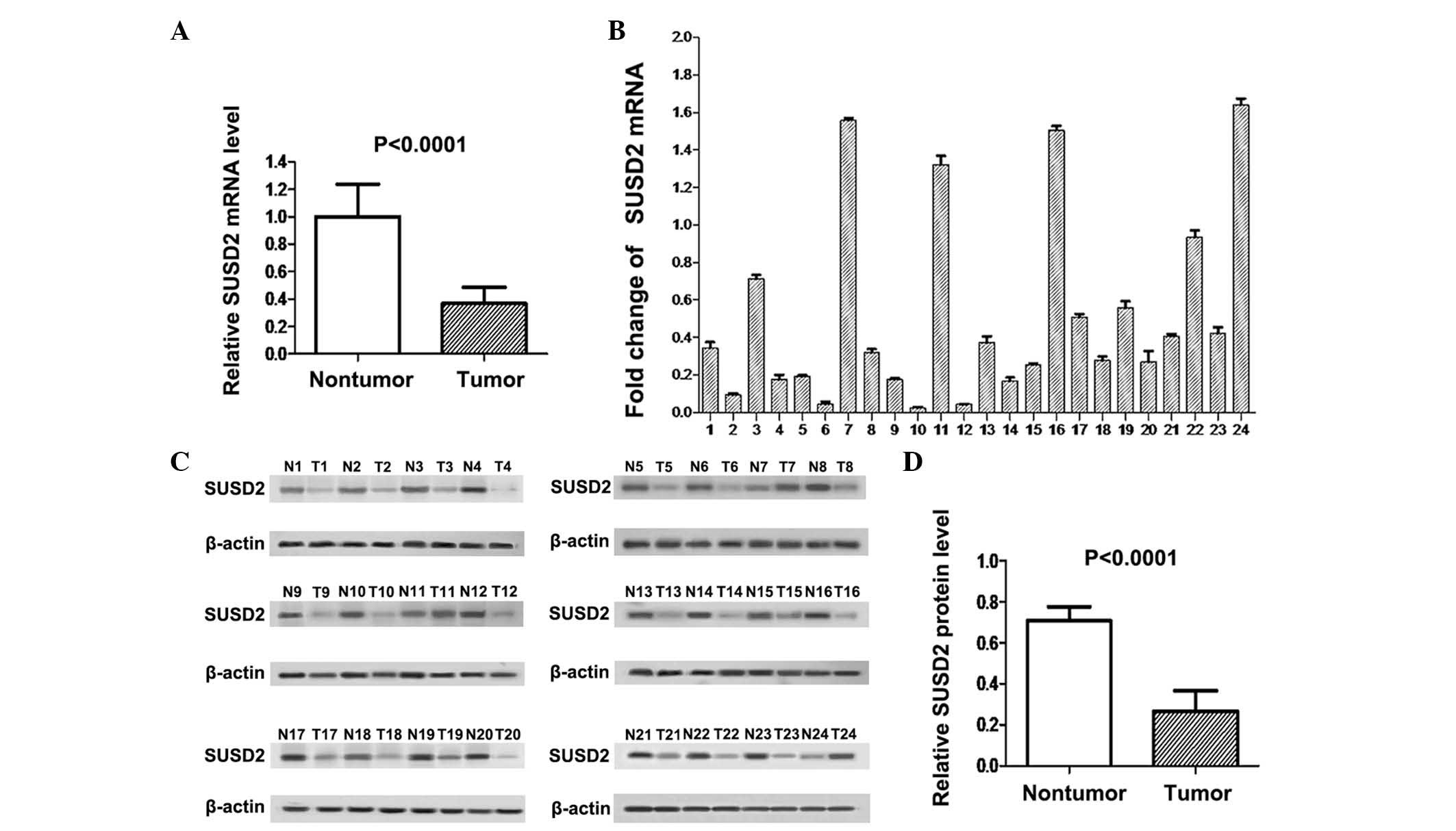
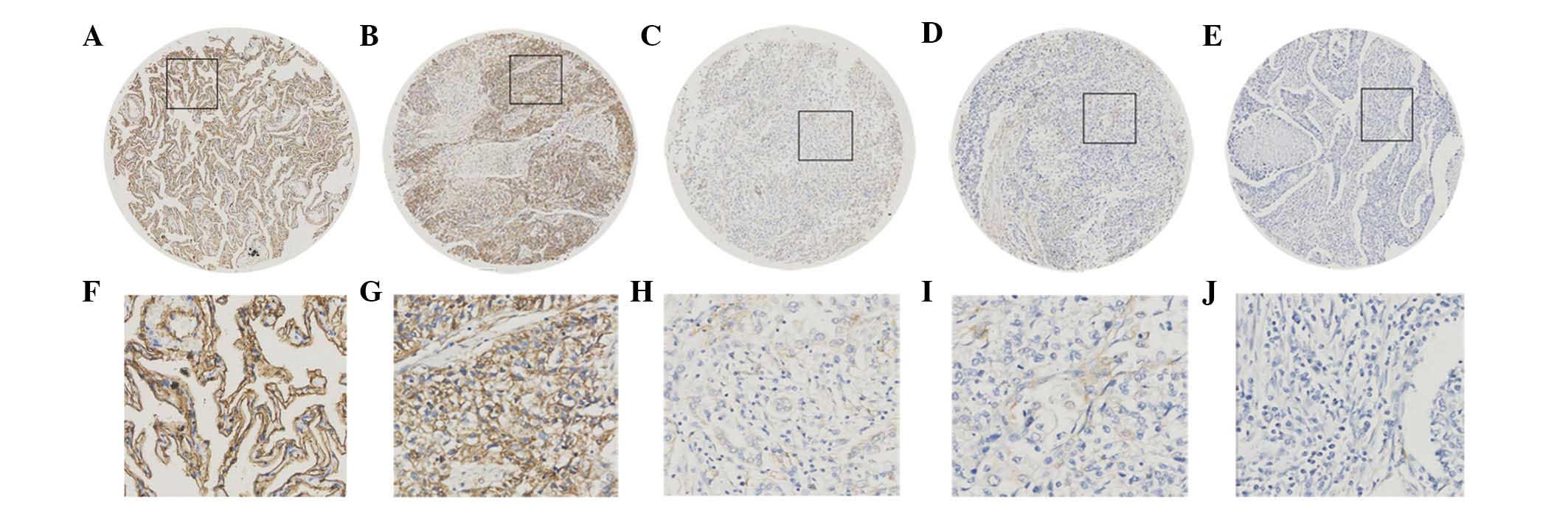
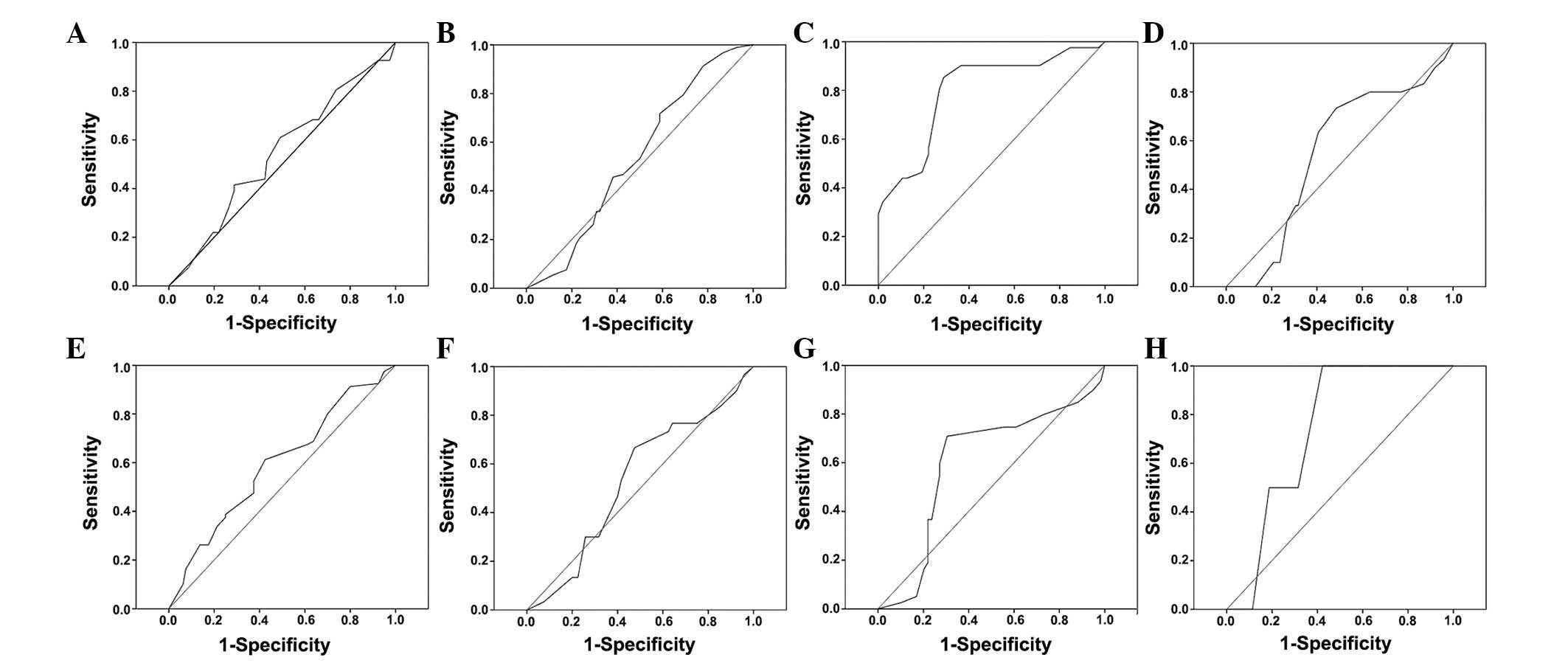
|
1
|
Brody H: Lung cancer. Nature. 513:S12014.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
Salgia R: Prognostic significance of
angiogenesis and angiogenic growth factors in nonsmall cell lung
cancer. Cancer. 117:3889–3899. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
Siegel R, Naishadham D and Jemal A: Cancer
statistics for Hispanics/Latinos, 2012. CA Cancer J Clin.
