Introduction
Survivin, encoded by baculoviral inhibitor of
apoptosis repeat-containing 5 (BIRC5), is the smallest member of
the inhibitor of apoptosis (IAP) family of proteins. It is widely
distributed during the embryonic and fetal developmental stages,
yet absent in terminally differentiated normal tissue (1). Previous studies have demonstrated that
survivin, unlike other IAPs, is strongly expressed in the majority
of neoplasms. Overexpression of survivin is also significantly
correlated with a poor prognosis and decreased survival rates in
breast and lung cancer, colon, bladder and Ewing sarcoma, and
lymphomas (2–7). BIRC5/survivin is an essential protein
involved in Ewing sarcoma cell growth and proliferation (7). In addition, BIRC5/survivin plays a
significant role in the pathogenesis of malignant tumors and the
progression of various types of cancer.
It is well known that the microRNA (miRNA) binding
regions variants influence altered gene functions. miRNAs regulate
the activity of BIRC5/survivin, and miRNA dysregulation has been
associated with malignant neoplasms. Zu et al evaluated the
association between genetic variants in the 3′ untranslated region
(3′UTR) of cancer-related genes and risk of lung cancer in Chinese
populations, and defined a 3′UTR single nucleotide polymorphism
(SNP) in the human BIRC5 oncogene that may increase individual
susceptibility to lung cancer, possibly by attenuating the
interaction between BIRC5 and miRNA-335 (8). BIRC5/survivin directly binds to the
promoter of the miRNA-335 cluster, activating its transcription,
and negatively modulating the translation of BIRC5/survivin miRNAs
by binding sites in their 3′UTRs (8).
In addition, a number of studies have revealed that BIRC5/survivin
variants may play crucial roles in carcinogenesis (2). Considering that survivin is a notable
member of the IAP family, but that the role of variants in miRNA
binding sites of survivin remains unknown, in the present study, we
performed a bioinformatic analysis and genotype-phenotype
association analysis based on the HapMap database to test our
hypothesis that BIRC5/survivin 3′UTR variants are associated with
its mRNA expression.
The study was approved by the Ethics Committee of
the Union Hospital, Tongji Medical College of Huazhong University
of Science and Technology, China.
Materials and methods
Bioinformatic analysis and selection
of polymorphisms
The SNPs of BIRC5/survivin were identified in the
gene region and the coding region using an online database
(http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/SNP/). The
bioinformatic tool SNP Function Prediction (FuncPred; http://snpinfo.niehs.nih.gov/cgi-bin/snpinfo/snpfunc.cgi)
was used to predict the potential functional relevance affecting
the miRNA binding sites. Additionally, SNPs were limited by a minor
allele frequency (MAF) of >0.05 in the HapMap population derived
from Utah residents with Northern and Western European ancestry.
Pairwise linkage disequilibrium (LD) values of all SNPs in the same
gene were calculated, then the SNPs that were not in LD
(r2<0.8) were selected, and LD maps of those SNPs in
BIRC5/survivin genes were plotted with the online program
http://snpinfo.niehs.nih.gov/cgi-bin/snpinfo/snpfunc.cgi.
Genotype and mRNA expression data of
lymphoblastoid cell lines from HapMap database
Additional data on BIRC5/survivin genotypes and mRNA
levels were available online (http://app3.titan.uio.no/biotools/help.php?app=snpexp)
for the genotype-phenotype association analysis (9). Genome-wide expression arrays (47,294
transcripts) from Epstein-Barr virus-transformed lymphoblastoid
cell lines were used from 270 HapMap individuals (142 males and 128
females) to analyze the gene expression variation (10). The genotyping data were from the
HapMap phase II release 23 data set consisting of 3.96 million SNP
genotypes from 270 individuals from four populations (11). The SNPexp v1.2 tool was used for
calculating and visualizing correlations between HapMap genotypes
and gene expression levels (Norwegian PSC Research Center, Clinic
for Specialized Surgery and Medicine, Oslo University Hospital
Rikshospitalet, Norway).
Statistical analysis
Genotype and phenotype correlation was analyzed
using the Chi-square test. All statistics tests were two-sided and
P<0.05 was considered to indicate a statistically significance
result.
