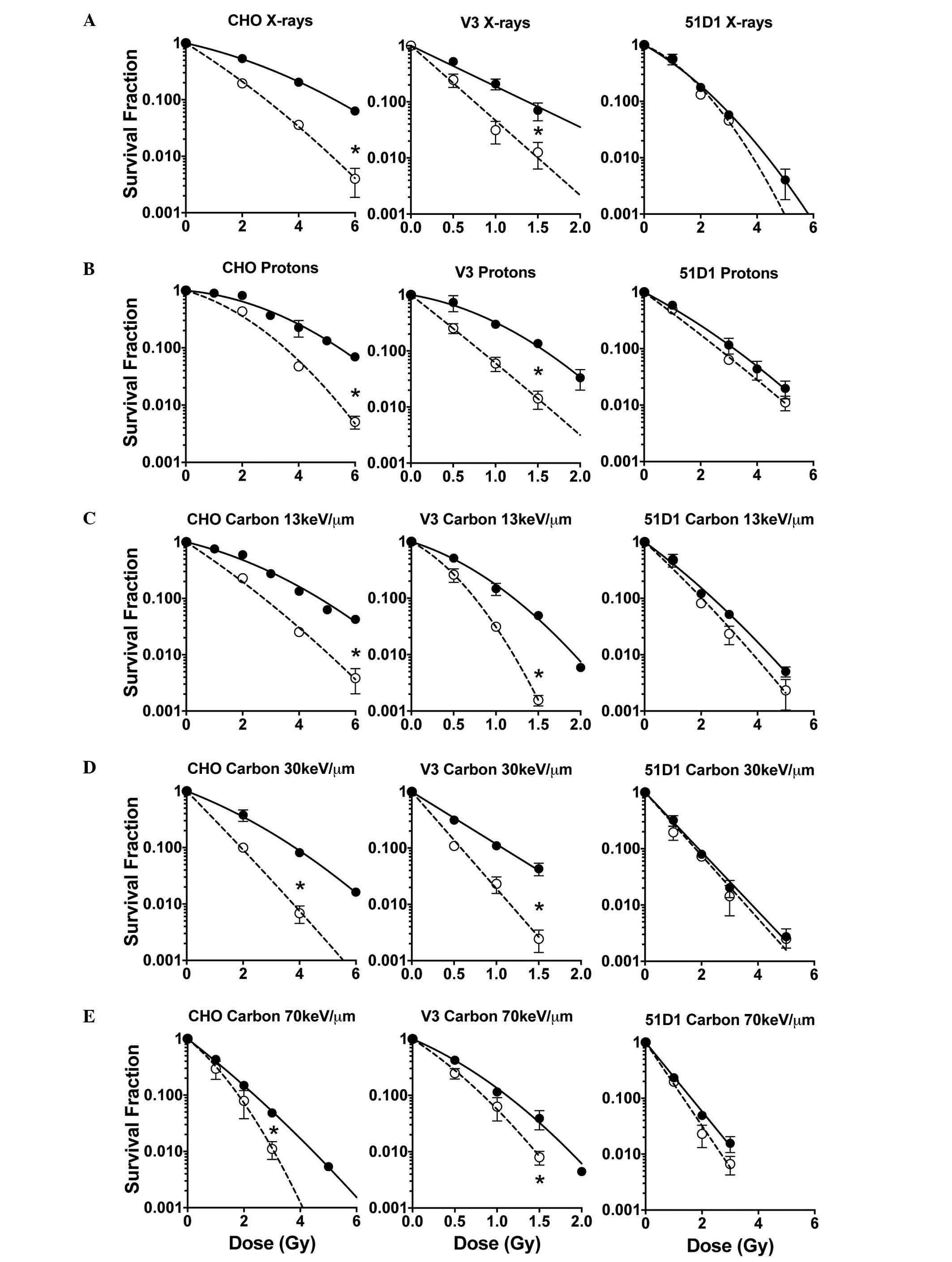
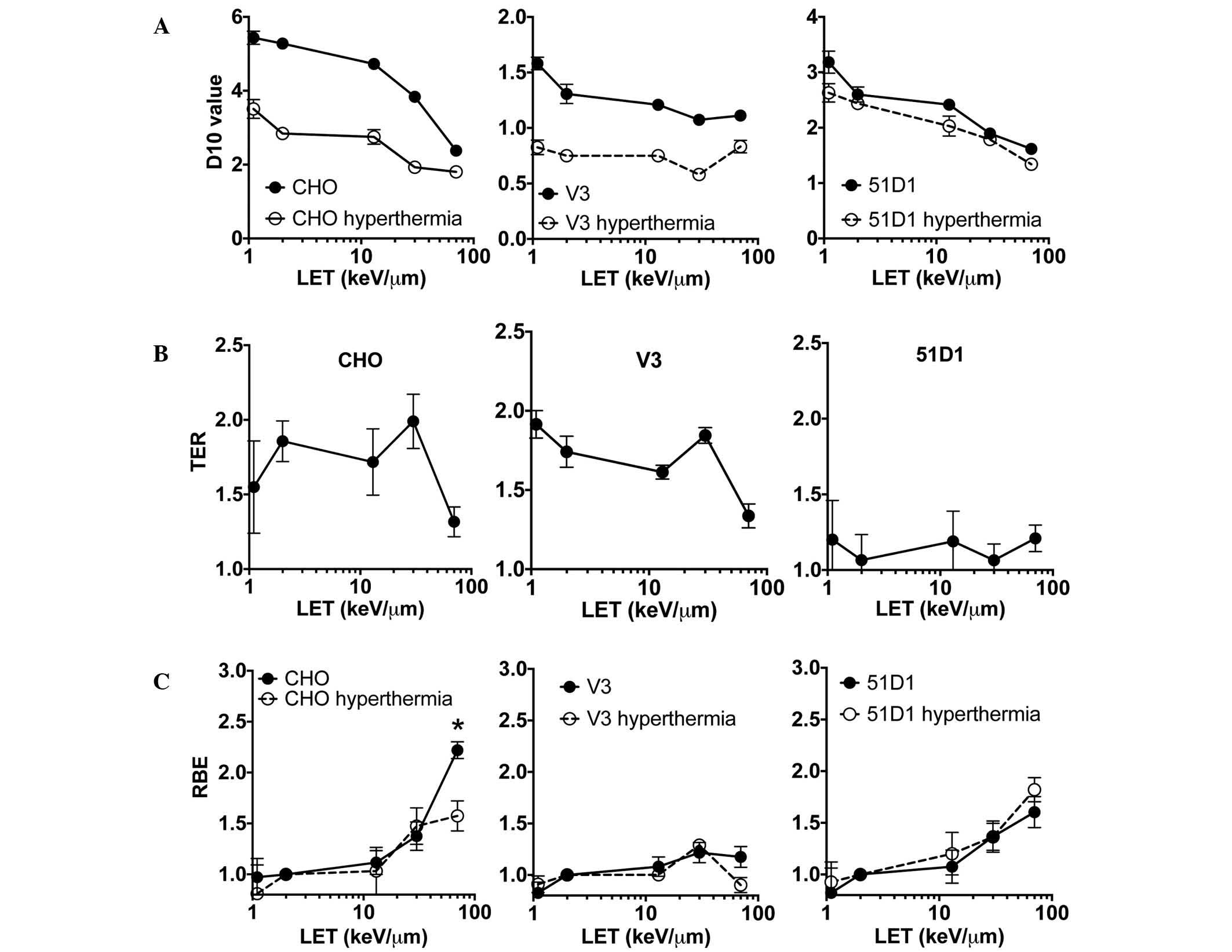
