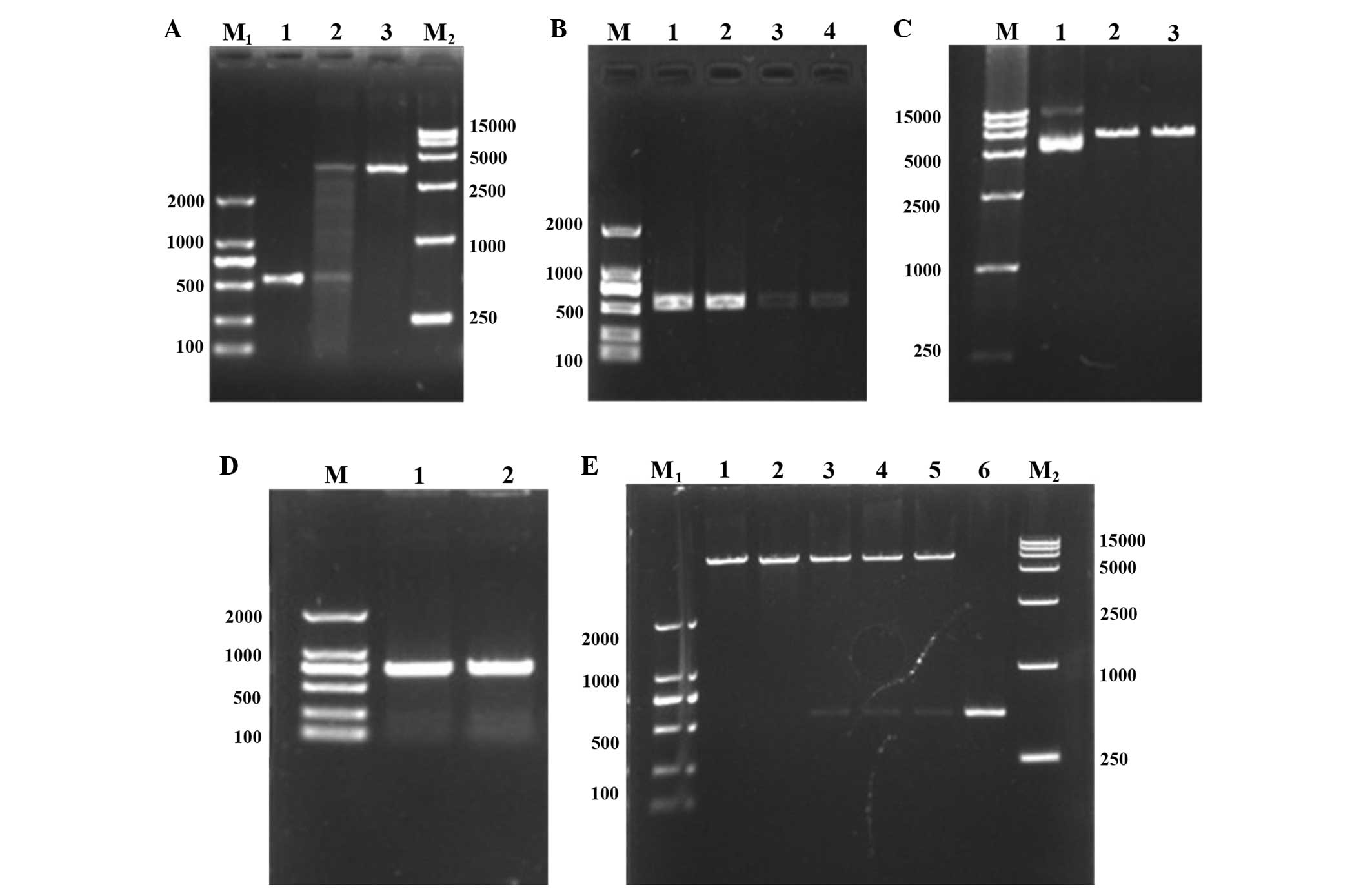
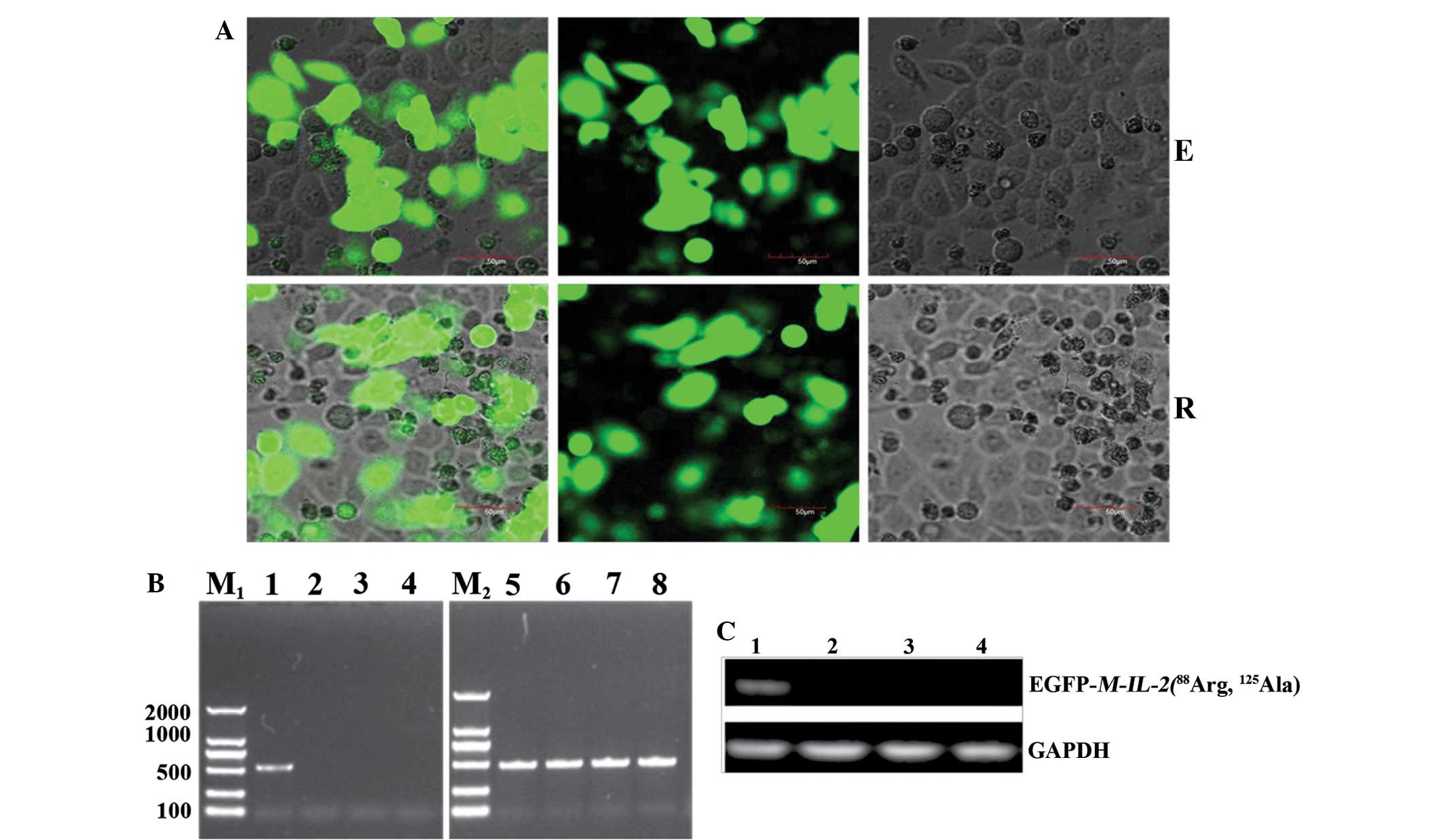
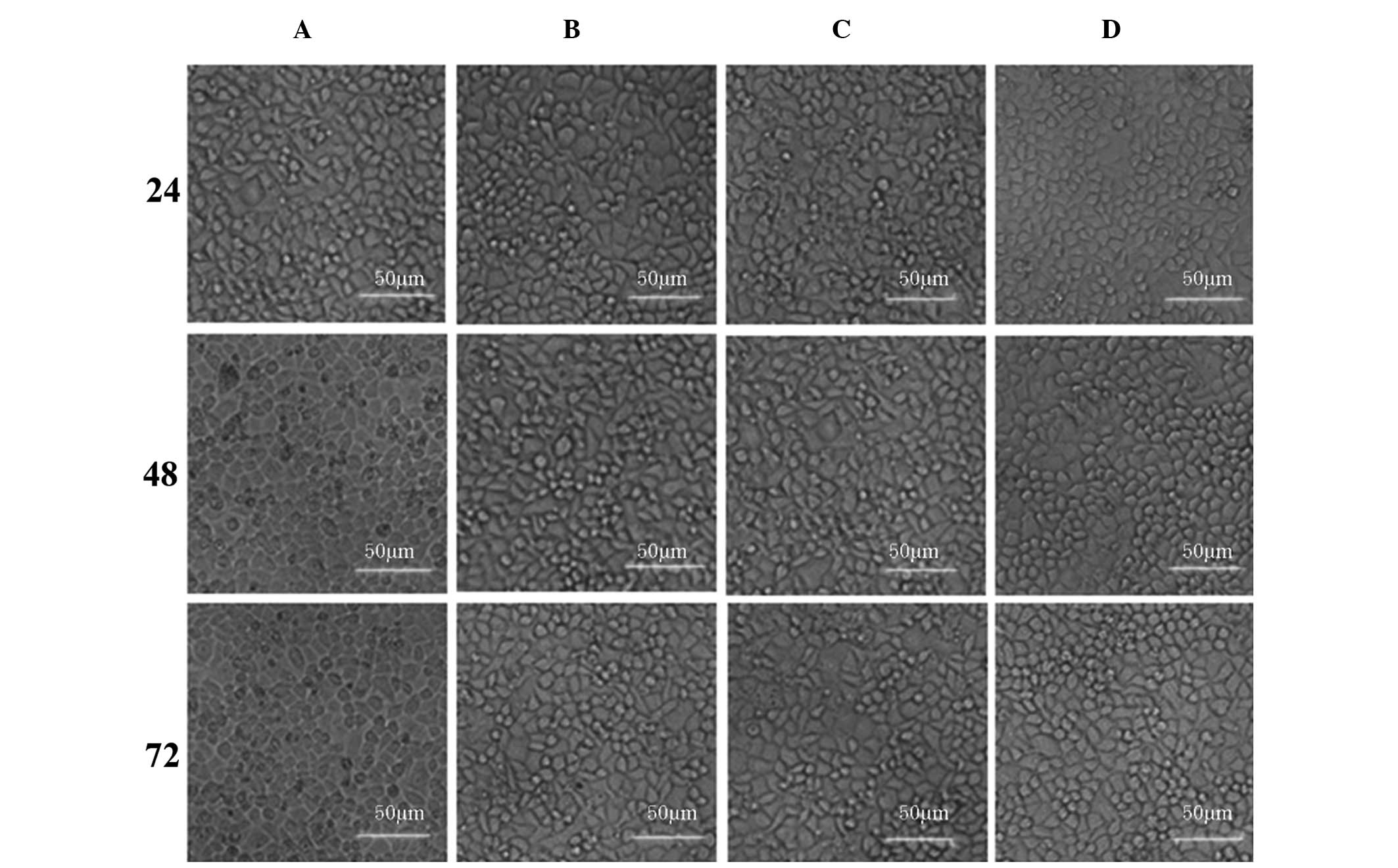
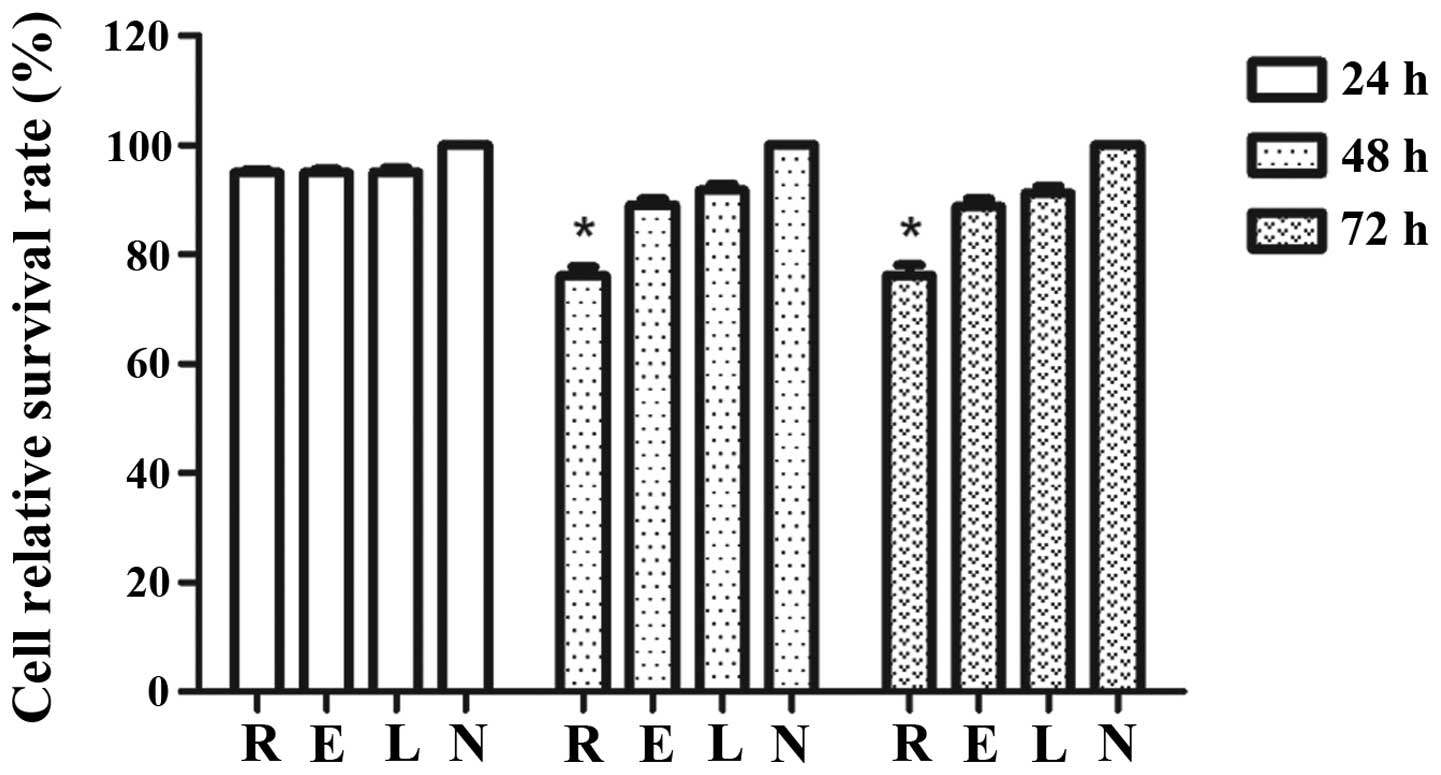
|
1
|
Takehara Y, Satoh T, Nishizawa A, Saeki K,
Nakamura M, Masuzawa M, Kaneda Y, Katayama I and Yokozeki H:
Anti-tumor effects of inactivated Sendai virus particles with an
IL-2 gene on angiosarcoma. Clin Immunol. 149:1–10. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
Gajski G and Garaj-Vrhovac V: Melittin: A
lytic peptide with anticancer properties. Environ Toxicol
Pharmacol. 36:697–705. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
Jo M, Park MH, Kollipara PS, An BJ, Song
HS, Han SB, Kim JH, Song MJ and Hong JT: Anti-cancer effect of bee
venom toxin and melittin in ovarian cancer cells through induction
of death receptors and inhibition of JAK2/STAT3 pathway. Toxicol
Appl Pharmacol. 258:72–81. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
Park HJ, Lee HJ, Choi MS, Son DJ, Song HS,
Song MJ, Lee JM, Han SB, Kim Y and Hong JT: JNK pathway is involved
in the inhibition of inflammatory target gene expression and
NF-kappaB activation by melittin. J Inflamm (Lond). 5:72008.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Adade CM, Oliveira IR, Pais JA and
Souto-Padron T: Melittin peptide kills Trypanosoma cruzi parasites
by inducing different cell death pathways. Toxicon. 69:227–239.
