Introduction
Major salivary gland carcinomas, which are distinct
from parotid gland carcinomas, submandibular gland carcinomas and
sublingual gland carcinomas, are rare malignant tumors, accounting
for <5% of all cancers of the head and neck (1). The histological classification of major
salivary gland carcinomas comprises 24 histological subtypes with
different malignant phenotypes and prognoses, according to the 2005
World Health Organization classification of tumors (2). To date, numerous studies have
investigated the characteristics and useful prognostic parameters
of major salivary gland carcinoma using various approaches,
including clinical, pathological and biological procedures
(1–4).
The lymph node density (LND), which is calculated as
the ratio of the number of positive lymph nodes to the number of
total lymph nodes, has been found to reliably predict the survival
of patients with oral squamous cell carcinoma (OSCC), bladder
carcinoma and other carcinomas with positive neck lymph nodes in
recent studies (5–12). However, the association between the
LND and overall survival in individuals with major salivary gland
carcinoma has not yet been investigated. The present study
investigated whether LND is correlated with overall survival in
cases of major salivary gland carcinoma with positive lymph
nodes.
Patients and methods
Population data
A total of 284 patients newly diagnosed with major
salivary gland tumor at the Department of Head and Neck Surgery,
Aichi Cancer Center Hospital (Nagoya, Japan), underwent tumor
resection between January 2004 and May 2014; 93 of these patients
were diagnosed with primary major salivary gland carcinoma on a
pathological examination. Of these 93 patients, 80 received primary
tumor resection with neck dissection, and 34 were diagnosed
pathologically with lymph node metastasis. One patient who received
preoperative chemotherapy and one patient with a past history of
radiotherapy for nasopharyngeal carcinoma were excluded. Therefore,
a total of 32 patients with pathologically positive lymph nodes
were enrolled in the study. This study protocol was approved by the
institutional review board of Aichi Cancer Center Hospital, and all
patients provided their informed consent for all treatments and
examinations. The anatomical locations of the primary tumor were as
follows: Parotid gland, 21 patients; submandibular gland, 10
patients; and sublingual gland, 1 patient.
Tumor-node-metastasis (TNM)
staging
A routine physical examination and chest radiography
were performed on the first visit. The clinical stage was
determined according to the findings of these examinations, as well
as enhanced cervical computed tomography (CT) or magnetic resonance
imaging. Where possible, 18F-2-fluorodeoxyglucose positron emission
tomography (18F-FDG PET), or 18F-FDG PET combined with CT were
performed. The findings of clinical lymph node metastasis as
detected on enhanced CT, included the presence of ringed
enhancement or a lymph node diameter of ≥10 mm. The TNM
classification criteria of the International Union Against Cancer
(seventh edition) were used (13).
Pathological examination
Neck dissection, as described by the Japan Neck
Dissection Study Group, was performed in an en bloc fashion
(14). After carefully dividing the
neck dissection samples based on the cervical region, the number of
total lymph nodes was recorded. The samples and records were used
in the pathological examination. In accordance with the process
described in our previous report, the samples of resected tumors
were fixed with formalin and embedded in paraffin (3). The pathological diagnosis (pathological
T and N classification, pathological stage, histological
classification, histological grade, positive surgical margin and
extracapsular spread) was made by two pathologists, who compiled
all reports.
Postoperative therapy
Following the pathological diagnosis, postoperative
therapy was performed in patients with a positive surgical margin,
extracapsular spread, multiple positive lymph nodes or high
histological grade carcinoma, where possible. Following the
completion of treatment, the patients were followed up at the
outpatient clinic. Efforts were made to identify individuals with
early locoregional recurrence and perform radical salvage therapy
in such cases. The clinicopathological parameters of the patients
are shown in Table I.
 | Table I.Clinicopathological parameters
(n=32). |
Table I.
