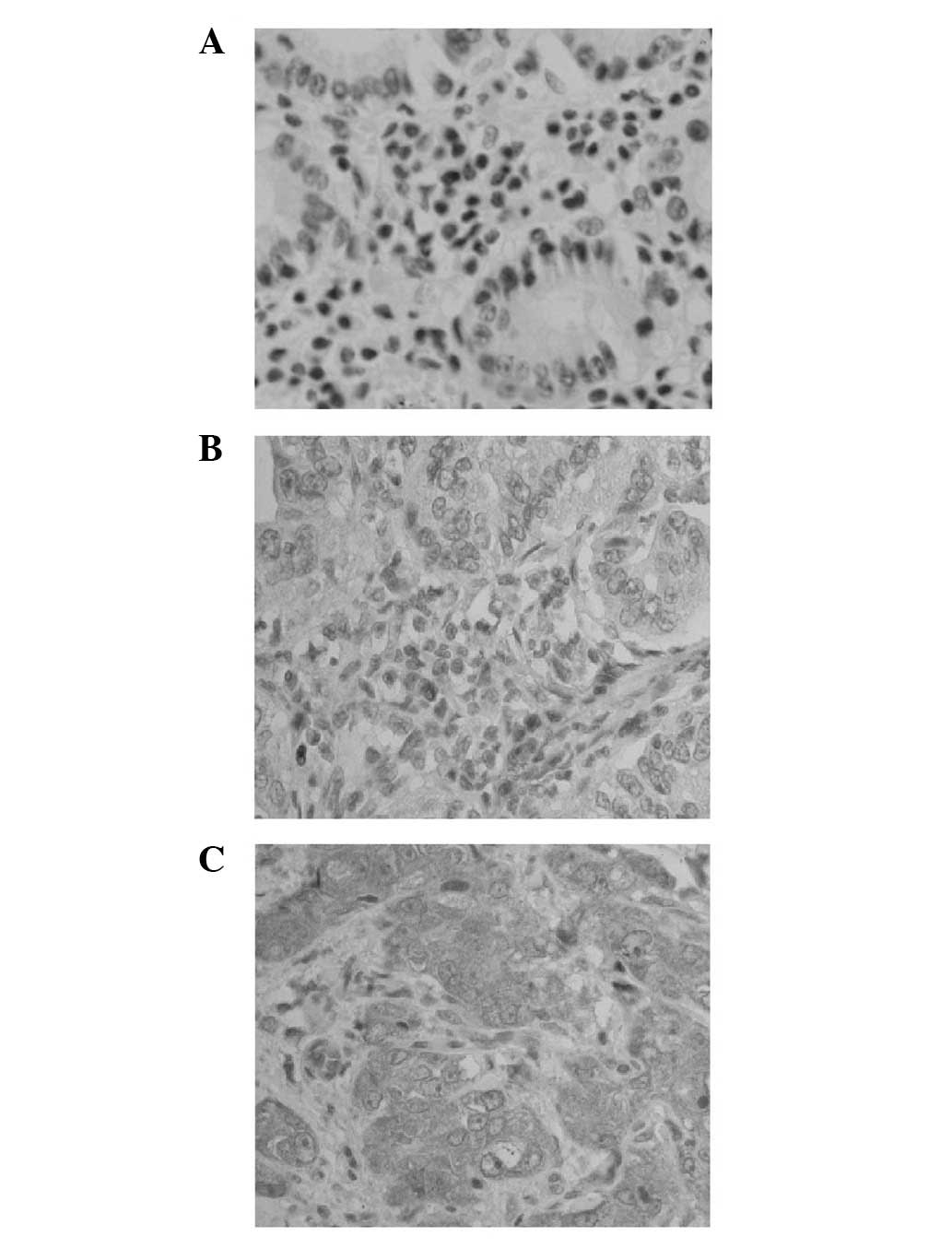
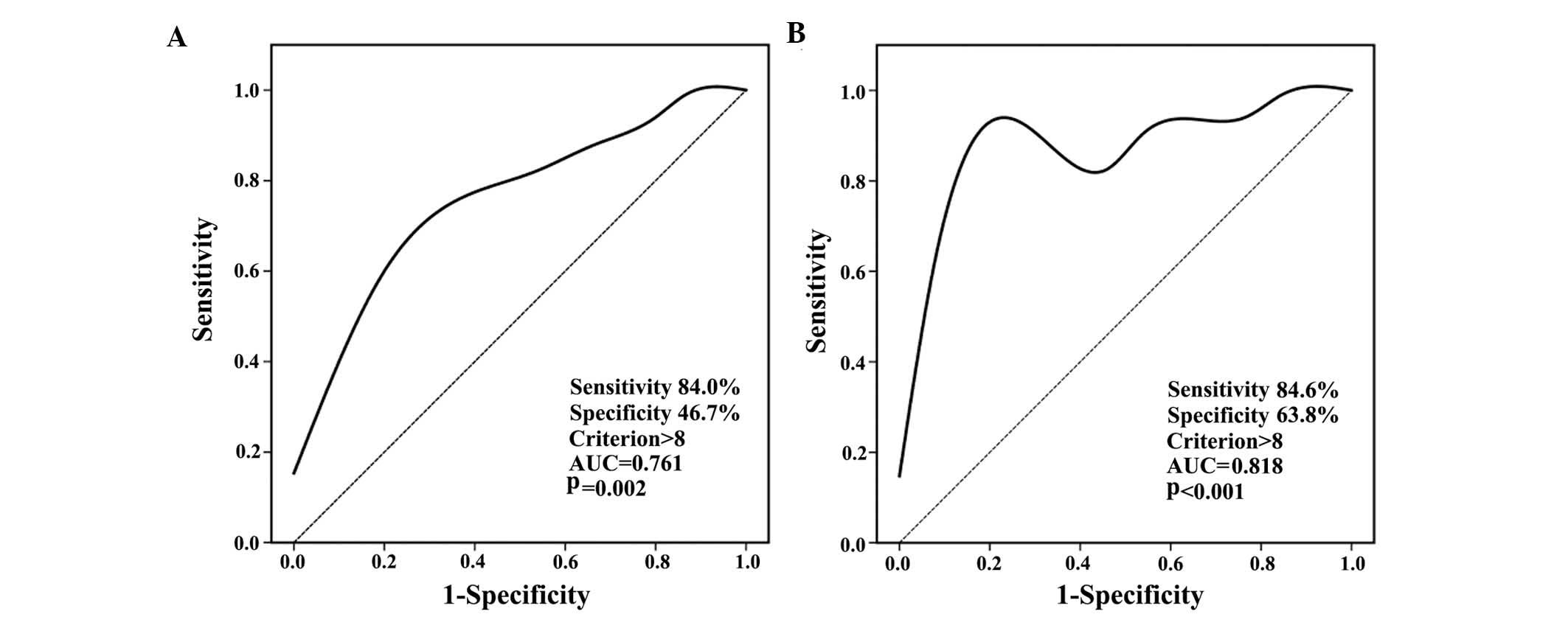
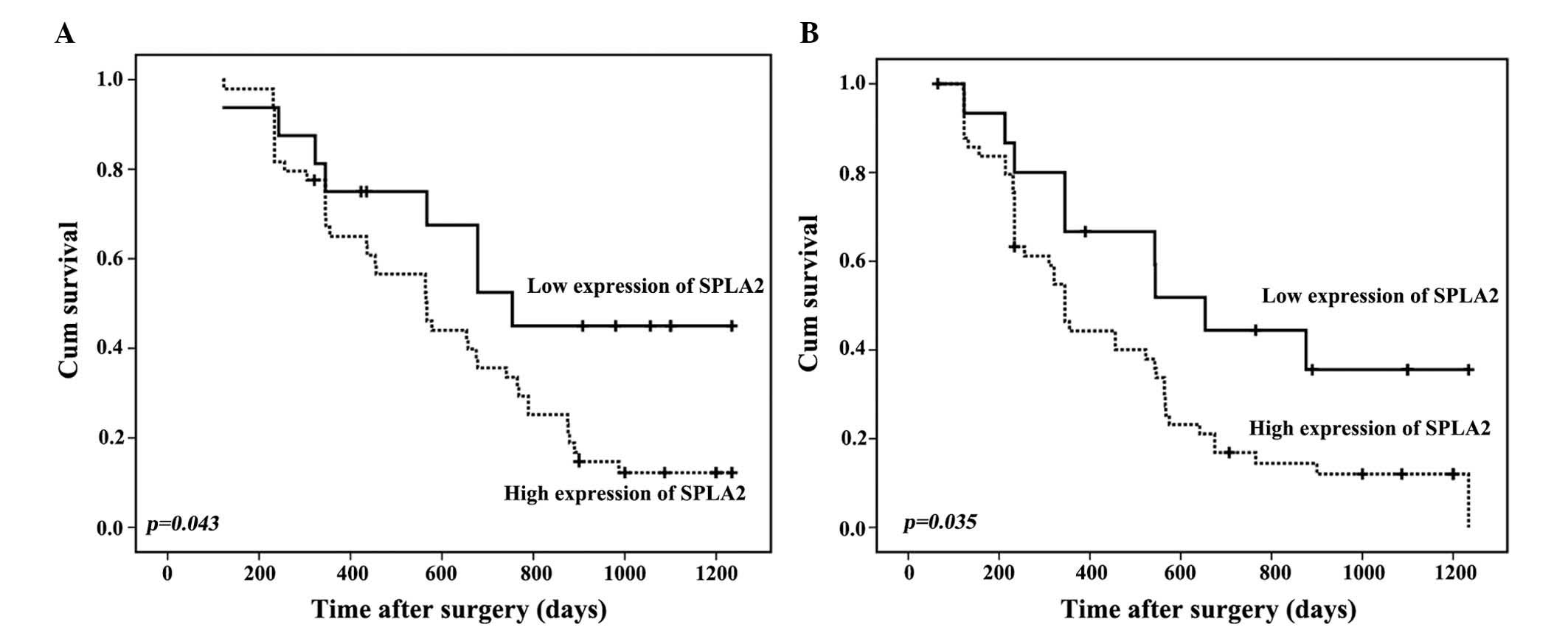
|
1
|
Rasool S, Rasool V, Naqvi T, Ganai BA and
Shah BA: Genetic unraveling of colorectal cancer. Tumour Biol.
35:5067–5082. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
Arnold CN, Goel A, Blum HE and Boland CR:
Molecular pathogenesis of colorectal cancer: Implications for
molecular diagnosis. Cancer. 104:2035–2047. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
Hayee B, Inoue H, Sato H, Santi EG,
Yoshida A, Onimaru M, Ikeda H and Kudo SE: Magnification
narrow-band imaging for the diagnosis of early gastric cancer: A
review of the Japanese literature for the Western endoscopist.
Gastrointest Endosc. 78:452–461. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
Clarke CJ, Forman S, Pritchett J, Ohanian
V and Ohanian J: Phospholipase C-delta1 modulates sustained
