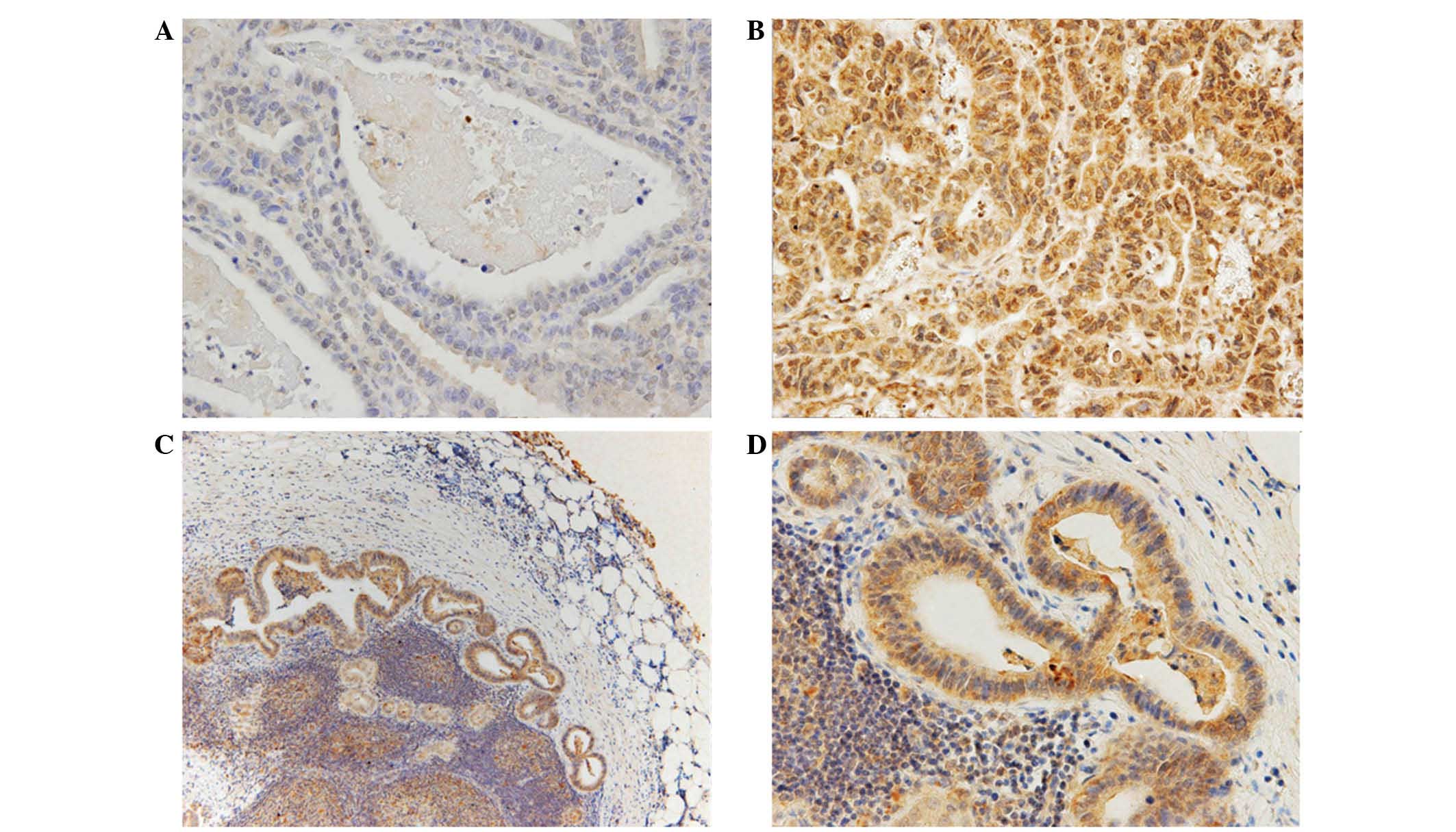
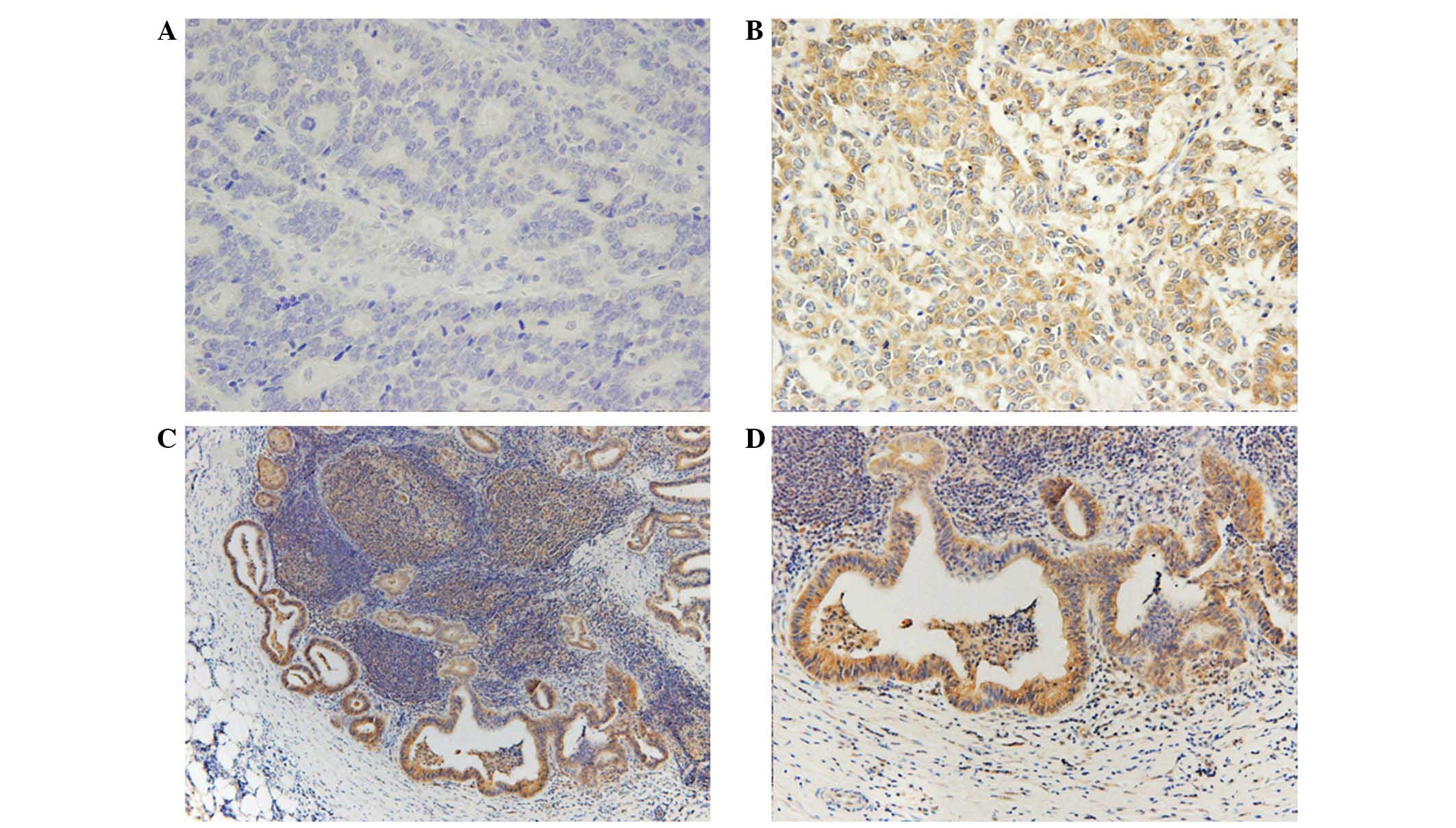
|
1
|
Jemal A, Bray F, Center MM, Ferlay J, Ward
E and Forman D: Global cancer statistics. CA Cancer J Clin.