Clinicopathological parameters
(n=32).
| Parameter | Value |
|---|
| Age, years |
|
| Mean ±
SD | 61.8±15.1 |
| Gender, n |
|
| Male | 25 |
|
Female | 7 |
| Clinical T
classification, n |
|
| T1 | 0 |
| T2 | 8 |
| T3 | 7 |
| T4 | 17 |
| Clinical N
classification, n |
|
| N0 | 7 |
| N1 | 4 |
| N2 | 21 |
| N3 | 0 |
| Clinical stage,
n |
|
| I | 0 |
| II | 2 |
| III | 3 |
| IV | 27 |
| Anatomical location,
n |
|
|
Parotid | 21 |
|
Submandibular | 10 |
|
Sublingual | 1 |
| Pathological T
classification, n |
|
| T1 | 1 |
| T2 | 0 |
| T3 | 13 |
| T4 | 18 |
| Pathological N
classification, n |
|
| N0 | 0 |
| N1 | 8 |
| N2 | 24 |
| N3 | 0 |
| Pathological stage,
n |
|
| I | 0 |
| II | 0 |
| III | 3 |
| IV | 29 |
| Histological
classification, n |
|
|
Adenocarcinoma, not otherwise
specified | 14 |
| Salivary
duct carcinoma | 6 |
|
Mucoepidermoid carcinoma | 4 |
| Adenoid
cystic carcinoma | 4 |
| Carcinoma
ex pleomorphic adenoma | 3 |
| Squamous
cell carcinoma | 1 |
| Histological grade,
n |
|
| High | 11 |
|
Others | 21 |
| Positive surgical
margin, n |
|
|
Presence | 19 |
|
Absence | 13 |
| Extracapsular spread,
n |
|
|
Presence | 15 |
|
Absence | 17 |
| Positive surgical
margin and/or extracapsular spread, n |
|
|
Presence | 24 |
|
Absence | 8 |
| Postoperative
therapy, n |
|
|
Chemoradiation | 2 |
|
Radiation | 21 |
|
Absence | 9 |
LND
A total of 1,346 lymph nodes were evaluated, of
which 317 (23.6%) were found to be pathologically positive. Based
on previous studies (5–12), the LND was calculated using the
following formula: LND = number of positive lymph nodes / total
number of excised lymph nodes.
Statistical analysis
Statistical analysis was conducted using the JMP
software package (version 9; SAS Institute, Cary, NC, USA).
Correlations between LND and clinicopathological parameters (age,
gender, clinical T and N classification, clinical stage, anatomical
location, pathological T and N classification, pathological stage,
histological classification, histological grade, positive surgical
margin, extracapsular spread, positive surgical margin and/or
extracapsular spread and postoperative therapy) were analyzed using
the Mann-Whitney U test. The survival time was defined as the
period from surgery to the target event or date of last contact;
target events comprised mortality for the overall survival
calculation. Applying the method described in previous studies, the
Kaplan-Meier technique was used to estimate survival curves, and
various LND cut-off values were tested using the log-rank test in a
univariate overall survival analysis (15,16).
Thirty-two patients were grouped into two groups based on the LND
(LND ≥0.38 and <0.38), as an LND of 0.38 was able to
statistically distinguish the shorter from the longer survival
group according to the log-rank test in the univariate survival
analyses. The associations between the two groups (LND ≥0.38 and
<0.38) with regard to the clinicopathological parameters (age,
gender, clinical T and N classification, clinical stage, anatomical
location, pathological T and N classification, pathological stage,
histological classification, histological grade, positive surgical
margin, extracapsular spread, positive surgical margin and/or
extracapsular spread and postoperative therapy) were compared using
Fisher's exact test. A Cox proportional hazards model was used for
the multivariate survival analysis. Multivariate analysis was
performed with adjustment for anatomical location (parotid
gland/others). P<0.05 was considered to indicate statistically
significant differences.