contraction of rat mesenteric small arteries in response to
noradrenaline, but not endothelin-1. Am J Physiol Heart Circ
Physiol. 295:H826–H834. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Samuelsson B: Role of basic science in the
development of new medicines: Examples from the eicosanoid field. J
Biol Chem. 287:10070–10080. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
D'Arrigo P and Servi S: Synthesis of
lysophospholipids. Molecules. 15:1354–1377. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Liang NS and Fang ZW: Platelet
phospholipase A2 and tumor. China Oncol. 12:555–558.
2002.
|
|
8
|
Hamilton JA: Stimulation of macrophage
prostaglandin and neutral protease production by phorbol esters as
a model for the induction of vascular changes associated with tumor
promotion. Cancer Res. 40:2273–2280. 1980.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Wang M, Hao FY, Wang JG and Xiao W: Group
IIa secretory phospholipase A2 (sPLA2IIa) and progression in
patients with lung cancer. Eur Rev Med Pharmacol Sci. 18:2648–2654.
2014.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Dikken JL, van de Velde CJ, Gönen M,
Verheij M, Brennan MF and Coit DG: The New American Joint Committee
on Cancer/International Union Against Cancer staging system for
adenocarcinoma of the stomach: Increased complexity without clear
improvement in predictive accuracy. Ann Surg Oncol. 19:2443–2451.
2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Berlth F, Bollschweiler E, Drebber U,
Hoelscher AH and Moenig S: Pathohistological classification systems
in gastric cancer: Diagnostic relevance and prognostic value. World
J Gastroenterol. 20:5679–5684. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Yousfi MM, el-Zimaity HM, Genta RM and
Graham DY: Evaluation of a new reagent strip rapid urease test for
detection of Helicobacter pylori infection. Gastrointest Endosc.
