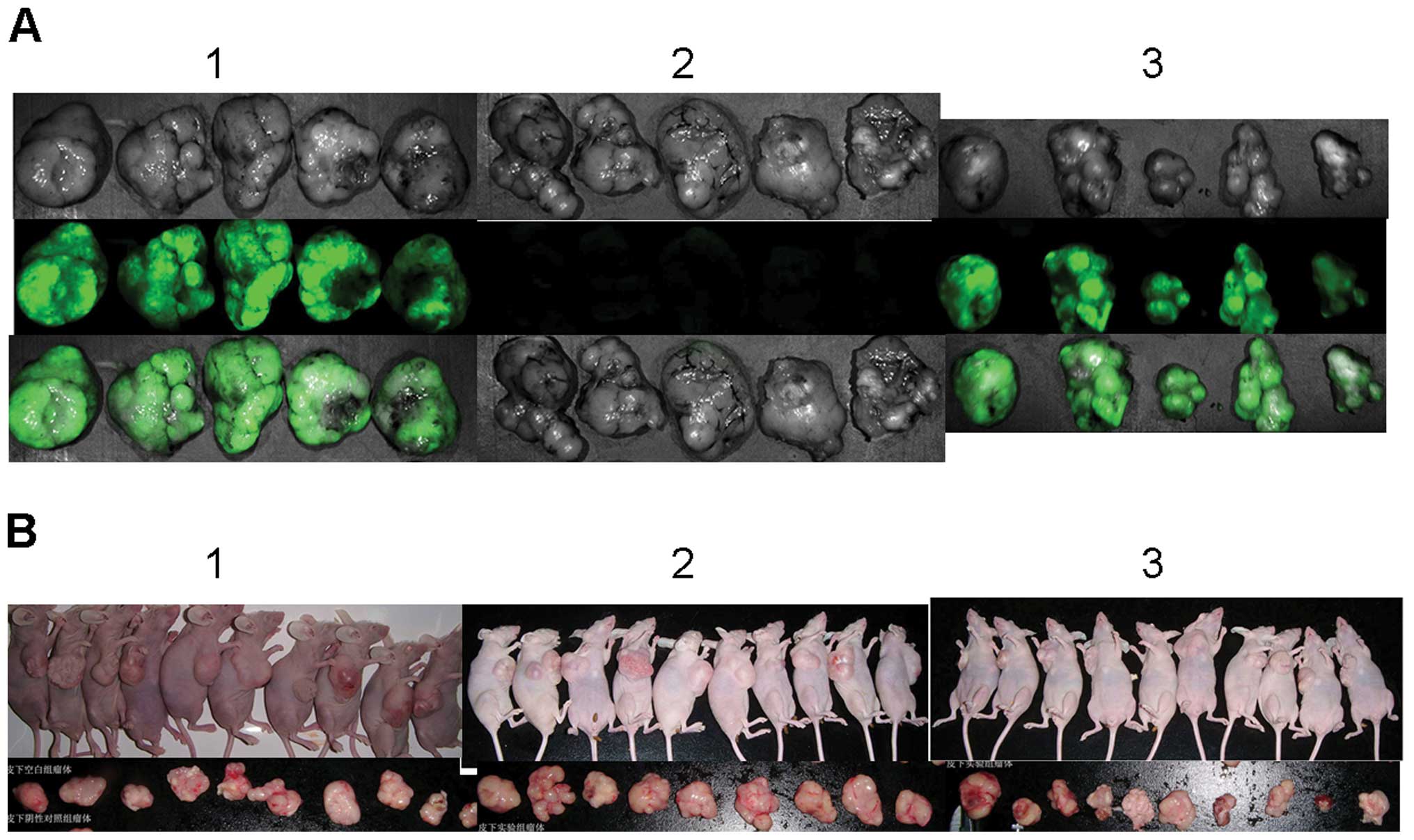
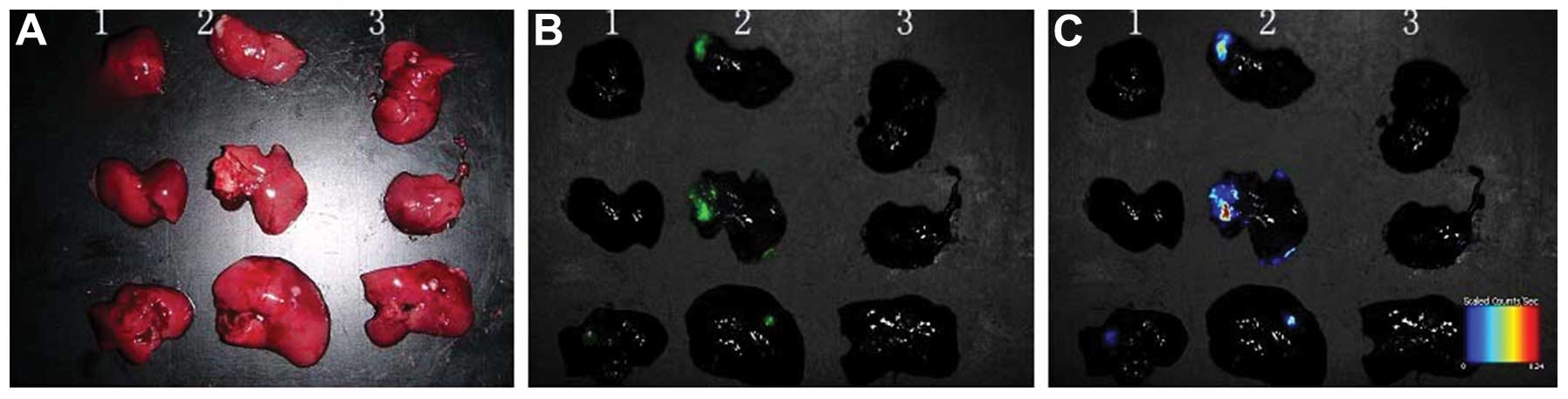
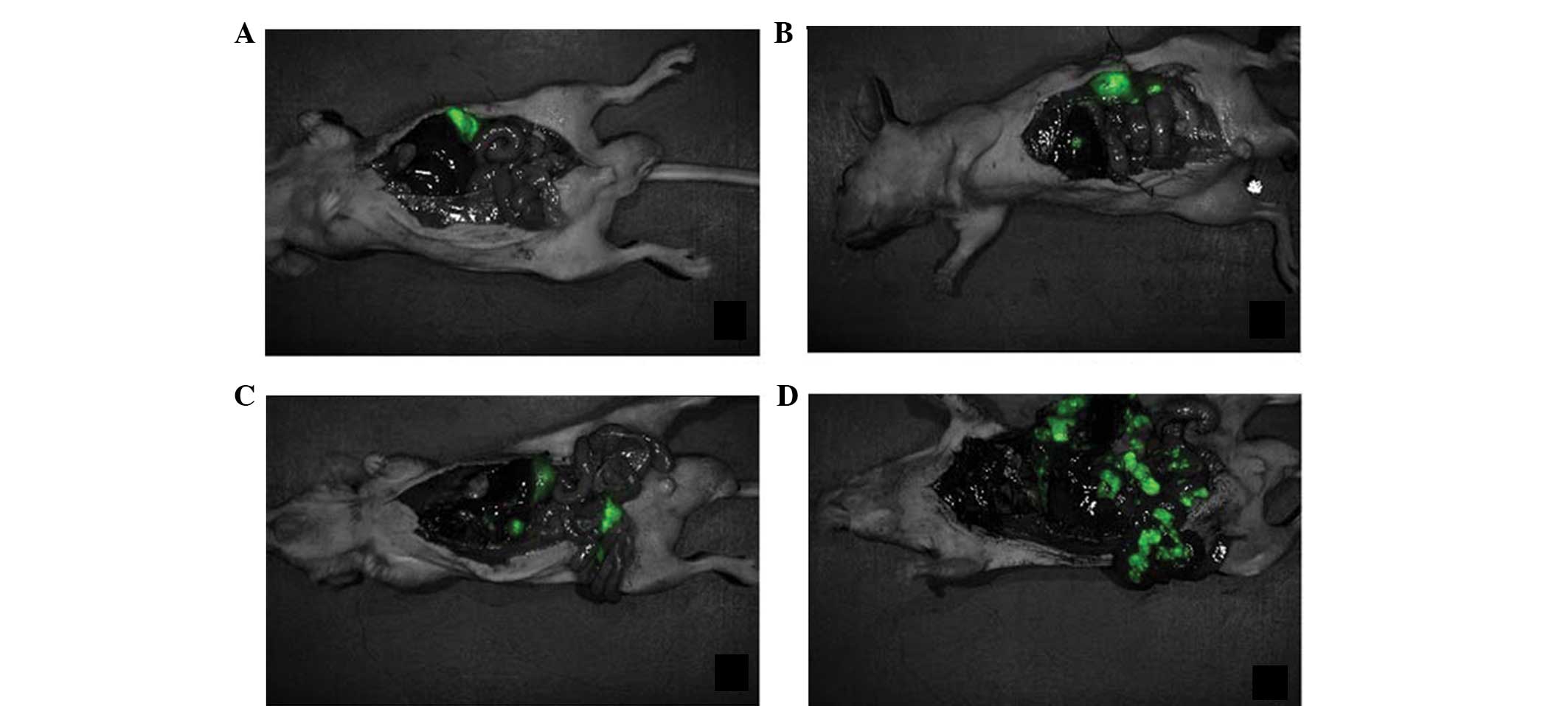
Nakanishi H, Yasui K, Ikehara Y, et al:
Establishment and characterization of three novel human gastric
cancer cell lines with differentiated intestinal phenotype derived
from liver metastasis. Clin Exp Metastasis. 22:137–147. 2005.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
26
|
Mei LJ, Yang XJ, Tang L, et al:
Establishment and identification of a rabbit model of peritoneal
carcinomatosis from gastric cancer. BMC Cancer. 10:1242010.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|