Results
LND and clinicopathological
parameters
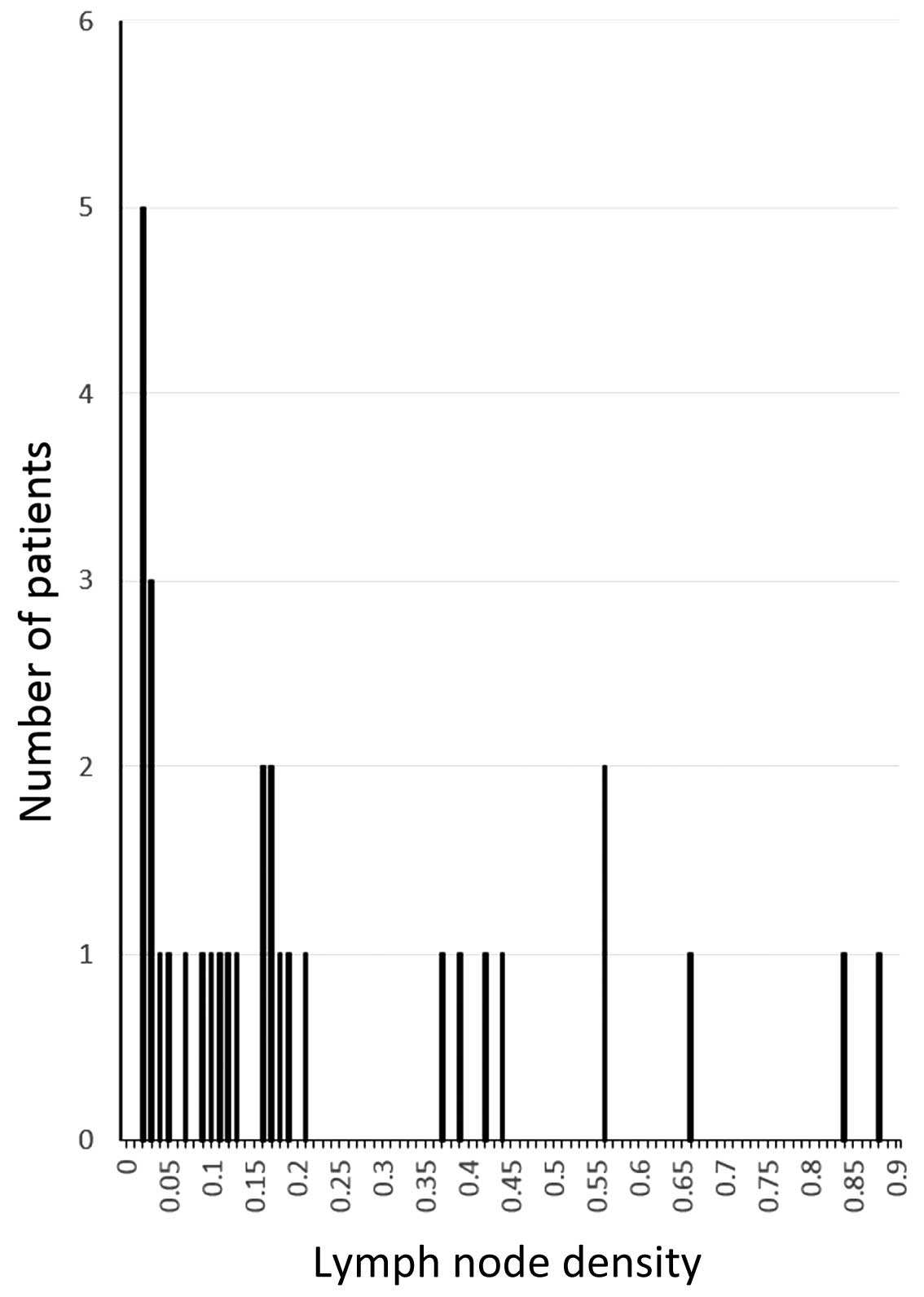
The median LND of all patients was 0.13 (range,
0.02–0.88). The LND distribution is shown in Fig. 1, and the associations between LND and
clinicopathological parameters are shown in Table II. LND was significantly correlated
with pathological N classification (P<0.01), pathological stage
(P=0.04), histological classification (P=0.02) and extracapsular
spread (P=0.01).
 | Table II.Associations between LND and
clinicopathological parameters (n=32). |
Table II.