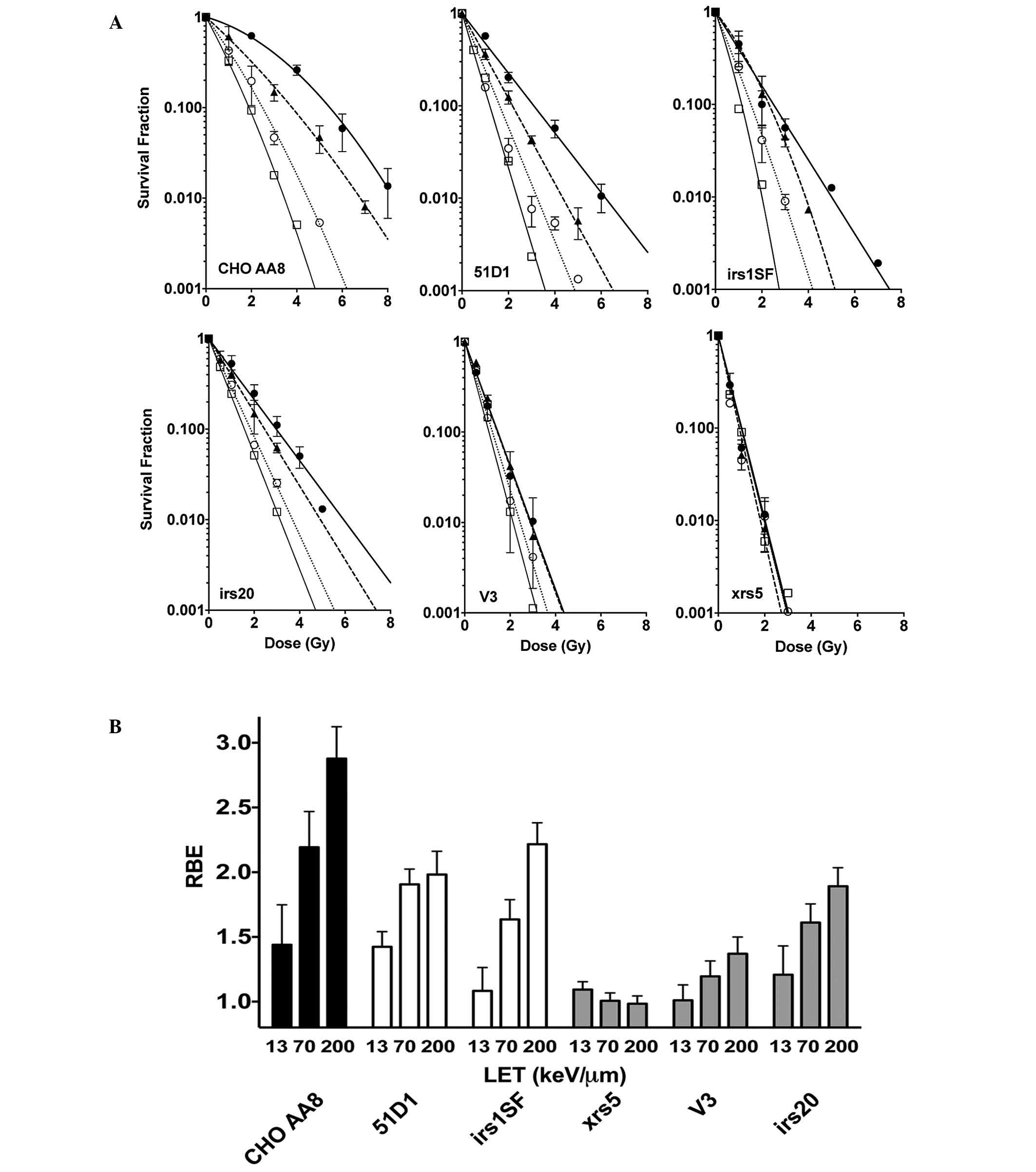
|
1
|
Dewey WC: Arrhenius relationships from the
molecule and cell to the clinic. Int J Hyperther. 25:3–20. 2009.