Results
BIRC5/survivin 3′UTR selected variants
and putative miRNA binding sites
In total, 372 SNPs were identified in the
BIRC5/survivin gene region and 28 in the coding region (http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/SNP/). Among them, 62
SNPs were reported in the 3′UTR, of which only 8 SNPs (rs2239680,
rs202011142, rs1042489, rs2661694, rs1042541, rs1042542, rs4789560
and rs17882360) had an available MAF value >0.05, and were
predicted to affect the miRNA binding site activity according to
the bioinformatics analysis, as shown in Table I. The most extensively studied
putative binding sites of these SNPs include hsa-miR-877,
hsa-miR-936, hsa-miR-939, hsa-miR-367, hsa-miR-493, hsa-miR-601,
hsa-miR-92a, hsa-miR-1256, hsa-miR-1285, hsa-miR-34a,
hsa-miR-34c-5p, hsa-miR-503, hsa-miR-612, hsa-miR-626,
hsa-miR-885-3p, hsa-miR-1276, hsa-miR-335, hsa-miR-577,
hsa-miR-1295, hsa-miR-24, hsa-miR-298, hsa-miR-510, hsa-miR-576-3p,
hsa-miR-1254 and hsa-miR-147 (http://snpinfo.niehs.nih.gov/cgi-bin/snpinfo/snpfunc.cgi).
Combined with other SNPs in the 3′UTR or promoter region, the
variant rs2239680 is jointly involved in cancer susceptibility
(8,12).
 | Table I.Selected single nucleotide
polymorphisms of BIRC5/survivin 3′ untranslated region and putative
microRNA binding sites. |
Table I.
Selected single nucleotide
polymorphisms of BIRC5/survivin 3′ untranslated region and putative
microRNA binding sites.
| Name | Alleles | MAF | Putative miRNA
binding sites |
|---|
| rs1042489 | C/T | 0.3848 | hsa-miR-877,
hsa-miR-936, hsa-miR-939 |
| rs1042541 | A/G | 0.3724 | NA |
| rs1042542 | C/T | 0.3875 | hsa-miR-367,
hsa-miR-493, hsa-miR-601, hsa-miR-92a |
| rs17882360 | A/T | 0.0569 | hsa-miR-1256,
hsa-miR-1285, hsa-miR-34a, hsa-miR-503, hsa-miR-34c-5p,
hsa-miR-612, hsa-miR-626, hsa-miR-885-3p |
| rs2239680 | (>6 bp) | 0.2319 | hsa-miR-1276,
hsa-miR-335, hsa-miR-577 |
| rs2661694 | A/C | 0.2185 | hsa-miR-1295,
hsa-miR-24, hsa-miR-298, hsa-miR-510, hsa-miR-576-3p |
