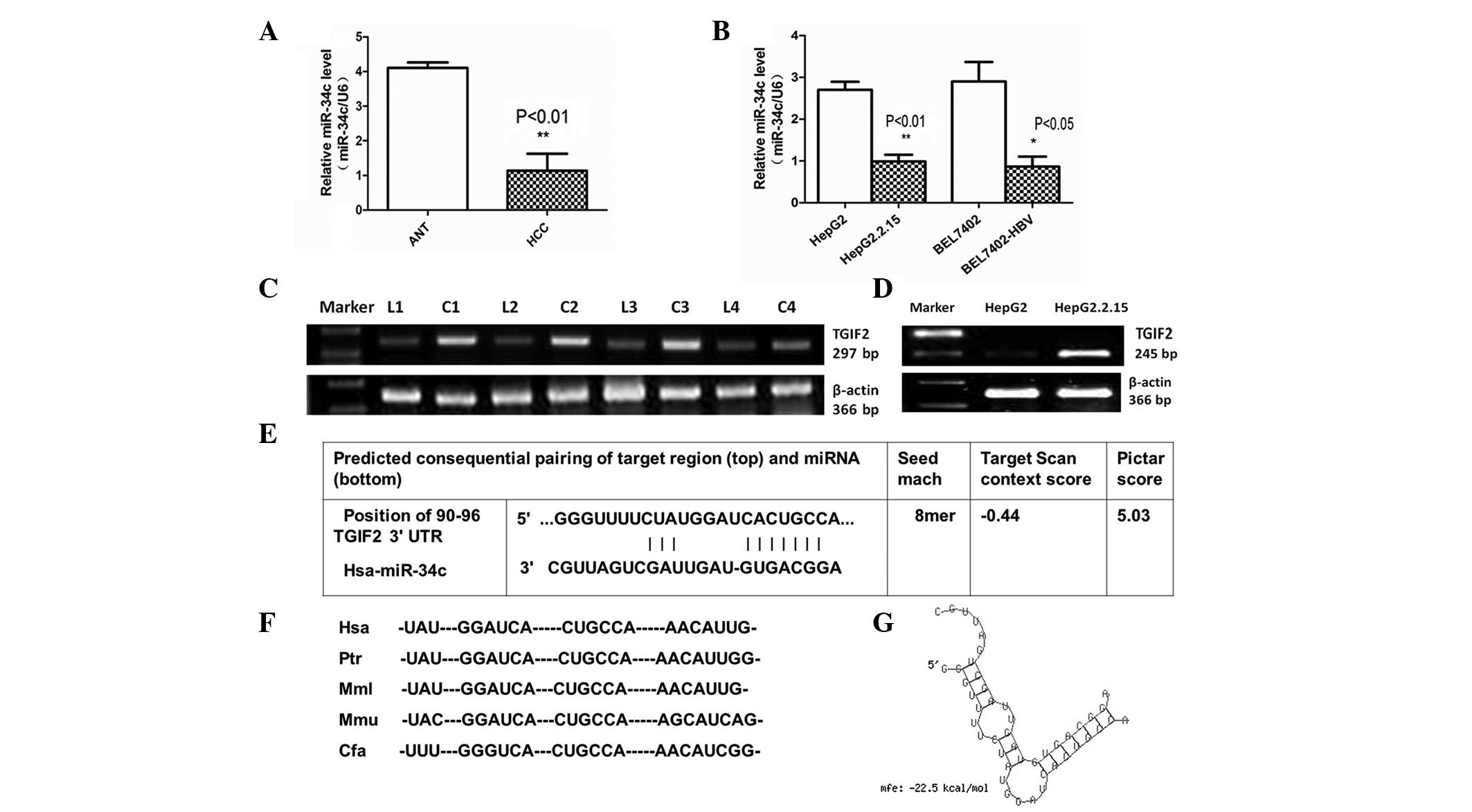
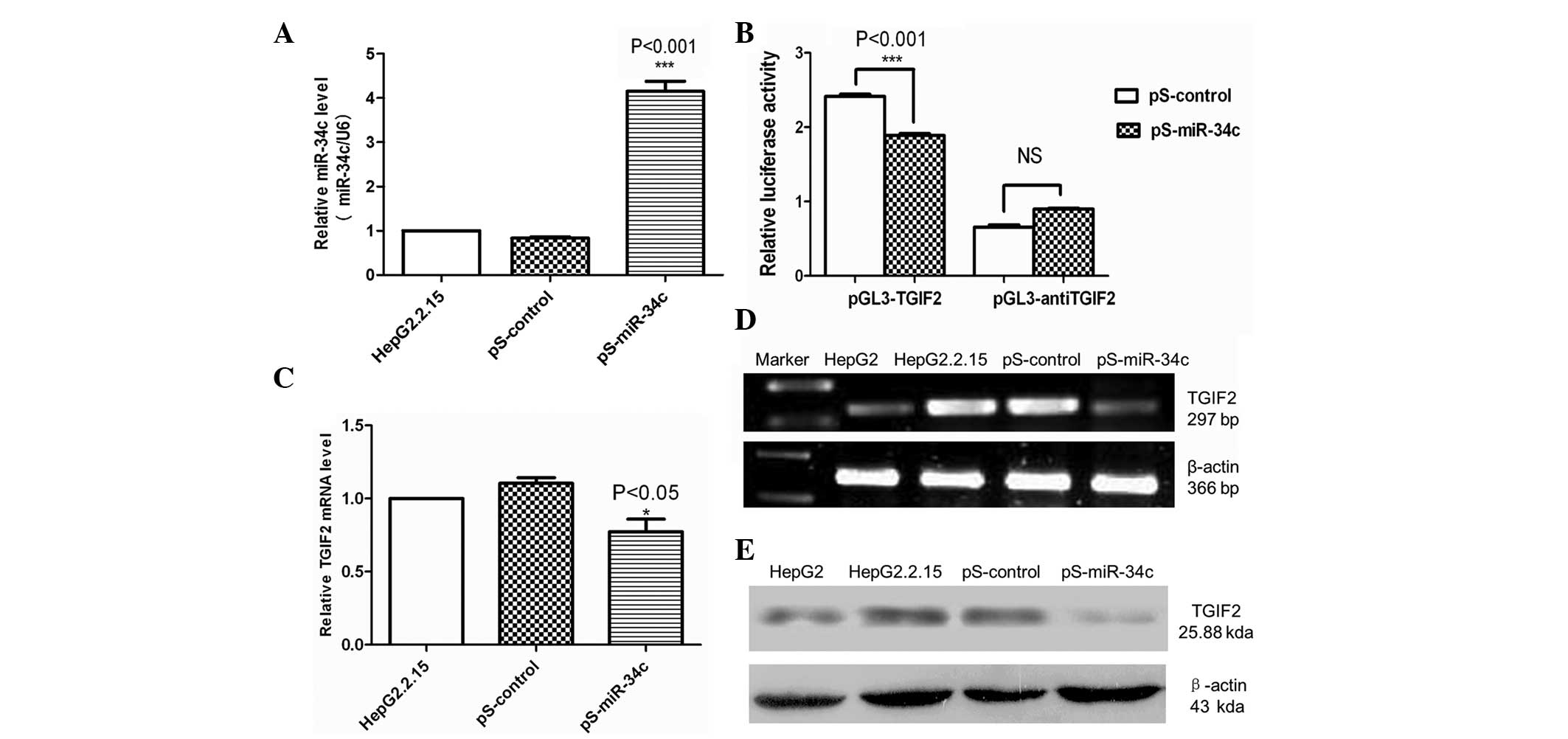
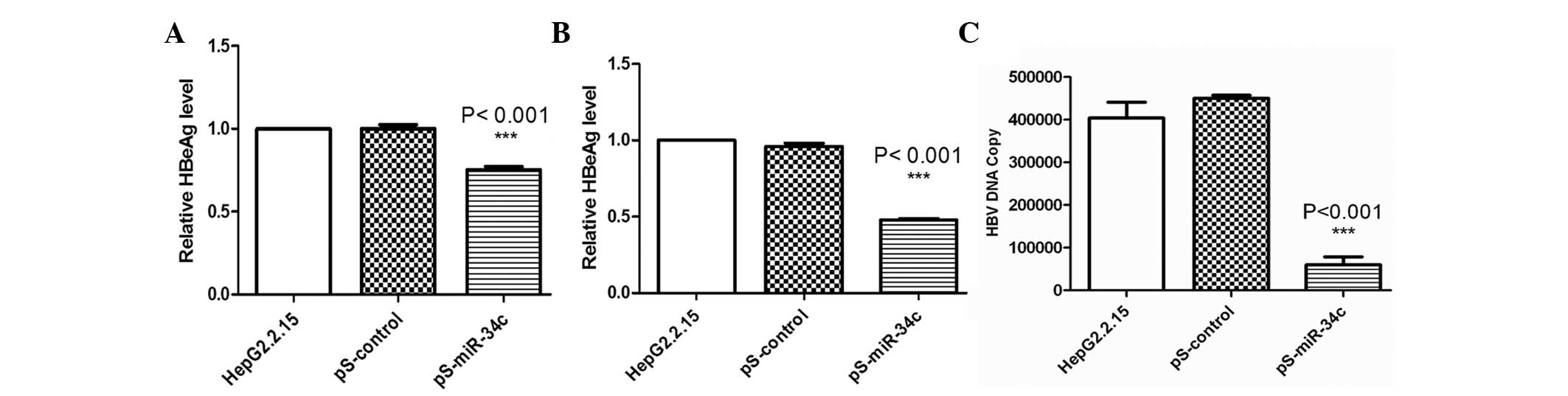
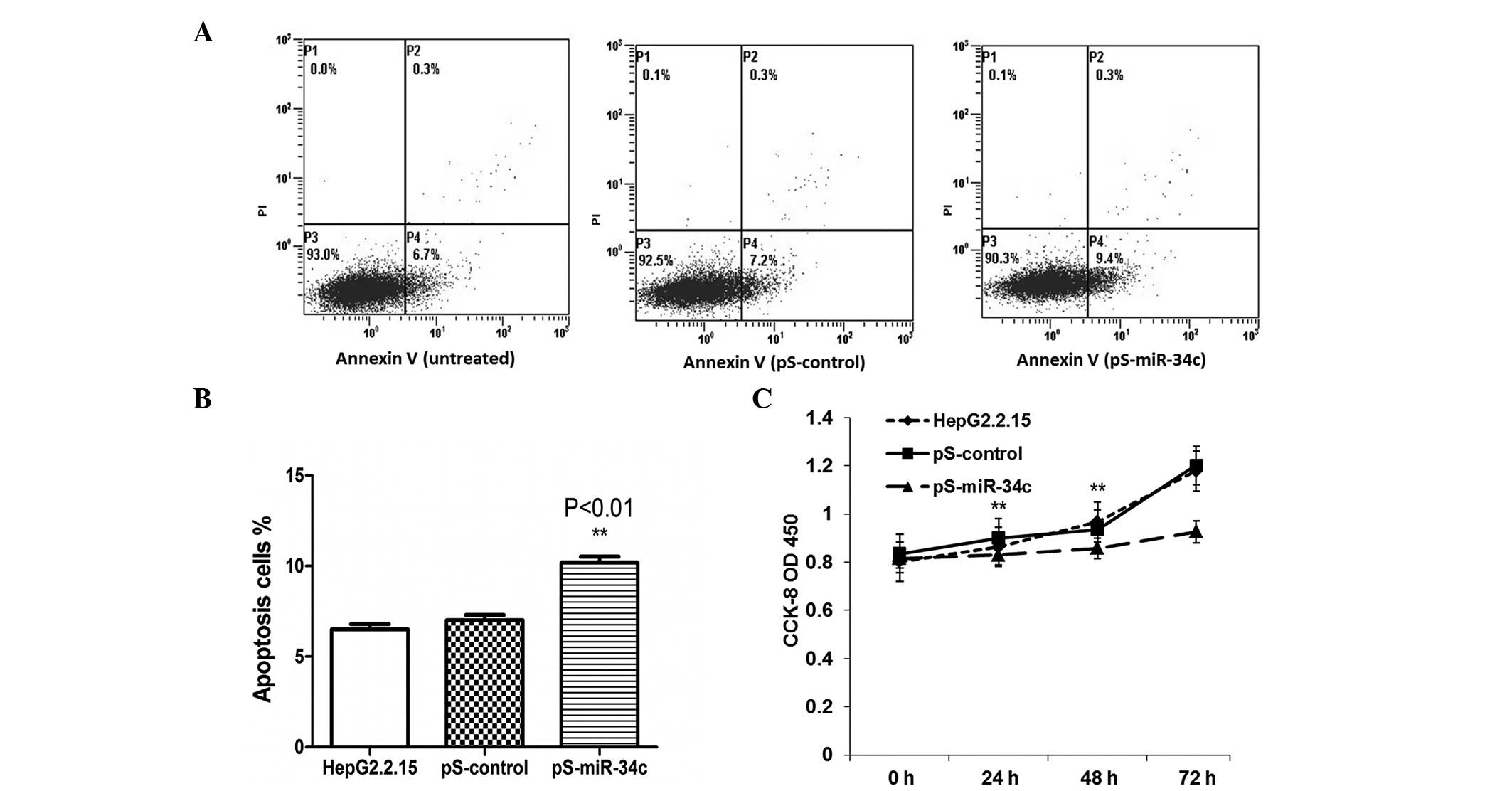