61:69–90. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
Catalano V, Labianca R, Beretta GD, Gatta
G, de Braud F and Van Cutsem E: Gastric cancer. Crit Rev Oncol
Hematol. 71:127–164. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
Koizumi W, Narahara H, Hara T, Takagane A,
Akiya T, Takagi M, Miyashita K, Nishizaki T, Kobayashi O, Takiyama
W, et al: S-1 plus cisplatin versus S-1 alone for first-line
treatment of advanced gastric cancer (SPIRITS trial): A phase III
trial. Lancet Oncol. 9:215–221. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
Terashima M, Kitada K, Ochiai A, Ichikawa
W, Kurahashi I, Sakuramoto S, Katai H, Sano T, Imamura H and Sasako
M: ACTS-GC group: Impact of expression of human epidermal growth
factor receptors EGFR and ERBB2 on survival in stage II/III gastric
cancer. Clin Cancer Res. 18:5992–6000. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Lieto E, Ferraraccio F, Orditura M,
Castellano P, Mura AL, Pinto M, Zamboli A, De Vita F and Galizia G:
Expresison of vascular endothelial growth factor (VEGF) and
epidermal growth factor receptor (EGFR) is an independent
prognostic indicator of worse outcome in gastric cancer patients.
Ann Surg Oncol. 15:69–79. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Hayashi M, Inokuchi M, Takagi Y, Yamada H,
Kojima K, Kumagai J, Kawano T and Sugihara K: High expression of
HER3 is associated with a decreased survival in gastric cancer.
Clin Cancer Res. 14:7843–7849. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Begnami MD, Fukuda E, Fregnani JH,
Nonogaki S, Montagnini AL, da Costa WL Jr and Soares FA: Prognostic
implications of altered human epidermal growth factor receptors
(HERs) in gastric carcinomas: HER2 and HER3 are predictors of poor
outcome. J Clin Oncol. 29:3030–3036. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Kim MA, Lee HS, Lee HE, Jeon YK, Yang HK
and Kim WH: EGFR in gastric carcinomas: Prognostic significance of
protein overexpression and high gene copy number. Histopathology.
52:738–746. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
García I, Vizoso F, Martín A, Sanz L,
Abdel-Lah O, Raigoso P and García-Muñiz JL: Clinical significance
of the epidermal growth factor receptor and HER2 receptor in
resectable gastric cancer. Ann Surg Oncol. 10:234–241. 2003.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Hirashima Y, Yamada Y, Matsubara J,
Takahari D, Okita N, Takashima A, Kato K, Hamaguchi T, Shirao K,
Shimada Y, et al: Impact of vascular endothelial growth factor
receptor 1, 2 and 3 expression on the outcome of patients with
gastric cancer. Cancer Sci. 100:310–315. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Jüttner S, Wissmann C, Jöns T, Vieth M,
Hertel J, Gretschel S, Schlag PM, Kemmner W and Höcker M: Vascular
endothelial growth factor-D and its receptor VEGFR-3: Two novel
independent prognostic markers in gastric adenocarcinoma. J Clin
Oncol. 24:228–240. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Ohtsu A, Shah MA, Van Cutsem E, Rha SY,
Sawaki A, Park SR, Lim HY, Yamada Y, Wu J, Langer B, et al:
Bevacizumab in combination with chemotherapy as first-line therapy
in advanced gastric cancer: A randomized, double-blind,
placebo-controlled phase III study. J Clin Oncol. 29:3968–3976.