Associations between LND and
clinicopathological parameters (n=32).
| Parameter | n | LND (mean ± SD) | P-valuea |
|---|
| Age, years |
|
| 0.07 |
|
<65 | 16 | 0.26±0.24 |
|
| ≥65 | 16 | 0.16±0.23 |
|
| Gender |
|
| 0.73 |
| Male | 25 | 0.21±0.22 |
|
|
Female | 7 | 0.21±0.30 |
|
| Clinical T
classification |
|
| 0.54 |
| T1–3 | 15 | 0.24±0.27 |
|
| T4 | 17 | 0.19±0.21 |
|
| Clinical N
classification |
|
| 0.10 |
| N0 | 7 | 0.11±0.14 |
|
| N1–2 | 25 | 0.24±0.25 |
|
| Clinical stage |
|
| 0.06 |
|
I–III | 5 | 0.06±0.04 |
|
| IV | 27 | 0.24±0.25 |
|
| Anatomical
location |
|
| 0.21 |
| Parotid
gland | 21 | 0.24±0.23 |
|
|
Others | 11 | 0.16±0.25 |
|
| Pathological T
classification |
|
| 0.83 |
|
T1–3 | 14 | 0.21±0.25 |
|
| T4 | 18 | 0.21±0.23 |
|
| Pathological N
classification |
|
| <0.01 |
| N1 | 8 | 0.03±0.01 |
|
| N2 | 24 | 0.27±0.25 |
|
| Pathological
stage |
|
| <0.04 |
|
III | 3 | 0.03±0.01 |
|
| IV | 29 | 0.23±0.24 |
|
| Histological
classification |
|
| <0.03 |
|
Adenocarcinoma, NOS | 14 | 0.33±0.29 |
|
|
Others | 18 | 0.12±0.14 |
|
| Histological
grade |
|
| 0.74 |
|
High | 8 | 0.14±0.11 |
|
|
Others | 16 | 0.25±0.28 |
|
| Positive surgical
margin |
|
| 0.31 |
|
Presence | 19 | 0.14±0.11 |
|
|
Absence | 13 | 0.25±0.28 |
|
| Extracapsular
spread |
|
| <0.02 |
|
Presence | 15 | 0.33±0.29 |
|
|
Absence | 17 | 0.11±0.10 |
|
| Positive surgical
margin and/or extracapsular spread |
|
| 0.07 |
|
Presence | 8 | 0.08±0.07 |
|
|
Absence | 24 | 0.25±0.26 |
|
| Postoperative
therapy |
|
| 0.90 |
|
Presence | 9 | 0.28±0.35 |
|
|
Absence | 23 | 0.18±0.18 |
|
Overall survival analysis
At the end of the study, the mean ± SD follow-up
periods among all patients, the 16 surviving patients (50.0% vs.