View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
2
|
Gerweck LE, Gillette EL and Dewey WC:
Effect of heat and radiation on synchronous Chinese hamster cells:
Killing and repair. Radiat Res. 64:611–623. 1975. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
Holahan EV, Highfield DP, Holahan PK and
Dewey WC: Hyperthermic killing and hyperthermic radiosensitization
in Chinese hamster ovary cells: Effects of pH and thermal
tolerance. Radiat Res. 97:108–131. 1984. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
Dewey WC and Miller HH: Effect of
temperature on x-ray induced cell lethality and chromosomal
aberrations. Int J Radiat Biol Relat Stud Phys Chem Med. 18:91–93.
1970. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Lee YJ and Dewey WC: Induction of heat
shock proteins in Chinese hamster ovary cells and development of
thermotolerance by intermediate concentrations of puromycin. J Cell
Physiol. 132:1–11. 1987. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Lee YJ and Dewey WC: Effect of
cycloheximide or puromycin on induction of thermotolerance by heat
in Chinese hamster ovary cells: Dose fractionation at 45.5 degrees
C1. Cancer Res. 47:5960–5966. 1987.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Genet SC, Fujii Y, Maeda J, Kaneko M,
Genet MD, Miyagawa K and Kato TA: Hyperthermia inhibits homologous
recombination repair and sensitizes cells to ionizing radiation in
a time- and temperature-dependent manner. J Cell Physiol.
228:1473–1481. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Krawczyk PM, Eppink B, Essers J, Stap J,
Rodermond H, Odijk H, Zelensky A, van Bree C, Stalpers LJ, Buist
MR, et al: Mild hyperthermia inhibits homologous recombination,
induces BRCA2 degradation, and sensitizes cancer cells to poly
(ADP-ribose) polymerase-1 inhibition. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA.
108:9851–9856. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Kamada T, Tsujii H, Tsuji H, Yanagi T,
Mizoe JE, Miyamoto T, Kato H, Yamada S, Morita S, Yoshikawa K, et
al: Working Group for the Bone and Soft Tissue Sarcomas: Efficacy
and safety of carbon ion radiotherapy in bone and soft tissue
sarcomas. J Clin Oncol. 20:4466–4471. 2002. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Tsujii H and Kamada T: A review of update
clinical results of carbon ion radiotherapy. Jpn J Clin Oncol.
42:670–685. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Takahashi A, Ohnishi K, Wang X, Kobayashi
M, Matsumoto H, Tamamoto T, Aoki H, Furusawa Y, Yukawa O and
Ohnishi T: The dependence of p53 on the radiation enhancement of
thermosensitivity at different let. Int J Radiat Oncol Biol Phys.
47:489–494. 2000. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Chang PY, Tobias CA and Blakely EA:
Protein synthesis modulates the biological effectiveness of the
combined action of hyperthermia and high-LET radiation. Radiat Res.
129:272–280. 1992. View
Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Kinashi Y, Masunaga SI, Suzuki M, Ono K
and Ohnishi T: Hyperthermia enhances thermal-neutron-induced cell
death of human glioblastoma cell lines at low concentrations of
10B. Int J Radiat Oncol Biol Phys. 40:1185–1192. 1998. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Takahashi A, Ohnishi K, Ota I, Asakawa I,
Tamamoto T, Furusawa Y, Matsumoto H and Ohnishi T: p53-dependent
thermal enhancement of cellular sensitivity in human squamous cell
carcinomas in relation to LET. Int J Radiat Biol. 77:1043–1051.
2001. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Stackhouse MA and Bedford JS: An ionizing
radiation-sensitive mutant of CHO cells: Irs-20. I. Isolation and
initial characterization. Radiat Res. 136:241–249. 1993. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Jeggo PA and Kemp LM: X-ray-sensitive
mutants of Chinese hamster ovary cell line. Isolation and
cross-sensitivity to other DNA-damaging agents. Mutat Res.
112:313–327. 1983.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Whitmore GF, Varghese AJ and Gulyas S:
Cell cycle responses of two X-ray sensitive mutants defective in
DNA repair. Int J Radiat Biol. 56:657–665. 1989. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
Fuller LF and Painter RB: A Chinese
hamster ovary cell line hypersensitive to ionizing radiation and
deficient in repair replication. Mutat Res. 193:109–121.