2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Jeong YJ, Cho HJ, Whang K, Lee IS, Park
KK, Choe JY, Han SM, Kim CH, Chang HW, Moon SK, et al: Melittin has
an inhibitory effect on TNF-α-induced migration of human aortic
smooth muscle cells by blocking the MMP-9 expression. Food Chem
Toxicol. 50:3996–4002. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Mizuno H, Yanoma S, Nishimura G, Hattori
S, Ito T, Okudera K and Tsukuda M: Therapeutic efficiency of IL-2
gene transduced tumor vaccine for head and neck carcinoma. Cancer
Lett. 152:175–185. 2000. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Hughes DP, Baskar D, Urban FF, Friedman
MS, Braun TM and McDonagh KT: Fate and function of
anti-CD3/CD28-activated T cells following adoptive transfer: IL-2
promotes development of anti-tumor memory T cells in vivo.
Cytotherapy. 7:396–407. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Rossowska J, Pajtasz-Piasecka E, Rysnik O,
Wojas J, Krawczenko A, Szyda A and Dus D: Generation of antitumor
response by IL-2-transduced JAWS II dendritic cells. Immunobiology.
216:1074–1084. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Taniguchi T, Matsui H, Fujita T, Takaoka
C, Kashima N, Yoshimoto R and Hamuro J: Structure and expression of
a cloned cDNA for human interleukin-2. Nature. 302:305–310. 1983.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Rosenberg SA, Lotze MT, Muul LM, Leitman
S, Chang AE, Ettinghausen SE, Matory YL, Skibber JM, Shiloni E,
Vetto JT, et al: Observations on the systemic administration of
autologous lymphokine-activated killer cells and recombinant
interleukin-2 to patients with metastatic cancer. N Engl J Med.
313:1485–1492. 1985. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Shanafelt AB, Lin Y, Shanafelt MC, Forte
CP, Dubois-Stringfellow N, Carter C, Gibbons JA, Cheng SL, Delaria
KA, Fleischer R, et al: A T-cell-selective interleukin 2 mutein
exhibits potent antitumor activity and is well tolerated in vivo.
Nat Biotechnol. 18:1197–1202. 2000. View
Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Liu Y, Xiao XY, Sun M, Hu YH, Ou-Yang KQ,
Cai SX and Hua ZC: Expression and purification of a mutant of human
interleukin-2 in Pichia pastoris. Appl Biochem Biotechnol.
133:77–86. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Ju G, Collins L, Kaffka KL, et al:
Structure-function analysis of human interleukin-2. J Biol Chem.
262:5723–5731. 1987.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Moya G, Gonzalez LJ, Huerta V, Garcia Y,
Morera V, Perez D, Brena F and Arana M: Isolation and
characterization of modified species of a mutated (Cys125 -Ala)
recombinant human interleukin-2. J Chromatogr A. 971:129–142. 2002.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Liu M, Wang B, Sun G, Qian D, Yan Z, Song
X and Ding S: Expression, purification, and characterization of a
functional mutant recombinant human interleukin-2. Protein Pept
Lett. 17:1280–1284. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Li L, Qian D, Shao G, et al: High-level
expression, purification and study of bioactivity of fusion protein
M-IL-2((88)Arg,(125) Ala) in Pichia pastoris. Protein Expr
Purif. 101:99–105. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
Glinka EM, Edelweiss EF, Sapozhnikov AM
and Deyev SM: A new vector for controllable expression of an
anti-HER2/neu mini-antibody-barnase fusion protein in HEK 293T
cells. Gene. 366:97–103. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
Glinka EM: Eukaryotic expression vectors
bearing genes encoding cytotoxic proteins for cancer gene therapy.
Plasmid. 68:69–85. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
Rosenberg SA, Yang JC, Topalian SL,
Schwartzentruber DJ, Weber JS, Parkinson DR, Seipp CA, Einhorn JH
and White DE: Treatment of 283 consecutive patients with metastatic
melanoma or renal cell cancer using high-dose bolus interleukin 2.
JAMA. 271:907–913. 1994. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
Ma D, Cao W, Kapur A, Felder M, Scarlett
CO, Patankar MS and Li L: Differential expression of proteins in
naive and IL-2 stimulated primary human NK cells identified by
global proteomic analysis. J Proteomics. 91:151–163. 2013.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22
|
Hider RC: Honeybee venom: A rich source of
pharmacologically active peptides. Endeavour. 12:60–65. 1988.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23
|
Son DJ, Lee JW, Lee YH, Song HS, Lee CK
and Hong JT: Therapeutic application of anti-arthritis,
pain-releasing, and anti-cancer effects of bee venom and its
constituent compounds. Pharmacol Ther. 115:246–270. 2007.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|