all) and the 16 deceased patients (50.0%) were 23.8±19.6, 25.1±19.9
and 22.4±19.8 months, respectively. In the entire patient group,
the overall 2-, 3- and 5-year survival rates were 59.2, 43.2 and
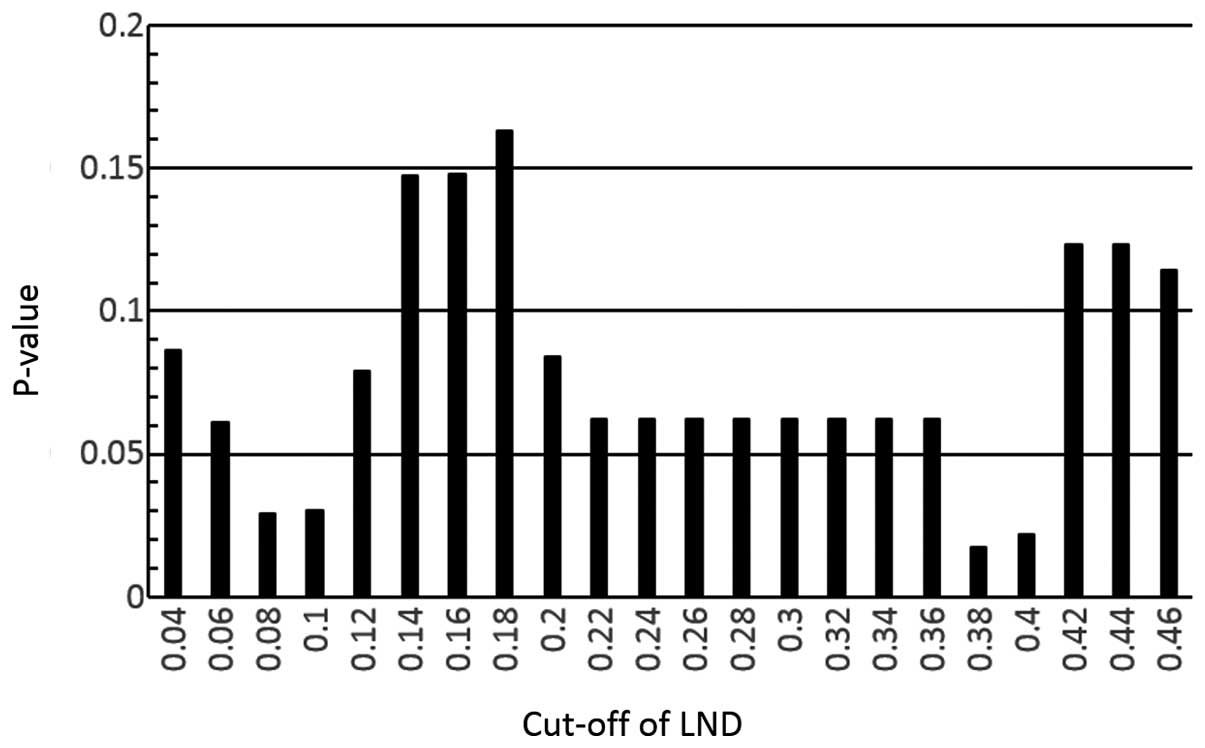
25.9%, respectively. Applying the method described previously, in
our study and others (14,15), various LND cut-off values were tested
using the log-rank test in the overall survival analysis. A cut-off
value of 0.38 for the LND had the lowest P-value in these analyses
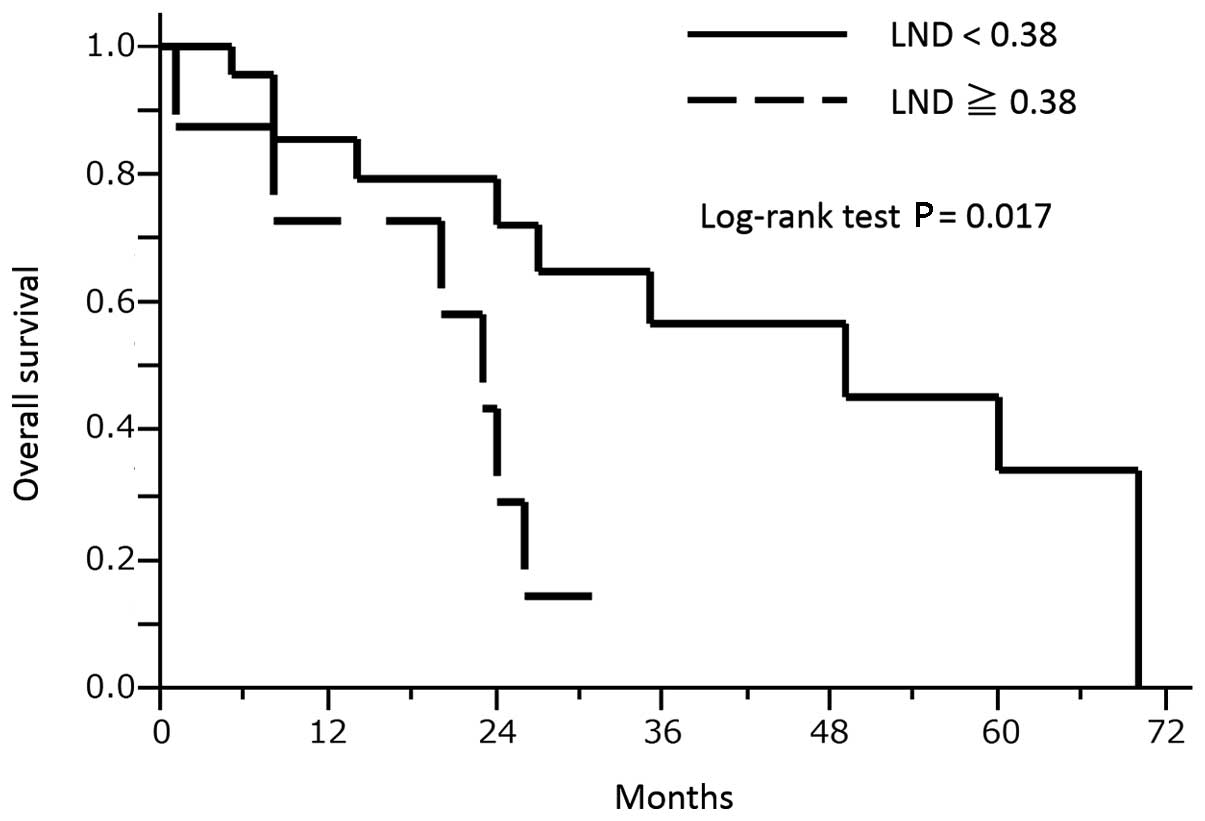
(Fig. 2) and could be used to
differentiate the shorter overall survival group (LND ≥0.38, n=8)
from the longer overall survival group (LND <0.38, n=24) based
on the log-rank test, as shown in Fig.
3 (P=0017). No significant associations with
clinicopathological parameters were observed in the two groups (LND
≥0.38 and <0.38), as shown in Table
III. A multivariate survival analysis was performed with
adjustment for anatomical location (parotid gland/others) for
overall survival. Consequently, an LND of ≥0.38 was confirmed to be
associated with a significantly shorter survival time. The results
of the multivariate analysis for survival are presented in Table IV.
 | Table III.Associations between LND (≥0.38 and
<0.38) and clinicopathological parameters (n=32). |
Table III.
Associations between LND (≥0.38 and