44:519–522. 1996. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Zhu ZH, Sun BY, Ma Y, Shao JY, Long H,
Zhang X, Fu JH, Zhang LJ, Su XD, Wu QL, et al: Three immunomarker
support vector machines-based prognostic classifiers for stage IB
non-small-cell lung cancer. J Clin Oncol. 27:1091–1099. 2009.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Constantine CE and Wreghitt TG: A rapid
micro-agglutination technique for the detection of antibody to
Legionella pneumophila serogroup 5. J Med Microbiol. 34:29–31.
1991. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Situ D, Wang J, Ma Y, Zhu Z, Hu Y, Long H
and Rong T: Expression and prognostic relevance of MUC1 in stage IB
non-small cell lung cancer. Med Oncol. 28(Suppl 1): S596–S604.
2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Zhao Jiuda, He Juxiang and Geng Paili:
PLA2G II A gene in gastric cancer tissues and its significance.
Shandong Medical Journal. 46:24–25. 2006.
|
|
17
|
Huhtinen HT, Grönroos JM, Uksila J, Grass
DS, Nevalainen TJ and Laine VJ: Experimental Helicobacter felis
infection in transgenic mice expressing human group IIA
phospholipase A2. Helicobacter. 9:408–416. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
Huhtinen HT, Grönroos JO, Grönroos JM,
Uksila J, Gelb MH, Nevalainen TJ and Laine VJ: Antibacterial
effects of human group IIA and group XIIA phospholipase A2 against
Helicobacter pylori in vitro. APMIS. 114:127–130. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
Menschikowski M, Rosner-Schiering A, Eckey
R, Mueller E, Koch R and Jaross W: Expression of secretory group
IIA phospholipase A(2) in relation to the presence of microbial
agents, macrophage infiltrates, and transcripts of proinflammatory
cytokines in human aortic tissues. Arterioscler Thromb Vasc Biol.
20:751–762. 2000. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
Pandey R, Misra V, Misra SP, Dwivedi M,
Kumar A and Tiwari BK: Helicobacter pylori and gastric cancer.
Asian Pac J Cancer Prev. 11:583–588. 2010.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
Hishida A, Matsuo K, Goto Y and Hamajima
N: Genetic predisposition to Helicobacter pylori-induced gastric
precancerous conditions. World J Gastrointest Oncol. 15:369–379.
2010. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
22
|
Fock KM, Talley N, Moayyedi P, Hunt R,
Azuma T, Sugano K, Xiao SD, Lam SK, Goh KL, Chiba T, et al:
Asia-Pacific Gastric Cancer Consensus Conference: Asia-Pacific
consensus guidelines on gastric cancer prevention. J Gastroenterol
Hepatol. 23:351–65. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23
|
Ren P, Zhang JG, Xiu L and Yu ZT: Clinical
significance of phospholipase A2 group IIA (PLA2G2A) expression in
primary resected esophageal squamous cell carcinoma. Eur Rev Med
Pharmacol Sci. 17:752–757. 2013.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24
|
Jiang J, Neubauer BL, Graff JR, Chedid M,
Thomas JE, Roehm NW, Zhang S, Eckert GJ, Koch MO, Eble JN and Cheng
L: Expression of group IIA secretory phospholipase A2 is elevated
in prostatic intraepithelial neoplasia and adenocarcinoma. Am J
Pathol. 160:667–671. 2002. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
25
|
Liao Z, Fu X, Liao XS, Wang SQ and Kang
GF: The change of serum phospholipase A2 activity and its clinical
significance in patient with primary liver cancer. Chongqing
Medical Journal. 3:203–204. 2000.(In Chinese).
|
|
26
|
Yamashita S, Ogawa M, Sakamoto K, Abe T,
Arakawa H and Yamashita J: Elevation of serum group II
phospholipase A2 levels in patients with advanced cancer. Clin Chim
Acta. 228:91–99. 1994. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
27
|
Cai H, Chiorean EG, Chiorean MV, Rex DK,
Robb BW, Hahn NM, Liu Z, Loehrer PJ, Harrison ML and Xu Y: Elevated
phospholipase A2 activities in plasma samples from multiple
cancers. PLoS One. 8:e570812013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
28
|
Yamashita S, Yamashita J and Ogawa M:
Overexpression of group II phospholipase A2 in human breast cancer
tissues is closely associated with their malignant potency. Br J
Cancer. 69:1166–1170. 1994. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
29
|
Scott KF, Sajinovic M, Hein J, Nixdorf S,
Galettis P, Liauw W, de Souza P, Dong Q, Graham GG and Russell PJ:
Emerging roles for phospholipase A2 enzymes in cancer. Biochimie.
