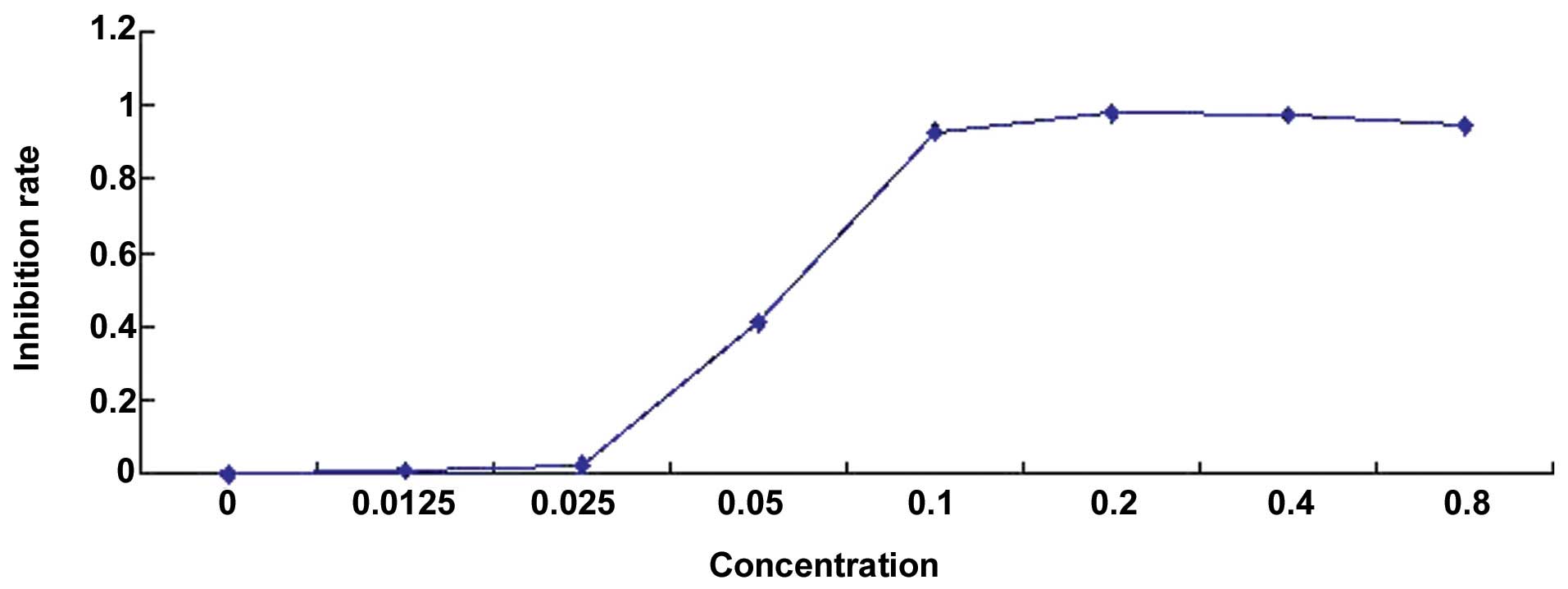
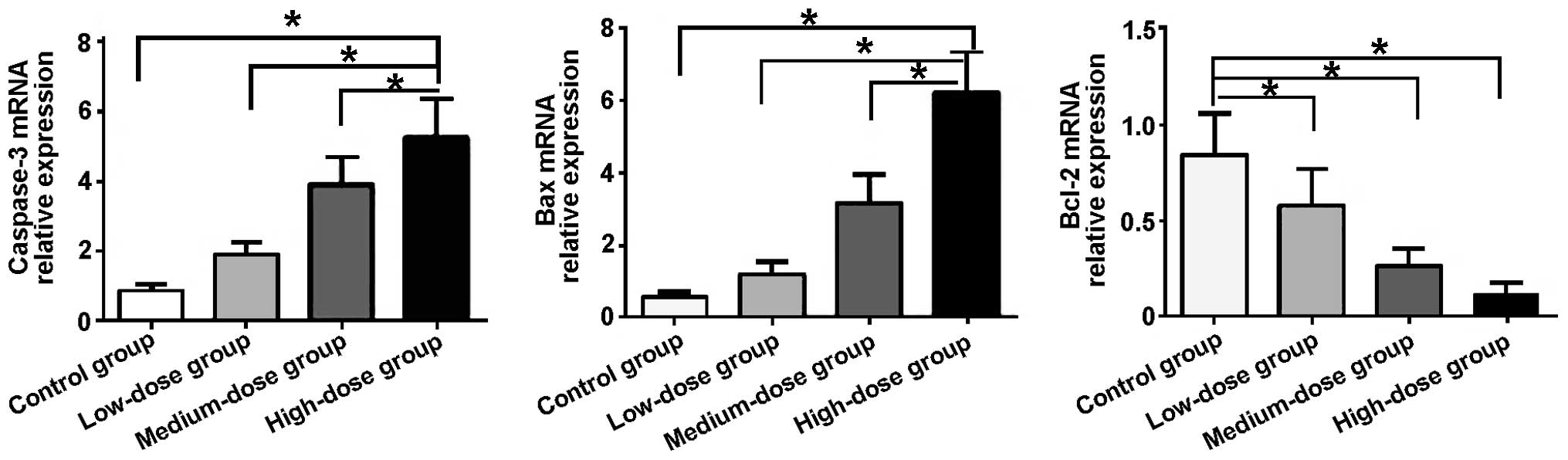
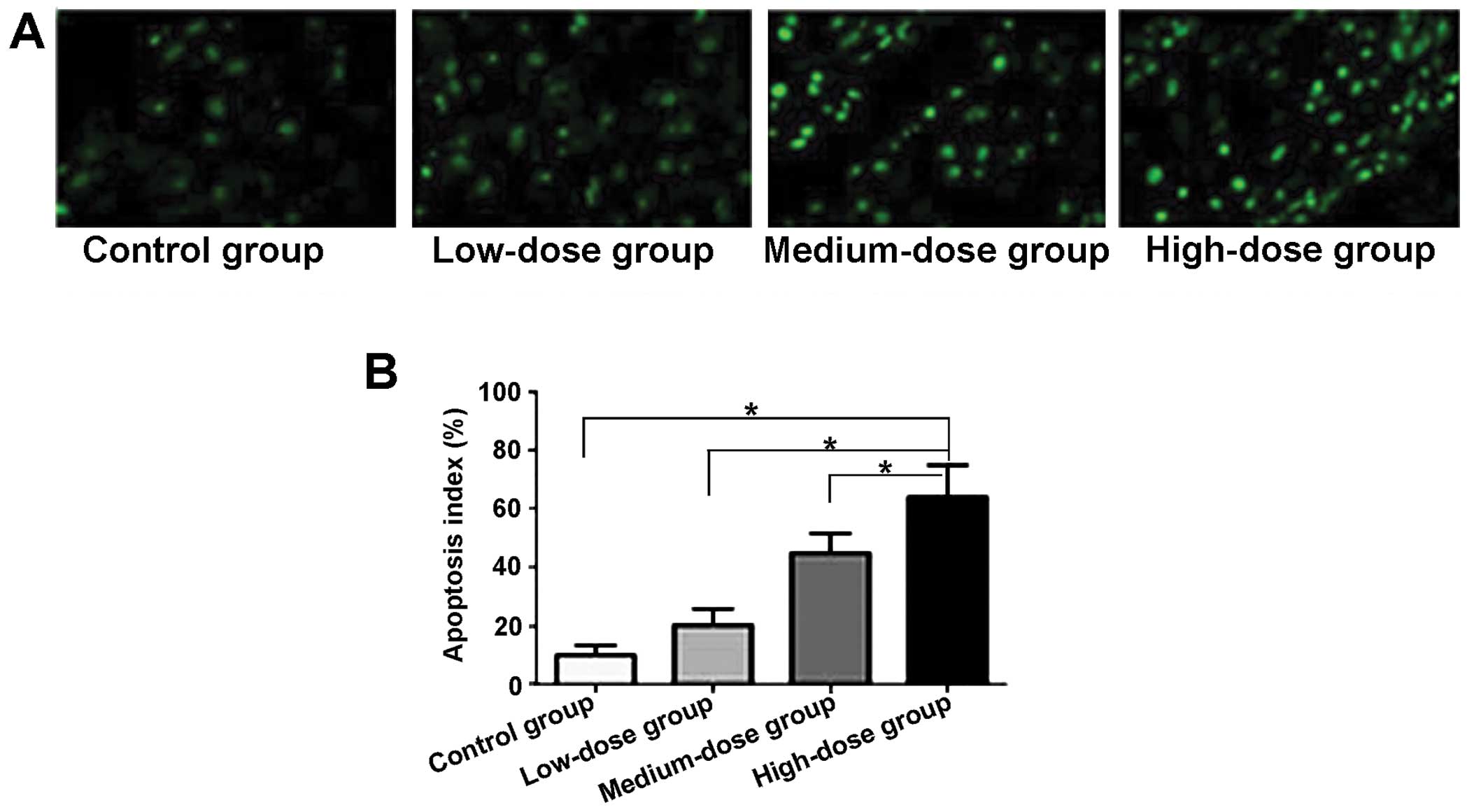
|
1
|
Dongxin L: Esophageal cancer molecular
epidemiology research in China. Zhonghua Liu Xing Bing Xue Za Zhi.