<0.38) and clinicopathological parameters (n=32).
| Parameter | LND ≥0.38
(n=24) | LND <0.38
(n=8) |
P-valuea |
|---|
| Age, years |
|
| 0.22 |
|
<65 | 10 | 6 |
|
|
≥65 | 14 | 2 |
|
| Gender |
|
| 0.65 |
|
Male | 18 | 7 |
|
|
Female | 6 | 1 |
|
| Clinical T
classification |
|
| 0.42 |
|
T1–3 | 10 | 5 |
|
| T4 | 14 | 3 |
|
| Clinical N
classification |
|
| 0.65 |
| N0 | 6 | 1 |
|
|
N1–2 | 18 | 7 |
|
| Clinical stage |
|
| 0.30 |
|
I–III | 5 | 0 |
|
| IV | 19 | 8 |
|
| Anatomical
location |
|
| 0.68 |
| Parotid
gland | 15 | 6 |
|
|
Others | 9 | 2 |
|
| Pathological T
classification |
|
| 0.70 |
|
T1–3 | 10 | 4 |
|
| T4 | 14 | 4 |
|
| Pathological N
classification |
|
| 0.08 |
| N1 | 8 | 0 |
|
| N2 | 16 | 8 |
|
| Pathological
stage |
|
| 0.55 |
|
III | 3 | 0 |
|
| IV | 21 | 8 |
|
| Histological
classification |
|
| 0.10 |
|
Adenocarcinoma, NOS | 8 | 6 |
|
|
Other | 16 | 2 |
|
| Histological
grade |
|
| 0.21 |
|
High | 10 | 1 |
|
|
Other | 14 | 7 |
|
| Positive surgical
margin |
|
| 0.42 |
|
Presence | 13 | 6 |
|
|
Absence | 11 | 2 |
|
| Extracapsular
spread |
|
| 0.11 |
|
Presence | 9 | 6 |
|
|
Absence | 15 | 2 |
|
| Positive surgical
margin and/or extracapsular spread |
|
| 0.08 |
|
Presence | 16 | 8 |
|
|
Absence | 8 | 0 |
|
| Postoperative
therapy |
|
| 0.18 |
|
Presence | 19 | 4 |
|
|
Absence | 5 | 4 |
|
 | Table IV.Multivariate survival
analysisa. |
Table IV.