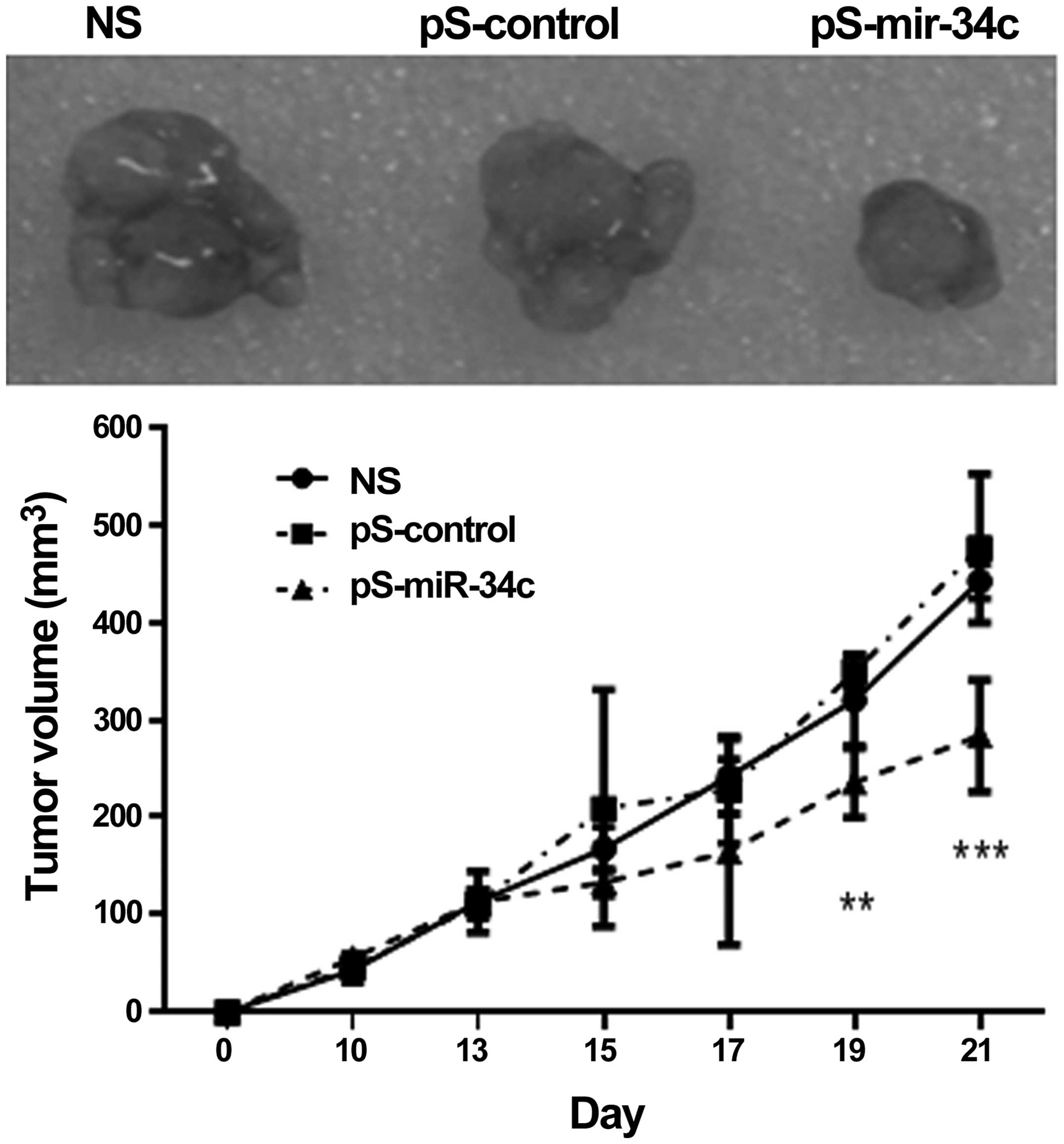
|
1
|
Lavanchy D: Hepatitis B virus
epidemiology, disease burden, treatment and current and emerging
prevention and control measures. J Viral Hepat. 11:97–107. 2004.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
Bruix J and Sherman M: American
Association for the Study of Liver Diseases: Management of
hepatocellular carcinoma: An update. Hepatology. 53:1020–1022.