| rs4789560 | C/T | 0.3675 | hsa-miR-1254,
hsa-miR-147 |
| rs202011142 | -/T | 0.3081 | NA |
LD of all SNPs in the BIRC5/survivin
gene calculation
The bioinformatic tool FuncPred (http://snpinfo.niehs.nih.gov/snpfunc.htm) was used to
identify the potential functional relevance of the SNPs. We
calculated pairwise LD values of all SNPs in the same gene to
determine the SNPs which were not in LD (r2<0.8), and
plotted the LD maps of those SNPs in BIRC5/survivin genes using
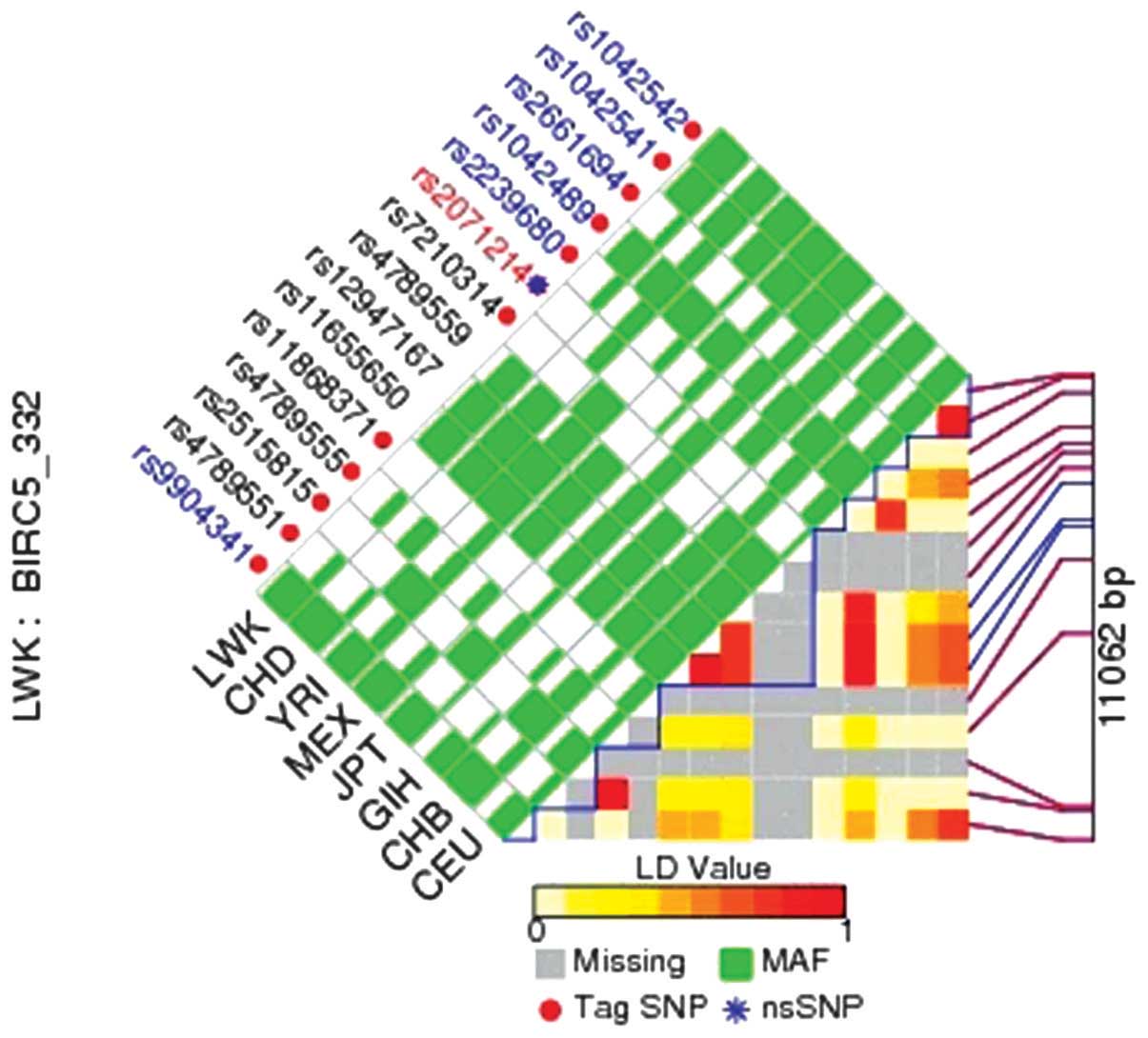
FuncPred (Fig. 1). The pairwise
r2 correlations between the relevant two SNPs are
represented by each square number. The color of each SNP spot
reflects its D′ value, and when the D′ value decreases, the color
changes from red to white. The haplotype blocks were estimated with
the FuncPred program. The minor allele frequency of all the above
alleles was greater than 0.05. rs1042489 was the predicted tag SNP
in our study, and rs1042542, rs2239680 and rs2661694 in
BIRC5/survivin were not included in the LD plot (Fig. 1).
BIRC5/survivin mRNA expression by
genotypes in lymphoblastoid cell lines
To assess the mRNA expression of the prohibitin gene
in the lymphoblastoid cell lines, the available HapMap-cDNA
expression database was used to analyze the correlation of the
prohibitin genotype and mRNA expression in 270 HapMap
lymphoblastoid cell lines. With the exception of the one cell line
with unavailable values for rs1042489, 49 (0.188) cell lines with
the CC genotype, 135 (0.517) cell lines with the CT genotype and 77
(0.295) cell lines with the TT genotype were identified. For
rs1042542, 30 (0.111) cell lines had the TT genotype, 140 (0.519)
had the TC genotype, and 100 (0.370) had the CC genotype. There
were 10 (0.037) cell lines with CC, 88 (0.327) with CT, and 171
(0.636) with TT genotype for rs2239680. For rs2661694, 6 (0.022)
cell lines with the AA genotype, 81 (0.301) cell lines with the AC
genotype and 182 (0.677) with the CC genotype were identified.