Multivariate survival
analysisa.
|
| Overall
survival |
|---|
|
|
|
|---|
| Parameter | HR | 95% CI | P-value |
|---|
| LND
(≥0.38/<0.38) | 4.02 | 1.21–13.43 | P<0.03 |
| Anatomical location
(parotid/others) | 2.81 | 0.87–12.53 | P=0.09 |
Discussion
The results of the current study demonstrated, for
the first time, that an LND of ≥0.38 in patients with major
salivary gland carcinoma exhibiting pathological lymph node
metastasis is significantly associated with a shorter overall
survival time.
The LND determined by pathological examination has
emerged as a prognostic parameter for various types of cancer,
including bladder, esophageal and oral cancers (5–12). The
ratio of the LND weights three factors that may influence nodal
staging: Tumor (the true number of positive lymph nodes), surgical
(the actual number of nodes removed during neck dissection) and
sampling (the completeness of the pathological analysis) factors
(5). Recently, a multi-institutional
international study group comprising 11 cancer centers across the
globe revealed the LND to be a significant predictor of overall
survival time among 4,254 patients with OSCC (5). Furthermore, a number of studies have
reported that LND may be used to predict the survival time of OSCC
patients treated with different neck dissection procedures, such as
unilateral or bilateral neck dissections (5–10). The
present findings, demonstrating an association between LND and
overall survival rate, are in concordance with this previous
evidence (5–10).
With regard to head and neck cancer, numerous
studies have reported an association between LND and overall
survival in patients with OSCC (5–9).
Furthermore, Rudra et al (10)
reported that LND predicts overall survival time in subjects with
lesions in various sites of the head and neck, including the
oropharynx, oral cavity and larynx/hypopharynx; however, this study
did not investigate the relationship between LND and overall
survival in patients with major salivary gland carcinoma (10). In the present study, the association
between LND and overall survival was assessed in subjects with
major salivary gland carcinoma, demonstrating that an LND of ≥0.38
in patients with pathological lymph node metastasis is
significantly associated with a shorter overall survival time.
The predominant limitation of the current study was
the relatively small number of subjects in the sample. Hence,
future analyses of large numbers of patients will yield more
statistically accurate results, with greater potential for
application of the findings.
In conclusion, the present study demonstrated, for
the first time, that an LND of ≥0.38 in patients with major
salivary gland carcinoma exhibiting pathological lymph node
metastasis is significantly associated with a shorter overall
survival time. Therefore, LND is a prognostic factor in individuals
with major salivary gland carcinoma.
Acknowledgements
The current study was supported by Japan Society for
the Promotion of Science Grants-in-Aid for Scientific Research
(grant no. 24791821). Part of this study was presented at the 2014
World Cancer Congress, December 3–6, 2014, Melbourne, Australia
(17).
References
|
1
|
Ettl T, Schwarz-Furlan S, Gosau M and
Reichert TE: Salivary gland carcinomas. Oral Maxillofac Surg.
16:267–283. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
Barnes L, Eveson JW, Reichart P and
Sidransky D: World Health Organization classification of tumours.
Pathology and genetics of head and neck tumours (Lyon). IARC Press.