2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Waddell T, Chau I, Cunningham D, Gonzalez
D, Okines AF, Okines C, Wotherspoon A, Saffery C, Middleton G,
Wadsley J, et al: Epirubicin, oxaliplatin, and capecitabine with or
without panitumumab for patients with previously untreated advanced
oesophagogastric cancer (REAL3): A randomised, open-label phase 3
trial. Lancet Oncol. 14:481–489. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Lordick F, Kang YK, Chung HC, Salman P, Oh
SC, Bodoky G, Kurteva G, Volovat C, Moiseyenko VM, Gorbunova V, et
al: Arbeitsgemeinschaft Internistische Onkologie and EXPAND
Investigators: Capecitabine and cisplatin with or without cetuximab
for patients with previously untreated advanced gastric cancer
(EXPAND): A randomised, open-label phase 3 trial. Lancet Oncol.
14:490–499. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Bang YJ, Van Cutsem E, Feyereislova A,
Chung HC, Shen L, Sawaki A, Lordick F, Ohtsu A, Omuro Y, Satoh T,
et al: Trastuzumab in combination with chemotherapy versus
chemotherapy alone for treatment of HER-2 positive advanced gastric
or gastro-oseophageal junction cancer (ToGA): A phase 3,
open-label, randomized controlled trial. Lancet. 376:687–697. 2010.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Tanner M, Hollmén M, Junttila TT, Kapanen
AI, Tommola S, Soini Y, Helin H, Salo J, Joensuu H, Sihvo E, et al:
Amplification of HER-2 in gastric carcinoma: Association with
topoisomerase IIalpha gene amplification, intestinal type, poor
prognosis and sensitivity to trastuzumab. Ann Oncol. 16:273–278.
2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Yano T, Doi T, Ohtsu A, Boku N, Hashizume
K, Nakanishi M and Ochiai A: Comparison of HER2 gene amplification
assessed by fluorescence in situ hybridization and HER2 protein
expression assessed by immunohistochemistry in gastric cancer.
Oncol Rep. 15:65–71. 2006.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
Ustach CV, Taube ME, Hurst NJ Jr, Bhagat
S, Bonfil RD, Cher ML, Schuger L and Kim HR: A potential oncogenic
activity of platelet-derived growth factor d in prostate cancer
progression. Cancer Res. 64:1722–1729. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
LaRochelle WJ, Jeffers M, McDonald WF,
Chillakuru RA, Giese NA, Lokker NA, Sullivan C, Boldog FL, Yang M,
Vernet C, et al: PDGF-D, new protease-actovated growth factor. Nat
Cell Biol. 3:517–521. 2001. View
Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
Andrae J, Gallini R and Betsholtz C: Role
of platelet-derived growth factors in physiology and medicine.
Genes Dev. 22:1276–1312. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
LaRochelle WJ, Jeffers M, Corvalan JR, Jia
XC, Feng X, Vanegas S, Vickroy JD, Yang XD, Chen F, Gazit G, et al:
Platelet-derived growth factor D: Tumorigenicity in mice and
dysregulated expression in human cancer. Cancer Res. 62:2468–2473.
2002.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22
|
Lokker NA, Sullivan CM, Hollenbach SJ,
Israel MA and Giese NA: Platelet-derived growth factor (PDGF)
autocrine signaling regulates survival and mitogenic pathways in
glioblastoma cells: Evidence that the novel PDGF-C and PDGF-D
ligands may play a role in the development of brain tumors. Cancer
Res. 62:3729–3735. 2002.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23
|
Zwerner JP and May WA: Dominant negative
PDGF-C inhibits growth of ewing family tumor cell lines. Oncogene.
21:3847–3854. 2002. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24
|
Tejada ML, Yu L, Dong J, Jung K, Meng G,
Peale FV, Frantz GD, Hall L, Liang X, Gerber HP and Ferrara N:
Tumor-driven paracrine platelet-derived growth factor receptor
alpha signaling is a key determinant of stromal cell recruitment in
a model of human lung carcinoma. Clin Cancer Res. 12:2676–2688.
