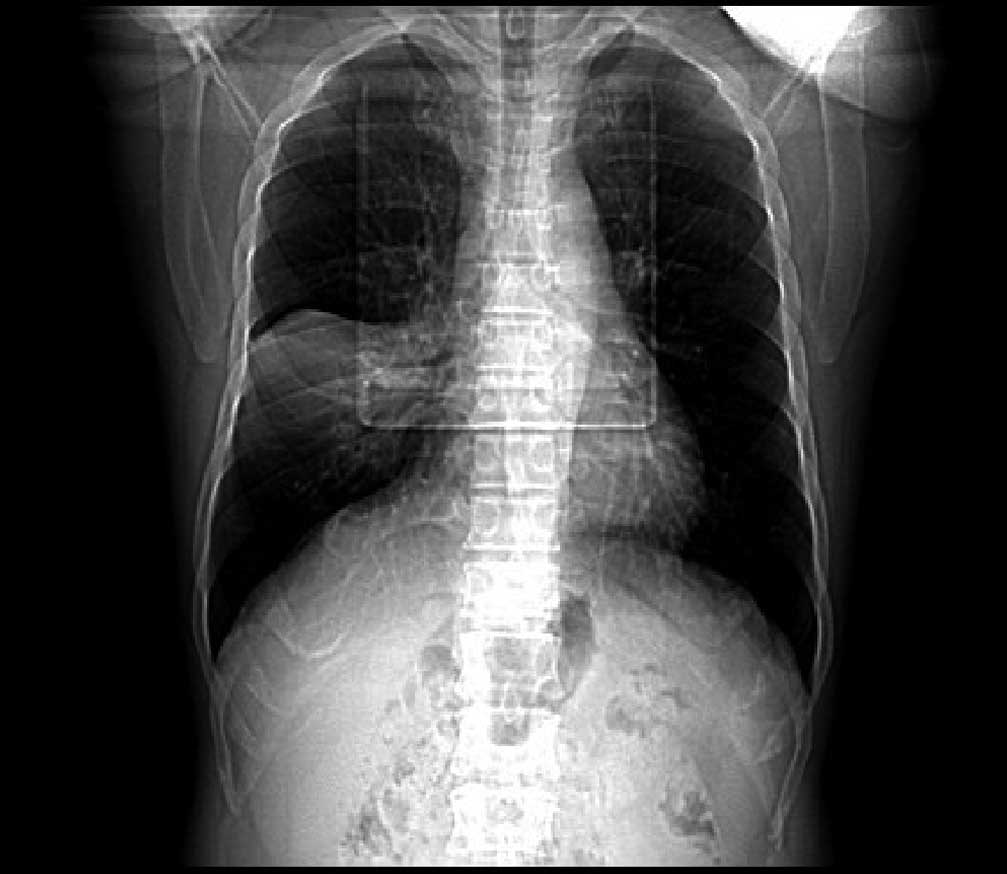
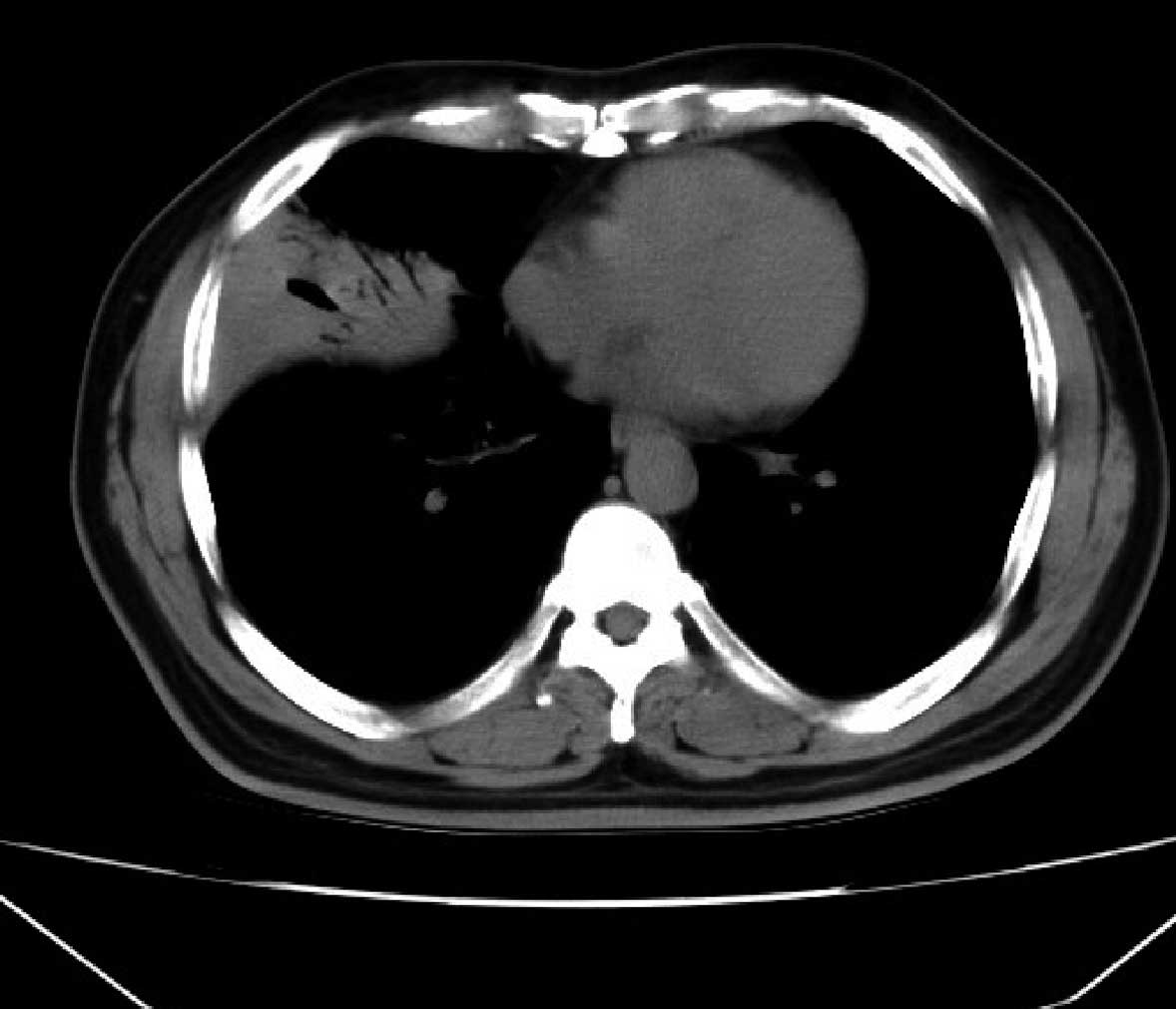
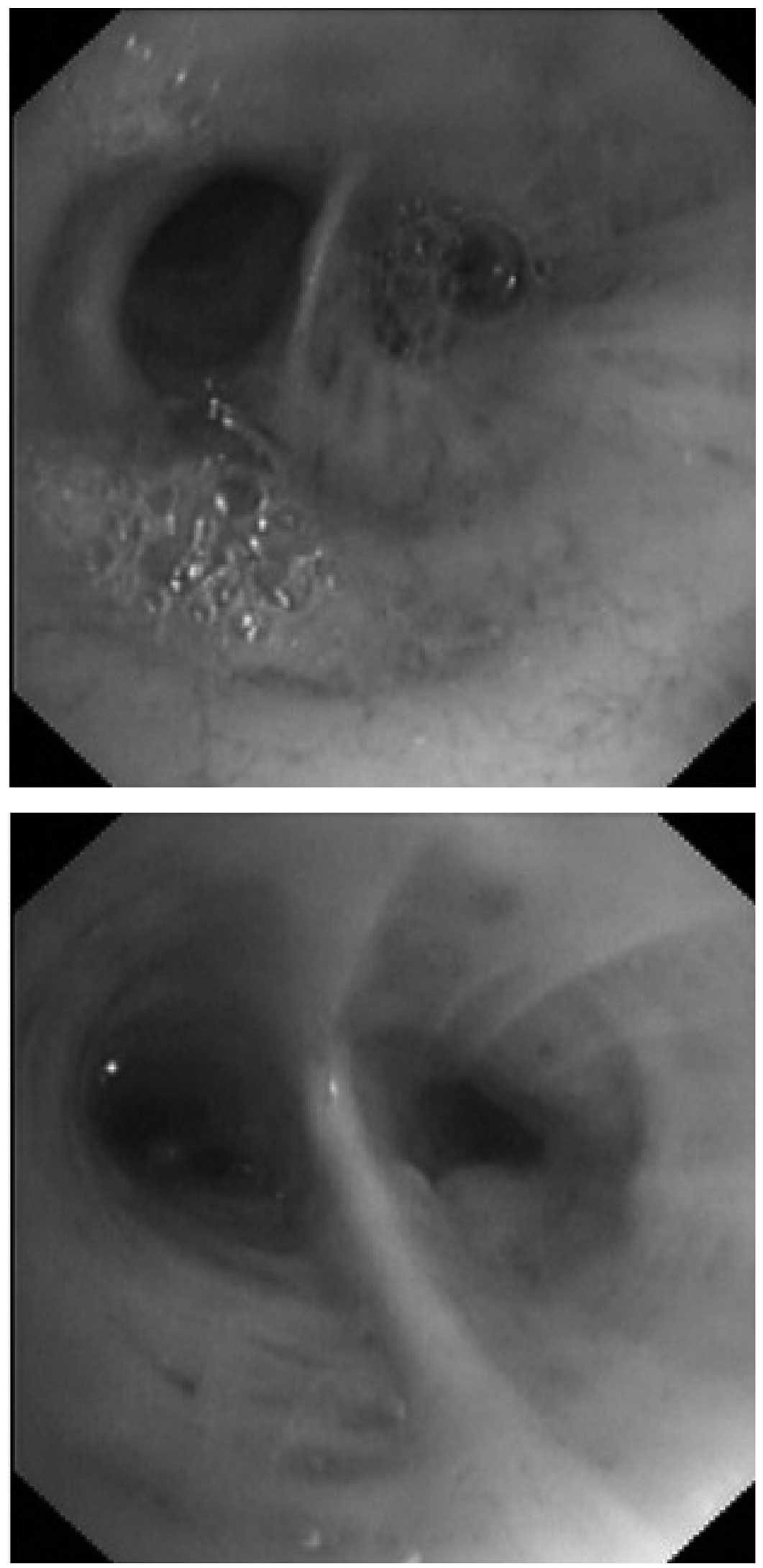