92:601–610. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
30
|
Yamashita S, Yamashita J, Sakamoto K,
Inada K, Nakashima Y, Murata K, Saishoji T, Nomura K and Ogawa M:
Increased expression of membrane-associated phospholipase A2 shows
malignant potential of human breast cancer cells. Cancer.
71:3058–3064. 1993. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
31
|
Kennedy BP, Soravia C, Moffat J, Xia L,
Hiruki T, Collins S, Gallinger S and Bapat B: Overexpression of the
nonpancreatic secretory group II PLA2 messenger RNA and protein in
colorectal adenomas from familial adenomatous polyposis patients.
Cancer Res. 58:500–503. 1998.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
32
|
Kudo I and Murakami M: Phospholipase A2
enzymes. Prostaglandins Other Lipid Mediat. 68(69): 3–58. 2002.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
33
|
Fenard D, Lambeau G, Maurin T, Lefebvre JC
and Doglio A: A peptide derived from bee venom-secreted
phospholipase A2 inhibits replication of T-cell tropic HIV-1
strains via interaction with the CXCR4 chemokine receptor. Mol
Pharmacol. 60:341–347. 2001.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
34
|
Yamashita S, Yamashita J and Ogawa M:
Overexpression of group II phospholipase A2 in human breast cancer
tissues is closely associated with their malignant potency. Br J
Cancer. 69:1166–1170. 1994. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
35
|
Leung SY, Chen X, Chu KM, Yuen ST, Mathy
J, Ji J, Chan AS, Li R, Law S, Troyanskaya OG, et al: Phospholipase
A2 group IIA expression in gastric adenocarcinoma is associated
with prolonged survival and less frequent metastasis. Proc Natl
Acad Sci USA. 99:16203–16208. 2002. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
36
|
Kiyohara H, Egami H, Kako H, Shibata Y,
Murata K, Ohshima S, Sei K, Suko S, Kurano R and Ogawa M:
Immunohistochemical localization of group II phospholipase A2 in
human pancreatic carcinomas. Int J Pancreatol. 13:49–57.
1993.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
37
|
Mannello F, Qin W, Zhu W, Fabbri L, Tonti
GA and Sauter ER: Nipple aspirate fluids from women with breast
cancer contain increased levels of group IIa secretory
phospholipase A2. Breast Cancer Res Treat. 111:209–218. 2008.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
38
|
Mauchley D, Meng X, Johnson T, Fullerton
DA and Weyant MJ: Modulation of growth in human esophageal
adenocarcinoma cells by group IIa secretory phospholipase A(2). J
Thorac Cardiovasc Surg. 139:591–599. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
39
|
Fijneman RJ and Cormier RT: The roles of
sPLA2-IIA (Pla2g2a) in cancer of the small and large intestine.
Front Biosci. 13:4144–4174. 2008. View
Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
40
|
Ikegami T, Matsuzaki Y, Fukushima S, Shoda
J, Olivier JL, Bouscarel B and Tanaka N: Suppressive effect of
ursodeoxycholic acid on type IIA phospholipase A2 expression in
HepG2 cells. Hepatology. 41:896–905. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
41
|
Zlobec I, Steele R, Terracciano L, Jass JR
and Lugli A: Selecting immunohistochemical cut-off scores for novel
biomarkers of progression and survival in colorectal cancer. J Clin
Pathol. 60:1112–1116. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
42
|
Liu R, Qi H, Wang J, Wang Y, Cui L, Wen Y
and Yin C: Ulinastatin activates the renin-angiotensin system to
ameliorate the pathophysiology of severe acute pancreatitis. J
Gastroenterol Hepatol. 29:1328–1337. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
43
|
Hughes-Fulford M, Li CF,
Boonyaratanakornkit J and Sayyah S: Arachidonic acid activates
phosphatidylinositol 3-kinase signaling and induces gene expression
in prostate cancer. Cancer Res. 66:1427–1433. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|