1988.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
Hinz JM, Tebbs RS, Wilson PF, Nham PB,
Salazar EP, Nagasawa H, Urbin SS, Bedford JS and Thompson LH:
Repression of mutagenesis by Rad51D-mediated homologous
recombination. Nucleic Acids Res. 34:1358–1368. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
Kato TA, Tsuda A, Uesaka M, Fujimori A,
Kamada T, Tsujii H and Okayasu R: In vitro characterization of
cells derived from chordoma cell line U-CH1 following treatment
with X-rays, heavy ions and chemotherapeutic drugs. Radiat Oncol.
6:1162011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
Maeda J, Roybal EJ, Brents CA, Uesaka M,
Aizawa Y and Kato TA: Natural and glucosyl flavonoids inhibit
poly(ADP-ribose) polymerase activity and induce synthetic lethality
in BRCA mutant cells. Oncol Rep. 31:551–556. 2014.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22
|
Zeng ZC, Jiang GL, Wang GM, Tang ZY,
Curran WJ and Iliakis G: DNA-PKcs subunits in radiosensitization by
hyperthermia on hepatocellular carcinoma hepG2 cell line. World J
Gastroenterol. 8:797–803. 2002.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23
|
Ihara M, Takeshita S, Okaichi K, Okumura Y
and Ohnishi T: Heat exposure enhances radiosensitivity by
depressing DNA-PK kinase activity during double strand break
repair. Int J Hyperthermia. 30:102–109. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24
|
Tomita M: Involvement of DNA-PK and ATM in
radiation- and heat-induced DNA damage recognition and apoptotic
cell death. J Radiat Res (Tokyo). 51:493–501. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
25
|
Umeda N, Matsumoto Y, Yin HL, Tomita M,
Enomoto A, Morita A, Mizukoshi T, Sakai K, Hosoi Y and Suzuki N:
Difference in the heat sensitivity of DNA-dependent protein kinase
activity among mouse, hamster and human cells. Int J Radiat Biol.
79:671–680. 2003. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
26
|
Woudstra EC, Konings AW, Jeggo PA and
Kampinga HH: Role of DNA-PK subunits in radiosensitization by
hyperthermia. Radiat Res. 152:214–218. 1999. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
27
|
Weyrather WK, Ritter S, Scholz M and Kraft
G: RBE for carbon track-segment irradiation in cell lines of
differing repair capacity. Int J Radiat Biol. 75:1357–1364. 1999.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
28
|
Olsson G, Czene S, Jenssen D and
Harms-Ringdahl M: Induction of homologous recombination in the hprt
gene of V79 Chinese hamster cells in response to low- and high-LET
irradiation. Cytogenet Genome Res. 104:227–231. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
29
|
Zafar F, Seidler SB, Kronenberg A, Schild
D and Wiese C: Homologous recombination contributes to the repair
of DNA double-strand breaks induced by high-energy iron ions.
Radiat Res. 173:27–39. 2010. View
Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
30
|
Genet SC, Maeda J, Fujisawa H, Yurkon CR,
Fujii Y, Romero AM, Genik PC, Fujimori A, Kitamura H and Kato TA:
Comparison of cellular lethality in DNA repair-proficient or
-deficient cell lines resulting from exposure to 70 MeV/n protons
or 290 MeV/n carbon ions. Oncol Rep. 28:1591–1596. 2012.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
31
|
Mitchel RE, Smith BP, Wheatly N, Chan A,
Child S and Paterson MC: Sensitivity of hyperthermia-treated human
cells to killing by ultraviolet or gamma radiation. Radiat Res.
104:234–241. 1985. View
Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
32
|
Mitchel RE, Chan A, Smith BP, Child SD and
Paterson MC: The effects of hyperthermia and ionizing radiation in
normal and ataxia telangiectasia human fibroblast lines. Radiat
Res. 99:627–635. 1984. View
Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|