2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
Suzuki K, Okuda Y, Ota M, Kojima F and
Horimoto M: Diagnosis of hepatocellular carcinoma nodules in
patients with chronic liver disease using contrast-enhanced
sonography: Usefulness of the combination of arterial- and
kupffer-phase enhancement patterns. J Ultrasound Med. 34:423–433.
2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
Bartel DP: MicroRNAs: genomics,
biogenesis, mechanism and function. Cell. 116:281–297. 2004.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Carleton M, Cleary MA and Linsley PS:
MicroRNAs and cell cycle regulation. Cell Cycle. 6:2127–2132. 2007.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Skaftnesmo KO, Prestegarden L, Micklem DR
and Lorens JB: MicroRNAs in tumorigenesis. Curr Pharm Biotechnol.
8:320–325. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Paris R, Henry RE, Stephens SJ, et al:
Multiple p53-independent gene silencing mechanisms define the
cellular response to p53 activation. Cell Cycle. 7:2427–2433. 2008.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Raver-Shapira N, Marciano E, Meiri E, et
al: Transcriptional activation of miR-34a contributes to
p53-mediated apoptosis. Mol Cell. 26:731–743. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
He L, He X, Lim LP, et al: A microRNA
component of the p53 tumor suppressor network. Nature.
447:1130–1134. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Kong YW, Cannell IG, de Moor CH, et al:
The mechanism of microRNA-mediated translation repression is
determined by the promoter of the target gene. Proc Natl Acad Sci
USA. 105:8866–8871. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Migliore C, Petrelli A, Ghiso E, et al:
MicroRNAs impair MET mediated invasive growth. Cancer Res.
68:10128–10136. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Wotton D, Lo RS, Lee S and Massagué J: A
Smad transcriptional corepressor. Cell. 97:29–39. 1999. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Yang P, Li Q-J, Feng Y, Zhang Y, Markowitz
GJ, Ning S, Deng Y, Zhao J, Jiang S, Yuan Y, et al:
TGF-β-miR-34a-CCL22 signaling-induced Treg cell recruitment
promotes venous metastases of HBV-positive hepatocellular
carcinoma. Cancer Cell. 22:291–303. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Karimi-Googheri M, Daneshvar H,
Nosratabadi R, Zare-Bidaki M, Hassanshahi G, Ebrahim M, Arababadi
MK and Kennedy D: Important roles played by TGF-β in hepatitis B
infection. J Med Virol. 86:102–108. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Liu N, Jiao T, Huang Y, Liu W, Li Z and Ye
X: Hepatitis B virus regulates apoptosis and tumorigenesis through
the microRNA-15a-Smad7-transforming growth factor beta pathway. J
Virol. 89:2739–2749. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Livak KJ and Schmittgen TD: Analysis of
relative gene expression data using real-time quantitative PCR and
the 2(−Delta Delta C(T)) method. Methods. 25:402–408. 2001.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
McGlynn KA and London WT: Epidemiology and
natural history of hepatocellular carcinoma. Best Pract Res Clin
Gastroenterol. 19:3–23. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
Cai KM, Bao XL, Kong XH, et al:
Hsa-miR-34c suppresses growth and invasion of human laryngeal
carcinoma cells via targeting c-Met. Int J Mol Med. 25:565–571.
2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
Tarasov V, Jung P, Verdoodt B, et al:
Differential regulation of microRNAs by p53 revealed by massively
parallel sequencing: miR-34a is a p53 target that induces apoptosis
and G1-arrest. Cell Cycle. 6:1586–1593. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
Li T, Chen JX, Fu XP, Yang S, Zhang Z,
Chen KH and Li Y: microRNA expression profiling of nasopharyngeal
carcinoma. Oncol Rep. 25:1353–1363. 2011.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
Toyota M, Suzuki H, Sasaki Y, Maruyama R,
Imai K, Shinomura Y and Tokino T: Epigenetic silencing of
microRNA-34b/c and B-cell translocation gene 4 is associated with
CpG island methylation in colorectal cancer. Cancer Res.