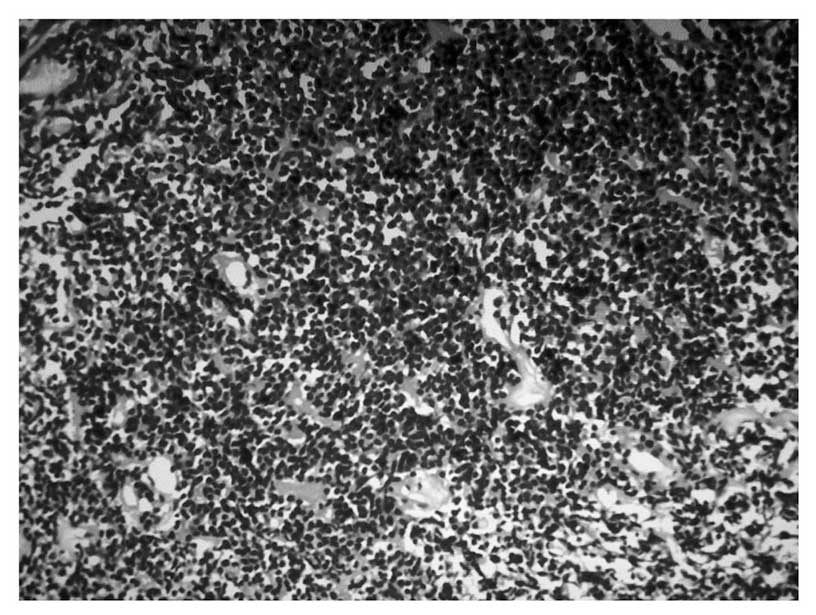
|
1
|
Harris NL, Jaffe ES, Stein H, et al: A
revised European-American classification of lymphoid neoplasms: a
proposal from the International Lymphoma Study Group. Blood.