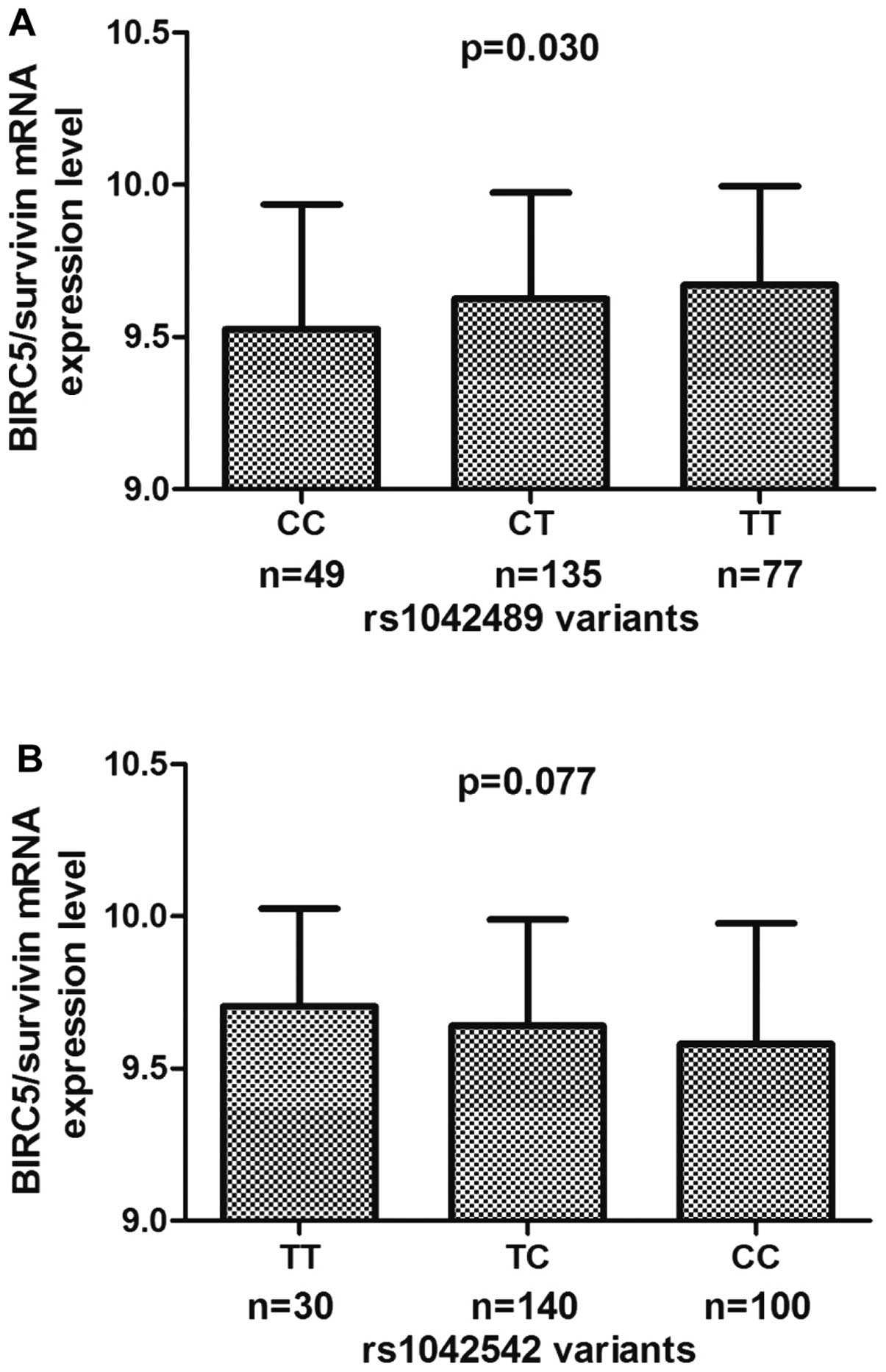
Fig. 2 shows the BIRC5/survivin mRNA
expression levels of cell lines by BIRC5 genotype. The rs1042489 CC
genotype was revealed to have significantly lower expression levels
than the CT and TT genotypes (P=0.030; Fig. 2A), and there was no significant
difference in BIRC5/survivin mRNA expression levels among cell
lines carrying rs1042542 (P=0.077), rs2239680 (P=0.364) and
rs2661694 (P=0.349) genotypes (Fig.
2B-D).
Discussion
Human BIRC5/survivin is the smallest member of the
IAP family, and encodes negative regulatory proteins that prevent
apoptotic cell death. It consists of a 16.5 kDa protein encoded by
a gene located on chromosome 17q25 (1). A number of studies, including tissue
expression studies, animal models and clinical trials, have
investigated BIRC5/survivin polymorphisms and cancer risk. The
results of these studies suggested that BIRC5/survivin plays a
significant role in carcinogenesis (1,4). The
present study confirmed that genetic susceptibility in miRNA
binding regions contributes to altered gene function. Although our
findings indicate that rs1042489, rs1042542, rs17882360, rs2239680,
rs2661694 and rs4789560 in the BIRC5/survivin 3′UTR have potential
miRNA binding sites using bioinformatics analysis, only rs1042489
was revealed to be significantly associated with BIRC5/survivin
mRNA expression in lymphoblastoid cell lines. Since rs1042489 has a
significant correlation with expression, it is implied that this
variant may contribute to BIRC5/survivin post-transcriptional
regulation to a certain extent. The results describe the mechanism
of the rs1042489 SNP functions in BIRC5/survivin regulation and
provide an explanation into the tumor susceptibility associated
with this SNP in chemistry research.