62:283–298. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
Govindan R, Page N, Morgensztern D, Read
W, Tierney R, Vlahiotis A, Spitznagel EL and Piccirillo J: Changing
epidemiology of small-cell lung cancer in the United States over
the last 30 years: Analysis of the surveillance, epidemiologic and
end results database. J Clin Oncol. 24:4539–4544. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Watson AP, Evans RL and Egland KA:
Multiple functions of sushi domain containing 2 (SUSD2) in breast
tumorigenesis. Mol Cancer Res. 11:74–85. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Sugahara T, Yamashita Y, Shinomi M,
Yamanoha B, Iseki H, Takeda A, Okazaki Y, Hayashizaki Y, Kawai K,
Suemizu H and Andoh T: Isolation of a novel mouse gene,
mSVS-1/SUSD2, reversing tumorigenic phenotypes of cancer cells in
vitro. Cancer Sci. 98:900–908. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Sugahara T, Yamashita Y, Shinomi M, Isobe
Y, Yamanoha B, Iseki H, Takeda A, Okazaki Y, Kawai K, Suemizu H and
Andoh T: von Willebrand factor type D domain mutant of SVS-1/SUSD2,
vWd(m), induces apoptosis in HeLa cells. Cancer Sci. 98:909–915.
2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Chheang S and Brown K: Lung Cancer
staging: Clinical and radiologic perspectives. Semin Intervent
Radiol. 30:99–113. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Kreuzer KA, Lass U, Landt O, Nitsche A,
Laser J, Ellerbrok H, Pauli G, Huhn D and Schmidt CA: Highly
sensitive and specific fluorescence reverse transcription-PCR assay
for the pseudogene-free detection of beta-actin transcripts as
quantitative reference. Clin Chem. 45:297–300. 1999.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Baine MJ, Mallya K and Batra SK:
Quantitative real-time PCR expression analysis of peripheral blood
mononuclear cells in pancreatic cancer patients. Methods Mol Biol.
980:157–173. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Livak KJ and Schmittgen TD: Analysis of
relative gene expression data using real-time quantitative PCR and
the 2 (-Delta Delta C(T)) method. Methods. 25:402–408. 2001.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Lee YJ, Kim DH, Lee SH, Kim DW, Nam HS and
Cho MK: Expression of the c-Met proteins in malignant skin cancers.
Ann Dermatol. 23:33–38. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Shi M, Yu DH, Chen Y, Zhao CY, Zhang J,
Liu QH, Ni CR and Zhu MH: Expression of fibroblast activation
protein in human pancreatic adenocarcinoma and its
clinicopathological significance. World J Gastroenterol.
18:840–846. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Shan LH, Sun WG, Han W, Qi L, Yang C, Chai
CC, Yao K, Zhou QF, Wu HM, Wang LF and Liu JR: Roles of fibroblasts
from the interface zone in invasion, migration, proliferation and
apoptosis of gastric adenocarcinoma. J Clin Pathol. 65:888–895.
2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Shi R, Zhao Z, Zhou H, Wei M, Ma WL, Zhou
JY and Tan WL: Reduced expression of PinX1 correlates to
progressive features in patients with prostate cancer. Cancer Cell
Int. 14:462014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Wang G, Wu J and Song H: LRIG2 expression
and prognosis in non-small cell lung cancer. Oncol Lett. 8:667–672.
2014.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Saintigny P and Burger JA: Recent advances
in non-small cell lung cancer biology and clinical management.
Discov Med. 13:287–297. 2012.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
Konishi J, Yamazaki K, Azuma M, Kinoshita
I, Dosaka-Akita H and Nishimura M: B7-H1 expression on non-small
cell lung cancer cells and its relationship with tumor-infiltrating
lymphocytes and their PD-1 expression. Clin Clin Cancer Res.
10:5094–5100. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
Molina JR, Yang P, Cassivi SD, Schild SE
and Adjei AA: Non-small cell lung cancer: Epidemiology, risk
factors, treatment and survivorship. Mayo Clin Proc. 83:584–594.
2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|