2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
25
|
Kong D, Banerjee S, Huang W, Li Y, Wang Z,
Kim HR and Sarkar FH: Mammalian target of rapamycin repression by
3,3′-diindolylmethane inhibits invasion and angiogenesis in
platelet-derived growth factor-D-overexpressing PC3 cells. Cancer
Res. 68:1927–1934. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
26
|
Wang Z, Kong D, Banerjee S, Li Y, Adsay
NV, Abbruzzese J and Sarkar FH: Down-regulation of platelet-derived
growth factor-D inhibits cell growth and angiogenesis through
inactivation of Notch-1 and nuclear factor-kappaB signaling. Cancer
Res. 67:11377–11385. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
27
|
Ustach CV, Taube ME, Hurst NJ Jr, Bhagat
S, Bonfil RD, Cher ML, Schuger L and Kim HR: A potential oncogenic
activity of platelet-derived growth factor d in prostate cancer
progression. Cancer Res. 64:1722–1729. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
28
|
Ustach CV and Kim HR: Platelet-derived
growth factor D is activated by urokinase plasminogen activator in
prostate carcinoma cells. Mol Cell Biol. 25:6279–6288. 2005.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
29
|
Xu L, Tong R, Cochran DM and Jain RK:
Blocking platelet-derived growth factor-D/platelet-derived growth
factor receptor beta signaling inhibits human renal cell carcinoma
progression in an orthotopic mouse model. Cancer Res. 65:5711–5719.
2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
30
|
Yang S, Shin J, Park KH, Jeung HC, Rha SY,
Noh SH, Yang WI and Chung HC: Molecular basis of the differences
between normal and tumor tissues of gastric cancer. Biochim Biophys
Acta. 1772:1033–1040. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
31
|
Sobin LH, Gospodarowicz MK and Wittekind
C: TNM Classification of Malignant Tumours (7th). Wiley-Blackwell.
2009.
|
|
32
|
Kong D, Wang Z, Sarkar SH, Li Y, Banerjee
S, Saliganan A, Kim HR, Cher ML and Sarkar FH: Platelet-derived
growth factor-D overexpression contributes to
epithelial-mesenchymal transition of PC3 prostate cancer cells.
Stem Cells. 26:1425–1435. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
33
|
Kong D, Li Y, Wang Z, Banerjee S, Ahmad A,
Kim HR and Sarkar FH: miR-200 regulates PDGF-D-mediated
epithelial-mesenchymal transition, adhesion and invasion of
prostate cancer cells. Stem Cells. 27:1712–1721. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
34
|
Wang Z, Ali S, Banerjee S, Bao B, Li Y,
Azmi AS, Korc M and Sarkar FH: Activated K-Ras and INK4a/Arf
deficiency promote aggressiveness of pancreatic cancer by induction
of EMT consistent with cancer stem cell phenotype. J Cell Physiol.
228:556–562. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
35
|
Zhao L, Zhang C, Liao G and Long J:
RNAi-mediated inhibition of PDGF-D leads to decreased cell growth,
invasion and angiogenesis in the SGC-7901 gastric cancer xenograft
model. Cancer Biol Ther. 9:42–48. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
36
|
Anderberg C, Li H, Fredriksson L, Andrae
J, Betsholtz C, Li X, Eriksson U and Pietras K: Paracrine signaling
by platelet-derived growth factor-CC promotes tumor growth by
recruitment of cancer-associated fibroblasts. Cancer Res.
69:369–378. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
37
|
Yamauchi S, Iida S, Ishiguro M, Ishikawa
T, Uetake H and Sugihara K: Clinical significance of
platelet-derived growth factor-C expression in colorectal cancer. J
Cancer Ther. 5:11–20. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
38
|
Guo Y, Yin J, Zha L and Wang Z:
Clinicopathological significance of platelet-derived growth factor
B, platelet-derived growth factor receptor-β and E-cadherin
expression in gastric carcinoma. Contemp Oncol (Pozn). 17:150–155.
2013.PubMed/NCBI
|