24:939–943. 2003.(In Chinese).
|
|
2
|
Chen J, Zhu J, Pan J, Zhu K, Zheng X, Chen
M, Wang J and Liao Z: Postoperative radiotherapy improved survival
of poor prognostic squamous cell carcinoma esophagus. Ann Thorac
Surg. 90:435–442. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
Mariette C, Piessen G and Triboulet JP:
Therapeutic strategies in oesophageal carcinoma: Role of surgery
and other modalities. Lancet Oncol. 8:545–553. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
Ando N, Iizuka T, Ide H, Ishida K, Shinoda
M, Nishimaki T, Takiyama W, Watanabe H, Isono K, Aoyama N, et al:
Japan Clinical Oncology Group: Surgery plus chemotherapy compared
with surgery alone for localized squamous cell carcinoma of the
thoracic esophagus: A Japan Clinical Oncology Group Study -
JCOG9204. J Clin Oncol. 21:4592–4596. 2003. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Rice TW, Adelstein DJ, Chidel MA, Rybicki
LA, DeCamp MM, Murthy SC and Blackstone EH: Benefit of
postoperative adjuvant chemoradiotherapy in locoregionally advanced
esophageal carcinoma. J Thorac Cardiovasc Surg. 126:1590–1596.
2003. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Qi L, Zhang J and Zhang Z: Determination
of four alkaloids in compound Kushen Injection by high performance
liquid chromatography with ionic liquid as mobile phase additive.
Se Pu. 31:249–253. 2013.(In Chinese). PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Dai ZJ, Gao J, Wang XJ, Ji ZZ, Wu WY, Liu
XX, Kang HF, Guan HT and Ren HT: Apoptotic mechanism of gastric
carcinoma cells induced by matrine injection. Zhonghua Wei Chang
Wai Ke Za Zhi. 11:261–265. 2008.(In Chinese). PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Dai ZJ, Gao J, Wu WY, Wang XJ, Li ZF, Kang
HF, Liu XX and Ma XB: Effect of matrine injections on invasion and
metastasis of gastric carcinoma SGC-7901 cells in vitro. Zhong Yao
Cai. 30:815–819. 2007.(In Chinese). PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Sun Q, Ma W, Gao Y, Zheng W, Zhang B and
Peng Y: Meta-analysis: therapeutic effect of transcatheter arterial
chemoembolization combined with compound kushen injection in
hepatocellular carcinoma. Afr J Tradit Complement Altern Med.
9:178–188. 2012.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Zhu JL and Chen JZ: Short-term observation
on the efficacy of matrine injection in treating 79 cases of late
stage cancers. Shandong Med J. 43:article 40. 2003.
|
|
11
|
Willert K, Brown JD, Danenberg E, Duncan
AW, Weissman IL, Reya T, Yates JR III and Nusse R: Wnt proteins are
lipid-modified and can act as stem cell growth factors. Nature.
423:448–452. 2003. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Zhou H and Huang GH: Cognition and
treatment research of traditional Chinese medicine for esophagus
cancer. Liaoning Zhong Yi Yao Da Xue Xue Bao. 2:212–215. 2012.(In
Chinese).
|
|
13
|
Hai LN, Zhang ZW and Wang JH: Effects of
compound Kushen injection on alalgesis, hemostasis and anti-stress
in mice. Zhongguo Shi Yan Fang Ji Xue Za Zhi. 50:199–202. 2012.(In
Chinese).
|
|
14
|
Ma Y, Zhang QW, Wang ZM and Gao HM:
Advance in study on compound Kushen injection. Zhongguo Shi Yan
Fang Ji Xue Za Zhi. 18:23–24. 2012.
|
|
15
|
Tuo XL and Bai M: Expression and
significance of human mismatch repair gene (Smsh2) and
proliferating cell nuclear antigen (PCNA) in lung cancer. China J
Modem Med. 15:6912005.
|
|
16
|
Simpson KL, Cawthorne C, Zhou C,
Hodgkinson CL, Walker MJ, Trapani F, Kadirvel M, Brown G, Dawson
MJ, MacFarlane M, et al: A caspase-3 ‘death-switch’ in colorectal
cancer cells for induced and synchronous tumor apoptosis in vitro
and in vivo facilitates the development of minimally invasive cell
death biomarkers. Cell Death Dis. 4:e6132013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Raisova M, Hossini AM, Eberle J, Riebeling
C, Wieder T, Sturm I, Daniel PT, Orfanos CE and Geilen CC: The
Bax/Bcl-2 ratio determines the susceptibility of human melanoma
cells to CD95/Fas-mediated apoptosis. J Invest Dermatol.
117:333–340. 2001. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
Salakou S, Kardamakis D, Tsamandas AC,
Zolota V, Apostolakis E, Tzelepi V, Papathanasopoulos P, Bonikos
DS, Papapetropoulos T, Petsas T, et al: Increased Bax/Bcl-2 ratio
up-regulates caspase-3 and increases apoptosis in the thymus of
patients with myasthenia gravis. In Vivo. 21:123–132.
2007.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
Adams JM and Cory S: Bcl-2-regulated
apoptosis: Mechanism and therapeutic potential. Curr Opin Immunol.
19:488–496. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|