68:4123–4132. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22
|
Mascaux C, Laes JF, Anthoine G, Haller A,
Ninane V, Burny A and Sculier JP: Evolution of microRNA expression
during human bronchial squamous carcinogenesis. Eur Respir J.
33:352–359. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23
|
Yu F, Jiao Y, Zhu Y, Wang Y, Zhu J, Cui X,
Liu Y, He Y, Park EY, Zhang H, Lv X, et al: MicroRNA 34c gene
down-regulation via DNA methylation promotes self-renewal and
epithelial-mesenchymal transition in breast tumor-initiating cells.
J Biol Chem. 87:465–473. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
24
|
Suzuki H, Yamamoto E, Nojima M, et al:
Methylation-associated silencing of microRNA-34b/c in gastric
cancer and its involvement in an epigenetic field defect.
Carcinogenesis. 31:2066–2073. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
25
|
Wang Z, Chen Z, Gao Y, Li N, Li B, Tan F,
Tan X, Lu N, Sun Y, Sun J, Sun N and He J: DNA hypermethylation of
microRNA-34b/c has prognostic value for stage I non-small cell lung
cancer. Cancer Biol Ther. 11:490–496. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
26
|
Garzon R, Marcucci G and Croce CM:
Targeting microRNAs in cancer: Rationale, strategies and
challenges. Nat Rev Drug Discov. 9:775–789. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
27
|
Shenouda SK and Alahari SK: MicroRNA
function in cancer: Oncogene or a tumor suppressor? Cancer
Metastasis Rev. 28:369–378. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
28
|
Hanahan D and Weinberg RA: Hallmarks of
cancer: The next generation. Cell. 144:646–674. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
29
|
Potenza N, Papa U, Mosca N, Zerbini F,
Nobile V and Russo A: Human microRNA hsa-miR-125a-5p interferes
with expression of hepatitis B virus surface antigen. Nucl Acids
Res. 39:5157–5163. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
30
|
Zhang GL, Li YX, Zheng SQ, Liu M, Li X and
Tang H: Suppression of hepatitis B virus replication by
microRNA-199a-3p and microRNA-210. Antiviral Res. 88:169–175. 2010.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
31
|
Qiu L, Fan H, Jin W, Zhao B, Wang Y, Ju Y,
Chen L, Chen Y, Duan Z and Meng S: miR-122-induced down-regulation
of HO-1 negatively affects miR-122-mediated suppression of HBV.
Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 398:771–777. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
32
|
Fan CG, Wang CM, Tian C, Wang Y, Li L, Sun
WS, Li RF and Liu YG: miR-122 inhibits viral replication and cell
proliferation in hepatitis B virus-related hepatocellular carcinoma
and targets NDRG3. Oncol Rep. 26:1281–1286. 2011.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
33
|
Yamada SD, Baldwin RL and Karlan BY:
Ovarian carcinoma cell cultures are resistant to TGF-beta1-mediated
growth inhibition despite expression of functional receptors.
Gynecol Oncol. 75:72–77. 1999. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
34
|
Lo RS, Wotton D and Massagué J: Epidermal
growth factor signaling via Ras controls the Smad transcriptional
co-repressor TGIF. EMBO J. 20:128–136. 2001. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
35
|
Corney DC, Flesken-Nikitin A, Godwin AK,
Wang W and Nikitin AY: MicroRNA-34b and microRNA-34c are targets of
p53 and cooperate in control of cell proliferation and
adhesion-independent growth. Cancer Res. 67:8433–8438. 2007.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
36
|
Yamakuchi M, Ferlito M and Lowenstein CJ:
miR-34a repression of SIRT1 regulates apoptosis. Proc Natl Acad Sci
USA. 105:13421–13426. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
37
|
Qu J, Lin J, Zhang S, Zhu Z, Ni C, Zhang
S, Gao H and Zhu M: HBV DNA can bind to P53 protein and influence
p53 transactivation in hepatoma cells. Biochem Biophys Res Commun.
386:504–509. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|