2005.
|
|
3
|
Okabe M, Miyabe S, Nagatsuka H, Terada A,
Hanai N, Yokoi M, Shimozato K, Eimoto T, Nakamura S, Nagai N, et
al: MECT1-MAML2 fusion transcript defines a favorable subset of
mucoepidermoid carcinoma. Clin Cancer Res. 12:3902–3907. 2006.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
Amit M, Na'ara S, Sharma K, Ramer N, Ramer
I, Agbetoba A, Glick J, Yang X, Lei D, Bjoerndal K, et al: Elective
neck dissection in patients with head and neck adenoid cystic
carcinoma: An international collaborative study. Ann Surg Oncol.
22:1353–1359. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Patel SG, Amit M, Yen TC, Liao CT,
Chaturvedi P, Agarwal JP, Kowalski LP, Ebrahimi A, Clark JR, Cernea
CR, et al: Lymph node density in oral cavity cancer: Results of the
International Consortium for Outcomes Research. Br J Cancer.
109:2087–2095. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Kim SY, Nam SY, Choi SH, Cho KJ and Roh
JL: Prognostic value of lymph node density in node-positive
patients with oral squamous cell carcinoma. Ann Surg Oncol.
18:2310–2317. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Gil Z, Carlson DL, Boyle JO, Kraus DH,
Shah JP, Shaha AR, Singh B, Wong RJ and Patel SG: Lymph node
density is a significant predictor of outcome in patients with oral
cancer. Cancer. 115:5700–5710. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Amar A, Rapoprt A, Curioni OA, Dedivitis
RA, Cernea CR and Brandáo LG: The density of metastatic lymph node
as prognostic factor in squamous cell carcinoma of the tongue and
floor of the mouth. Braz J Otorhinolaryngol. 78:86–90. 2012.(In
Portuguese). View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Liao CT, Hsueh C, Lee LY, Lin CY, Fan KH,
Wang HM, Huang SF, Chen IH, Kang CJ, Ng SH, et al: Neck dissection
field and lymph node density predict prognosis in patients with
oral cavity cancer and pathological node metastases treated with
adjuvant therapy. Oral Oncol. 48:329–336. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Rudra S, Spiotto MT, Witt ME, Blair EA,
Stenson K and Haraf DJ: Lymph node density - prognostic value in
head and neck cancer. Head Neck. 36:266–272. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Kassouf W, Leibovici D, Munsell MF, Dinney
CP, Grossman HB and Kamat AM: Evaluation of the relevance of lymph
node density in a contemporary series of patients undergoing
radical cystectomy. J Urol. 176:53–57. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Ooki A, Yamashita K, Kobayashi N, Katada
N, Sakuramoto S, Kikuchi S and Watanabe M: Lymph node metastasis
density and growth pattern as independent prognostic factors in
advanced esophageal squamous cell carcinoma. World J Surg.
31:2184–2191. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Sobin LH, Wittekind C and Gospodarowicz M:
International Union Against Cancer TNM classification of malignant
tumours (7th). New York, NY, USA: Wiley-Blackwell. 2009.
|
|
14
|
Hasegawa Y and Saikawa M: Update on the
classification and nomenclature system for neck dissection:
Revisions proposed by the Japan Neck Dissection Study Group. Int J
Clin Oncol. 15:5–12. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Van Baardwijk A, Dooms C, van Suylen RJ,
Verbeken E, Hochstenbag M, Dehing-Oberije C, Rupa D, Pastorekova S,
Stroobants S, Buell U, et al: The maximum uptake of
(18)F-deoxyglucose on positron emission tomography scan correlates
with survival, hypoxia inducible factor-1alpha and GLUT-1 in
non-small cell lung cancer. Eur J Cancer. 43:1392–1398. 2007.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Suzuki H, Kato K, Fujimoto Y, Itoh Y,
Hiramatsu M, Naganawa S, Hasegawa Y and Nakashima T: Prognostic
value of (18)F-fluorodeoxyglucose uptake before treatment for
pharyngeal cancer. Ann Nucl Med. 28:356–362. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Suzuki H: Lymph node density is a
prognostic factor in patients with major salivary gland carcinoma.
Asia-Pacific Journal of Clinical Oncology. 10:1–264. 2014.
|