It is possible that the genetic variants in the
BIRC5/survivin 3′UTR may modulate its expression, and that the
variants in the BIRC5/survivin miRNA binding site are associated
with carcinogenesis. It was suggested that carriers of rs1042489, a
common polymorphism in the BIRC5/survivin gene, have a worse
survival compared with the major homozygotes by breast
cancer-specific survival analysis of BIRC5/survivin (13). rs1042489 was also observed to have a
significant association with expression, implying that this variant
may contribute in part to BIRC5/survivin post-transcriptional
regulation. It may improve our understanding of the regulatory
roles of miRNA variants in BIRC5/survivin 3′UTR in its mRNA
expression.
In summary, BIRC5/survivin variant plays a
significant role in post-transcriptional regulation, which may
highlight the contribution of miRNA-mediated regulation of
cancer-associated gene expression and lead to its consideration as
a prognostic and diagnostic marker of malignancy. In addition,
these findings improve our understanding of how the 3′UTR variants
regulate BIRC5/survivin activity and may pave the way to targeting
the BIRC5/survivin pathway in cancer therapy. However, this finding
needs to be validated by functional analysis of the underlying
mechanism involving BIRC5/survivin transcriptional activity
associated with variants in the 3′UTR.
References
|
1
|
Ambrosini G, Adida C and Altieri DC: A
novel anti-apoptosis gene, survivin, expressed in cancer and
lymphoma. Nat Med. 3:917–921. 1997. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
Waligórska-Stachura J, Jankowska A, Waśko
R, Liebert W, Biczysko M, Czarnywojtek A, Baszko-Błaszyk D, Shimek
V and Ruchała M: Survivin - prognostic tumor biomarker in human
neoplasms - review. Ginekol Pol. 83:537–540. 2012.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
Farnebo L, Tiefenböck K, Ansell A, Thunell
LK, Garvin S and Roberg K: Strong expression of survivin is
associated with positive response to radiotherapy and improved
overall survival in head and neck squamous cell carcinoma patients.
Int J Cancer. 133:1994–2003. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
Knizhnik AV, Kovaleva OB, Laktionov KK,
Mochal'nikova VV, Komel'kov AV, Chevkina EM and Zborovskaia IB:
Arf6, RalA and BIRC5 protein expression in non small cell lung
cancer. Mol Biol (Mosk). 45:307–315. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Wang H, Zhang X, Wang L, Zheng G, Du L,
Yang Y, Dong Z, Liu Y, Qu A and Wang C: Investigation of cell free
BIRC5 mRNA as a serum diagnostic and prognostic biomarker for
colorectal cancer. J Surg Oncol. 109:574–579. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Lv S, Turlova E, Zhao S, Kang H, Han M and
Sun HS: Prognostic and clinicopathological significance of survivin
expression in bladder cancer patients: A meta-analysis. Tumour
Biol. 35:1565–1574. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Hingorani P, Dickman P, GarciaFilion P,
WhiteCollins A, Kolb EA and Azorsa DO: BIRC5 expression is a poor
prognostic marker in Ewing sarcoma. Pediatr Blood Cancer. 60:35–40.
2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Zu Y, Ban J, Xia Z, Wang J, Cai Y, Ping W
and Sun W: Genetic variation in a miR-335 binding site in BIRC5
alters susceptibility to lung cancer in Chinese Han populations.
Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 430:529–534. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Holm K, Melum E, Franke A and Karlsen TH:
SNPexp-A web tool for calculating and visualizing correlation
between HapMap genotypes and gene expression levels. BMC
Bioinformatics. 11:6002010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Stranger BE, Forrest MS, Dunning M, Ingle
CE, Beazley C, Thorne N, Redon R, Bird CP, de Grassi A, Lee C, et
al: Relative impact of nucleotide and copy number variation on gene
expression phenotypes. Science. 315:848–853. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
International HapMap Consortium: The
International HapMap Project. Nature. 426:789–796. 2003. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Cunningham JM, Vierkant RA, Sellers TA,
Phelan C, Rider DN, Liebow M, Schildkraut J, Berchuck A, Couch FJ,
Wang X, et al: Cell cycle genes and ovarian cancer susceptibility:
A tagSNP analysis. Br J Cancer. 101:1461–1468. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Shi H, Bevier M, Johansson R,
EnquistOlsson K, Henriksson R, Hemminki K, Lenner P and Försti A:
Prognostic impact of polymorphisms in the MYBL2 interacting genes
in breast cancer. Breast Cancer Res Treat. 131:1039–1047. 2012.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|