84:1361–1392. 1994.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
Armitage JO and Weisenburger DD: New
approach to classifying non-Hodgkin's lymphomas: clinical features
of the major histologic subtypes. Non-Hodgkin's Lymphoma
Classification Project. J Clin Oncol. 16:2780–2795. 1998.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
Zucca E, Conconi A, Pedrinis E, et al:
Nongastric marginal zone B-cell lymphoma of mucosa-associated
lymphoid tissue. Blood. 101:2489–2495. 2003. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
Jaffe ES, Harris NL, Stein H and Vardiman
JW: World Health Organization Classification of TumoursPathology
and Genetics of Tumours of Haematopoietic and Lymphoid Tissues.
IARC Press; Lyon: pp. 171–181. 2001
|
|
5
|
Ahmed S, Siddiqui AK and Rai KR: Low-grade
B-cell bronchial associated lymphoid tissue (BALT) lymphoma. Cancer
Invest. 20:1059–1068. 2002. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Koss MN: Malignant and benign lymphoid
lesions of the lung. Ann Diagn Pathol. 8:167–187. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Travis WD, Brambilla E, Müller-Hermelink
HK and Harris CC: World Health Organization Classification of
TumoursPathology and Genetics of Tumours of the Lung, Pleura,
Thymus and Heart. 3rd. IARC Press; Lyon: pp. 95–98. 2004
|
|
8
|
Cordier JF, Chailleux E, Lauque D, et al:
Primary pulmonary lymphomas. A clinical study of 70 cases in
nonimmunocompromised patients. Chest. 103:201–208. 1993. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Wislez M, Cadranel J, Antoine M, Milleron
B, Bazot M, Mayaud C and Carette MF: Lymphoma of pulmonary
mucosa-associated lymphoid tissue: CT scan findings and
pathological correlations. Eur Respir J. 14:423–429. 1999.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Cadranel J, Wislez M and Antoine M:
Primary pulmonary lymphoma. Eur Respir J. 20:750–762. 2002.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Zhang LB, Sun YE, Yu CH and Liu Y:
Clinical diagnosis and surgical treatment of primary pulmonary
lymphoma. Zhonghua Wai Ke Za Zhi. 44:97–99. 2006.(In Chinese).
PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Vanden Eynden F, Fadel E, de Perrot M, et
al: Role of surgery in the treatment of primary pulmonary B-cell
lymphoma. Ann Thorac Surg. 83:236–240. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Li G, Hansmann ML, Zwingers T and Lennert
K: Primary lymphomas of the lung: morphological,
immunohistochemical and clinical features. Histopathology.
16:519–531. 1990. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Isaacson P and Wright DH: Malignant
lymphoma of mucosa-associated lymphoid tissue. A distinctive type
of B-cell lymphoma. Cancer. 52:1410–1416. 1983. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Bae YA, Lee KS, Han J, et al: Marginal
zone B-cell lymphoma of bronchus-associated lymphoid tissue:
imaging findings in 21 patients. Chest. 133:433–440. 2008.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Elstrom R, Guan L, Baker G, et al: Utility
of FDG-PET scanning in lymphoma by WHO classification. Blood.
101:3875–3876. 2003. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Perry C, Herishanu Y, Metzer U, et al:
Diagnostic accuracy of PET/CT in patients with extranodal marginal
zone MALT lymphoma. Eur J Haematol. 79:205–209. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
Hoffmann M, Kletter K, Becherer A, et al:
18F-fluorodeoxyglucose positron emission tomography (18F-FDG-PET)
for staging and follow-up of marginal zone B-cell lymphoma.
Oncology. 64:336–340. 2003. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
Oh SY, Kim WS, Kim JS, et al: Pulmonary
marginal zone B-cell lymphoma of MALT type-what is a prognostic
factor and which is the optimal treatment, operation, or
chemotherapy?: Consortium for Improving Survival of Lymphoma (CISL)
study. Ann Hematol. 89:563–568. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
Ahmed S, Kussick SJ, Siddiqui AK, et al:
Bronchial-associated lymphoid tissue lymphoma: a clinical study of
a rare disease. Eur J Cancer. 40:1320–1326. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|